Abstract
In the title compound, C17H20ClFN2O3, the dihedral angle between the pyridazine and benzene rings is 41.37 (10)°. In the crystal, there are no significant intermolecular interactions present. The terminal –CH2F group is disordered over two sets of sites with an occupancy ratio of 0.737 (2):0.263 (2).
Related literature
For details of the synthesis, see: Mou et al. (2010 ▶, 2012 ▶). For possible applications of the title compound as a myocardial perfusion imaging agent for positron emission tomography (when labelled with 18F), see: Mou et al. (2011 ▶); Mou et al. (2012 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C17H20ClFN2O3
M r = 354.80
Triclinic,
a = 8.7170 (14) Å
b = 9.5850 (16) Å
c = 11.8524 (19) Å
α = 110.475 (2)°
β = 107.185 (2)°
γ = 96.424 (3)°
V = 860.3 (2) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.25 mm−1
T = 150 K
0.47 × 0.38 × 0.35 mm
Data collection
Bruker APEXII CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2009 ▶) T min = 0.892, T max = 0.918
4337 measured reflections
3090 independent reflections
2788 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.016
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.036
wR(F 2) = 0.094
S = 1.05
3090 reflections
227 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.32 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.28 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2009 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2009 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812020491/aa2046sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812020491/aa2046Isup4.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812020491/aa2046Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr Xuebin Deng, from the College of Chemistry, Beijing Normal University, for his kind help with the diffraction data collection. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (20871020), Beijing Natural Science Foundation (2092018) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Myocardial uptake of the pyridaben analogues, which is correlated with blood flow, makes them potential myocardial perfusion imaging (MPI) agents for the positron emission tomography (PET) when labeled with 18F (Mou et al., 2010; Mou et al., 2011; Mou et al., 2012). Thus, the development of pyridaben analogues may lead to discover new valuable PET MPI agents.
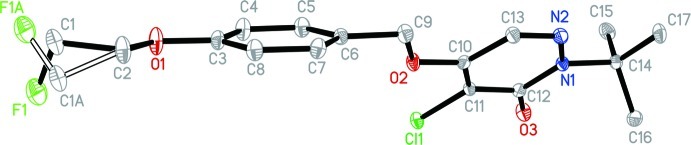
The molecular structure of the title compound (measured at 150 K) is shown in Fig. 1. The dihedral angle between the pyridazine ring and the benzene ring is 41.37 (10)°. The terminal CH2F group is disordered between two positions with occupancies 0.737 (2) for C1F1 and 0.263 (2) for C1AF1A.
Experimental
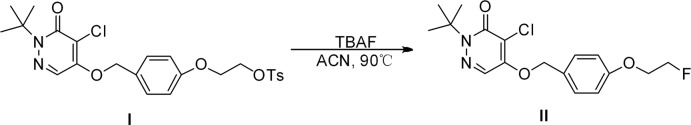
The synthesis route is shown in Fig. 2. The solution of tert-butylammonium fluoride (1 mmol in 1 ml tetrahydrofuran) was stirred in a stream of nitrogen at 110 °C to remove the solvent. Then 2-tert-butyl-4-chloro-5-(4-(2-tosylethoxy-ethoxy)-benzyloxy)-2H-pyridazin-3-one (compound I, 0.30 mmol in 3 ml anhydrous CH3CN) was added to the above evaporation residue, and refluxed for 40 min at 90 °C. After concentration under reduced pressure, the residue was chromatographed over a column of silica gel and eluted with the mixture of dichloromethane and methanol (100:1). The product was obtained as white solid. The product was then recrystallized from the mixture of hexane and methanol (2:1) yielding colorless crystals of the title compound suitable for the single-crystal X-ray diffraction.
Refinement
The H atoms bound to C atoms were positioned geometrically and refined using a riding model, with C—H = 0.99 Å for CH2 groups, 0.95 Å for aryl and 0.98 Å for methyl H atoms, Uiso(H) =1.2Ueq(C) for CH2 groups and aryl, and Uiso(H) =1.5Ueq(C) for methyl H atoms.
Figures
Fig. 1.
Molecular structure of the title compound showing the atom labeling scheme and 30% probability displacement ellipsoids. H atoms are omitted for clarity.
Fig. 2.
The synthesis route of the title compound.
Crystal data
| C17H20ClFN2O3 | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 354.80 | F(000) = 372 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.370 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Melting point: 396 K |
| a = 8.7170 (14) Å | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| b = 9.5850 (16) Å | Cell parameters from 2518 reflections |
| c = 11.8524 (19) Å | θ = 2.3–27.5° |
| α = 110.475 (2)° | µ = 0.25 mm−1 |
| β = 107.185 (2)° | T = 150 K |
| γ = 96.424 (3)° | Column, colourless, colourless |
| V = 860.3 (2) Å3 | 0.47 × 0.38 × 0.35 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD area-detector diffractometer | 3090 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2788 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.016 |
| phi and ω scans | θmax = 25.3°, θmin = 2.3° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2009) | h = −6→10 |
| Tmin = 0.892, Tmax = 0.918 | k = −11→10 |
| 4337 measured reflections | l = −14→13 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.036 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.094 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.05 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0431P)2 + 0.4066P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3090 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 227 parameters | Δρmax = 0.32 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.28 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All s.u.'s (except the s.u. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell s.u.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of s.u.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between s.u.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell s.u.'s is used for estimating s.u.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | Occ. (<1) | |
| C1 | 0.7610 (4) | 1.6895 (3) | 0.6672 (3) | 0.0356 (7) | 0.737 (2) |
| H1A | 0.7483 | 1.7463 | 0.7502 | 0.043* | 0.737 (2) |
| H1B | 0.8756 | 1.7279 | 0.6751 | 0.043* | 0.737 (2) |
| F1 | 0.6489 (2) | 1.71415 (19) | 0.56807 (19) | 0.0563 (5) | 0.737 (2) |
| C1A | 0.6652 (12) | 1.6621 (10) | 0.6292 (9) | 0.0356 (7) | 0.263 (2) |
| H1A1 | 0.5919 | 1.6389 | 0.5400 | 0.043* | 0.263 (2) |
| H1A2 | 0.6036 | 1.6957 | 0.6880 | 0.043* | 0.263 (2) |
| F1A | 0.8073 (7) | 1.7730 (6) | 0.6664 (5) | 0.0563 (5) | 0.263 (2) |
| C2 | 0.7295 (3) | 1.5215 (2) | 0.63796 (19) | 0.0357 (5) | |
| H2A | 0.7927 | 1.5042 | 0.7142 | 0.043* | |
| H2B | 0.6104 | 1.4780 | 0.6141 | 0.043* | |
| C3 | 0.7804 (2) | 1.29834 (18) | 0.49589 (16) | 0.0253 (4) | |
| C4 | 0.8406 (2) | 1.2381 (2) | 0.39752 (17) | 0.0301 (4) | |
| H4 | 0.8787 | 1.3019 | 0.3607 | 0.036* | |
| C5 | 0.8452 (2) | 1.08544 (19) | 0.35314 (16) | 0.0278 (4) | |
| H5 | 0.8883 | 1.0456 | 0.2867 | 0.033* | |
| C6 | 0.7879 (2) | 0.98912 (18) | 0.40407 (15) | 0.0224 (4) | |
| C7 | 0.7268 (2) | 1.05060 (19) | 0.50116 (16) | 0.0267 (4) | |
| H7 | 0.6861 | 0.9860 | 0.5363 | 0.032* | |
| C8 | 0.7234 (2) | 1.2049 (2) | 0.54876 (17) | 0.0276 (4) | |
| H8 | 0.6827 | 1.2454 | 0.6165 | 0.033* | |
| C9 | 0.7940 (2) | 0.82347 (19) | 0.35594 (16) | 0.0271 (4) | |
| H9A | 0.9074 | 0.8134 | 0.3944 | 0.032* | |
| H9B | 0.7176 | 0.7643 | 0.3796 | 0.032* | |
| C10 | 0.74817 (19) | 0.62230 (17) | 0.15061 (16) | 0.0205 (3) | |
| C11 | 0.69499 (19) | 0.56701 (17) | 0.01958 (15) | 0.0196 (3) | |
| C12 | 0.69623 (19) | 0.41371 (18) | −0.05951 (15) | 0.0205 (3) | |
| C13 | 0.8067 (2) | 0.52043 (18) | 0.20730 (16) | 0.0244 (4) | |
| H13 | 0.8450 | 0.5560 | 0.2986 | 0.029* | |
| C14 | 0.7659 (2) | 0.16475 (18) | −0.05844 (16) | 0.0224 (4) | |
| C15 | 0.8931 (2) | 0.1704 (2) | −0.12319 (19) | 0.0319 (4) | |
| H15A | 0.8604 | 0.2209 | −0.1825 | 0.048* | |
| H15B | 0.8984 | 0.0657 | −0.1714 | 0.048* | |
| H15C | 1.0020 | 0.2281 | −0.0571 | 0.048* | |
| C16 | 0.5943 (2) | 0.06939 (19) | −0.15633 (18) | 0.0324 (4) | |
| H16A | 0.5141 | 0.0780 | −0.1127 | 0.049* | |
| H16B | 0.5978 | −0.0383 | −0.1945 | 0.049* | |
| H16C | 0.5612 | 0.1075 | −0.2244 | 0.049* | |
| C17 | 0.8217 (2) | 0.09524 (19) | 0.03935 (18) | 0.0308 (4) | |
| H17A | 0.9307 | 0.1564 | 0.1034 | 0.046* | |
| H17B | 0.8286 | −0.0101 | −0.0049 | 0.046* | |
| H17C | 0.7419 | 0.0946 | 0.0827 | 0.046* | |
| Cl1 | 0.62207 (5) | 0.67867 (4) | −0.06075 (4) | 0.02475 (13) | |
| N1 | 0.75585 (16) | 0.32789 (14) | 0.01074 (12) | 0.0199 (3) | |
| N2 | 0.81035 (17) | 0.38114 (15) | 0.14042 (13) | 0.0241 (3) | |
| O1 | 0.78194 (18) | 1.45135 (14) | 0.53292 (12) | 0.0356 (3) | |
| O2 | 0.74477 (15) | 0.76678 (12) | 0.21681 (10) | 0.0246 (3) | |
| O3 | 0.64984 (16) | 0.36158 (13) | −0.17774 (11) | 0.0292 (3) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0526 (19) | 0.0305 (15) | 0.0392 (17) | 0.0225 (17) | 0.0274 (16) | 0.0189 (13) |
| F1 | 0.0628 (11) | 0.0390 (9) | 0.0698 (12) | 0.0205 (8) | 0.0142 (9) | 0.0304 (9) |
| C1A | 0.0526 (19) | 0.0305 (15) | 0.0392 (17) | 0.0225 (17) | 0.0274 (16) | 0.0189 (13) |
| F1A | 0.0628 (11) | 0.0390 (9) | 0.0698 (12) | 0.0205 (8) | 0.0142 (9) | 0.0304 (9) |
| C2 | 0.0596 (13) | 0.0248 (9) | 0.0333 (10) | 0.0188 (9) | 0.0280 (10) | 0.0119 (8) |
| C3 | 0.0340 (10) | 0.0181 (8) | 0.0221 (8) | 0.0079 (7) | 0.0098 (7) | 0.0057 (7) |
| C4 | 0.0469 (11) | 0.0229 (9) | 0.0271 (9) | 0.0100 (8) | 0.0203 (8) | 0.0114 (7) |
| C5 | 0.0380 (10) | 0.0247 (9) | 0.0220 (9) | 0.0098 (7) | 0.0151 (8) | 0.0068 (7) |
| C6 | 0.0266 (9) | 0.0197 (8) | 0.0159 (8) | 0.0058 (7) | 0.0038 (7) | 0.0048 (6) |
| C7 | 0.0355 (10) | 0.0225 (8) | 0.0239 (9) | 0.0055 (7) | 0.0131 (7) | 0.0097 (7) |
| C8 | 0.0378 (10) | 0.0253 (9) | 0.0225 (9) | 0.0104 (7) | 0.0160 (8) | 0.0075 (7) |
| C9 | 0.0376 (10) | 0.0228 (9) | 0.0176 (8) | 0.0094 (7) | 0.0076 (7) | 0.0059 (7) |
| C10 | 0.0196 (8) | 0.0163 (7) | 0.0229 (8) | 0.0034 (6) | 0.0071 (7) | 0.0057 (7) |
| C11 | 0.0197 (8) | 0.0184 (8) | 0.0220 (8) | 0.0052 (6) | 0.0076 (6) | 0.0095 (7) |
| C12 | 0.0212 (8) | 0.0206 (8) | 0.0207 (8) | 0.0056 (6) | 0.0095 (7) | 0.0077 (7) |
| C13 | 0.0294 (9) | 0.0203 (8) | 0.0178 (8) | 0.0068 (7) | 0.0044 (7) | 0.0042 (7) |
| C14 | 0.0243 (8) | 0.0166 (8) | 0.0237 (9) | 0.0072 (6) | 0.0085 (7) | 0.0046 (7) |
| C15 | 0.0329 (10) | 0.0327 (10) | 0.0375 (10) | 0.0167 (8) | 0.0188 (8) | 0.0147 (8) |
| C16 | 0.0280 (10) | 0.0188 (8) | 0.0366 (10) | 0.0057 (7) | 0.0058 (8) | 0.0003 (8) |
| C17 | 0.0422 (11) | 0.0195 (8) | 0.0308 (10) | 0.0119 (8) | 0.0126 (8) | 0.0094 (7) |
| Cl1 | 0.0323 (2) | 0.0221 (2) | 0.0243 (2) | 0.01014 (16) | 0.01102 (17) | 0.01263 (17) |
| N1 | 0.0233 (7) | 0.0167 (7) | 0.0173 (7) | 0.0053 (5) | 0.0062 (6) | 0.0048 (5) |
| N2 | 0.0277 (8) | 0.0217 (7) | 0.0188 (7) | 0.0063 (6) | 0.0046 (6) | 0.0065 (6) |
| O1 | 0.0646 (9) | 0.0198 (6) | 0.0329 (7) | 0.0160 (6) | 0.0302 (7) | 0.0104 (5) |
| O2 | 0.0353 (7) | 0.0166 (6) | 0.0177 (6) | 0.0091 (5) | 0.0069 (5) | 0.0035 (5) |
| O3 | 0.0432 (7) | 0.0261 (6) | 0.0187 (6) | 0.0131 (5) | 0.0117 (5) | 0.0075 (5) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| C1—F1 | 1.400 (4) | C9—H9B | 0.9900 |
| C1—C2 | 1.497 (3) | C10—O2 | 1.3405 (19) |
| C1—H1A | 0.9900 | C10—C11 | 1.361 (2) |
| C1—H1B | 0.9900 | C10—C13 | 1.426 (2) |
| C1A—F1A | 1.383 (11) | C11—C12 | 1.444 (2) |
| C1A—C2 | 1.541 (9) | C11—Cl1 | 1.7215 (16) |
| C1A—H1A1 | 0.9900 | C12—O3 | 1.2276 (19) |
| C1A—H1A2 | 0.9900 | C12—N1 | 1.400 (2) |
| C2—O1 | 1.425 (2) | C13—N2 | 1.302 (2) |
| C2—H2A | 0.9900 | C13—H13 | 0.9500 |
| C2—H2B | 0.9900 | C14—N1 | 1.5169 (19) |
| C3—O1 | 1.373 (2) | C14—C17 | 1.518 (2) |
| C3—C8 | 1.385 (2) | C14—C15 | 1.529 (2) |
| C3—C4 | 1.388 (2) | C14—C16 | 1.531 (2) |
| C4—C5 | 1.381 (2) | C15—H15A | 0.9800 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9500 | C15—H15B | 0.9800 |
| C5—C6 | 1.390 (2) | C15—H15C | 0.9800 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9500 | C16—H16A | 0.9800 |
| C6—C7 | 1.383 (2) | C16—H16B | 0.9800 |
| C6—C9 | 1.501 (2) | C16—H16C | 0.9800 |
| C7—C8 | 1.393 (2) | C17—H17A | 0.9800 |
| C7—H7 | 0.9500 | C17—H17B | 0.9800 |
| C8—H8 | 0.9500 | C17—H17C | 0.9800 |
| C9—O2 | 1.450 (2) | N1—N2 | 1.3469 (18) |
| C9—H9A | 0.9900 | ||
| F1—C1—C2 | 109.6 (2) | H9A—C9—H9B | 108.6 |
| F1—C1—H1A | 109.8 | O2—C10—C11 | 118.74 (14) |
| C2—C1—H1A | 109.8 | O2—C10—C13 | 124.85 (14) |
| F1—C1—H1B | 109.8 | C11—C10—C13 | 116.40 (14) |
| C2—C1—H1B | 109.8 | C10—C11—C12 | 122.61 (14) |
| H1A—C1—H1B | 108.2 | C10—C11—Cl1 | 121.01 (12) |
| F1A—C1A—C2 | 103.9 (6) | C12—C11—Cl1 | 116.38 (12) |
| F1A—C1A—H1A1 | 111.0 | O3—C12—N1 | 122.25 (14) |
| C2—C1A—H1A1 | 111.0 | O3—C12—C11 | 123.81 (15) |
| F1A—C1A—H1A2 | 111.0 | N1—C12—C11 | 113.94 (14) |
| C2—C1A—H1A2 | 111.0 | N2—C13—C10 | 123.44 (15) |
| H1A1—C1A—H1A2 | 109.0 | N2—C13—H13 | 118.3 |
| O1—C2—C1 | 106.72 (17) | C10—C13—H13 | 118.3 |
| O1—C2—C1A | 110.7 (4) | N1—C14—C17 | 109.19 (13) |
| O1—C2—H2A | 110.4 | N1—C14—C15 | 108.07 (13) |
| C1—C2—H2A | 110.4 | C17—C14—C15 | 109.53 (14) |
| C1A—C2—H2A | 130.3 | N1—C14—C16 | 109.30 (13) |
| O1—C2—H2B | 110.4 | C17—C14—C16 | 108.73 (14) |
| C1—C2—H2B | 110.4 | C15—C14—C16 | 111.99 (15) |
| C1A—C2—H2B | 81.7 | C14—C15—H15A | 109.5 |
| H2A—C2—H2B | 108.6 | C14—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| O1—C3—C8 | 124.76 (15) | H15A—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| O1—C3—C4 | 115.27 (15) | C14—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| C8—C3—C4 | 119.97 (15) | H15A—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 120.07 (16) | H15B—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 120.0 | C14—C16—H16A | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 120.0 | C14—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 121.06 (16) | H16A—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.5 | C14—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.5 | H16A—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—C5 | 118.15 (15) | H16B—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—C9 | 121.02 (15) | C14—C17—H17A | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—C9 | 120.83 (15) | C14—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—C8 | 121.73 (16) | H17A—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—H7 | 119.1 | C14—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—H7 | 119.1 | H17A—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C3—C8—C7 | 119.02 (16) | H17B—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C3—C8—H8 | 120.5 | N2—N1—C12 | 124.27 (13) |
| C7—C8—H8 | 120.5 | N2—N1—C14 | 115.40 (12) |
| O2—C9—C6 | 107.02 (13) | C12—N1—C14 | 120.33 (13) |
| O2—C9—H9A | 110.3 | C13—N2—N1 | 119.34 (14) |
| C6—C9—H9A | 110.3 | C3—O1—C2 | 117.83 (13) |
| O2—C9—H9B | 110.3 | C10—O2—C9 | 118.79 (12) |
| C6—C9—H9B | 110.3 |
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: AA2046).
References
- Bruker (2009). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Mou, T. T., Jing, H. H., Yang, W. J., Fang, W., Peng, C., Guo, F., Zhang, X. Z., Pang, Y. & Ma, Y. C. (2010). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 18, 1312–1320. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Mou, T. T., Zhao, Z. Q., Fang, W., Peng, C., Guo, F., Liu, B. L., Ma, Y. C. & Zhang, X. Z. (2012). J. Nucl. Med. 53, 472–479. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Mou, T. T., Zhao, Z. Q., Fang, W., Peng, C., Zhang, X. Z. & Liu, B. L. (2011). J. Nucl. Med. 52(Suppl. 1), 77.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812020491/aa2046sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812020491/aa2046Isup4.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812020491/aa2046Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report