Abstract
In the title hydrated molecular salt, C11H14N3O+·Br−·H2O, the Br− anion is split and appears as two independent half-occupied Br− anions on twofold rotation axes. The dihedral angle between the phenyl ring and the mean plane of the 2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrazole ring (r.m.s. devation = 0.014 Å) is 62.43 (7)°. In the crystal, the components are connected via O—H⋯Br and N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds to form a one-dimensional polymeric structure propagating along [001].
Related literature
For general background on pyrazolone derivatives, see: Casas et al. (2007 ▶); Jain et al. (2003 ▶); Zhang et al. (2008 ▶). For related structures, see: Chitradevi et al. (2009 ▶); Murtaza et al.(2011 ▶). For bond-length data, see: Allen et al. (1987 ▶).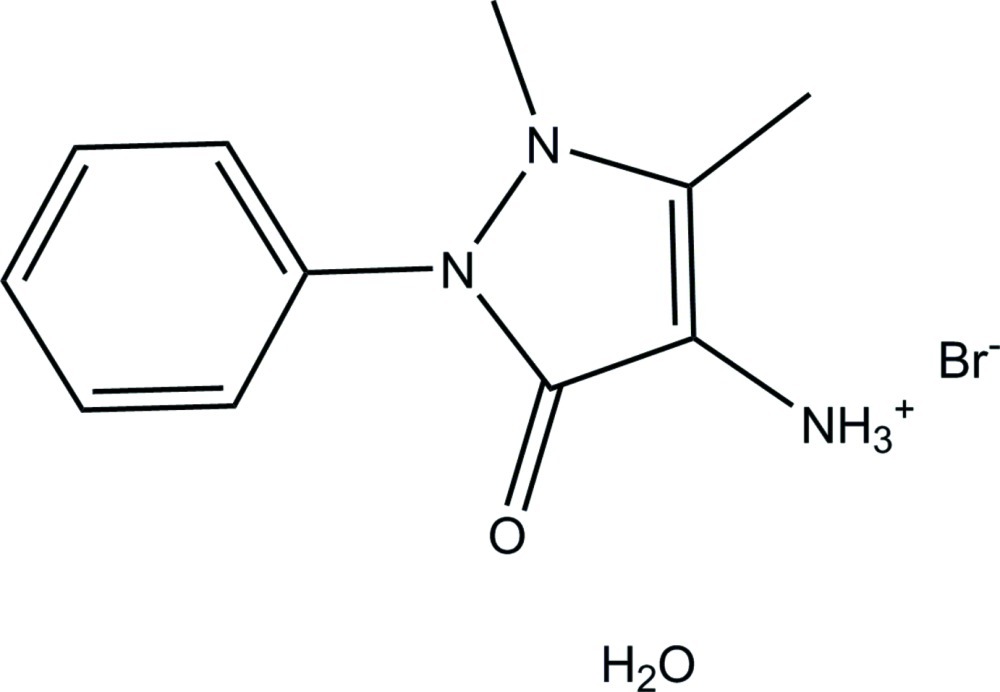
Experimental
Crystal data
C11H14N3O+·Br−·H2O
M r = 302.17
Monoclinic,

a = 14.9080 (19) Å
b = 15.3961 (19) Å
c = 11.1501 (14) Å
β = 93.657 (2)°
V = 2554.0 (6) Å3
Z = 8
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 3.21 mm−1
T = 296 K
0.22 × 0.20 × 0.18 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996 ▶) T min = 0.489, T max = 0.556
11995 measured reflections
3222 independent reflections
2081 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.044
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.039
wR(F 2) = 0.108
S = 1.04
3222 reflections
155 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.48 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.40 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 1998 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 1998 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812023550/su2432sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812023550/su2432Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812023550/su2432Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1W—H1WA⋯Br1 | 0.85 | 2.51 | 3.360 (2) | 173 |
| O1W—H1WB⋯Br2 | 0.85 | 2.52 | 3.371 (3) | 173 |
| N3—H3B⋯O1i | 0.89 | 1.89 | 2.692 (3) | 150 |
| N3—H3C⋯O1W | 0.89 | 2.55 | 3.321 (3) | 146 |
| N3—H3C⋯O1ii | 0.89 | 2.37 | 3.004 (3) | 129 |
| N3—H3D⋯O1Wii | 0.89 | 1.99 | 2.817 (4) | 153 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 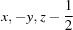 ; (ii)
; (ii) 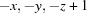 .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine for supporting this study (grant No. YXRC0920).
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
4-Aminoantipyrene, which contains a pyrazolone ring, is an important compound in the class of analgesic agents used in otic solutions in combination with other analgesics such as benzocaine and phenylephrine (Jain et al., 2003). Pyrazolone is a five-membered lactam ring compound containing two N atoms and a ketone in the same molecule. Such pyrazolone derivatives form a very important class of heterocycles due to their properties and applications (Casas et al., 2007; Zhang et al., 2008). We report herein on the synthesis and crystal structure of the title compound.
The asymmetric unit of title compound, Fig. 1, consists of three components: a 1,5-dimethyl-3-oxo-2-phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-4-aminium cation, a bromide ion and a water molecule. The Br anion is split and appears as two independent half-occupied Br anions, Br1 and Br2, on two-fold rotation axes. In cation, the phenyl ring A (C1–C6) and the 2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrazole ring B (N1/N2/C7/C8/C11) are planar with r.m.s. deviations of 0.019 and 0.014 Å. The dihedral angle between A/B is 62.43 (7)°. The attached atoms O1, N3, C9 and C10 are at a distance of 0.030 (3), 0.053 (3), 0.130 (3) and 0.140 (3) Å respectively, from the mean plane of B. The bond lengths (Allen et al., 1987) and angles are within normal ranges. The crystal structure of some similar compounds have been reported (Chitradevi et al., 2009; Murtaza et al., 2011).
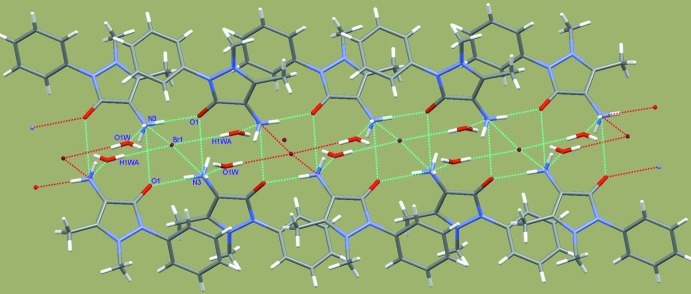
In the crystal, the various components are connected by N—H···O and O—H···Br hydrogen bonds (Table 1 and Fig. 2) to form an infinite one-dimensional arrangement parallel to [001].
Experimental
4-Aminoantipyrine (0.203 g, 1.0 mmol) and dibromomethane (0.173 g, 1.0 mmol) were dissolved in water (15 ml). The mixture was refluxed for 3 h and then the solvent was evaporated on rotary evaporator to almost dryness. The crude product was recrystallized from water yielding block-like yellow crystals of the title compound.
Refinement
The H atoms were included calculated positions and treated as riding atoms: O—H = 0.85 Å, N—H = 0.89 Å, C—H = 0.93–0.96 Å, with Uiso(H) = x × Ueq(C,N,O), where x = 1.5 for CH3 and NH3 H atoms and = 1.2 for other H-atoms.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound with the atom numbering. The displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 30% probability level.
Fig. 2.
A view along the c axis of the crystal packing of the title compound. H-bonds are shown as dashed lines; see Table 1 for details.
Crystal data
| C11H14N3O+·Br−·H2O | F(000) = 1232 |
| Mr = 302.17 | Dx = 1.572 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, C2/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -C 2yc | Cell parameters from 2078 reflections |
| a = 14.9080 (19) Å | θ = 2.7–23.6° |
| b = 15.3961 (19) Å | µ = 3.21 mm−1 |
| c = 11.1501 (14) Å | T = 296 K |
| β = 93.657 (2)° | Block, yellow |
| V = 2554.0 (6) Å3 | 0.22 × 0.20 × 0.18 mm |
| Z = 8 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART CCD diffractometer | 3222 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2081 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.044 |
| ω scans | θmax = 28.4°, θmin = 2.7° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996) | h = −19→19 |
| Tmin = 0.489, Tmax = 0.556 | k = −20→20 |
| 11995 measured reflections | l = −14→14 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.039 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.108 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.04 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0493P)2 + 2.161P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3222 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 155 parameters | Δρmax = 0.48 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.40 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. Bond distances, angles etc. have been calculated using the rounded fractional coordinates. All su's are estimated from the variances of the (full) variance-covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account in the estimation of distances, angles and torsion angles |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R-factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.11377 (13) | 0.01137 (15) | 0.64912 (16) | 0.0377 (6) | |
| N1 | 0.24203 (15) | 0.09233 (18) | 0.61672 (19) | 0.0346 (8) | |
| N2 | 0.28247 (16) | 0.12321 (17) | 0.5164 (2) | 0.0353 (8) | |
| N3 | 0.08569 (14) | 0.01740 (16) | 0.38186 (18) | 0.0286 (7) | |
| C1 | 0.2831 (2) | 0.0971 (2) | 0.7361 (2) | 0.0330 (9) | |
| C2 | 0.2374 (2) | 0.1400 (2) | 0.8221 (3) | 0.0437 (10) | |
| C3 | 0.2752 (3) | 0.1419 (3) | 0.9393 (3) | 0.0630 (16) | |
| C4 | 0.3572 (4) | 0.1054 (3) | 0.9670 (3) | 0.080 (2) | |
| C5 | 0.4009 (3) | 0.0627 (4) | 0.8813 (4) | 0.0781 (18) | |
| C6 | 0.3637 (2) | 0.0573 (3) | 0.7639 (3) | 0.0551 (13) | |
| C7 | 0.15821 (17) | 0.05670 (17) | 0.4544 (2) | 0.0256 (8) | |
| C8 | 0.22945 (18) | 0.10325 (18) | 0.4178 (2) | 0.0275 (8) | |
| C9 | 0.2493 (2) | 0.1347 (2) | 0.2962 (3) | 0.0391 (10) | |
| C10 | 0.3605 (2) | 0.1798 (2) | 0.5249 (3) | 0.0466 (10) | |
| C11 | 0.16456 (18) | 0.04939 (18) | 0.5808 (2) | 0.0281 (8) | |
| Br1 | 0.00000 | 0.19903 (3) | 0.25000 | 0.0427 (2) | |
| Br2 | 0.00000 | 0.29956 (4) | 0.75000 | 0.0536 (2) | |
| O1W | −0.04198 (19) | 0.14894 (18) | 0.5343 (2) | 0.0651 (10) | |
| H2A | 0.18260 | 0.16700 | 0.80220 | 0.0530* | |
| H3A | 0.24430 | 0.16840 | 0.99940 | 0.0760* | |
| H3B | 0.09260 | 0.02850 | 0.30470 | 0.0430* | |
| H3C | 0.03360 | 0.03920 | 0.40250 | 0.0430* | |
| H3D | 0.08620 | −0.03980 | 0.39370 | 0.0430* | |
| H4A | 0.38340 | 0.10970 | 1.04480 | 0.0950* | |
| H5A | 0.45620 | 0.03670 | 0.90140 | 0.0940* | |
| H6A | 0.39310 | 0.02730 | 0.70560 | 0.0660* | |
| H9A | 0.30540 | 0.16560 | 0.30100 | 0.0590* | |
| H9B | 0.20210 | 0.17280 | 0.26610 | 0.0590* | |
| H9C | 0.25330 | 0.08610 | 0.24290 | 0.0590* | |
| H10A | 0.37780 | 0.19340 | 0.44560 | 0.0700* | |
| H10B | 0.40920 | 0.15110 | 0.56910 | 0.0700* | |
| H10C | 0.34590 | 0.23250 | 0.56550 | 0.0700* | |
| H1WA | −0.02990 | 0.16590 | 0.46460 | 0.0780* | |
| H1WB | −0.02990 | 0.18990 | 0.58390 | 0.0780* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0326 (10) | 0.0618 (14) | 0.0186 (9) | −0.0133 (10) | 0.0006 (8) | 0.0052 (10) |
| N1 | 0.0309 (13) | 0.0554 (16) | 0.0174 (10) | −0.0125 (12) | 0.0004 (9) | 0.0000 (11) |
| N2 | 0.0365 (14) | 0.0473 (15) | 0.0222 (11) | −0.0144 (11) | 0.0023 (10) | 0.0009 (11) |
| N3 | 0.0255 (11) | 0.0427 (14) | 0.0174 (10) | −0.0025 (10) | −0.0004 (8) | −0.0018 (10) |
| C1 | 0.0337 (14) | 0.0450 (18) | 0.0199 (13) | −0.0118 (14) | −0.0022 (11) | 0.0009 (13) |
| C2 | 0.062 (2) | 0.0393 (18) | 0.0301 (16) | −0.0069 (16) | 0.0059 (15) | −0.0011 (14) |
| C3 | 0.106 (4) | 0.056 (2) | 0.0272 (17) | −0.026 (2) | 0.006 (2) | −0.0081 (17) |
| C4 | 0.105 (4) | 0.098 (4) | 0.032 (2) | −0.057 (3) | −0.026 (2) | 0.014 (2) |
| C5 | 0.047 (2) | 0.126 (4) | 0.058 (3) | −0.022 (2) | −0.023 (2) | 0.028 (3) |
| C6 | 0.0382 (18) | 0.082 (3) | 0.044 (2) | −0.0042 (18) | −0.0058 (15) | 0.0046 (18) |
| C7 | 0.0251 (13) | 0.0337 (14) | 0.0180 (12) | −0.0002 (11) | 0.0006 (9) | −0.0022 (11) |
| C8 | 0.0283 (14) | 0.0347 (15) | 0.0197 (12) | −0.0011 (12) | 0.0032 (10) | 0.0006 (11) |
| C9 | 0.0439 (18) | 0.0505 (19) | 0.0232 (13) | −0.0086 (14) | 0.0043 (12) | 0.0062 (14) |
| C10 | 0.0380 (17) | 0.065 (2) | 0.0369 (17) | −0.0226 (16) | 0.0040 (13) | −0.0049 (16) |
| C11 | 0.0264 (13) | 0.0388 (16) | 0.0191 (12) | −0.0037 (12) | 0.0011 (10) | 0.0002 (12) |
| Br1 | 0.0493 (3) | 0.0400 (3) | 0.0371 (2) | 0.0000 | −0.0094 (2) | 0.0000 |
| Br2 | 0.0436 (3) | 0.0828 (4) | 0.0347 (3) | 0.0000 | 0.0055 (2) | 0.0000 |
| O1W | 0.097 (2) | 0.0533 (16) | 0.0461 (14) | −0.0197 (15) | 0.0132 (14) | 0.0000 (13) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—C11 | 1.253 (3) | C4—C5 | 1.360 (7) |
| O1W—H1WB | 0.8500 | C5—C6 | 1.391 (6) |
| O1W—H1WA | 0.8500 | C7—C8 | 1.365 (4) |
| N1—C11 | 1.368 (4) | C7—C11 | 1.411 (3) |
| N1—C1 | 1.431 (3) | C8—C9 | 1.487 (4) |
| N1—N2 | 1.388 (3) | C2—H2A | 0.9300 |
| N2—C8 | 1.348 (3) | C3—H3A | 0.9300 |
| N2—C10 | 1.452 (4) | C4—H4A | 0.9300 |
| N3—C7 | 1.441 (3) | C5—H5A | 0.9300 |
| N3—H3C | 0.8900 | C6—H6A | 0.9300 |
| N3—H3D | 0.8900 | C9—H9B | 0.9600 |
| N3—H3B | 0.8900 | C9—H9C | 0.9600 |
| C1—C2 | 1.380 (4) | C9—H9A | 0.9600 |
| C1—C6 | 1.367 (5) | C10—H10C | 0.9600 |
| C2—C3 | 1.390 (5) | C10—H10A | 0.9600 |
| C3—C4 | 1.363 (7) | C10—H10B | 0.9600 |
| H1WA—O1W—H1WB | 109.00 | N2—C8—C7 | 107.6 (2) |
| N2—N1—C1 | 123.4 (2) | N1—C11—C7 | 104.8 (2) |
| N2—N1—C11 | 109.4 (2) | O1—C11—C7 | 129.8 (2) |
| C1—N1—C11 | 126.9 (2) | O1—C11—N1 | 125.4 (2) |
| N1—N2—C8 | 108.5 (2) | C3—C2—H2A | 121.00 |
| N1—N2—C10 | 122.7 (2) | C1—C2—H2A | 121.00 |
| C8—N2—C10 | 128.0 (2) | C2—C3—H3A | 120.00 |
| C7—N3—H3D | 109.00 | C4—C3—H3A | 120.00 |
| C7—N3—H3B | 109.00 | C5—C4—H4A | 120.00 |
| C7—N3—H3C | 109.00 | C3—C4—H4A | 120.00 |
| H3C—N3—H3D | 110.00 | C4—C5—H5A | 120.00 |
| H3B—N3—H3C | 110.00 | C6—C5—H5A | 120.00 |
| H3B—N3—H3D | 109.00 | C5—C6—H6A | 121.00 |
| N1—C1—C6 | 120.4 (3) | C1—C6—H6A | 121.00 |
| N1—C1—C2 | 118.0 (3) | C8—C9—H9A | 109.00 |
| C2—C1—C6 | 121.5 (3) | C8—C9—H9B | 109.00 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 118.4 (3) | H9A—C9—H9B | 109.00 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 120.6 (3) | H9A—C9—H9C | 109.00 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 120.2 (4) | C8—C9—H9C | 110.00 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 120.7 (4) | H9B—C9—H9C | 109.00 |
| C1—C6—C5 | 118.6 (3) | N2—C10—H10B | 110.00 |
| N3—C7—C11 | 121.8 (2) | N2—C10—H10C | 109.00 |
| C8—C7—C11 | 109.7 (2) | N2—C10—H10A | 109.00 |
| N3—C7—C8 | 128.5 (2) | H10A—C10—H10C | 109.00 |
| N2—C8—C9 | 121.9 (2) | H10B—C10—H10C | 109.00 |
| C7—C8—C9 | 130.3 (2) | H10A—C10—H10B | 110.00 |
| C1—N1—N2—C8 | 175.6 (3) | N1—C1—C2—C3 | 177.5 (3) |
| C1—N1—N2—C10 | −13.9 (4) | C6—C1—C2—C3 | −0.2 (5) |
| C11—N1—N2—C8 | 2.5 (3) | N1—C1—C6—C5 | −179.3 (4) |
| C11—N1—N2—C10 | 173.0 (3) | C2—C1—C6—C5 | −1.8 (6) |
| N2—N1—C1—C2 | 122.6 (3) | C1—C2—C3—C4 | 2.8 (6) |
| C11—N1—C1—C2 | −65.5 (4) | C2—C3—C4—C5 | −3.4 (7) |
| N2—N1—C1—C6 | −59.8 (4) | C3—C4—C5—C6 | 1.5 (8) |
| C11—N1—C1—C6 | 112.1 (4) | C4—C5—C6—C1 | 1.1 (7) |
| N2—N1—C11—C7 | −1.1 (3) | N3—C7—C8—C9 | 6.8 (5) |
| C1—N1—C11—C7 | −174.0 (3) | C11—C7—C8—N2 | 2.1 (3) |
| N2—N1—C11—O1 | 177.5 (3) | C11—C7—C8—C9 | −174.3 (3) |
| C1—N1—C11—O1 | 4.7 (5) | N3—C7—C11—O1 | −0.1 (5) |
| C10—N2—C8—C9 | 4.1 (5) | N3—C7—C11—N1 | 178.5 (2) |
| C10—N2—C8—C7 | −172.6 (3) | C8—C7—C11—O1 | −179.2 (3) |
| N1—N2—C8—C9 | 174.0 (3) | C8—C7—C11—N1 | −0.6 (3) |
| N1—N2—C8—C7 | −2.7 (3) | N3—C7—C8—N2 | −176.9 (3) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O1W—H1WA···Br1 | 0.85 | 2.51 | 3.360 (2) | 173 |
| O1W—H1WB···Br2 | 0.85 | 2.52 | 3.371 (3) | 173 |
| N3—H3B···O1i | 0.89 | 1.89 | 2.692 (3) | 150 |
| N3—H3C···O1W | 0.89 | 2.55 | 3.321 (3) | 146 |
| N3—H3C···O1ii | 0.89 | 2.37 | 3.004 (3) | 129 |
| N3—H3D···O1Wii | 0.89 | 1.99 | 2.817 (4) | 153 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, −y, z−1/2; (ii) −x, −y, −z+1.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: SU2432).
References
- Allen, F. H., Kennard, O., Watson, D. G., Brammer, L., Orpen, A. G. & Taylor, R. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. S1–19.
- Bruker (1998). SMART and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Casas, J. S., García-Tasende, M. S., Sánchez, A., Sordo, J. & Touceda, Á. (2007). Coord. Chem. Rev. 251, 1561–1589.
- Chitradevi, A., Athimoolam, S., Sridhar, B. & Bahadur, S. A. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, o3041–o3042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Jain, S. C., Sinha, S., Bhagat, S., Errington, W. & Olsen, C. E. (2003). Synth. Commun. 33, 563–577.
- Murtaza, S., Hamza, M. & Tahir, M. N. (2011). Acta Cryst. E67, o2193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1996). SADABS University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H. Q., Li, J. Z., Zhang, Y. & Zhang, D. (2008). Chin. J. Inorg. Chem. 24, 990–993.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812023550/su2432sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812023550/su2432Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812023550/su2432Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report