Abstract
In the title molecule, C18H17N5O2, the dihedral angle between the benzene plane and the benzimidazole plane is 19.8 (1)° and the angle between the benzene plane and the triazole plane is 16.7 (1)°. In the crystal, molecules are connected by O—H⋯N hydrogen bonds, forming zigzag chains along the c-axis direction. The chains are connected by bifurcated N—H⋯(N,N) hydrogen bonds into layers parallel to (100). These layers are connected along the a-axis direction by weak C—H⋯O contacts, forming a three-dimensional network.
Related literature
For the bioactivity of benzimidazoles, see: Tebbe et al. (1997 ▶); Andrzejewska et al. (2002 ▶); Navarrete-Vázquez et al. (2003 ▶); Terzioglu et al. (2004 ▶); Özden et al. (2005 ▶). For the bioactivity of 1,2,3-triazoles, see: Chen et al. (2000 ▶); Manfredini et al. (2000 ▶). For the synthetic methods, see: Huisgen (1963 ▶); Crisp & Flynn (1993 ▶); Wu et al. (2004 ▶); Navarrete-Vázquez et al. (2007 ▶); Krim et al. (2009 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C18H17N5O2
M r = 335.37
Monoclinic,
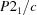
a = 10.4449 (5) Å
b = 7.7754 (4) Å
c = 20.2119 (10) Å
β = 99.354 (1)°
V = 1619.65 (14) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.09 mm−1
T = 170 K
0.40 × 0.32 × 0.11 mm
Data collection
Siemens SMART 1K CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 2000 ▶) T min = 0.953, T max = 0.990
15768 measured reflections
3295 independent reflections
2562 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.047
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.059
wR(F 2) = 0.102
S = 1.14
3295 reflections
235 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.20 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.19 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Siemens, 1995 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Siemens, 1995 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812023410/nc2282sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812023410/nc2282Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812023410/nc2282Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1A⋯N4i | 0.89 (2) | 2.50 (2) | 3.244 (2) | 141.7 (17) |
| N1—H1A⋯N5i | 0.89 (2) | 2.21 (2) | 3.088 (2) | 170.4 (19) |
| O2—H2A⋯N2ii | 0.92 (3) | 1.85 (3) | 2.761 (2) | 171 (2) |
| C15—H15A⋯O2iii | 0.95 | 2.54 | 3.271 (2) | 134 |
| C16—H16A⋯O2iii | 0.99 | 2.54 | 3.258 (2) | 129 |
| C17—H17B⋯O1iv | 0.99 | 2.35 | 3.279 (2) | 155 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 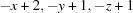 ; (ii)
; (ii) 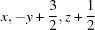 ; (iii)
; (iii) 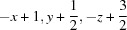 ; (iv)
; (iv) 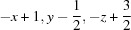 .
.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Benzimidazoles are important pharmacophores in modern drug discovery (Tebbe et al., 1997). They are present in various bioactive compounds, possessing, e.g. antiparasitic (Navarrete-Vázquez et al., 2003), antimicrobial (Özden et al., 2005), antihistaminic (Terzioglu et al., 2004) and antitumor (Andrzejewska et al., 2002) activities. In addition, 1,2,3-triazoles are potent antibacterial (Chen et al., 2000) and antiproliferative (Manfredini et al., 2000) agents. The most widely used method for their synthesis is the Huisgen 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition of alkynes with organic azides (Huisgen, 1963). Copper-catalyzed click chemistry, involving azides and terminal acetylenes, has enabled practical and efficient preparation of 1,4-disubstituted 1,2,3-triazoles, from a wide range of substrates with excellent selectivity (Wu et al., 2004). In connection to our previous studies on the synthesis of acyclonucleosides (Krim et al., 2009), we decided to explore the feasibility of the click chemistry for the synthesis of novel 1,2,3-triazoles containing a benzimidazole moiety coupled via a benzene ring. Thus the title compound was prepared and its crystal structure is reported herein.
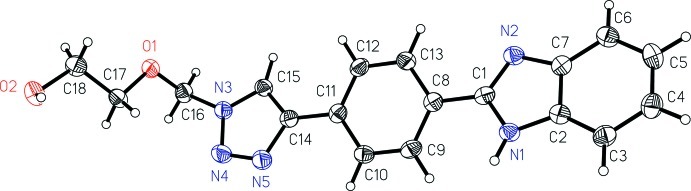
A view of the molecular structure of the title compound is shown in Fig. 1. The molecule contains three planar parts: the benzimidazole, the benzene and the triazole groups. The angle between the benzene and benzimidazole planes is 19.8 (1)°, while the angle between the benzene and triazole planes is 16.7 (1)°. The (2-hydroxyethoxy)methyl group points away from the triazole plane [torsion angle N4—N3—C16—O1: 88.6 (2)°]. The C16—O1 bond has a gauche conformation, while the O1—C17 and the C17—C18 bonds have trans conformations.
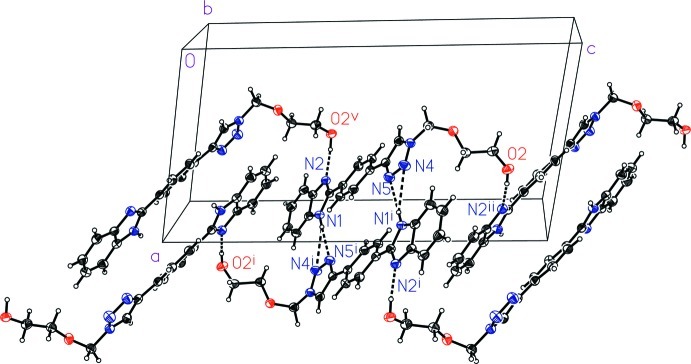
The molecules of the title compound are connected by intermolecular O—H···N hydrogen bonds to form zigzag chains along the c axis direction (Fig.2, Table 1). Adjacent molecules in each chain are related by c-gilde plane symmetry. Neighboring chains are connected by intermolecular N—H···N hydrogen bonds between imidazole and triazole groups to form layers parallel to (1 0 0). The N—H···N hydrogen bond is bifurcated with both atoms N4 and N5 acting as acceptor atoms. There are two symmetry-related N—H···N bonds between each pair of molecules. The hydrogen bonded layers are connected along the a axis direction by additional intermolecular weak C—H···O contacts to form a three-dimensional framework.
Experimental
The title compound has been prepared in four steps starting from 4-[(trimethylsilyl)ethynyl]benzaldehyde. The starting material was reacted with benzimidazole in the presence of sodium metabisulfite using microwave irradiation (Navarrete-Vázquez et al., 2007). The resulting product was deprotected with tetrabutylammonium fluoride in tetrahydrofuran to 2-(4-ethynylphenyl)-1H-benzimidazole (Crisp & Flynn, 1993). Cycloaddition of the latter product with [(2-acetoxyethoxy)methyl]azide in the presence of CuI, followed by deprotection of the acetyl group (Krim et al., 2009), afforded the title compound in good yield. The crude product was purified by passing through a column packed with silica gel. Single crystals suitable for X-ray analysis were obtained by slow recrystallizion from ethanol. The melting point is approximately 502–504 K.
Refinement
The H atoms on C atoms were positioned geometrically and treated as riding: Cplanar—H=0.95 Å, Cmethylene—H=0.99 Å, Uiso(H)=1.2Ueq(parent C-atom). The H atoms on the N and O atoms were taken from a difference Fourier synthesis and were refined.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The structure of the title compound, showing the atom-labelling scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level. H atoms are drawn as small spheres of an arbitrary radius.
Fig. 2.
A view of the hydrogen bonding network of the title compound. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probabilty level. Intermolecular hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines. The symmetry codes are: (i) 2 - x, 1 - y, 1 - z; (ii) x, 3/2 - y, 1/2 + z; (v) x, 3/2 - y, -1/2 + z.
Crystal data
| C18H17N5O2 | F(000) = 704 |
| Mr = 335.37 | Dx = 1.375 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 8027 reflections |
| a = 10.4449 (5) Å | θ = 3–24° |
| b = 7.7754 (4) Å | µ = 0.09 mm−1 |
| c = 20.2119 (10) Å | T = 170 K |
| β = 99.354 (1)° | Block, yellow |
| V = 1619.65 (14) Å3 | 0.40 × 0.32 × 0.11 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Siemens SMART 1K CCD diffractometer | 3295 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: normal-focus sealed tube | 2562 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.047 |
| ω scans | θmax = 26.8°, θmin = 2.0° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 2000) | h = −13→13 |
| Tmin = 0.953, Tmax = 0.990 | k = −9→9 |
| 15768 measured reflections | l = −25→25 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.059 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.102 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.023P)2 + 0.6P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.14 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 3295 reflections | Δρmax = 0.20 e Å−3 |
| 235 parameters | Δρmin = −0.19 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Extinction correction: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction coefficient: 0.0056 (7) |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.50237 (13) | 0.39456 (17) | 0.71767 (6) | 0.0308 (3) | |
| O2 | 0.67189 (14) | 0.21899 (18) | 0.87378 (7) | 0.0335 (4) | |
| N1 | 1.07016 (15) | 0.9376 (2) | 0.37941 (8) | 0.0265 (4) | |
| N2 | 0.91403 (15) | 1.1341 (2) | 0.37934 (8) | 0.0277 (4) | |
| N3 | 0.56182 (15) | 0.3846 (2) | 0.60950 (7) | 0.0272 (4) | |
| N4 | 0.65832 (16) | 0.2730 (2) | 0.60375 (8) | 0.0350 (4) | |
| N5 | 0.73569 (16) | 0.3493 (2) | 0.56742 (8) | 0.0331 (4) | |
| C1 | 0.95442 (18) | 0.9778 (2) | 0.39886 (9) | 0.0252 (4) | |
| C2 | 1.10804 (18) | 1.0777 (2) | 0.34516 (9) | 0.0265 (4) | |
| C3 | 1.21525 (18) | 1.1085 (3) | 0.31418 (10) | 0.0317 (5) | |
| H3A | 1.2823 | 1.0256 | 0.3148 | 0.038* | |
| C4 | 1.2198 (2) | 1.2654 (3) | 0.28242 (10) | 0.0350 (5) | |
| H4A | 1.2918 | 1.2912 | 0.2608 | 0.042* | |
| C5 | 1.12061 (19) | 1.3873 (3) | 0.28139 (10) | 0.0343 (5) | |
| H5A | 1.1267 | 1.4936 | 0.2589 | 0.041* | |
| C6 | 1.01424 (19) | 1.3565 (3) | 0.31228 (9) | 0.0310 (5) | |
| H6A | 0.9471 | 1.4393 | 0.3112 | 0.037* | |
| C7 | 1.00880 (17) | 1.1996 (2) | 0.34504 (9) | 0.0257 (4) | |
| C8 | 0.88408 (17) | 0.8577 (2) | 0.43576 (9) | 0.0253 (4) | |
| C9 | 0.91089 (18) | 0.6817 (2) | 0.43692 (9) | 0.0283 (5) | |
| H9A | 0.9749 | 0.6389 | 0.4127 | 0.034* | |
| C10 | 0.84603 (18) | 0.5686 (2) | 0.47263 (9) | 0.0268 (4) | |
| H10A | 0.8647 | 0.4491 | 0.4721 | 0.032* | |
| C11 | 0.75345 (18) | 0.6289 (2) | 0.50939 (9) | 0.0258 (4) | |
| C12 | 0.72431 (18) | 0.8045 (3) | 0.50722 (9) | 0.0288 (5) | |
| H12A | 0.6595 | 0.8469 | 0.5310 | 0.035* | |
| C13 | 0.78828 (18) | 0.9175 (3) | 0.47105 (9) | 0.0289 (5) | |
| H13A | 0.7671 | 1.0364 | 0.4701 | 0.035* | |
| C14 | 0.68875 (18) | 0.5107 (2) | 0.55019 (9) | 0.0256 (4) | |
| C15 | 0.57733 (18) | 0.5326 (2) | 0.57719 (9) | 0.0265 (4) | |
| H15A | 0.5229 | 0.6312 | 0.5738 | 0.032* | |
| C16 | 0.46450 (19) | 0.3426 (3) | 0.65116 (9) | 0.0302 (5) | |
| H16A | 0.3817 | 0.3995 | 0.6326 | 0.036* | |
| H16B | 0.4495 | 0.2168 | 0.6499 | 0.036* | |
| C17 | 0.59651 (18) | 0.2857 (2) | 0.75702 (9) | 0.0288 (4) | |
| H17A | 0.6829 | 0.3018 | 0.7438 | 0.035* | |
| H17B | 0.5713 | 0.1634 | 0.7505 | 0.035* | |
| C18 | 0.59977 (19) | 0.3374 (3) | 0.82907 (10) | 0.0334 (5) | |
| H18A | 0.6391 | 0.4531 | 0.8364 | 0.040* | |
| H18B | 0.5099 | 0.3439 | 0.8387 | 0.040* | |
| H1A | 1.118 (2) | 0.846 (3) | 0.3930 (10) | 0.040 (6)* | |
| H2A | 0.756 (3) | 0.258 (3) | 0.8779 (12) | 0.068 (8)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0328 (8) | 0.0313 (8) | 0.0286 (7) | 0.0077 (6) | 0.0061 (6) | 0.0048 (6) |
| O2 | 0.0256 (8) | 0.0346 (8) | 0.0382 (8) | −0.0039 (7) | −0.0008 (6) | 0.0083 (6) |
| N1 | 0.0222 (9) | 0.0261 (9) | 0.0313 (9) | 0.0041 (7) | 0.0043 (7) | 0.0013 (7) |
| N2 | 0.0257 (9) | 0.0280 (9) | 0.0289 (9) | 0.0042 (7) | 0.0026 (7) | −0.0002 (7) |
| N3 | 0.0248 (9) | 0.0285 (9) | 0.0286 (9) | 0.0033 (7) | 0.0053 (7) | 0.0029 (7) |
| N4 | 0.0326 (10) | 0.0313 (10) | 0.0427 (10) | 0.0087 (8) | 0.0114 (8) | 0.0057 (8) |
| N5 | 0.0304 (9) | 0.0340 (10) | 0.0362 (9) | 0.0060 (8) | 0.0096 (8) | 0.0050 (8) |
| C1 | 0.0226 (10) | 0.0288 (11) | 0.0234 (10) | 0.0030 (8) | 0.0015 (8) | −0.0039 (8) |
| C2 | 0.0250 (10) | 0.0266 (10) | 0.0267 (10) | 0.0009 (8) | 0.0002 (8) | −0.0009 (8) |
| C3 | 0.0246 (11) | 0.0352 (12) | 0.0357 (11) | 0.0023 (9) | 0.0063 (9) | −0.0009 (9) |
| C4 | 0.0291 (11) | 0.0408 (13) | 0.0358 (11) | −0.0034 (10) | 0.0073 (9) | 0.0024 (9) |
| C5 | 0.0342 (12) | 0.0337 (12) | 0.0334 (11) | −0.0038 (10) | 0.0003 (9) | 0.0079 (9) |
| C6 | 0.0292 (11) | 0.0302 (11) | 0.0316 (11) | 0.0036 (9) | −0.0007 (9) | 0.0012 (9) |
| C7 | 0.0224 (10) | 0.0289 (11) | 0.0251 (10) | −0.0009 (8) | 0.0017 (8) | −0.0018 (8) |
| C8 | 0.0226 (10) | 0.0296 (11) | 0.0225 (9) | 0.0023 (8) | 0.0000 (8) | −0.0002 (8) |
| C9 | 0.0222 (10) | 0.0340 (12) | 0.0287 (10) | 0.0040 (9) | 0.0041 (8) | −0.0043 (9) |
| C10 | 0.0244 (10) | 0.0265 (10) | 0.0289 (10) | 0.0029 (8) | 0.0020 (8) | −0.0011 (8) |
| C11 | 0.0233 (10) | 0.0315 (11) | 0.0215 (9) | 0.0014 (8) | 0.0003 (8) | 0.0002 (8) |
| C12 | 0.0274 (11) | 0.0338 (11) | 0.0262 (10) | 0.0061 (9) | 0.0075 (8) | −0.0007 (9) |
| C13 | 0.0313 (11) | 0.0270 (11) | 0.0282 (10) | 0.0059 (9) | 0.0043 (9) | 0.0020 (8) |
| C14 | 0.0248 (10) | 0.0277 (10) | 0.0229 (10) | 0.0040 (8) | 0.0000 (8) | −0.0013 (8) |
| C15 | 0.0280 (11) | 0.0258 (11) | 0.0250 (10) | 0.0036 (8) | 0.0019 (8) | 0.0005 (8) |
| C16 | 0.0259 (10) | 0.0335 (11) | 0.0318 (11) | 0.0004 (9) | 0.0063 (9) | 0.0048 (9) |
| C17 | 0.0271 (11) | 0.0250 (10) | 0.0344 (11) | 0.0022 (9) | 0.0054 (9) | 0.0051 (8) |
| C18 | 0.0266 (11) | 0.0368 (12) | 0.0360 (11) | 0.0048 (9) | 0.0019 (9) | 0.0020 (9) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—C16 | 1.398 (2) | C6—C7 | 1.394 (3) |
| O1—C17 | 1.436 (2) | C6—H6A | 0.9500 |
| O2—C18 | 1.418 (2) | C8—C9 | 1.396 (3) |
| O2—H2A | 0.92 (3) | C8—C13 | 1.399 (3) |
| N1—C1 | 1.367 (2) | C9—C10 | 1.383 (3) |
| N1—C2 | 1.382 (2) | C9—H9A | 0.9500 |
| N1—H1A | 0.89 (2) | C10—C11 | 1.393 (3) |
| N2—C1 | 1.325 (2) | C10—H10A | 0.9500 |
| N2—C7 | 1.394 (2) | C11—C12 | 1.398 (3) |
| N3—C15 | 1.346 (2) | C11—C14 | 1.471 (3) |
| N3—N4 | 1.349 (2) | C12—C13 | 1.382 (3) |
| N3—C16 | 1.458 (2) | C12—H12A | 0.9500 |
| N4—N5 | 1.318 (2) | C13—H13A | 0.9500 |
| N5—C14 | 1.371 (2) | C14—C15 | 1.374 (3) |
| C1—C8 | 1.465 (3) | C15—H15A | 0.9500 |
| C2—C3 | 1.390 (3) | C16—H16A | 0.9900 |
| C2—C7 | 1.404 (3) | C16—H16B | 0.9900 |
| C3—C4 | 1.383 (3) | C17—C18 | 1.506 (3) |
| C3—H3A | 0.9500 | C17—H17A | 0.9900 |
| C4—C5 | 1.402 (3) | C17—H17B | 0.9900 |
| C4—H4A | 0.9500 | C18—H18A | 0.9900 |
| C5—C6 | 1.381 (3) | C18—H18B | 0.9900 |
| C5—H5A | 0.9500 | ||
| C16—O1—C17 | 115.06 (14) | C8—C9—H9A | 119.4 |
| C18—O2—H2A | 104.2 (16) | C9—C10—C11 | 120.37 (18) |
| C1—N1—C2 | 107.60 (16) | C9—C10—H10A | 119.8 |
| C1—N1—H1A | 125.3 (13) | C11—C10—H10A | 119.8 |
| C2—N1—H1A | 126.2 (14) | C10—C11—C12 | 118.60 (18) |
| C1—N2—C7 | 105.41 (15) | C10—C11—C14 | 120.69 (17) |
| C15—N3—N4 | 110.95 (15) | C12—C11—C14 | 120.70 (17) |
| C15—N3—C16 | 128.43 (16) | C13—C12—C11 | 121.04 (18) |
| N4—N3—C16 | 120.43 (15) | C13—C12—H12A | 119.5 |
| N5—N4—N3 | 107.03 (15) | C11—C12—H12A | 119.5 |
| N4—N5—C14 | 109.09 (15) | C12—C13—C8 | 120.37 (18) |
| N2—C1—N1 | 112.19 (17) | C12—C13—H13A | 119.8 |
| N2—C1—C8 | 125.05 (17) | C8—C13—H13A | 119.8 |
| N1—C1—C8 | 122.75 (17) | N5—C14—C15 | 107.68 (17) |
| N1—C2—C3 | 132.73 (18) | N5—C14—C11 | 122.44 (17) |
| N1—C2—C7 | 105.15 (16) | C15—C14—C11 | 129.88 (17) |
| C3—C2—C7 | 122.11 (18) | N3—C15—C14 | 105.25 (17) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 116.87 (19) | N3—C15—H15A | 127.4 |
| C4—C3—H3A | 121.6 | C14—C15—H15A | 127.4 |
| C2—C3—H3A | 121.6 | O1—C16—N3 | 112.07 (15) |
| C3—C4—C5 | 121.50 (19) | O1—C16—H16A | 109.2 |
| C3—C4—H4A | 119.3 | N3—C16—H16A | 109.2 |
| C5—C4—H4A | 119.3 | O1—C16—H16B | 109.2 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 121.51 (19) | N3—C16—H16B | 109.2 |
| C6—C5—H5A | 119.2 | H16A—C16—H16B | 107.9 |
| C4—C5—H5A | 119.2 | O1—C17—C18 | 106.53 (15) |
| C5—C6—C7 | 117.71 (19) | O1—C17—H17A | 110.4 |
| C5—C6—H6A | 121.1 | C18—C17—H17A | 110.4 |
| C7—C6—H6A | 121.1 | O1—C17—H17B | 110.4 |
| C6—C7—N2 | 130.04 (18) | C18—C17—H17B | 110.4 |
| C6—C7—C2 | 120.30 (18) | H17A—C17—H17B | 108.6 |
| N2—C7—C2 | 109.64 (16) | O2—C18—C17 | 111.68 (16) |
| C9—C8—C13 | 118.37 (17) | O2—C18—H18A | 109.3 |
| C9—C8—C1 | 121.16 (17) | C17—C18—H18A | 109.3 |
| C13—C8—C1 | 120.47 (17) | O2—C18—H18B | 109.3 |
| C10—C9—C8 | 121.20 (18) | C17—C18—H18B | 109.3 |
| C10—C9—H9A | 119.4 | H18A—C18—H18B | 107.9 |
| C15—N3—N4—N5 | −0.3 (2) | C13—C8—C9—C10 | −0.8 (3) |
| C16—N3—N4—N5 | −175.62 (15) | C1—C8—C9—C10 | 178.93 (16) |
| N3—N4—N5—C14 | 0.3 (2) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | −1.1 (3) |
| C7—N2—C1—N1 | 0.1 (2) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | 2.4 (3) |
| C7—N2—C1—C8 | −178.63 (17) | C9—C10—C11—C14 | −176.93 (17) |
| C2—N1—C1—N2 | 0.3 (2) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | −1.9 (3) |
| C2—N1—C1—C8 | 179.09 (16) | C14—C11—C12—C13 | 177.50 (17) |
| C1—N1—C2—C3 | −179.47 (19) | C11—C12—C13—C8 | 0.0 (3) |
| C1—N1—C2—C7 | −0.60 (19) | C9—C8—C13—C12 | 1.4 (3) |
| N1—C2—C3—C4 | 178.25 (19) | C1—C8—C13—C12 | −178.36 (17) |
| C7—C2—C3—C4 | −0.5 (3) | N4—N5—C14—C15 | −0.3 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.2 (3) | N4—N5—C14—C11 | −179.91 (16) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.3 (3) | C10—C11—C14—N5 | 16.1 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | 0.3 (3) | C12—C11—C14—N5 | −163.22 (17) |
| C5—C6—C7—N2 | −179.28 (18) | C10—C11—C14—C15 | −163.43 (18) |
| C5—C6—C7—C2 | −1.0 (3) | C12—C11—C14—C15 | 17.2 (3) |
| C1—N2—C7—C6 | 177.95 (19) | N4—N3—C15—C14 | 0.1 (2) |
| C1—N2—C7—C2 | −0.5 (2) | C16—N3—C15—C14 | 174.99 (17) |
| N1—C2—C7—C6 | −177.94 (16) | N5—C14—C15—N3 | 0.1 (2) |
| C3—C2—C7—C6 | 1.1 (3) | C11—C14—C15—N3 | 179.71 (18) |
| N1—C2—C7—N2 | 0.7 (2) | C17—O1—C16—N3 | −77.18 (19) |
| C3—C2—C7—N2 | 179.71 (16) | C15—N3—C16—O1 | −85.9 (2) |
| N2—C1—C8—C9 | 160.37 (18) | N4—N3—C16—O1 | 88.6 (2) |
| N1—C1—C8—C9 | −18.3 (3) | C16—O1—C17—C18 | −166.70 (15) |
| N2—C1—C8—C13 | −19.9 (3) | O1—C17—C18—O2 | 169.44 (15) |
| N1—C1—C8—C13 | 161.50 (17) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1A···N4i | 0.89 (2) | 2.50 (2) | 3.244 (2) | 141.7 (17) |
| N1—H1A···N5i | 0.89 (2) | 2.21 (2) | 3.088 (2) | 170.4 (19) |
| O2—H2A···N2ii | 0.92 (3) | 1.85 (3) | 2.761 (2) | 171 (2) |
| C15—H15A···O2iii | 0.95 | 2.54 | 3.271 (2) | 134 |
| C16—H16A···O2iii | 0.99 | 2.54 | 3.258 (2) | 129 |
| C17—H17B···O1iv | 0.99 | 2.35 | 3.279 (2) | 155 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+2, −y+1, −z+1; (ii) x, −y+3/2, z+1/2; (iii) −x+1, y+1/2, −z+3/2; (iv) −x+1, y−1/2, −z+3/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: NC2282).
References
- Andrzejewska, M., Yépez-Mulia, L., Cedillo-Rivera, R., Tapia, A., Vilpo, L., Vilpo, J. & Kazimierczuk, Z. (2002). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 37, 973–978. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Chen, M. D., Lu, S. J., Yuan, G. P., Yang, S. Y. & Du, X. L. (2000). Heterocycl. Commun. 6, 421–426.
- Crisp, G. T. & Flynn, B. L. (1993). J. Org. Chem. 58, 6614–6619.
- Huisgen, R. (1963). Angew. Chem. Int Ed 2, 565–598.
- Krim, J., Sillahi, B., Taourirte, M., Rakib, E. M. & Engels, J. W. (2009). ARKIVOC, xiii, 142–152.
- Manfredini, S., Vicentini, C. B., Manfrini, M., Bianchi, N., Rutigliano, C., Mischiati, C. & Gambari, R. (2000). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 8, 2343–2346. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Navarrete-Vázquez, G., Morena-Diaz, H., Estrado-Soto, S., Torres-Piedra, M., León-Rivera, I., Tlahuext, H., Muñoz-Muñiz, O. & Torres-Gómez, H. (2007). Synth. Commun. 37, 2815–2825.
- Navarrete-Vázquez, G., Yépez, L., Hernández-Campos, A., Tapia, A., Hernández-Luis, F., Cedillo, R., González, J., Martínez-Fernández, A., Martínez-Grueiro, M. & Castillo, R. (2003). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 11, 4615–4622. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Özden, S., Atabey, D., Yildiz, S. & Göker, H. (2005). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 13, 1587–1597. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2000). SADABS University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Siemens (1995). SMART and SAINT Siemens Analytical X-ray Instruments Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Tebbe, M. J., Spitzer, W. A., Victor, F., Miller, S. C., Lee, C. C., Sattelberg Sr, T. R., McKinney, E. & Tang, J. C. (1997). J. Med. Chem. 40, 3937–3946. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Terzioglu, N., van Rijn, R. M., Bakker, R. A., De Esch, I. J. P. & Leurs, R. (2004). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 14, 5251–5256. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Wu, P., Feldman, A. K., Nugent, A. K., Hawker, C. J., Scheel, A., Voit, B., Pyun, J., Fréchet, J. M. J., Sharpless, K. B. & Fokin, V. V. (2004). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 43, 3928–3932. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812023410/nc2282sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812023410/nc2282Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812023410/nc2282Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report