Abstract
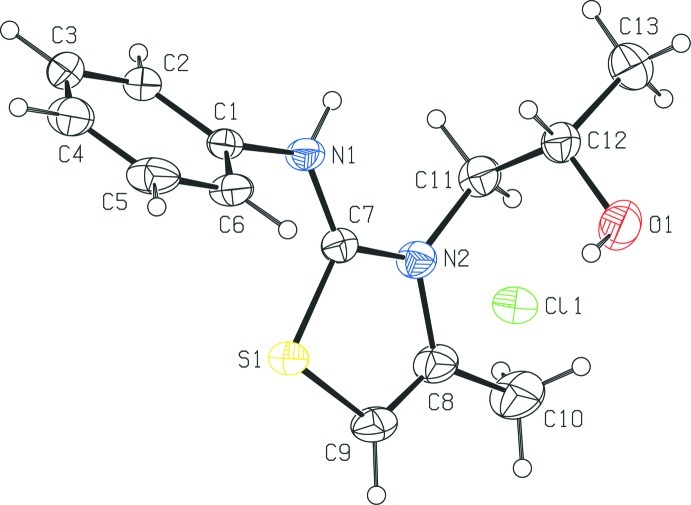
In the title compound, C13H17N2OS+·Cl−, the thiazolium ring mean plane makes a dihedral angle of 55.46 (9)° with the benzene ring. In the propanol group, the N—C—C—C and N—C—C—O torsion angles are 172.58 (15) and 52.9 (2)°, respectively, and the S—C—C—C torsion angle is 178.99 (18)°. In the crystal, molecules are linked by O—H⋯Cl and N—H⋯Cl hydrogen bonds, forming zigzag chains along [001]. There is also a C—H⋯Cl interaction present.
Related literature
The title compound was prepared as part of an ongoing investigation into the synthesis and biological properties of thiazole compounds: see; Abdel-Wahab et al. (2009 ▶); Baia et al. (2008 ▶); Lesyk et al. (2007 ▶); Mohamed et al. (2012a
▶,b
▶); Potikha et al. (2008 ▶); Shiradkar et al. (2007 ▶); Soliman et al. (2012 ▶); Wu & Yang (2007 ▶). For related structures, see: Lynch & McClenaghan (2004 ▶); Liu et al. (2011 ▶); Wang (2011 ▶).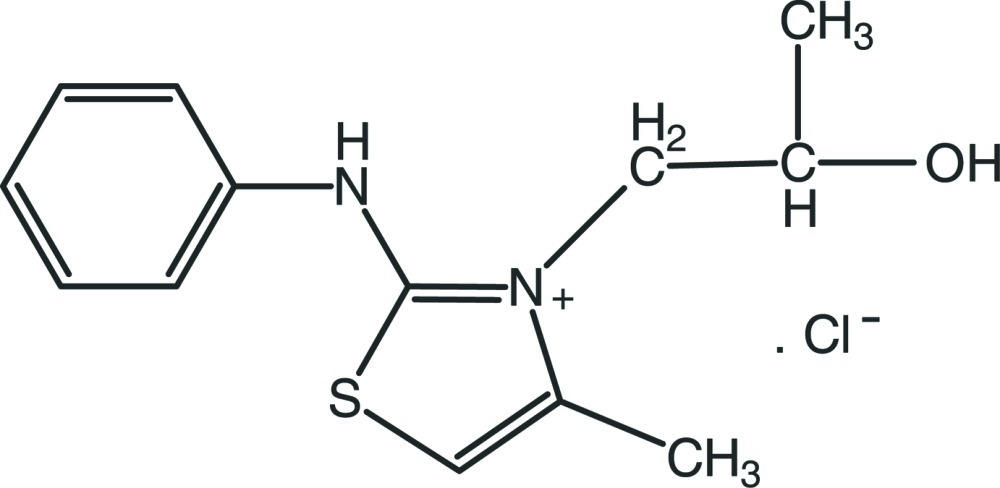
Experimental
Crystal data
C13H17N2OS+·Cl−
M r = 284.81
Monoclinic,
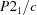
a = 11.7570 (4) Å
b = 12.2477 (4) Å
c = 10.2954 (3) Å
β = 106.532 (1)°
V = 1421.21 (8) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.41 mm−1
T = 296 K
0.35 × 0.22 × 0.20 mm
Data collection
Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2005 ▶) T min = 0.898, T max = 0.922
10535 measured reflections
2641 independent reflections
2172 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.024
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.032
wR(F 2) = 0.084
S = 1.03
2641 reflections
166 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.17 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.18 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2007 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2007 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 1997 ▶) and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: WinGX (Farrugia, 1999 ▶) and PLATON.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812023197/su2431sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812023197/su2431Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812023197/su2431Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1—H1A⋯Cl1 | 0.82 | 2.36 | 3.1681 (16) | 169 |
| N1—H1⋯Cl1i | 0.86 | 2.34 | 3.1675 (14) | 163 |
| C11—H11A⋯Cl1i | 0.97 | 2.81 | 3.6440 (19) | 144 |
Symmetry code: (i) 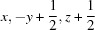 .
.
Acknowledgments
SKM and AAA thank the Ministry of Higher Education, Egypt, for financial support of this project. Manchester Metropolitan University and the University of Sargodha are also gratefully acknowledged for supporting this study.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Natural compounds such as, bistratamide H, archazolid A & B, siomycin A, didmolamide A, scleritodermin A, etc. (Wu & Yang, 2007) and thiamine (vitamin B1) (Baia et al., 2008), were found to have a thiazol ring system. In addition, thiazole compounds have been reported to exhibit different pharmaceutical properties, for example antibacterial, antifungal (Abdel-Wahab et al., 2009), antitubercular (Shiradkar et al., 2007), anticancer (Lesyk et al., 2007). These compounds have been synthesized using different methods (Potikha et al., 2008). Further to our interest of bioactive compounds (Mohamed et al., 2012a,b; Soliman et al., 2012) we were interested in synthesizing new amino-thiazole derivatives via a one pot reaction protocol. We report herein on the synthesis and crystal structure of the title compound.
In the title compound, (Fig. 1), the dihedral angle between the thiazole ring (S1/N2/C7–C9) and the benzene ring (C1–C6) is 55.46 (9)°. The thiazolium ring is essentialy co-planar with the methyl group which is attached to it, with torsion angle S1—C9—C8—C10 being 178.99 (18)°. In the propanol group, torsion angles N2–C11–C12–C13 and N2–C11–C12–O1 are 172.58 (15) and 52.9 (2)°, respectively. Bond lengths and angles have normal values and are comparable to those reported for similar structures (Lynch & McClenaghan, 2004; Liu et al., 2011; Wang, 2011).
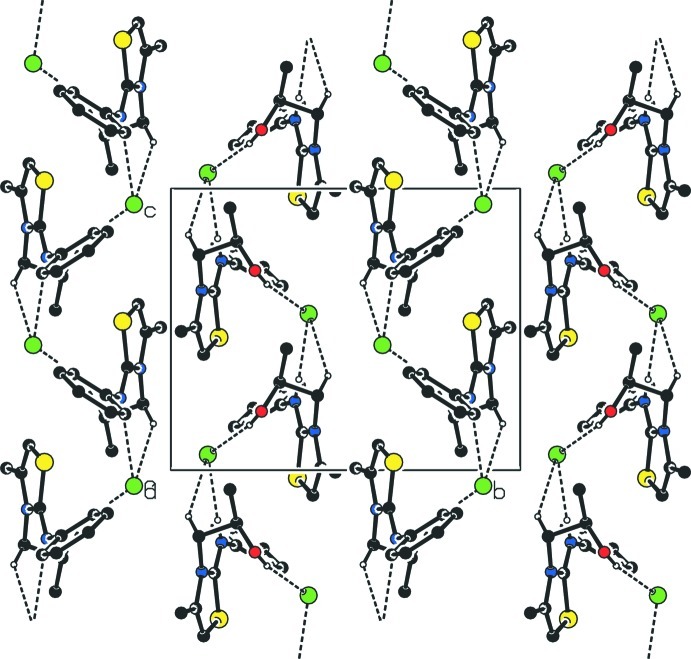
In the crystal, molecules are linked by O-H···Cl, N—H···Cl and C—H···Cl hydrogen bonds, into infinite zigzag chains propagating along the [001] direction (Table 1, Fig. 2).
Experimental
A mixture of 75 mg (1 mmol) 1-aminopropan-2-ol, 135 mg (1 mmol) phenyl isothiocyanate and 93 mg (1 mmol) 1-chloropropan-2-one in 50 ml ethanol was refluxed at 351 K. The reaction was monitored by TLC until completion after four hours then cooled to room temperature. The resulting solid was filtered off, dried under vacuum and recrystallized from ethanol to afford colourless crystals suitable for X-ray analysis [Yield 79%; M.p. 419 K].
Refinement
The H atoms were located in a difference Fourier map. In the final cycles of refinement they were included in calculated poitions and refined using a riding model: N—H = 0.86 Å and C—H = 0.93 Å (aromatic), 0.96 Å (methyl), 0.97 Å (methylene) and 0.98 Å (methine), with Uiso(H) = 1.5Ueq(C) for methyl groups and = 1.2Ueq(C,N) for other H atoms.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure and atom-numbering scheme for the title compound. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 30% probability level.
Fig. 2.
The crystal packing of the title compound, viewing along the a axis. H atoms not involved in hydrogen bonds (dashed lines) have been omitted for clarity.
Crystal data
| C13H17N2OS+·Cl− | F(000) = 600 |
| Mr = 284.81 | Dx = 1.331 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 447 reflections |
| a = 11.7570 (4) Å | θ = 3.5–21.2° |
| b = 12.2477 (4) Å | µ = 0.41 mm−1 |
| c = 10.2954 (3) Å | T = 296 K |
| β = 106.532 (1)° | Rod, colourless |
| V = 1421.21 (8) Å3 | 0.35 × 0.22 × 0.20 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer | 2641 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2172 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.024 |
| Detector resolution: 0.81 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 25.5°, θmin = 2.5° |
| ω scans | h = −14→11 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2005) | k = −14→14 |
| Tmin = 0.898, Tmax = 0.922 | l = −12→12 |
| 10535 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.032 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.084 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.03 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0393P)2 + 0.3249P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2641 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 166 parameters | Δρmax = 0.17 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.18 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. Bond distances, angles etc. have been calculated using the rounded fractional coordinates. All su's are estimated from the variances of the (full) variance-covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account in the estimation of distances, angles and torsion angles |
| Refinement. Refinement on F2 for ALL reflections except those flagged by the user for potential systematic errors. Weighted R-factors wR and all goodnesses of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The observed criterion of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating -R-factor-obs etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R-factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| S1 | 0.53335 (4) | 0.36209 (4) | −0.02819 (4) | 0.0436 (2) | |
| O1 | 0.92376 (12) | 0.25939 (14) | 0.20894 (15) | 0.0722 (6) | |
| N1 | 0.58597 (12) | 0.35477 (12) | 0.24335 (13) | 0.0424 (4) | |
| N2 | 0.73113 (12) | 0.41117 (12) | 0.13880 (14) | 0.0447 (5) | |
| C1 | 0.47013 (14) | 0.31414 (14) | 0.23234 (15) | 0.0382 (5) | |
| C2 | 0.40120 (15) | 0.36823 (15) | 0.30052 (17) | 0.0455 (6) | |
| C3 | 0.29021 (17) | 0.3281 (2) | 0.29410 (19) | 0.0586 (7) | |
| C4 | 0.24821 (17) | 0.2359 (2) | 0.22085 (19) | 0.0673 (8) | |
| C5 | 0.31707 (18) | 0.18174 (19) | 0.15336 (18) | 0.0612 (7) | |
| C6 | 0.42873 (16) | 0.22021 (15) | 0.15893 (16) | 0.0471 (6) | |
| C7 | 0.62227 (15) | 0.37561 (13) | 0.13445 (16) | 0.0384 (5) | |
| C8 | 0.74511 (17) | 0.42898 (16) | 0.00903 (19) | 0.0522 (7) | |
| C9 | 0.64774 (18) | 0.40625 (15) | −0.08878 (19) | 0.0527 (7) | |
| C10 | 0.8594 (2) | 0.4705 (2) | −0.0071 (2) | 0.0812 (9) | |
| C11 | 0.82819 (15) | 0.41979 (16) | 0.26481 (18) | 0.0509 (6) | |
| C12 | 0.88729 (16) | 0.31168 (18) | 0.31206 (19) | 0.0544 (7) | |
| C13 | 0.99588 (18) | 0.3309 (2) | 0.4314 (2) | 0.0775 (9) | |
| Cl1 | 0.71127 (4) | 0.10568 (4) | 0.05541 (4) | 0.0553 (2) | |
| H1 | 0.63390 | 0.36620 | 0.32250 | 0.0510* | |
| H1A | 0.86790 | 0.22510 | 0.16010 | 0.1080* | |
| H2 | 0.42940 | 0.43100 | 0.35010 | 0.0550* | |
| H3 | 0.24340 | 0.36390 | 0.33990 | 0.0700* | |
| H4 | 0.17300 | 0.20970 | 0.21670 | 0.0810* | |
| H5 | 0.28820 | 0.11910 | 0.10390 | 0.0730* | |
| H6 | 0.47560 | 0.18360 | 0.11400 | 0.0560* | |
| H9 | 0.64160 | 0.41330 | −0.18050 | 0.0630* | |
| H10A | 0.85460 | 0.47390 | −0.10170 | 0.1220* | |
| H10B | 0.92260 | 0.42230 | 0.03820 | 0.1220* | |
| H10C | 0.87460 | 0.54220 | 0.03170 | 0.1220* | |
| H11A | 0.79720 | 0.44960 | 0.33520 | 0.0610* | |
| H11B | 0.88720 | 0.47040 | 0.25100 | 0.0610* | |
| H12 | 0.83160 | 0.26440 | 0.34050 | 0.0650* | |
| H13A | 1.05130 | 0.37610 | 0.40350 | 0.1160* | |
| H13B | 1.03240 | 0.26220 | 0.46350 | 0.1160* | |
| H13C | 0.97260 | 0.36660 | 0.50290 | 0.1160* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.0486 (3) | 0.0486 (3) | 0.0332 (2) | −0.0003 (2) | 0.0112 (2) | 0.0015 (2) |
| O1 | 0.0544 (8) | 0.0909 (12) | 0.0737 (10) | 0.0018 (8) | 0.0221 (8) | −0.0187 (8) |
| N1 | 0.0389 (7) | 0.0577 (9) | 0.0305 (7) | −0.0068 (7) | 0.0095 (6) | −0.0046 (6) |
| N2 | 0.0429 (8) | 0.0501 (9) | 0.0424 (8) | −0.0073 (7) | 0.0145 (6) | 0.0013 (6) |
| C1 | 0.0368 (9) | 0.0496 (10) | 0.0277 (8) | −0.0008 (8) | 0.0083 (7) | 0.0037 (7) |
| C2 | 0.0466 (10) | 0.0562 (11) | 0.0339 (9) | 0.0062 (8) | 0.0120 (8) | 0.0041 (8) |
| C3 | 0.0417 (10) | 0.0936 (16) | 0.0433 (11) | 0.0091 (11) | 0.0167 (9) | 0.0074 (10) |
| C4 | 0.0415 (11) | 0.1137 (19) | 0.0455 (11) | −0.0179 (12) | 0.0106 (9) | 0.0083 (12) |
| C5 | 0.0641 (13) | 0.0781 (15) | 0.0387 (10) | −0.0288 (11) | 0.0103 (9) | −0.0025 (9) |
| C6 | 0.0539 (11) | 0.0570 (11) | 0.0318 (9) | −0.0069 (9) | 0.0146 (8) | −0.0020 (8) |
| C7 | 0.0415 (9) | 0.0381 (9) | 0.0364 (9) | −0.0001 (7) | 0.0123 (7) | −0.0007 (7) |
| C8 | 0.0578 (11) | 0.0555 (12) | 0.0491 (11) | −0.0065 (9) | 0.0245 (10) | 0.0092 (9) |
| C9 | 0.0665 (12) | 0.0551 (12) | 0.0417 (10) | −0.0017 (9) | 0.0239 (10) | 0.0093 (8) |
| C10 | 0.0748 (15) | 0.1027 (19) | 0.0776 (15) | −0.0227 (14) | 0.0402 (13) | 0.0156 (14) |
| C11 | 0.0423 (10) | 0.0619 (12) | 0.0494 (11) | −0.0140 (9) | 0.0144 (8) | −0.0084 (9) |
| C12 | 0.0401 (10) | 0.0747 (14) | 0.0485 (11) | −0.0024 (9) | 0.0127 (8) | −0.0044 (9) |
| C13 | 0.0479 (12) | 0.117 (2) | 0.0612 (13) | −0.0011 (13) | 0.0050 (10) | −0.0043 (13) |
| Cl1 | 0.0614 (3) | 0.0629 (3) | 0.0409 (3) | 0.0018 (2) | 0.0135 (2) | 0.0051 (2) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| S1—C7 | 1.7111 (17) | C11—C12 | 1.510 (3) |
| S1—C9 | 1.723 (2) | C12—C13 | 1.517 (3) |
| O1—C12 | 1.407 (2) | C2—H2 | 0.9300 |
| O1—H1A | 0.8200 | C3—H3 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C7 | 1.333 (2) | C4—H4 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C1 | 1.424 (2) | C5—H5 | 0.9300 |
| N2—C8 | 1.409 (2) | C6—H6 | 0.9300 |
| N2—C11 | 1.468 (2) | C9—H9 | 0.9300 |
| N2—C7 | 1.341 (2) | C10—H10A | 0.9600 |
| N1—H1 | 0.8600 | C10—H10B | 0.9600 |
| C1—C2 | 1.383 (2) | C10—H10C | 0.9600 |
| C1—C6 | 1.387 (2) | C11—H11A | 0.9700 |
| C2—C3 | 1.378 (3) | C11—H11B | 0.9700 |
| C3—C4 | 1.370 (3) | C12—H12 | 0.9800 |
| C4—C5 | 1.378 (3) | C13—H13A | 0.9600 |
| C5—C6 | 1.381 (3) | C13—H13B | 0.9600 |
| C8—C9 | 1.321 (3) | C13—H13C | 0.9600 |
| C8—C10 | 1.490 (3) | ||
| C7—S1—C9 | 90.08 (9) | C4—C3—H3 | 120.00 |
| C12—O1—H1A | 109.00 | C3—C4—H4 | 120.00 |
| C1—N1—C7 | 121.86 (14) | C5—C4—H4 | 120.00 |
| C7—N2—C11 | 123.21 (14) | C4—C5—H5 | 120.00 |
| C8—N2—C11 | 123.78 (15) | C6—C5—H5 | 120.00 |
| C7—N2—C8 | 112.74 (14) | C1—C6—H6 | 120.00 |
| C7—N1—H1 | 119.00 | C5—C6—H6 | 120.00 |
| C1—N1—H1 | 119.00 | S1—C9—H9 | 124.00 |
| N1—C1—C2 | 118.53 (15) | C8—C9—H9 | 124.00 |
| N1—C1—C6 | 120.85 (15) | C8—C10—H10A | 109.00 |
| C2—C1—C6 | 120.58 (16) | C8—C10—H10B | 110.00 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 119.24 (17) | C8—C10—H10C | 109.00 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 120.57 (19) | H10A—C10—H10B | 109.00 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 120.2 (2) | H10A—C10—H10C | 109.00 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 120.2 (2) | H10B—C10—H10C | 109.00 |
| C1—C6—C5 | 119.21 (17) | N2—C11—H11A | 109.00 |
| S1—C7—N1 | 123.50 (14) | N2—C11—H11B | 109.00 |
| S1—C7—N2 | 112.07 (12) | C12—C11—H11A | 109.00 |
| N1—C7—N2 | 124.42 (15) | C12—C11—H11B | 109.00 |
| N2—C8—C9 | 112.37 (18) | H11A—C11—H11B | 108.00 |
| N2—C8—C10 | 120.73 (16) | O1—C12—H12 | 109.00 |
| C9—C8—C10 | 126.90 (18) | C11—C12—H12 | 109.00 |
| S1—C9—C8 | 112.74 (15) | C13—C12—H12 | 109.00 |
| N2—C11—C12 | 113.11 (15) | C12—C13—H13A | 109.00 |
| O1—C12—C11 | 111.54 (16) | C12—C13—H13B | 109.00 |
| O1—C12—C13 | 108.34 (16) | C12—C13—H13C | 109.00 |
| C11—C12—C13 | 109.20 (18) | H13A—C13—H13B | 109.00 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 120.00 | H13A—C13—H13C | 109.00 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 120.00 | H13B—C13—H13C | 109.00 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 120.00 | ||
| C9—S1—C7—N1 | 178.77 (15) | C8—N2—C7—N1 | −178.65 (16) |
| C9—S1—C7—N2 | −0.17 (14) | C8—N2—C11—C12 | −94.2 (2) |
| C7—S1—C9—C8 | 0.00 (17) | N1—C1—C2—C3 | −178.13 (16) |
| C7—N1—C1—C2 | −127.80 (17) | C2—C1—C6—C5 | 0.7 (3) |
| C7—N1—C1—C6 | 54.5 (2) | N1—C1—C6—C5 | 178.37 (16) |
| C1—N1—C7—S1 | 3.0 (2) | C6—C1—C2—C3 | −0.4 (3) |
| C1—N1—C7—N2 | −178.18 (16) | C1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.2 (3) |
| C8—N2—C7—S1 | 0.27 (19) | C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.4 (3) |
| C11—N2—C7—S1 | −173.96 (13) | C3—C4—C5—C6 | −0.1 (3) |
| C11—N2—C7—N1 | 7.1 (3) | C4—C5—C6—C1 | −0.4 (3) |
| C7—N2—C8—C9 | −0.3 (2) | N2—C8—C9—S1 | 0.1 (2) |
| C11—N2—C8—C9 | 173.93 (17) | C10—C8—C9—S1 | −178.99 (18) |
| C7—N2—C8—C10 | 178.92 (18) | N2—C11—C12—O1 | 52.9 (2) |
| C11—N2—C8—C10 | −6.9 (3) | N2—C11—C12—C13 | 172.58 (15) |
| C7—N2—C11—C12 | 79.4 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O1—H1A···Cl1 | 0.82 | 2.36 | 3.1681 (16) | 169 |
| N1—H1···Cl1i | 0.86 | 2.34 | 3.1675 (14) | 163 |
| C11—H11A···Cl1i | 0.97 | 2.81 | 3.6440 (19) | 144 |
Symmetry code: (i) x, −y+1/2, z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: SU2431).
References
- Abdel-Wahab, B. F., Abdel-Aziz, H. A. & Ahmad, E. M. (2009). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 44, 2632–2635. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Baia, M., Astilean, S. & Iliescu, T. (2008). Raman and SERS Investigations of Pharmaceuticals, pp. 125–142. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer.
- Bruker (2005). SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Bruker (2007). APEX2 and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst. 30, 565.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst. 32, 837–838.
- Lesyk, R., Vladzimirska, O., Holota, S., Zaprutko, L. & Gzella, A. (2007). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 42, 641–648. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.-J., Fu, X.-K., Hu, Z.-K., Wu, X.-J. & Wu, L. (2011). Acta Cryst. E67, o1562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Lynch, D. E. & McClenaghan, I. (2004). Acta Cryst. C60, o815–o817. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, S. K., Abdelhamid, A. A., Maharramov, A. M., Khalilov, A. N., Gurbanov, A. V. & Allahverdiyev, M. A. (2012a). J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 4, 955–965.
- Mohamed, S. K., Abdelhamid, A. A., Maharramov, A. M., Khalilov, A. N., Nagiyev, F. N. & Allahverdiyev, M. A. (2012b). J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 4, 966–971.
- Potikha, L. M., Turov, A. V. & Kovtunenko, V. A. (2008). Chem. Heterocycl. Compd, 44, 86–91.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Shiradkar, M., Kumar, G. V. S., Dasari, V., Tatikonda, S., Akula, K. C. & Shah, R. (2007). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 42, 807–816. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Soliman, A. M., Mohamed, S. K., El Remail, M. A. & Abdel Ghany, H. (2012). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 47, 138–142. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.-F. (2011). Acta Cryst. E67, o1581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y. J. & Yang, B. V. (2007). Prog. Heterocycl. Chem. 18, 247–275.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812023197/su2431sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812023197/su2431Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812023197/su2431Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report