Abstract
Bad bedfellows – autonomic dysfunction, inflammation, and diabetes! Are they related? How? Evidence suggests the activation of inflammatory cytokines like IL-6 and TNFα in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes and that the inflammatory change correlates with abnormalities in sympathovagal balance. Dysfunction of the autonomic system predicts cardiovascular risk and sudden death in patients with type 2 diabetes. It occurs in prediabetes, providing opportunities for early intervention. The importance of recognizing autonomic dysfunction as a predictor of morbidity and mortality with intensification of treatment suggests that all patients with type 2 diabetes at onset, and those with type 1 diabetes after 5 years should be screened for autonomic imbalance. These tests can be performed at the bedside with real time output of information – within the scope of the practicing physician – facilitates diagnosis and allows the application of sound strategies for management. The window of opportunity for aggressive control of all the traditional risk factors for cardiovascular events or sudden death with intensification of therapy is with short duration diabetes, the absence of cardiovascular disease, and a history of severe hypoglycemic events. To this list we can now add autonomic dysfunction and neuropathy, which have become the most powerful predictors of risk for mortality. It seems prudent that practitioners should be encouraged to become familiar with this information and apply risk stratification in clinical practice. After all, how difficult is it to ask patients “do you have numb feet?” and to determine their heart rate variability – it could be lifesaving. Ultimately methods to reset the hypothalamus and the inflammatory cascade are needed if we are to impact the care of patients with this compendium of conditions.
Keywords: inflammation, autonomic, cardiovascular risk, hypothalamic
My mind sent a message to my hypothalamus, told it to release the hormone CRF into the short vessels connecting my hypothalamus and my pituitary gland. The CRF inspired my pituitary gland to dump the hormone ACTH into my bloodstream. My pituitary had been making and storing ACTH for just such an occasion, and nearer and nearer the zeppelin came. And some of the ACTH in my bloodstream reached the outer shell of my adrenal gland, which had been My adrenal gland added the glucocorticoids to my bloodstream. They went all over my body, changing glycogen into glucose. Glucose was muscle food. It would help me fight like a wildcat or run like a deer.
Kurt Vonnegut, Jr., Breakfast of Champions, 1973
The Link between Autonomic Function and Inflammation
There has been an increasing shift to consider that inflammation is central to the pathogenesis of diabetes and its complications including macrovascular disease and microvascular disease, but the origin for the inflammation has not been clearly delineated. While inflammation can cause extensive tissue damage and death it is also essential in the protection of the host and is a defense mechanism against trauma, infection, and stress amongst other provocative agents. What controls this response to trauma and infection has been the focus of energetic pursuits over the past decade and has revealed a potential answer. The inflammatory response is controlled by neural circuitry of the autonomic nervous system. The afferent arc consists of nerves that sense the injury and infection and this in turn activates a cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway that modulates the response and is the potential target for future therapies of diabetes (Borovikova et al., 2000; Tracey, 2009). The lymphoid organs of the immune system are innervated by cholinergic, catecholaminergic, dopaminergic, and peptidergic neurons and the neurotransmitters can interact with immune cells and alter their level of function. For instance in the non-obese diabetic (NOD) mouse (as animal model for type 1 diabetes) neurons surrounding the pancreatic beta cells are lost before there is damage to the islet, and the loss of tonic inhibitory signals contributes to the subsequent beta cell destruction (Saravia and Homo-Delarche, 2003). In addition destruction of the capsaicin sensitive nerve fibers of the pancreas protect the beta cell from streptozotocin induced beta cell injury (Capsaicin and STZ; Razavi et al., 2006). Thus it seems that to begin to understand the role of the autonomic nervous system in its more complex role in inflammation and autoimmunity one needs to delve further into this complexity. Like St Thomas we need to probe deeper!
Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Nervous Systems
Traditionally the organization of the physiologic control of autonomic nervous system functions has relied upon the division into two main branches, the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems (PNS). Stimulation of the sympathetic Brauch mediates physiologic responses of fight and flight that are manifest as increases in heart rate (HR) and blood pressure (BP), mobilization of needed energy stores, and heightened arousal. The major neurotransmitters are epinephrine, norepinephrine, and dopamine and these neurotransmitters mediate cellular responses by interacting with G-protein coupled adrenergic receptors (α1, α2, β1, β2, β3) and dopaminergic receptors (D1, D2, D3). In contrast stimulation of the PNS tends to produce effects which are in general opposite to those of the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) such as slowing of the HR, decreased cardiac contractility, and enhanced digestive functions. The principal neurotransmitter acetylcholine interacts with G-protein coupled muscarinic acetylcholine receptors M1–M5 and nicotinic ligand–gated ion channels (termed neuronal type 1-111 and muscle type 1V; Wess et al., 2007).
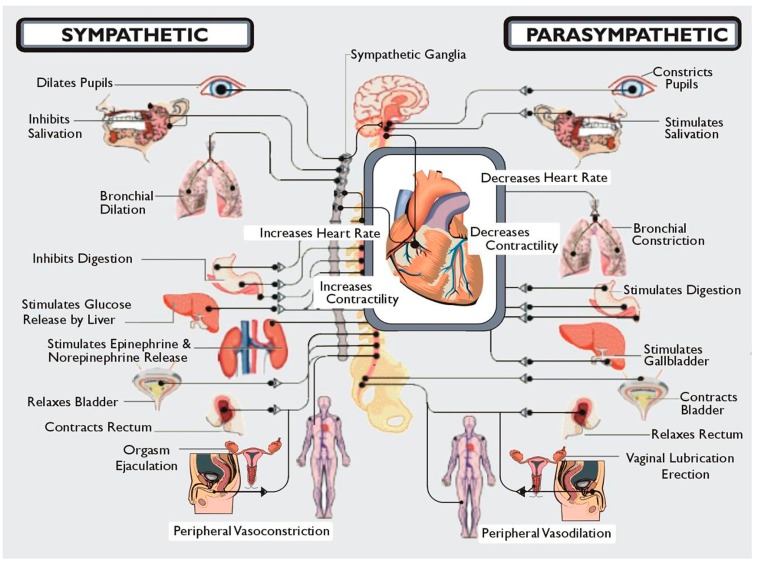
In addition, the systems are distinguished by unique anatomical features. Parasympathetic neurons reside in the brainstem medulla and sacral portions of the spinal cord and sympathetic neuronal cell bodies in the thoracic and lumbar spinal cord. Presynaptic myelinated axons are projected through cranial nerves and/or spinal nerves to synapses located in ganglia. From these postsynaptic unmyelinated fibers are derived, which themselves target the innervated organ. It is also important to realize that although at first glance these systems appear to have opposing effects, e.g., sympathetic increases HR and parasympathetic slows HR, stimulation of both results in a greater increase in cardiac output because sympathetic stimulation increases the ejection fraction and parasympathetic stimulation slows the heart, thus allowing increased efficiency of cardiac filling. Similarly, baroreceptors which perceive stretch in the aorta with increasing BP send signals via the sensory component of the vagus terminating in the nucleus of the tractus solitarius in the medulla. From here presynaptic fibers of the SNS project to the ventrolateral nucleus of the medulla and parasympathetic presynaptic neurons to nucleus ambiguous in the medulla. Coordinated firing of both arms of the autonomic nervous system is necessary to respond to changes in BP and, if damage occurs, is reset to accommodate new levels which may be too high or too low for the individual. Thus, one needs to consider the system in its entirety. Damage to one or another component may not have as devastating an effect as damage to the whole system. Within this framework Figure 1 illustrates the entire workings of the autonomic nervous system.
Figure 1.
A diagrammatic illustration of the role of the two arms of the autonomic nervous system. Note that in general the actions of the sympathetic nervous system are illustrated as being in the opposite direction to that of the parasympathetic nervous system. Not shown here but discussed below is the CNS regulation of the immune system via the vagal cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway adding yet another dimension to the role of the autonomic nervous system in survival of the organism. Note that Kurt Vonnegut recognized the importance of the CNS in stress but failed to recognize its role as the conductor of the endocrine and autonomic orchestra. But then he was not a biologist!
Autonomic Nervous System Control of Inflammation
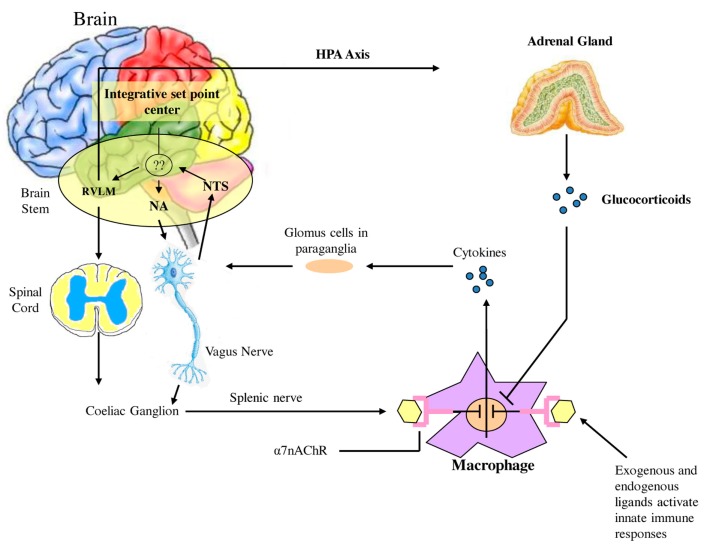
Watkins et al. (1995) discovered that sensory neurons detect the presence of inflammation in tissues (Figure 2). These responses to IL-1 induced inflammation were mediated by the vagus, and could be abolished by vagotomy or a selective competitive antagonist of the IL-1 receptor (Goehler et al., 1997; Hansen et al., 2001). In cardiovascular physiology, oxygen, glucose, and other metabolites are sensed by specialized glomus cells in the association with the nervous system. Upon activation, these cells release dopamine and norepinephrine causing depolarization of the sensory fibers in the vagus which propagate to the brainstem and initiate a motor efferent arc. It appears that IL-1 binds to the glomus cells initiating the afferent arc; however there are a number of other ligands derived from macrophages, monocytes, and dendritic cells referred to as pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPS) which activate Toll-like receptors (TLR) and lead to increased expression of NF-κB and increased release of inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-a and IL-6. Endogenous molecular products are also released from damaged cells and are referred to as damage associated molecular patterns (DAMPS). Thus the nervous system is capable of initiating a response to tissue injury and inflammation and can per se initiate a pro-inflammatory response. One must therefore add a neuro-regulatory role for the autonomic nervous system to the one outlined above.
Figure 2.
Afferent sensory signals are transmitted by the vagus to the nucleus of the solitary tract (NTS) and polysynaptic receptors relay to the sympathetic via the rostral ventromedullary nucleus (RVLS) and the parasympathetic nucleus ambiguous (NA and the dorsal vagal nucleus. There is both sympathetic and parasympathetic output to the celiac ganglion and the splenic nerve activates the inflammatory cascade in macrophages which may be in the spleen but occur diffusely throughout the body. Stimulation of the vagus inhibits this activation by acetylcholine binding to the α7nACHR receptor which curtails the response. Also shown is the coactivation of the hypothalamic pituitary axis with release of glucocorticoids which also modulate the inflammatory response. It is however unclear how this set point is determined in the body but what is clear is that autonomic modulation of inflammation can be achieved by altering sympathetic/parasympathetic balance.
The efferent arc of this inflammatory response is termed the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway. The neurotransmitter acetylcholine interacts with the innate immune cells that express the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunit α7 (α7nAChR). The receptor is widely expressed in neurons which function as ligand-gated ion channels encoded by CHRNA 7 on chromosome 15q14 and is a product of 10 exons yielding a mature protein of 50kDa. α7nAChR has a tonic inhibitory role in the immune cells similar to the effects of the parasympathetic system on inhibition of HR. Exaggerated responses to inflammatory molecules are caused by vagotomy, whereas stimulation of the vagus downregulates the production of TNFα, IL-1, IL-6, and IL-8but does not alter the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 and TGFβ. This ACh activates the JAK/STAT pathway, affecting the inflammatory responses mediated by NF-kB and initiating the release of a variety of inflammatory cytokines. Thus this is a defensive reflex protecting the organism from organ damage and death when exposed to syndromes of excess cytokine release such as infection, trauma, and stress.
Diabetes – a State of Faulty Sympathetic Balance and Chronic Inflammation
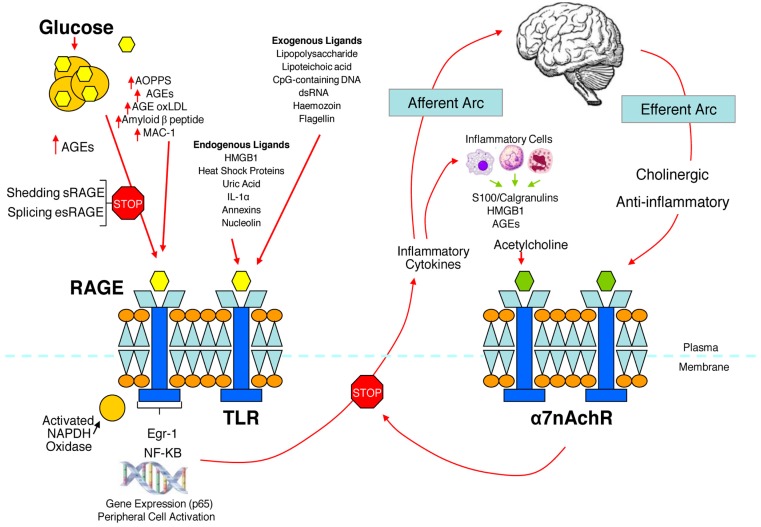
We have hypothesized that in the metabolic syndrome and diabetes there is a constant increase in low grade inflammation mediated by a large cadre of exogenous and endogenous ligands (Figure 3). These in turn are capable of binding to the advanced glycation end product receptor (RAGE) and thereby activating NF-kB pathway and increasing the production of inflammatory cytokines. In addition there are a number of other ligands capable of activating the inflammatory cascade. DAMPS for example, can stimulate innate immune responses culminating in NF-kB activation as with the ligands for RAGE. This is further compounded by the ligands binding to the TLR which potentiate the activation of NF-kB. The balance occurs by binding of acetylcholine to the α7nACHR receptor and via JAK2 and Stat restraining the activation of NF-kB. Thus the loss of autonomic control with reduction of parasympathetic activity, hallmark autonomic dysfunction in diabetes, initiates a cascade of inflammatory responses that, if continued unabated will culminate in considerable morbidity and mortality. The possible approaches to enhancing parasympathetic function will be discussed below.
Figure 3.
The relationship between binding of ligands to the pattern recognition AGE receptor (RAGE) and inflammation, gene expression, oxidative and nitrosative stress, and damage to the macro- and microvasculature. Elevated levels of glucose bind to proteins and form AGEs, which bind to RAGEs. RAGE signaling activates NADPH oxidase and production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Increased ROS increases advanced oxidation protein products (AOPPs), more AGEs, and AGE-modification of oxidized LDLs (oxLDLs). Furthermore, increased ROS may deplete glutathione, thereby suppressing glyoxalase I activity, a mechanism favoring further AGE accumulation. AGEs, AOPPs, macrophage glycoprotein (MAC-1), and AGE-oxLDL ligands of RAGE sustain stimulation of RAGE, and these processes, together with increased ROS, activate key transcription factors such as nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and Egr-1, which increase gene transcription factors and activate inflammatory mechanisms. Consequences include increased migration and activation of RAGE-expressing neutrophils, monocytes/macrophages, T-cells, and dendritic cells. This results in the release of the pro-inflammatory RAGE ligands S100/calgranulins and high-mobility group protein box-1 (HMGB1). In this inflammatory environment, further AGEs may be formed as well. Via interaction with RAGE, these ligands magnify activation of NF-κB, Agr-1, and other factors, thereby amplifying cellular stress and tissue damage leading to neurovascular dysfunction. Soluble RAGE (sRAGE) is formed from the cleavage of RAGE by disintegrins such as ADAM 10, a metalloproteinase, and β- and γ-secretases. sRAGE or a spliced variant (esRAGE) compete for binding of ligands to RAGE, and a deficiency could theoretically initiate the sequence of events activating an inflammatory cascade with an increase in the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines [E-selectin, endothelin-1 tissue factor, vascular endothelial growth factor, and other pro-inflammatory cytokines (interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α)] and damage to neurons, kidney, eye, the vasculature, and even bone. Increasing sRAGE or its administration could competitively reduce activation of the AGE/RAGE pathway and it consequences. In addition endogenous and exogenous ligands bind to Toll-like receptors (TLR) also targeting NF-KB as well as inducing the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines which activate afferent sensory neurons reaching the brainstem via axons in the vagus. This in turn activates the cholinergic anti-inflammatory efferent arc which inhibits response in cytokine producing immune cells and signal through the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunit α7 (α7nACHR). This in turn inhibits NF-κB activation. Thus the pathways of AGE/RAGE activation of the inflammatory cascade and the inflammatory ligands target activation of an inflammatory cascade that can be abrogated by either competing with the binding of ligands to RAGE or by vagal activation of the anti-inflammatory reflex. Thus central to curtailing unbridled activation of the inflammatory cascade is the integrity of parasympathetic autonomic function or balance between the two arms of the autonomic nervous system.
The Consequence of Autonomic Dysfunction in Diabetes
Cardiac autonomic neuropathy (CAN) and sympathetic/parasympathetic imbalance is a significant cause of morbidity and mortality associated with a high risk of cardiac arrhythmias and sudden death, possibly related to silent myocardial ischemia. The prevalence of CAN may be high. In a large cohort of patients with T2DM, Ziegler et al. (1995), using predefined heart rate variability (HRV) and spectral analysis of the R–R intervals, found that 34.3% of those with T2DM had abnormal findings. Newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes (Lieb et al., 2011) and prediabetes stages [(i.e., impaired glucose tolerance (IGT)] are associated with a decreased parasympathetic modulation of the heart and a shift toward augmented sympathetic tone. Factors that influence the prevalence of CAN include the diagnostic criteria used, patient age, and the duration of diabetes (Vinik and Ziegler, 2007). Additional clinical correlates and predictors of CAN include glycemic control; presence of distal peripheral neuropathy (DPN), nephropathy, and retinopathy; BP levels, obesity; smoking; cholesterol; and triglycerides levels (Vinik and Ziegler, 2007). Additional factors which emerged as identifying susceptibility to cardiovascular events with intensification of glycemic control included: duration of diabetes >12–15 years, impaired renal function, coronary artery calcification, a previous cardiovascular event, being African American, being female, aging, a history of neuropathy or numb feet, and loss in HRV (Calles-Escandon et al., 2010; Pop-Busui et al., 2010; Vinik et al., 2011). Parasympathetic tone may decline with an autonomic imbalance shifting toward augmented sympathetic tone during the development from normal glucose tolerance to IGT and finally diabetes (Wu et al., 2007).
Morbidity and Mortality in Cardiac Autonomic Neuropathy
Cardiac autonomic neuropathy defined by measures of abnormalities in PNS and SNS, is a significant cause of morbidity and mortality associated with a high risk of cardiac arrhythmias and sudden death, possibly related to silent myocardial ischemia. Cardiovascular disease (CVD) remains the main cause of excess mortality among patients with type1 (T1DM) and type 2 diabetes (T2DM). The prevalence of CAN varies greatly depending on the criteria used to identify CAN as well as the population studied. These range from as low as 2.5% of the primary prevention cohort in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT, 1998) to as high as 90% of patients with long-standing T1DM who were potential candidates for a pancreas transplant (Kennedy et al., 1995). In a large cohort of patients with T1DM and T2DM, Ziegler et al. (1995), using predefined HRV and spectral analysis of the R–R intervals, found that 25.3% of patients with T1DM and 34.3% of those with T2DM had abnormal findings. Even the prediabetic stage (i.e., IGT) is associated with a decreased parasympathetic modulation of the heart and a shift toward augmented sympathetic tone. Parasympathetic tone may decline with an autonomic imbalance shifting toward augmented sympathetic tone during the development from normal glucose tolerance to IGT and finally diabetes (Wu et al., 2007). Reduced HRV as a marker of autonomic dysfunction has been shown to have dire consequences in terms of morbidity (e.g., progression of coronary atherosclerosis; Huikuri et al., 1999), and mortality independent of cardiovascular risk factors (La Rovere et al., 2003; Maser et al., 2003; Hadase et al., 2004; Janszky et al., 2004) in various populations including those with prediabetes and diabetes (Ziegler et al., 2008; Beijers et al., 2009). In T1DM there is a fourfold increased risk of death (Orchard et al., 1996). CAN is significantly associated with overall mortality (Maser et al., 2003; Vinik et al., 2010) and in some – but not all – studies with morbidity such as silent myocardial ischemia, coronary artery disease, stroke, diabetic nephropathy progression, and perioperative morbidity. Some pathogenetic mechanisms may link CAN to cardiovascular dysfunction and diabetic complications (Vinik et al., 2011). Thus, CAN assessment may be used for cardiovascular risk stratification in patients with and without established CVD; as a marker for patients requiring more intensive monitoring during the perioperative period and other physiological stresses; and as an indicator for more intensive pharmacotherapeutic and lifestyle management of comorbid conditions. Clearly the role of autonomic imbalance and the mechanisms underlying the risk require further exploration if we are to achieve benefit for all. However foremost in our minds is the issue of why diagnose if we cannot treat?
Consequences of AGE/RAGE Interactions in Diabetes
Hyperglycemia increases protein glycation and causes a gradual accumulation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) in body tissues. These AGEs form on intra- and extra-cellular proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids, in complex arrangements that lead to cross-linking. It has also been shown that an accumulation of AGEs in collagen tissue such as skin, measured by skin autofluorescence, correlates with severity of peripheral and autonomic nerve abnormalities in diabetes, even before being clinically manifest (Meerwaldt et al., 2005). Both immunohistochemical and biochemical studies have shown that carboxymethyllysine (CML)-modified proteins are AGEs that accumulate in tissues affected by diabetic complications, such as bone. This process is mediated through RAGE, the pattern recognition receptor for AGE. Of the three known receptors for AGE, RAGE is of particular interest because it is found on many cell types, especially those affected by diabetes. RAGE is constitutively expressed but is also induced by reactions known to initiate inflammation. Patients with diabetes often display elevated CML levels that can bind and activate RAGE signaling (Schmidt et al., 2001). Furthermore, AGE-RAGE interaction creates a chronic cascade of inflammation and tissue injury. Of further interest, RAGE knockout mice have a reduced capacity to develop neuropathy (Toth et al., 2008; Takuma et al., 2009), and the soluble form of the AGE receptor sRAGE, can act as a decoy molecule, thereby reducing the binding of ligands to RAGE and inhibiting the inflammatory cascade (Figure 3). Our studies in Charcot neuroarthropathy show the presence of severe somatic and autonomic neuropathy in association with reduced levels of sRAGE (Witzke et al., 2011) (Table 1).
Table 1.
Peripheral and autonomic nerve dysfunction and reduction of sRAGE in diabetes and Charcot neuroarthropathy (mean ± SD).
| Control (n = 30) | Diabetes (n = 30) | Charcot (n = 20) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tibia-ankle | |||
| Amplitude | 8.9 ± 4.1 | 4.3 ± 3.8* | 0.6 ± 1.0† |
| Latency | 4.7 ± 0.7 | 4.2 ± 1.8 | 3.6 ± 5.5 |
| Conduction velocity | 45.4 ± 3.7 | 35.4 ± 15.2* | 7.7 ± 13.1† |
| F-wave | 54.7 ± 6.4 | 47.5 ± 23.3 | 17.5 ± 29.7† |
| Sural Response (number with positive response) | 30 | 28 | 4 |
| Vibration perception (μ) | 10.6 ± 11.1 | 31.7 ± 27.3* | 100.5 ± 31.5† |
| Pressure perception (g) | 2.9 ± 0.4 | 3.1 ± 0.3 | 5.9 ± 1.2† |
| Cold sensation (°C) | 5.5 ± 2.7 | 7.7 ± 5.2 | 20.9 ± 9.9† |
| Warm sensation (°C) | 7.1 ± 3.1 | 10.3 ± 3.2* | 14.9 ± 3.2† |
| Cold pain | 24.5 ± 9.0 | 26.4 ± 6.6 | 30.6 ± 3.5† |
| Warm pain | 14.0 ± 3.3 | 15.4 ± 2.5* | 17.5 ± 1.0† |
| Valsalva ratio | 1.43 ± 0.25 | 1.36 ± 0.31 | 1.18 ± 0.28† |
| Parasympathetic deep breathing | 611 ± 13 | 617 ± 13 | 632 ± 18† |
| Sympathetic Valsalva response | 714 ± 17 | 713 ± 16 | 717 ± 20 |
| N telopeptide (NTx; nmol/L) | 13.6 ± 5.5 | 11.4 ± 5.7 | 13.8 ± 8.2 |
| Osteocalcin (ng/mL) | 1.29 ± 0.96 | 1.23 ± 5.7 | 2.29 ± 2.57* |
| sRAGE (pg/mL) | 1140 ± 471 | 522 ± 660‡ | 162 ± 67* |
| Bone mass density (BMD; g/cm2) | |||
| Femoral neck | 1.004 ± 0.141 | 1.048 ± 0.184‡ | 0.904 ± 0.219 |
| Greater trochanter | 1.080 ± 0.157 | 1.116 ± 0.165‡ | 0.987 ± 0.185 |
| Total hip | 1.018 ± 0.129 | 1.037 ± 0.150 | 0.955 ± 0.252 |
| Foot | 0.754 ± 0.081 | 0.792 ± 0.105 | 0.788 ± 0.120 |
| Calcaneal stiffness index | 105.2 ± 14.0 | 103.3 ± 18.6 | 77.1 ± 26.2* |
Continuous data are expressed as mean ± SD; categoric data as n. *p < 0.05 vs control subjects. †p < 0.05 vs diabetic and control subjects. ‡p < 0.05 vs Charcot subjects (Witzke et al., 2011) with permission.
In homeostasis, RAGE is expressed at low levels but during biological stresses such as inflammation and diabetes, RAGE expression is greatly upregulated as a direct result of AGE accumulation. Many studies have now shown that AGE-RAGE interactions alter intracellular signaling via pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6, TNF-α, and free radicals that further propagate diabetic complications. Interestingly the two pathways, autonomic function and inflammation may be linked since it has become evident that autonomic dysfunction is associated with an increase in circulating inflammatory cytokines (Lieb et al., 2011). Furthermore, recent studies support the notion that autonomic reflexes may control the inflammatory response (Tracey, 2009).
Cardiovascular Autonomic Balance
Autonomic balance involves complex interactions with several physiologic mechanisms that act to maintain HR and BP within normal limits. Recent investigations have suggested that autonomic dysfunction (e.g., heightened activity of the SNS and suppressed activity of the PNS) impairs the ability of the ANS to regulate the cardiovascular system. Thus, autonomic imbalance may be a key component involved in both the etiology and the clinical course of CVD. What is also emerging is that one needs to distinguish the difference between autonomic imbalance and clear evidence of autonomic neuropathy. Autonomic imbalance produces a number of interesting and trying clinical situations such as orthostatic tachycardia, orthostatic bradycardia, and hypotension and can be responsible for predisposition to arrhythmias and sudden death (Vinik et al., 2011). The most interesting implication of loss of autonomic imbalance derives from the catastrophic increase of sudden death in the ACCORD study with intensive lowering of blood glucose in which the combination of numbness of the feet and loss of HR variability increased the susceptibility to an event with a risk ratio (RR) of 4.43 (Calles-Escandon et al., 2010; Vinik et al., 2011). Most recently an International Group has updated definitions of diabetic neuropathy including autonomic neuropathy and reported upon these (Tesfaye et al., 2010).
Cardiac Autonomic Assessment
Cardiovascular reflex tests are the gold standard in clinical autonomic testing. These tests have good sensitivity, specificity, and reproducibility and are non-invasive, safe, well-standardized, and easily performed (Vinik and Ziegler, 2007). The most widely used tests assessing cardiac parasympathetic function are based on the time-domain HR response to deep breathing, a Valsalva maneuver, and postural change. However, a Valsalva maneuver must not be performed in patients with proliferative retinopathy. Of these tests, HR to deep breathing has the greatest specificity (−80%). Cardiovascular sympathetic function is assessed by measuring the BP response to orthostatic change and a Valsalva maneuver. The performance of these tests should be standardized, and the influence of confounding variables such as medications, hydration, and antecedent activity should be minimized. Age normative values should be used. The combination of cardiovascular autonomic tests with sudomotor function tests may allow a more accurate diagnosis of diabetic autonomic neuropathy (DAN), but this is still in the research arena.
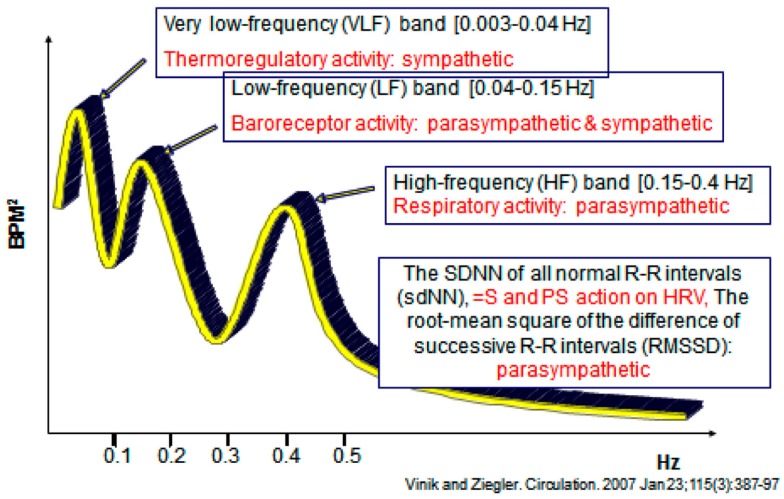
Analysis of HRV is a non-invasive electrocardiographic method for assessing overall autonomic activity (Malik and the Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology, 1996). Analysis of HRV, with analysis of respiratory activity, independently and simultaneously measures parasympathetic and sympathetic activity (Akselrod et al., 1981), and thereby provides information with regard to autonomic balance of the cardiovascular system. Power spectral analysis of HRV can be performed under resting conditions with demonstration of low-frequency (LF) and high-frequency (HF) components. The LF component of the power spectrum of HRV primarily reflects sympathetic activity, while the HF component (also termed the respiratory-frequency, RF) primarily reflects parasympathetic activity. LF/RF ratios are calculated and provide a measure of sympathetic/parasympathetic activity. The total spectral power (TSP) is calculated, as are the standard deviation of all normal R–R intervals (sdNN; a measure of both sympathetic and parasympathetic action on HRV) and the root-mean square of the difference of successive R–R intervals (rmSSD), a measure primarily of parasympathetic activity (Vinik and Ziegler, 2007).
Diabetic patients with features of cardiac autonomic dysfunction such as unexplained tachycardia, orthostatic hypotension, and poor exercise tolerance, or with other symptoms of autonomic dysfunction should be evaluated for the presence of autonomic dysfunction. Screening for autonomic dysfunction should be performed at the diagnosis of type 2 diabetes and 5 years after the diagnosis of type 1 diabetes, particularly in patients at greater risk due to a history of poor glycemic control, cardiovascular risk factors, DPN, and macro- or microangiopathic diabetic complications. While a number of tests for autonomic dysfunction are in the research arena some have been shown to be sufficiently robust to be incorporated into routine clinical care (Tesfaye et al., 2010; Spallone et al., 2011) (Table 2).
Table 2.
Cardiovascular autonomic tests and suggested indications for their use.
| Clinical diagnosis | Research end point | Clinical trials | |
|---|---|---|---|
| HR cardiovascular tests | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Orthostatic hypotension test | Yes | Yes | No (low sensitivity) |
| QT interval | Yes (additional information and risk stratification) | Yes | No (low sensitivity) |
| ABPM for dipping status | Yes (risk stratification) | Yes | No (low sensitivity) |
| HRV time- and frequency-domain indices | Yes (early additional information and risk stratification) | Yes | Yes |
CAN testing for clinical trials and research
The time-domain HR tests and the BP response to postural change have the reproducibility necessary for clinical trials. These tests were used as end points in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications Study (DCCT EDIC Research Group, 2005) and other clinical trials.
Frequency-domain indices obtained by applying spectral analysis to HR variability of short (5–7 min) and long (24-h) electrocardiogram recordings provide a measure of sympathetic and parasympathetic modulation of HR as described before. HR spectral power in the HF region is a measure of parasympathetic modulation, while spectral power in the LF region provides a measure of both sympathetic and parasympathetic modulation. The LF BP variability may provide a measure of sympathetic modulation. To correctly assess the significance of the different regions, respiration should be measured or controlled breathing performed. These methods, which need standardization, have been widely used in research and as end points in clinical trials. These have now been shown to be invaluable in patients with clinical syndromes of autonomic excess or deficiency and can be accomplished in 15 min at the bedside without need to resort to more complex studies using tilt table testing, for example. In addition it is a sound general rule that an autonomic function test becomes useful when suspecting autonomic nerve dysfunction (gastroparesis, erectile dysfunction or diabetic diarrhea, and syncope amongst other conditions). A negative test has >95% negative predictive value for autonomic dysfunction and becomes the relatively simple surrogate for more expensive, complex, and at times invasive tests (Figure 4).
Figure 4.
Spectral analysis of heart rate variability.
Treatment of Autonomic Dysfunction
Targeting inflammation
The treatment of inflammatory diseases including chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP) and autonomic neuropathy has had a significant boost by the use of immunoglobulin, and biological agents that modulate the activity of TNF-a, IL-1, and IL-6 (Pittenger et al., 1997; Vinik et al., 2006b; Anandacoomaraswamy et al., 2008; Bourcier and Vinik, 2010; Handelsman et al., 2011). These agents have been shown to ameliorate rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease, which is what serendipitously directed us to the use of an anti-TNFα in diabetic neuropathies. They are, however, potentially harmful as they are immunosuppressants and a more benign intervention is clearly necessary. For example, electrical stimulation of the vagus nerve or administration of the a7nACHR agonists reduces the magnitude of the inflammatory response by 50–75% without compromising cytokine activity (Borovikova et al., 2000; Bernik et al., 2002; Saeed et al., 2005; Huston et al., 2006). Depressed vagal activity or the loss of sympathovagal balance has been shown to cause exaggerated pro-inflammatory responses and increased morbidity and mortality (Thayer and Sternberg, 2006; Thayer and Fischer, 2009). Vagus nerve activity can be measured in humans by time and frequency-domain analysis of instantaneous HRV in the resting state as well as with provocative testing of the effects of vagal stimulation using the respiratory variation, the Valsalva maneuver, and the effects of standing (Vinik and Ziegler, 2007). Also, peripheral vagal activity can be measured using the pancreatic polypeptide response to insulin hypoglycemia or beef meals (Glaser et al., 1980), and peripheral preganglionic measures of acetylcholine effects on sweating can be determined using sudorimetry, and quantitative sudorimetry (Low et al., 1983; Vinik and Ziegler, 2007).
Indeed in our studies of the regulation of skin blood flow we have shown that there are major differences in the autonomic regulation of blood flow in hairy skin of the forearm, which is almost entirely dependent on sympathetic/parasympathetic control (Vinik et al., 2006a). By contrast in glabrous skin there is a dependence on vasodilatory peptides such as CGRP and Neurokinin A as well as certain vasodilatory and vasoconstrictive prostaglandins (Vinik and Kles, 2006). In rheumatoid arthritis high-frequency oscillation which reflect vagal activity are depressed compared with healthy controls (Pontet et al., 2003). Pontet and colleagues evaluated the effects of HRV on the critical care setting in patients with sepsis a low HRV is associated with organ failure whereas subjects with a normal HRV had uneventful hospital stays (Pontet et al., 2003). The mortality rate of individuals with low HRV on admission was 63.6% compared with 0% in the group with normal HRV (Pontet et al., 2003). Of greater interest is the association between atheroma and reduced HRV (Hanson and Libby, 2006; von Kanel et al., 2008).
Therapeutic implications of altering autonomic balance
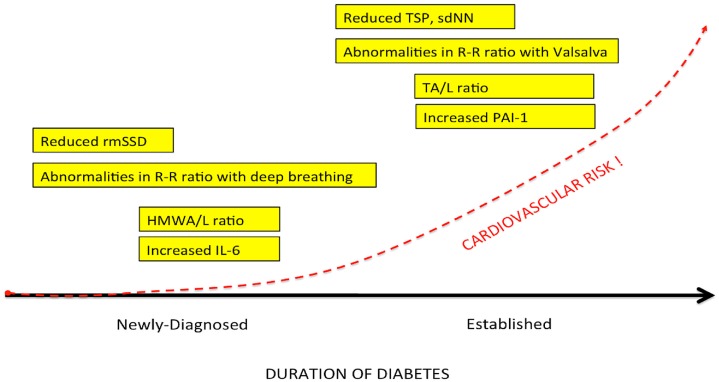
We (Lieb et al., 2011) examined patients with newly diagnosed diabetes, established diabetes, and healthy controls and analyzed a cadre of inflammatory markers in addition to time and frequency-domain measures of autonomic function. Of great interest to us is the appearance before the advent of inflammation of loss of HRV as well as loss of sympathetic/parasympathetic balance (Figure 5; Table 3). Early in the development of autonomic dysfunction there is loss of HRV and this correlates with an increase in circulating markers of inflammation such as CRP and IL-6 (Lieb et al., 2011).
Figure 5.
The natural history of autonomic balance.
Table 3.
Measures of autonomic function and inflammation in healthy controls, newly diagnosed and established diabetes.
| Measure | Controls (n = 15) | Newly diagnosed T2D (n = 15) | Established T2D (n = 15) | p value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R–R ratio (deep breathing) | 1.26 ± 0.04 | 1.20 ± 0.03 | 1.17 ± 0.05 | 0.0325# |
| R–R ratio (Valsalva) | 1.58 ± 0.21 | 1.37 ± 0.06 | 1.24 ± 0.05 | 0.0270* |
| R–R ratio (standing) | 1.29 ± 0.04 | 1.26 ± 0.05 | 1.18 ± 0.02 | NS |
| LFa | 1.60 ± 0.43 | 1.90 ± 0.39 | 1.37 ± 0.37 | NS |
| RFa | 1.21 ± 0.27 | 1.89 ± 0.79 | 0.73 ± 0.29 | NS |
| LFa/RFa ratio | 1.53 ± 0.24 | 2.51 ± 0.51 | 2.88 ± 0.56 | NS |
| TSP baseline | 950.88 ± 191.95 | 772.94 ± 290.95 | 416.95 ± 142.61 | 0.0023* |
| sdNN baseline | 47.66 ± 4.87 | 41.04 ± 3.92 | 28.92 ± 4.65 | 0.0008* |
| rmSSD baseline | 30.18 ± 3.76 | 28.77 ± 6.97 | 18.97 ± 3.38 | 0.0356# |
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | 2.84 ± 0.68 (n = 14) | 11.58 ± 2.83 | 12.04 ± 1.20 (n = 12) | <0.0001# |
| TNF-α (pg/mL) | 9.32 ± 2.18 (n = 14) | 9.14 ± 1.15 | 27.93 ± 15.4 (n = 12) | NS |
| PAI-1 (ng/mL) | 3.05 ± 0.56 | 5.23 ± 0.76 | 6.41 ± 1.36 | 0.0305* |
| Total adiponectin (mg/mL) | 6.76 ± 0.78 | 7.48 ± 1.11 | 8.91 ± 2.3 | NS |
| High-molecular weight adiponectin (μg/mL) | 1.78 ± 0.26 | 2.33 ± 0.60 | 2.71 ± 1.54 | NS |
| Leptin (ng/mL) | 28.66 ± 7.93 | 46.87 ± 7.96 | 55.93 ± 11.39 | NS |
| TA/L ratio | 1.17 ± 0.76 | 0.24 ± 0.05 | 0.53 ± 0.32 | 0.0340* |
| HMWA/L ratio | 0.49 ± 0.40 | 0.07 ± 0.02 | 0.26 ± 0.22 | 0.0442# |
Modified from Lieb et al. (2011).
Data are presented as means ± SE. NS, not significant. *Established T2D vs controls/newly diagnosed T2D.
#Newly diagnosed/established T2D vs controls.
TSP, total spectral power; SDNN, standard deviation of all normal R–R intervals; rmSSD, root-mean square of the difference of successive R–R intervals.
IL-6, interleukin-6; TNFα, tumor necrosis factor alpha; PAI, plasminogen activator Inhibitor 1; TA/L, total adiponectin/leptin ratio; HMWA/L, high-molecular weight adiponectin/leptin ratio.
Analysis of 102 healthy middle aged individuals found an association between loss in HRV and IL-6 levels. The authors concluded that low grade inflammation is associated with loss in HRV (von Kanel et al., 2008). Another study on 611 healthy adults showed an inverse correlation between HRV and CRP levels. The authors concluded that the effect could be attributed to low grade inflammation due to a decrease in the cholinergic pathway of anti-inflammatory cascades with implications for addressing inflammation in the prevention and management of heart diseases (Thayer and Fischer, 2009). HRV, CRP, and IL-6 levels were measured in 757 young adults and HRV was significantly related to IL-6 and CRP levels which was thought to be consistent with the notion that the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathways exert a tonic inhibitory influence on innate immune responses and could be the potential target for future interventions. Of particular note is the sequence of events shown in Figure 5 suggesting that circulating adiponectin (HMW) and leptin levels may be early predictive markers, and the mechanism may be via insulin resistance or direct actions of Leptin on the hypothalamus and the autonomic nervous system. In our study, we found that newly diagnosed diabetic subjects had significantly lower HMW adiponectin/leptin ratios when compared with control subjects, and saw significant correlations between the HMWA/leptin ratio and multiple measures of autonomic function (LFa/RFa ratio, TSP baseline, and rmSSD baseline) (Lieb et al., 2011). In a study of 120 non-obese humans without diabetes, Paolisso et al. (2000) demonstrated that increasing plasma leptin concentrations were associated with increasing LFa/HFa ratios, suggesting greater SNS activity as compared with PSN activity. Studies have also shown interesting correlations between adiponectin and autonomic function. Wakabayashi and Aso (2004) studied 105 men and women with T2D and found that adiponectin concentrations correlated negatively with the LFa/RFa ratio. Of note, changes in the adiponectin/leptin balance in the course of diabetes may first be seen by utilizing measures of high-molecular weight adiponectin rather than total adiponectin, as demonstrated by our findings (Table 3). These findings and the results in animal studies again suggest that the effects on adipose tissue cytokine release may be a consequence of autonomic dysfunction as opposed to the corollary. Clearly a closer look at the relationship between adipose tissue cytokines, obesity, and the impact of weight reduction on the relationship between inflammation and HRV is warranted. With the explosive developments in global obesity and the proliferation of gastric bypass procedures on adults and even children, no doubt this will yield a fertile field for exploring these relationships and their potential for therapeutic intervention.
Restoring Autonomic Balance
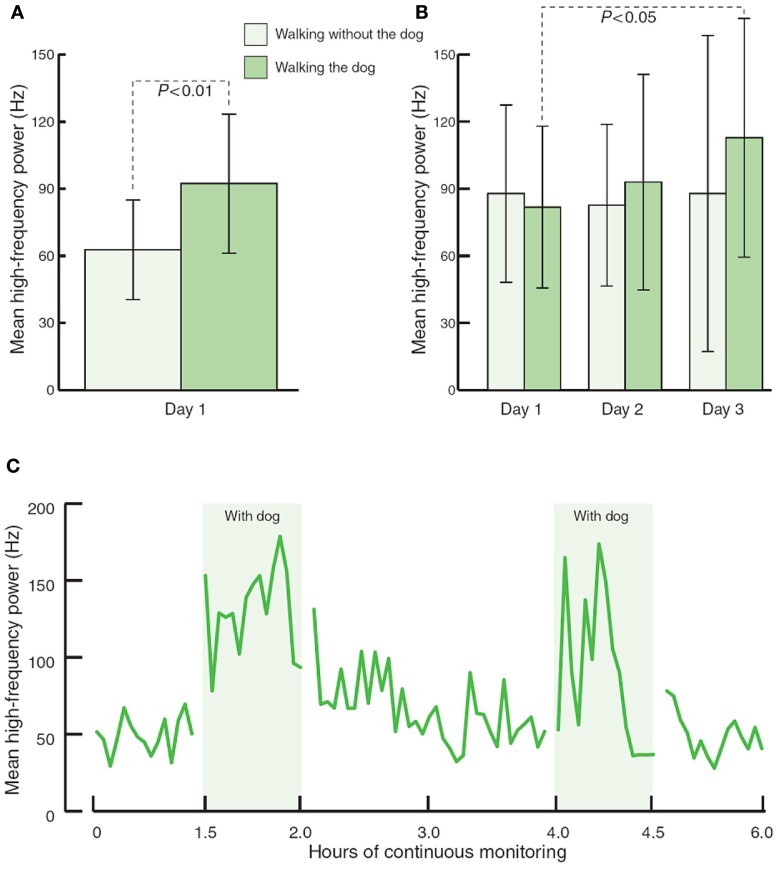
Physiological health is characterized by organized variability in organ functions which are controlled by neural networks that provide compensatory output to maintain homeostasis around set points which are appropriate for the system in time, gender, age, body weight, and BP among other variables such as exercise, sedentary habits, and smoking. While these neural network imbalances can theoretically be corrected by relatively simple maneuvers they are in general difficult to obtain and maintain. However this is possible. Our interest in falling and fractures in older diabetics has taught us that much of these injuries are due to the loss of the organized variability, strength, and reaction times; furthermore, with very simple strength and balance training falls risk can be significantly reduced (Morrison et al., 2010). Just as when landing planes in Hong Kong the pilot indulges in serial deviations in wing tip position to allow the computer to correct these and ensure a safe landing we have a need to enhance the imbalance in autonomic and inflammatory reflexes that characterize the loss of physiological and pathological flexibility. Just as in diabetes management, this requires work and of course we all want the magic bullet. Some are on the horizon. However, even simple maneuvers such as walking the dog can restore autonomic balance (Figure 6). For the abnormalities in autonomic balance adrenergic excess can be addressed with beta blockers and parasympathetic excess with anticholinergic drugs (Vinik and Erbas, 2006; Table 4).
Figure 6.
The effects of walking with and without a pet dog, on parasympathetic function (mean high frequency power). (A) 80-min walking programme including two 30-min walks without and with the dog (n = 13). (B) 80-min walking programme over three consecutive days (n = 3). (C) Interaction with the dog at home during 6 h of continuous monitoring (n = 4).
Table 4.
Diagnosis and management of autonomic dysfunction.
| Symptoms | Assessment Modalities | Management |
|---|---|---|
| Resting tachycardia, exercise intolerance, early fatigue, and weakness with exercise | HRV, respiratory HRV, MUGA thallium scan, 123I MIBG scan | Graded supervised exercise, beta blockers, ACE-inhibitors |
| Postural hypotension, dizziness, lightheadedness, weakness, fatigue, syncope, tachycardia/bradycardia | HRV, blood pressure measurement lying, and standing | Mechanical measures, clonidine, midodrine, octreotide, erythropoietin, pyridostigmine |
| Hyperhidrosis | Sympathetic/parasympathetic balance | Clonidine, amitryptylline, trihexyphenidyle, propantheline, or scopolamine, botox, glycopyrrolate |
Reversibility of Autonomic Imbalance
We have reported simple pharmacological manipulation of situations of parasympathetic and sympathetic imbalance with important changes in the symptom complex and quality of life of the afflicted individuals (Vinik et al., 2011). Intervention studies have documented the protective effects of glycemic control in type 1 diabetes (DCCT) and of multifactorial strategy aimed at lifestyle change with pharmacological correction of hyperglycemia, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and microalbuminuria (Gaede et al., 2003).
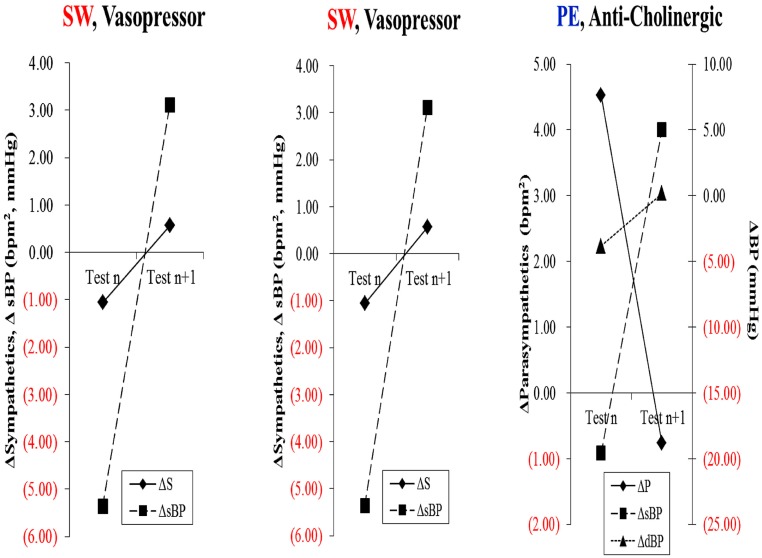
Immune therapy for patients with antibodies to the ACH receptor has been effective in relieving postural hypotension (Bourcier and Vinik, 2010). Antioxidant therapy with alpha lipoic acid restores autonomic function toward normal (Ziegler et al., 2011). More recently interest in the selective muscarinic acetylcholine receptor has been shown to suppress innate immune responses in the periphery by increasing the firing rate of action potential in the vagus (Pavlov et al., 2007). To quote “The end products of a search for agents with which to restore balance will be a map of the homunculus of sensory and motor components corresponding to neuroanatomical and functional neurophysiologic pathways linking the autonomic and inflammatory pathways and their response to endogenous as well as exogenous stressors of the system.” While Kurt Vonnegut had insights in Breakfast of Champions in 1973 it is only now that this link is gaining recognition for the havoc it wreaks and the potential for avoidance and therapeutic intervention. Of great interest are the abnormalities in the diurnal regulation of dopaminergic tone. In type 2 diabetes a reduction in dopaminergic tone in the early morning results in increased hepatic gluconeogenesis, a rise in circulating free fatty acids, resistance to the action of insulin, increases in markers of inflammation and hypercoagulation, all of which can be restored toward normality by treatment with a dopaminergic agonist (Scranton et al., 2007) which reverses the metabolic abnormalities simply by enhancing parasympathetic dominance. There are simple maneuvers to improve HRV as shown by Motooka et al. (2006). Little old ladies walking the dog have enhanced parasympathetic function. Removing the dog is enough to incite sympathetic overactivity. We have shown that balance can be adjusted with agents that act on one or other arm of the autonomic nervous system (Vinik et al., 2011; Figure 7)
Figure 7.
Restoration of autonomic balance.
Gaede in the Steno memorial study (Gaede et al., 1999, 2008) showed that a multifactorial intervention controlling BP, lipids, and hyperglycemia reduces abnormalities in autonomic function by 68%, and Ziegler et al. (1997) report that alpha lipoic acid improves autonomic function. In fact, it is one of the only drugs targeting the nervous system to be endorsed by the Toronto consensus (Tesfaye et al., 2010). In contrast failure to identify loss of parasympathetic integrity is accompanied by dire consequences as witnessed by the 22% increase in sudden death in the ACCORD study with intensification of therapy (Calles-Escandon et al., 2010; Pop-Busui et al., 2010). Clearly this is discord rather than accord.
Conclusion
There is now strong evidence of inflammation with activation of inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6 and leptin in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes. These changes correlate with abnormalities in sympathetic-vagal balance. Autonomic dysfunction has been shown to be a predictor of cardiovascular risk and sudden death in patients with type 2 diabetes. A better understanding of the autonomic dysfunction and adipose tissue inflammation seen early in the development of diabetes will lead to further measures for determining which individuals are at the highest risk for CVD and mortality, and will also lead to the development of new therapies for reducing that risk. Activation of the efferent arm of the reflex arc (through the administration of an acetylcholine receptor agonist) causes a decrease in pro-inflammatory cytokine production, and a reduction in disease severity (Bernik et al., 2002; Van Maanen et al., 2009). In his review Tracey (2009) points out a number of important clinical studies that show correlations between vagal nerve activity and inflammatory human diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus. Our results are in keeping with this research, and suggest that such a reflex arc may be involved in the inflammation seen early in T2D. However, our studies implicate the hypothalamus as the conductor of the endocrine orchestra and show that the earliest changes that are detectable in the evolution of diabetes are abnormalities in autonomic balance (Figure 5). It is not beyond the realms of reason that we could reverse the unfortunate evolutionary profile by targeting the hypothalamic set point of autonomic balance.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Akselrod S., Gordon D., Ubel F. A., Shannon D. C., Berger A. C., Cohen R. J. (1981). Power spectrum analysis of heart rate fluctuation: a quantitative probe of beat-to-beat cardiovascular control. Science 213, 220–222 10.1126/science.6166045 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anandacoomaraswamy D., Ullal J., Vinik A. I. (2008). A 70-year-old male with peripheral neuropathy, ataxia and antigliadin antibodies shows improvement, but not ataxia, after intravenous immunoglobin and gluten-free diet. J. Multidiscip. Healthc. 1, 93–96 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beijers H. J., Ferreira I., Bravenboer B., Dekker J. M., Nijpels G., Heine R. J., Stehouwer C. D. (2009). Microalbuminuria and cardiovascular autonomic dysfunction are independently associated with cardiovascular mortality: evidence for distinct pathways: the Hoorn Study. Diabetes Care 32, 1698–1703 10.2337/dc08-1544 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernik T. R., Friedman S. G., Ochani M., DiRaimo R., Ulloa L., Yang H., Sudan S., Czura C. J., Ivanova S. M., Tracey K. J. (2002). Pharmacological stimulation of the cholinergic antiinflammatory pathway. J. Exp. Med. 195, 781–788 10.1084/jem.20011714 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borovikova L. V., Ivanova S., Zhang M., Yang H., Botchkina G. I., Watkins L. R., Wang H., Abumrad N., Eaton J. W., Tracey K. J. (2000). Vagus nerve stimulation attenuates the systemic inflammatory response to endotoxin. Nature 405, 458–462 10.1038/35013070 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourcier M. E., Vinik A. I. (2010). Case 1: a novel treatment for pain in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Pain Medicine News 78–80 Available at: www.painmedicinenews.com [Google Scholar]
- Calles-Escandon J., Lovato L., Simons-Morton D., Kendall D., Pop-Busui R., Cohen R., Bonds D., Fonseca V., Ismail-Beigi F., Banerji M., Failor A., Hamilton B. (2010). Effect of intensive compared with standard glycemia treatment strategies on mortality by baseline subgroup characteristics. Diabetes Care 33, 721–727 10.2337/dc09-1471 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DCCT. (1998). The effect of intensive diabetes therapy on measures of autonomic nervous system function in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT). Diabetologia 41, 416–423 10.1007/s001250050924 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DCCT EDIC Research Group. (2005). Intensive diabetes treatment and cardiovascular disease in patients with type 1 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 353, 2643–2653 10.1056/NEJMoa052187 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaede P., Lund-Andersen H., Parving H. H., Pedersen O. (2008). Effect of a multifactorial intervention on mortality in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 358, 580–591 10.1056/NEJMoa0706245 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaede P., Vedel P., Larsen N., Jensen G., Parving H., Pedersen O. (2003). Multifactorial intervention and cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 348, 383–393 10.1056/NEJMoa021778 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaede P., Vedel P., Parving H. H., Pedersen O. (1999). Intensified multifactorial intervention in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and microalbuminuria: the Steno type 2 randomized study. Lancet 353, 617–622 10.1016/S0140-6736(98)07368-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser B., Vinik A. I., Sive A. A., Floyd J. C., Jr. (1980). Plasma human pancreatic polypeptide responses to administered secretin: effects of surgical vagotomy, cholinergic blockade, and chronic pancreatitis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 50, 1094–1099 10.1210/jcem-50-6-1094 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goehler L. E., Relton J. K., Dripps D., Kiechle R., Tartaglia N., Maier S. F., Watkins L. R. (1997). Vagal paraganglia bind biotinylated interleukin-1 receptor antagonist: a possible mechanism for immune-to-brain communication. Brain Res. Bull. 43, 357–364 10.1016/S0361-9230(97)00020-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadase M., Azuma A., Zen K., Asada S., Kawasaki T., Kamitani T., Kawasaki S., Sugihara H., Matsubara H. (2004). Very low frequency power of heart rate variability is a powerful predictor of clinical prognosis in patients with congestive heart failure. Circ. J. 68, 343–347 10.1253/circj.68.343 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handelsman Y., Mechanick J., Blond L., Grunberger G., Bloomgarden Z., Bray G., Dagogo-Jack S., Davidson J. A., Einhorn D., Ganda O., Garber A. J., Hirsch I. B., Horton E. S., Ismail-Beigi F., Jellinger P. S., Jones K. L., Jovanovic L., Lebovitz H., Levy P., Moghissi E. S., Orzeck E. A., Vinik A. I., Wyne K. L., AACE Task Force for Developing Diabetes Comprehensive Care Plan (2011). American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists Medical Guidelines for Clinical Practice for developing a diabetes mellitus comprehensive care plan. Endocr. Pract. 17, 1–53 10.4158/EP10242.CR [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen M. K., O’Connor K. A., Goehler L. E., Watkins L. R., Maier S. F. (2001). The contribution of the vagus nerve in interleukin-1beta-induced fever is dependent on dose. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 280, R929–R934 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson G. K., Libby P. (2006). The immune response in atherosclerosis: a double-edged sword. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 6, 508–519 10.1038/nri1882 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huikuri H. V., Jokinen V., Syvanne M., Nieminen M. S., Airaksinen K. E., Ikaheimo M. J., Koistinen J. M., Kauma H., Kesaniemi A. Y., Majahalme S., Niemelä K. O., Frick M. H. (1999). Heart rate variability and progression of coronary atherosclerosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 19, 1979–1985 10.1161/01.ATV.19.8.1979 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huston J. M., Ochani M., Rosas-Ballina M., Liao H., Ochani K., Pavlov V. A., Gallowitsch-Puerta M., Ashok M., Czura C. J., Foxwell B., Tracey K. J., Ulloa L. (2006). Splenectomy inactivates the cholinergic antiinflammatory pathway during lethal endotoxemia and polymicrobial sepsis. J. Exp. Med. 203, 1623–1628 10.1084/jem.20052362 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janszky I., Ericson M., Mittleman M. A., Wamala S., Al-Khalili F., Schenck-Gustafsson K., Orth-Gomer K. (2004). Heart rate variability in long-term risk assessment in middle-aged women with coronary heart disease: the Stockholm Female Coronary Risk Study. J. Intern. Med. 255, 13–21 10.1046/j.0954-6820.2003.01250.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy W. R., Navarro X., Sutherland D. E. (1995). Neuropathy profile of diabetic patients in a pancreas transplantation program. Neurology 45, 773–780 10.1212/WNL.45.4.773 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Rovere M. T., Pinna G. D., Maestri R., Mortara A., Capomolla S., Febo O., Ferrari R., Franchini M., Gnemmi M., Opasich C., Riccardi P. G., Traversi E., Cobelli F. (2003). Short-term heart rate variability strongly predicts sudden cardiac death in chronic heart failure patients. Circulation 107, 565–570 10.1161/01.CIR.0000047275.25795.17 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieb D., Parson H., Mamikunian G., Vinik A. (2011). Cardiac autonomic imbalance in newly diagnosed and established diabetes is associated with markers of adipose tissue inflammation. Exp. Diabetes Res. 2012, 1–8 10.1155/2012/878760 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low P. A., Caskey P. E., Tuck R. R., Fealey R. D., Dyck P. J. (1983). Quantitative sudomotor axon reflex test in normal and neuropathic subjects. Ann. Neurol. 14, 573–580 10.1002/ana.410140513 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malik M., the Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology (1996). Heart rate variability, standards of measurement, physiological interpretation, and clinical use. Circulation 93, 1043–1065 10.1161/01.CIR.93.5.1043 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maser R. E., Mitchell B. D., Vinik A. I., Freeman R. (2003). The association between cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy and mortality in individuals with diabetes: a meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 26, 1895–1901 10.2337/diacare.26.6.1895 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meerwaldt R., Links T. P., Graaff R., Hoogenberg K., Lefrandt J. D., Baynes J. W., Gans R. O., Smit A. J. (2005). Increased accumulation of skin advanced glycation end-products precedes and correlates with clinical manifestation of diabetic neuropathy. Diabetologia 48, 1637–1644 10.1007/s00125-005-1828-x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison S., Colberg S. R., Mariano M., Parson H. K., Vinik A. I. (2010). Balance training reduces falls risk in older individuals with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 33, 748–750 10.2337/dc09-1699 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motooka M., Koike H., Yokoyama T., Kennedy N. L. (2006). Effect of dog-walking on autonomic nervous activity in senior citizens. Med. J. Aust. 184, 60–63 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orchard T. J., Lloyd C. E., Maser R. E., Kuller L. H. (1996). Why does diabetic autonomic neuropathy predict IDDM mortality? An analysis from the Pittsburgh Epidemiology of Diabetes Complications Study. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 34:S165-S171 10.1016/S0168-8227(96)90025-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paolisso G., Manzella D., Montano N., Gambardella A., Varricchio M. (2000). Plasma leptin concentrations and cardiac autonomic nervous system in healthy subjects with different body weights. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 85, 1810–1814 10.1210/jc.85.1.109 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlov V. A., Ochani M., Yang L. H., Gallowitsch-Puerta M., Ochani K., Lin X., Levi J., Parrish W. R., Rosas-Ballina M., Czura C. J., Larosa G. J., Miller E. J., Tracey K. J., Al-Abed Y. (2007). Selective alpha7-nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist GTS-21 improves survival in murine endotoxemia and severe sepsis. Crit. Care Med. 35, 1139–1144 10.1097/01.CCM.0000259381.56526.96 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittenger G. L., Liu D., Vinik A. I. (1997). The apoptotic death of neuroblastoma cells caused by serum from patients with insulin-dependent diabetes and neuropathy may be Fas-mediated. J. Neuroimmunol. 76, 153–160 10.1016/S0165-5728(97)00042-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pontet J., Contreras P., Curbelo A., Medina J., Noveri S., Bentancourt S., Migliaro E. R. (2003). Heart rate variability as early marker of multiple organ dysfunction syndrome in septic patients. J. Crit. Care 18, 156–163 10.1016/j.jcrc.2003.08.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pop-Busui R., Evans G., Gerstein H., Fonseca V., Fleg J., Hoogwerf B., Genuth S., Grimm R., Corson M., Prineas R., Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes Study Group (2010). Effects of cardiac autonomic dysfunction on mortality risk in the action to control cardiovascular risk in diabetes (ACCORD) trial. Diabetes Care 33, 1578–1584 10.2337/dc10-0125 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razavi R., Chan Y., Afifiyan F. N., Liu X. J., Wan X., Yantha J., Tsui H., Tang L., Tsai S., Santamaria P., Driver J. P., Serreze D., Salter M. W., Dosch H. M. (2006). TRPV1 (sensory neurons control beta cell stress and islet inflammation in autoimmune diabetes. Cell 127, 1123–1135 10.1016/j.cell.2006.10.038 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saeed R. W., Varma S., Peng-Nemeroff T., Sherry B., Balakhaneh D., Huston J., Tracey K. J., Al-Abed Y., Metz C. N. (2005). Cholinergic stimulation blocks endothelial cell activation and leukocyte recruitment during inflammation. J. Exp. Med. 201, 1113–1123 10.1084/jem.20040463 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saravia F., Homo-Delarche F. (2003). Is innervation an early target in autoimmune diabetes? Trends Immunol. 24, 574–579 10.1016/j.it.2003.09.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt A. M., Yan S. D., Yan S. F., Stern D. M. (2001). The multiligand receptor RAGE as a progression factor amplifying immune and inflammatory responses. J. Clin. Invest. 108, 949–955 10.1172/JCI14002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scranton R. E., Gaziano J. M., Rutty D., Ezrokhi M., Cincotta A. (2007). A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial to assess safety and tolerability during treatment of type 2 diabetes with usual diabetes therapy and either Cycloset or placebo. BMC Endocr. Disord. 7, 3 10.1186/1472-6823-7-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spallone V., Ziegler D., Freeman R., Bernardi L., Frontoni S., Pop-Busui R., Stevens M., Kempler P., Hilsted J., Tesfaye S., Low P., Valensi P., On Behalf of the Toronto Consensus Panel on Diabetic Neuropathy (2011). Cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy in diabetes: clinical impact, assessment, diagnosis, and management. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 10.1002/dmrr.1239 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takuma K., Fang F., Zhang W., Yan S., Fukuzaki E., Du H., Sosunov A., McKhann G., Funatsu Y., Nakamichi N., Nagai T., Mizoguchi H., Ibi D., Hori O., Ogawa S., Stern D. M., Yamada K., Yan S. S. (2009). RAGE-mediated signaling contributes to intraneuronal transport of amyloid-beta and neuronal dysfunction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 106, 20021–20026 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tesfaye S., Boulton A. J., Dyck P. J., Freeman R., Horowitz M., Kempler P., Lauria G., Malik R. A., Spallone V., Vinik A., Bernardi L., Valensi P., Toronto Diabetic Neuropathy Expert Group (2010). Diabetic neuropathies: update on definitions, diagnostic criteria, estimation of severity, and treatments. Diabetes Care 33, 2285–2293 10.2337/dc10-1303 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thayer J. F., Fischer J. E. (2009). Heart rate variability, overnight urinary norepinephrine and C-reactive protein: evidence for the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway in healthy human adults. J. Intern. Med. 265, 439–447 10.1111/j.1365-2796.2008.02023.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thayer J. F., Sternberg E. (2006). Beyond heart rate variability: vagal regulation of allostatic systems. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1088, 361–372 10.1196/annals.1366.014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toth C., Rong L. L., Yang C., Martinez J., Song F., Ramji N., Brussee V., Liu W., Durand J., Nguyen M. D., Schmidt A. M., Zochodne D. W. (2008). Receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGEs) and experimental diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes 57, 1002–1017 10.2337/db07-0339 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J. (2009). Reflex control of immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 9, 418–428 10.1038/nri2566 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Maanen M. A., Vervoordeldonk M. J., Tak P. P. (2009). The cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway: towards innovative treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 5, 229–232 10.1038/nrrheum.2009.31 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinik A., Kles K. (2006). Pathophysiology and treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathy: the case for diabetic neurovascular function as an essential component. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2, 131–145 10.2174/157339906776818569 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinik A., Maser R., Ziegler D. (2011). Autonomic imbalance: prophet of doom or scope for hope? Diabetic Med. 28, 643–651 10.1111/j.1464-5491.2010.03184.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinik A., Parson H., Ullal J. (2006a). The role of PPARs in the microvascular dysfunction in diabetes. Vascul. Pharmacol. 45, 54–64 10.1016/j.vph.2006.08.143 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinik A., Ullal J., Parson H. K., Casellini C. M. (2006b). Diabetic neuropathies: clinical manifestations and current treatment options. Nat. Clin. Pract. Endocrinol. Metab. 2, 269–281 10.1038/ncpendmet0142 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinik A. I., Erbas T. (2006). Cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy: diagnosis and management. Curr. Diab. Rep. 6, 424–430 10.1007/s11892-006-0074-z [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinik A. I., Maser R. E., Ziegler D. (2010). Neuropathy: the crystal ball for cardiovascular disease? Diabetes Care 33, 1688–1690 10.2337/dc10-0745 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinik A. I., Ziegler D. (2007). Diabetic cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy. Circulation 115, 387–397 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.634949 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Kanel R., Nelesen R. A., Mills P. J., Ziegler M. G., Dimsdale J. E. (2008). Relationship between heart rate variability, interleukin-6, and soluble tissue factor in healthy subjects. Brain Behav. Immun. 22, 461–468 10.1016/j.bbi.2007.09.009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakabayashi S., Aso Y. (2004). Adiponectin concentrations in sera from patients with type 2 diabetes are negatively associated with sympathovagal balance as evaluated by power spectral analysis of heart rate variation. Diabetes Care 27, 2392–2397 10.2337/diacare.27.10.2392 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins L. R., Goehler L. E., Relton J. K., Tartaglia N., Silbert L., Martin D., Maier S. F. (1995). Blockade of interleukin-1 induced hyperthermia by subdiaphragmatic vagotomy: evidence for vagal mediation of immune-brain communication. Neurosci. Lett. 183, 27–31 10.1016/0304-3940(94)11105-R [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wess J., Eglen R. M., Gautam D. (2007). Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors: mutant mice provide new insights for drug development. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 6, 721–733 10.1038/nrd2379 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witzke K., Vinik A., Grant L., Parson H., Pittenger G. (2011). Loss of RAGE defense: a cause of Charcot neuroarthropathy? Diabetes Care 34, 1617–1621 10.2337/dc10-2315 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. S., Yang Y. C., Lin T. S., Huang Y. H., Chen J. J., Lu F. H., Wu C. H., Chang C. J. (2007). Epidemiological evidence of altered cardiac autonomic function in subjects with impaired glucose tolerance but not isolated impaired fasting glucose. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 92, 3885–3889 10.1210/jc.2006-2175 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler D., Hanefeld M., Ruhnau K. J., Meissner H. P., Lobisch M., Schutte K., Gries F. A. (1995). Treatment of symptomatic diabetic peripheral neuropathy with the anti-oxidant alpha-lipoic acid. A 3-week multicentre randomized controlled trial (ALADIN Study). Diabetologia 38, 1425–1433 10.1007/BF00400603 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler D., Low P. A., Boulton A. J. M. (2011). Antioxidant treatment with alpha-lipoic acid in diabetic polyneuropathy: a 4-year randomized double-blind trial (NATHAN 1). Diabetologia 50, S63 [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler D., Schatz H., Conrad F., Gries F. A., Ulrich H., Reichel G. (1997). Effects of treatment with the antioxidant alpha-lipoic acid on cardiac autonomic neuropathy in NIDDM patients. A 4-month randomized controlled multicenter trial (DEKAN Study). Deutsche Kardiale Autonome Neuropathie. Diabetes Care 20, 369–373 10.2337/diacare.20.3.369 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler D., Zentai C. P., Perz S., Rathmann W., Haastert B., Doring A., Meisinger C. (2008). Prediction of mortality using measures of cardiac autonomic dysfunction in the diabetic and nondiabetic population: the MONICA/KORA Augsburg Cohort Study. Diabetes Care 31, 556–561 10.2337/dc08-1136 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]