Abstract
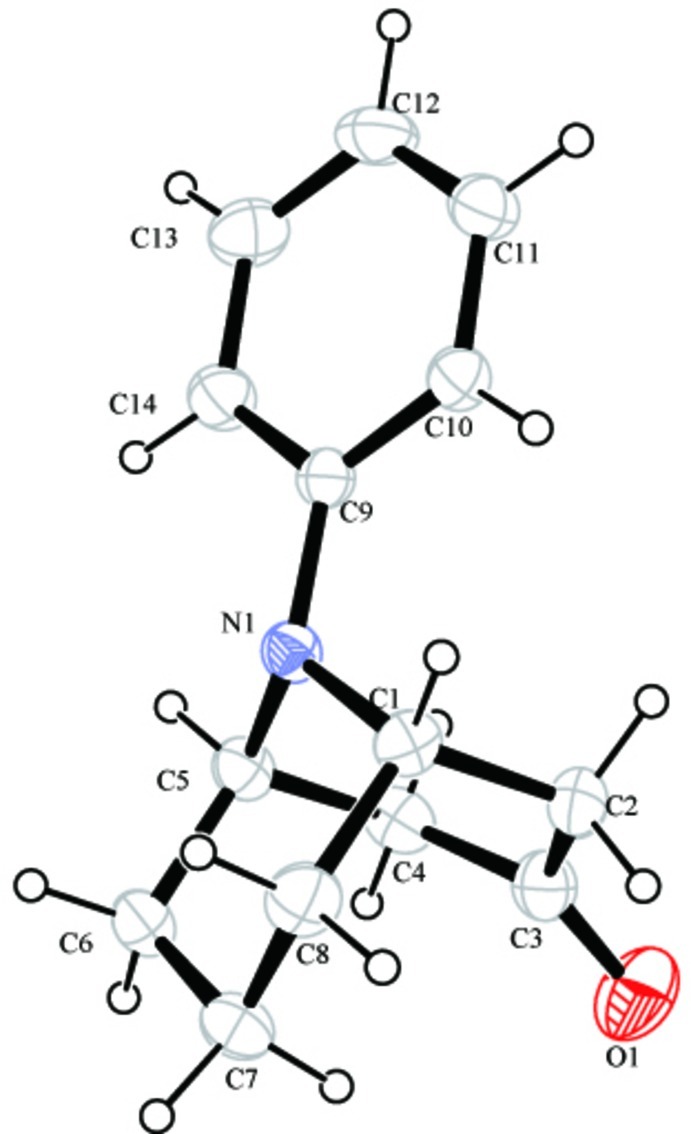
In the title compound, C14H17NO, the piperidinone and piperidine rings both adopt a chair conformation. The chiral crystals were obtained from a racemic reaction product via spontaneous resolution.
Related literature
For the synthesis, see: Zhang (2003 ▶). For applications of the compound, see: Vernekar et al. (2010 ▶); Lazny et al. (2011 ▶). For puckering analysis, see: Cremer & Pople (1975 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C14H17NO
M r = 215.29
Orthorhombic,
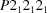
a = 9.4028 (3) Å
b = 10.2524 (5) Å
c = 12.0473 (6) Å
V = 1161.38 (9) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.08 mm−1
T = 293 K
0.40 × 0.40 × 0.35 mm
Data collection
Agilent Xcalibur Eos diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (ABSPACK in CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2011 ▶) T min = 0.918, T max = 1.000
3285 measured reflections
2218 independent reflections
1722 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.015
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.043
wR(F 2) = 0.092
S = 1.02
2218 reflections
145 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.12 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.13 e Å−3
Data collection: CrysAlis PRO (Agilent, 2011 ▶); cell refinement: CrysAlis PRO; data reduction: CrysAlis PRO; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: OLEX2 (Dolomanov et al., 2009 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: OLEX2.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812020065/fy2049sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812020065/fy2049Isup3.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812020065/fy2049Isup4.cdx
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812020065/fy2049Isup4.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Open Fund of the Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province (grant No. Szjj2011-005) and the Research Fund of the Key Laboratory of TCM Biotechnology (Xihua University).
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The compound 1S*,5R*-9-phenyl-9-aza-bicyclo[3.3.1]nonan-3-one is an important intermediate for synthesizing granisetron derivatives. The bicyclic skeleton of 9-azabicyclo[3.3.1]nonane is a key substructure of a variety of bioactive compounds (Vernekar et al., 2010; Lazny et al., 2011). The racemic title compound was synthesized by the Mannich reaction and spontaneous resolution occurred on recrystallization from a mixture of ethyl acetate and petroleum ether.
In the title structure the N1/C1—C5 piperidinone ring adopts a chair conformation with puckering parameters (Cremer & Pople, 1975): Q = 0.5159 (3) Å, θ = 158.26 (3)° and φ = 173.0692 (12)°. The N1/C1/C8—C5 piperidine ring has a chair conformation, too [Q = 0.5727 (3) Å, θ = 7.74 (12)° and φ = 23.8669 (13)°]. The relative configuration of C1 and C5 is S*, R* respectively.
Experimental
To a stirred solution of glutaraldehyde (1.32 ml, 5 mmol) and aniline (0.55 ml,6 mmol) in water (10 ml), 3-oxopentanedioic acid (0.88 g,6 mmol) was added. The mixture was stirred overnight at room temperature. Then the pH was adjusted to 5 with aq. HCl and the mixture was refluxed for another one hour. Then sodium hydroxide was added to increase the pH to 9. The mixture was extracted with ethyl-acetate. The combined extract was dried over anhydrous MgSO4 and evaporated in vacuo. The residue was purified through column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: hexane/EtOAc = 4/1) to give 9-phenyl-9-aza-bicyclo[3.3.1]nonan-3-one. Then the racemic mixture was crystallized from a solution in a 1:10 (v/v) mixture of ethyl acetate and petroleum ether to produce the title compound.
Refinement
All H atoms were positioned geometrically and treated using a riding model, fixing the bond lengths at 0.97 Å for aliphatic CH, 0.98 Å for CH2 and 0.93 Å for aromatic CH groups, respectively. The displacement parameters of the H atoms were constrained with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C). In the absence of significant anomalous scattering effects, the absolute configuration is not determined.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound.
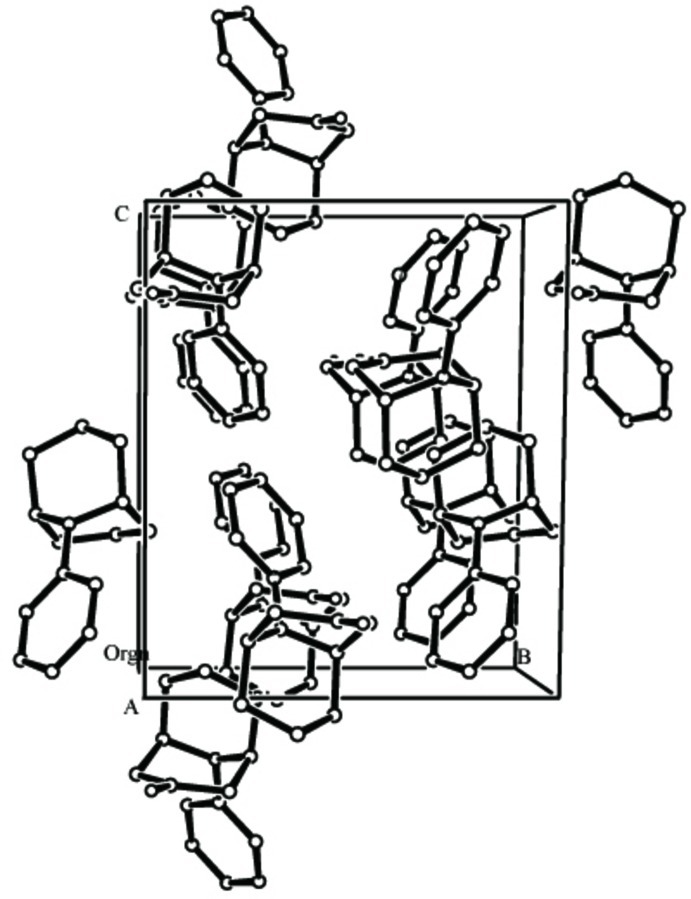
Fig. 2.
A packing diagram for the title compound.
Crystal data
| C14H17NO | Dx = 1.231 Mg m−3 |
| Mr = 215.29 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.7107 Å |
| Orthorhombic, P212121 | Cell parameters from 1237 reflections |
| a = 9.4028 (3) Å | θ = 2.9–29.0° |
| b = 10.2524 (5) Å | µ = 0.08 mm−1 |
| c = 12.0473 (6) Å | T = 293 K |
| V = 1161.38 (9) Å3 | Block, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.40 × 0.40 × 0.35 mm |
| F(000) = 464 |
Data collection
| Agilent Xcalibur Eos diffractometer | 2218 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: Enhance (Mo) X-ray Source | 1722 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.015 |
| Detector resolution: 16.0874 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 26.4°, θmin = 2.9° |
| ω scans | h = −11→7 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (ABSPACK in CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2011) | k = −9→12 |
| Tmin = 0.918, Tmax = 1.000 | l = −8→15 |
| 3285 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.043 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.092 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.02 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0394P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2218 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 145 parameters | Δρmax = 0.12 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.13 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | −0.58709 (17) | −0.01586 (16) | −0.68342 (15) | 0.0838 (6) | |
| N1 | −0.19284 (14) | −0.18245 (14) | −0.65084 (12) | 0.0368 (4) | |
| C1 | −0.31907 (18) | −0.26416 (18) | −0.63463 (16) | 0.0409 (5) | |
| H1 | −0.2985 | −0.3506 | −0.6653 | 0.049* | |
| C2 | −0.4480 (2) | −0.20832 (19) | −0.69713 (16) | 0.0472 (5) | |
| H2A | −0.4367 | −0.2265 | −0.7757 | 0.057* | |
| H2B | −0.5329 | −0.2532 | −0.6721 | 0.057* | |
| C3 | −0.4692 (2) | −0.0642 (2) | −0.68231 (16) | 0.0510 (6) | |
| C4 | −0.3376 (2) | 0.01633 (18) | −0.67070 (17) | 0.0489 (5) | |
| H4A | −0.3618 | 0.0971 | −0.6332 | 0.059* | |
| H4B | −0.3032 | 0.0386 | −0.7442 | 0.059* | |
| C5 | −0.2173 (2) | −0.05077 (18) | −0.60634 (17) | 0.0412 (5) | |
| H5 | −0.1302 | 0.0001 | −0.6174 | 0.049* | |
| C6 | −0.2468 (2) | −0.0573 (2) | −0.48223 (17) | 0.0494 (5) | |
| H6A | −0.1612 | −0.0854 | −0.4442 | 0.059* | |
| H6B | −0.2703 | 0.0293 | −0.4556 | 0.059* | |
| C7 | −0.3672 (2) | −0.1497 (2) | −0.45334 (16) | 0.0522 (6) | |
| H7A | −0.3705 | −0.1626 | −0.3736 | 0.063* | |
| H7B | −0.4571 | −0.1122 | −0.4766 | 0.063* | |
| C8 | −0.3452 (2) | −0.2797 (2) | −0.51068 (17) | 0.0510 (5) | |
| H8A | −0.4286 | −0.3338 | −0.4994 | 0.061* | |
| H8B | −0.2646 | −0.3239 | −0.4774 | 0.061* | |
| C9 | −0.11420 (18) | −0.19480 (18) | −0.75009 (15) | 0.0363 (4) | |
| C10 | −0.1472 (2) | −0.28634 (19) | −0.83142 (16) | 0.0435 (5) | |
| H10 | −0.2261 | −0.3400 | −0.8221 | 0.052* | |
| C11 | −0.0647 (2) | −0.2989 (2) | −0.92593 (16) | 0.0537 (6) | |
| H11 | −0.0896 | −0.3602 | −0.9794 | 0.064* | |
| C12 | 0.0534 (2) | −0.2223 (2) | −0.94206 (16) | 0.0597 (6) | |
| H12 | 0.1084 | −0.2308 | −1.0058 | 0.072* | |
| C13 | 0.0880 (2) | −0.1329 (2) | −0.8617 (2) | 0.0605 (6) | |
| H13 | 0.1680 | −0.0807 | −0.8712 | 0.073* | |
| C14 | 0.0069 (2) | −0.1187 (2) | −0.76732 (18) | 0.0497 (5) | |
| H14 | 0.0333 | −0.0574 | −0.7142 | 0.060* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0585 (9) | 0.0818 (13) | 0.1110 (16) | 0.0252 (10) | −0.0147 (10) | 0.0074 (12) |
| N1 | 0.0385 (8) | 0.0357 (8) | 0.0362 (9) | −0.0040 (7) | 0.0001 (7) | −0.0009 (7) |
| C1 | 0.0411 (10) | 0.0361 (10) | 0.0455 (12) | −0.0027 (9) | 0.0024 (9) | 0.0022 (9) |
| C2 | 0.0401 (10) | 0.0537 (12) | 0.0478 (13) | −0.0053 (10) | −0.0056 (9) | −0.0027 (11) |
| C3 | 0.0514 (12) | 0.0589 (13) | 0.0428 (13) | 0.0091 (12) | −0.0071 (10) | 0.0064 (11) |
| C4 | 0.0646 (13) | 0.0389 (10) | 0.0431 (12) | 0.0059 (11) | 0.0016 (11) | 0.0032 (9) |
| C5 | 0.0461 (11) | 0.0371 (10) | 0.0405 (11) | −0.0071 (9) | 0.0010 (9) | −0.0024 (9) |
| C6 | 0.0536 (11) | 0.0577 (13) | 0.0370 (12) | 0.0021 (11) | −0.0035 (10) | −0.0052 (11) |
| C7 | 0.0590 (13) | 0.0634 (13) | 0.0343 (11) | −0.0013 (11) | 0.0053 (10) | 0.0057 (10) |
| C8 | 0.0501 (12) | 0.0536 (12) | 0.0494 (12) | −0.0058 (11) | 0.0045 (10) | 0.0128 (11) |
| C9 | 0.0371 (9) | 0.0379 (10) | 0.0340 (10) | 0.0052 (9) | −0.0020 (8) | 0.0040 (9) |
| C10 | 0.0425 (10) | 0.0446 (11) | 0.0434 (11) | 0.0035 (10) | −0.0026 (9) | −0.0023 (10) |
| C11 | 0.0581 (13) | 0.0581 (14) | 0.0450 (13) | 0.0129 (12) | −0.0016 (11) | −0.0081 (11) |
| C12 | 0.0618 (14) | 0.0737 (16) | 0.0436 (13) | 0.0145 (13) | 0.0173 (12) | 0.0027 (12) |
| C13 | 0.0533 (13) | 0.0651 (15) | 0.0630 (16) | −0.0072 (12) | 0.0156 (12) | 0.0051 (13) |
| C14 | 0.0495 (11) | 0.0528 (13) | 0.0467 (13) | −0.0078 (11) | 0.0043 (10) | −0.0023 (10) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—C3 | 1.215 (2) | C6—C7 | 1.517 (3) |
| N1—C1 | 1.466 (2) | C7—H7A | 0.9700 |
| N1—C5 | 1.471 (2) | C7—H7B | 0.9700 |
| N1—C9 | 1.412 (2) | C7—C8 | 1.516 (3) |
| C1—H1 | 0.9800 | C8—H8A | 0.9700 |
| C1—C2 | 1.537 (3) | C8—H8B | 0.9700 |
| C1—C8 | 1.522 (3) | C9—C10 | 1.392 (3) |
| C2—H2A | 0.9700 | C9—C14 | 1.396 (3) |
| C2—H2B | 0.9700 | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| C2—C3 | 1.501 (3) | C10—C11 | 1.384 (3) |
| C3—C4 | 1.494 (3) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C4—H4A | 0.9700 | C11—C12 | 1.374 (3) |
| C4—H4B | 0.9700 | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| C4—C5 | 1.534 (3) | C12—C13 | 1.373 (3) |
| C5—H5 | 0.9800 | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| C5—C6 | 1.522 (3) | C13—C14 | 1.376 (3) |
| C6—H6A | 0.9700 | C14—H14 | 0.9300 |
| C6—H6B | 0.9700 | ||
| C1—N1—C5 | 110.46 (14) | C7—C6—C5 | 112.88 (17) |
| C9—N1—C1 | 119.07 (15) | C7—C6—H6A | 109.0 |
| C9—N1—C5 | 118.22 (14) | C7—C6—H6B | 109.0 |
| N1—C1—H1 | 107.9 | C6—C7—H7A | 109.6 |
| N1—C1—C2 | 111.11 (15) | C6—C7—H7B | 109.6 |
| N1—C1—C8 | 108.76 (15) | H7A—C7—H7B | 108.2 |
| C2—C1—H1 | 107.9 | C8—C7—C6 | 110.08 (16) |
| C8—C1—H1 | 107.9 | C8—C7—H7A | 109.6 |
| C8—C1—C2 | 113.10 (16) | C8—C7—H7B | 109.6 |
| C1—C2—H2A | 108.7 | C1—C8—H8A | 109.2 |
| C1—C2—H2B | 108.7 | C1—C8—H8B | 109.2 |
| H2A—C2—H2B | 107.6 | C7—C8—C1 | 112.14 (16) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 114.39 (17) | C7—C8—H8A | 109.2 |
| C3—C2—H2A | 108.7 | C7—C8—H8B | 109.2 |
| C3—C2—H2B | 108.7 | H8A—C8—H8B | 107.9 |
| O1—C3—C2 | 121.5 (2) | C10—C9—N1 | 122.68 (16) |
| O1—C3—C4 | 122.1 (2) | C10—C9—C14 | 117.02 (18) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 116.42 (18) | C14—C9—N1 | 120.20 (17) |
| C3—C4—H4A | 108.7 | C9—C10—H10 | 119.4 |
| C3—C4—H4B | 108.7 | C11—C10—C9 | 121.13 (19) |
| C3—C4—C5 | 114.20 (16) | C11—C10—H10 | 119.4 |
| H4A—C4—H4B | 107.6 | C10—C11—H11 | 119.5 |
| C5—C4—H4A | 108.7 | C12—C11—C10 | 121.1 (2) |
| C5—C4—H4B | 108.7 | C12—C11—H11 | 119.5 |
| N1—C5—C4 | 110.04 (15) | C11—C12—H12 | 120.9 |
| N1—C5—H5 | 108.0 | C13—C12—C11 | 118.28 (19) |
| N1—C5—C6 | 110.25 (16) | C13—C12—H12 | 120.9 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 108.0 | C12—C13—H13 | 119.3 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 112.44 (16) | C12—C13—C14 | 121.5 (2) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 108.0 | C14—C13—H13 | 119.3 |
| C5—C6—H6A | 109.0 | C9—C14—H14 | 119.5 |
| C5—C6—H6B | 109.0 | C13—C14—C9 | 121.0 (2) |
| H6A—C6—H6B | 107.8 | C13—C14—H14 | 119.5 |
| O1—C3—C4—C5 | 146.4 (2) | C5—N1—C1—C2 | 61.85 (19) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | −46.2 (2) | C5—N1—C1—C8 | −63.28 (19) |
| N1—C1—C8—C7 | 58.9 (2) | C5—N1—C9—C10 | −142.12 (17) |
| N1—C5—C6—C7 | −54.0 (2) | C5—N1—C9—C14 | 41.6 (2) |
| N1—C9—C10—C11 | −177.64 (17) | C5—C6—C7—C8 | 49.0 (2) |
| N1—C9—C14—C13 | 177.52 (18) | C6—C7—C8—C1 | −51.6 (2) |
| C1—N1—C5—C4 | −63.47 (19) | C8—C1—C2—C3 | 76.4 (2) |
| C1—N1—C5—C6 | 61.12 (19) | C9—N1—C1—C2 | −79.9 (2) |
| C1—N1—C9—C10 | −3.3 (2) | C9—N1—C1—C8 | 155.02 (16) |
| C1—N1—C9—C14 | −179.62 (16) | C9—N1—C5—C4 | 78.60 (18) |
| C1—C2—C3—O1 | −148.4 (2) | C9—N1—C5—C6 | −156.81 (15) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 34.0 (2) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | 0.7 (3) |
| C2—C1—C8—C7 | −65.0 (2) | C10—C9—C14—C13 | 1.0 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −35.9 (2) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | 0.2 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—N1 | 49.8 (2) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | −0.4 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −73.5 (2) | C12—C13—C14—C9 | −0.2 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | 69.2 (2) | C14—C9—C10—C11 | −1.2 (3) |
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: FY2049).
References
- Agilent (2011). CrysAlis PRO Agilent Technologies UK Ltd, Yarnton, Oxfordshire, England.
- Cremer, D. & Pople, J. A. (1975). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 97, 1354–1358.
- Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K. & Puschmann, H. (2009). J. Appl. Cryst. 42, 339–341.
- Lazny, R., Wolosewicz, K., Zielinska, P., Lipkowska, Z. U. & Kalicki, P. (2011). Tetrahedron, 67, 9433–9439.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Vernekar, S. K. V., Hallaq, H. Y., Clarkson, G., Thompson, A. J., Silvestri, L., Lummis, S. C. R. & Lochner, M. (2010). J. Med. Chem. 53, 2324–2328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y. (2003). CN Patent 1451660A.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812020065/fy2049sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812020065/fy2049Isup3.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812020065/fy2049Isup4.cdx
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812020065/fy2049Isup4.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report