SUMMARY
The mechanism of action of Salmonella enterotoxin (Stn) as a virulence factor in disease is controversial. Studies of Stn have indicated both positive and negative effects on Salmonella virulence. In this study, we attempted to evaluate Stn function and its effects on Salmonella virulence. To investigate Stn function, we first performed in vitro and in vivo analysis using mammalian cells and a murine ileal loop model. In these systems, we did not observe differences in virulence phenotypes between wild-type Salmonella and an stn gene-deleted mutant. We next characterized the phenotypes and molecular properties of the mutant strain under various in vitro conditions. The proteomic profiles of the total cell membrane protein fraction differed between wild type and mutant in that there was an absence of a protein in the mutant strain, which was identified as OmpA. By far-western blotting, OmpA was found to interact directly with Stn. To verify this result, the morphology of Salmonella was examined by transmission electron microscopy, with OmpA localization being analyzed by immunogold labeling. Compared with wild-type Salmonella, the mutant strain had a different pole structure and a thin periplasmic space; OmpA was not seen in the mutant. These results indicate that Stn, via regulation of OmpA membrane localization, functions in the maintenance of membrane composition and integrity.
INTRODUCTION
Salmonella is a food-borne pathogen that is typically acquired through consumption of contaminated food and water. This bacterium causes severe clinical manifestations, including acute gastroenteritis and typhoid fever (Boyle et al., 2007). Many studies have shown that type III secretion systems, which are encoded within pathogenicity island 1 and 2 (SPI-1 and SPI-2, respectively), are important for the virulence of this organism. These secretion systems are involved in invasion of intestinal epithelial cells and Salmonella survival in macrophages (Grassl and Finlay, 2008).
It has been proposed that Salmonella enterotoxin (Stn) is a putative virulence factor and causative agent of diarrhea (Chopra et al., 1994; Chopra et al., 1999). Interestingly, it has been shown that the stn gene is specifically distributed in Salmonella spp. irrespective of their serotypes (Dinjus et al., 1997; Makino et al., 1999; Moore et al., 2007; Lee et al., 2009). This second finding indicates that the stn gene might be useful for the identification or detection of Salmonella and that Stn might be involved in functions unique to Salmonella. Chopra et al. cloned the stn gene and showed that it had an enterotoxic activity in a murine ileal loop model (Chopra et al., 1999). Therefore, they proposed that Stn is a Salmonella virulence factor and is responsible for the enterotoxicity of Salmonella. However, research by other groups did not support this conclusion (Lindgren et al., 1996; Watson et al., 1998; Wallis et al., 1999) and did not show an association of Stn with Salmonella virulence. These investigations did not detect differences of virulence phenotypes between wild-type and an stn gene-deleted (Δstn) mutant. Thus, the role of Stn in Salmonella virulence is still debated.
In this study, we examined the relationship between Stn and Salmonella virulence using the Δstn mutant strain in in vitro and in vivo models. Our studies reveal new insights into Stn function in Salmonella, suggesting that Stn is involved in the maintenance of membrane composition and integrity.
RESULTS
Role of Stn for the virulence of Salmonella
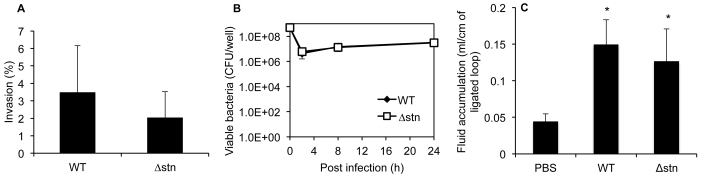
To determine whether Stn contributes to Salmonella virulence, we examined Salmonella virulence in vitro and in vivo using wild-type and Δstn mutant Salmonella. We did not observe statistically significant differences in invasion ability or intramacrophage survival between wild-type Salmonella and the Δstn mutant (Fig. 1A,B). Because Chopra et al. showed that Stn exhibits enterotoxic activity in a murine ileal loop model (Chopra et al., 1999), we next investigated the activity of the Δstn mutant in that system. The mutant strain still induced fluid accumulation in the ligated murine ileal loop compared with the control loop and behaved in the same manner as a wild-type strain (Fig. 1C).
Fig. 1.
Roles of Stn in Salmonella virulence. (A) Invasion assay using HeLa cells. Invasion assay was performed at 37°C, 5% CO2 for 1 hour at MOI=10. (B) Survival assay using human macrophages. Differentiated U937 cells were infected at MOI=10 for 10 minutes. Data are means ± s.d. of three independent experiments with assays in duplicate. (C) Enterotoxicity of Salmonella strains. Fluid accumulation was measured as the amount of fluid content (in ml) per length (in cm) of ligated murine intestinal loop. PBS was used as the control reaction of this experiment. The results are mean ± s.d. values in five experimental animals. Statistical significance was set at P<0.05 (*, vs PBS). WT, wild-type strain.
To investigate the effect of Stn on chemokine transcriptional levels (i.e. RANTES, GM-CSF, MCP-3, CXCL1 CXCL2, CXCL3) in infected HeLa cells, real-time PCR analysis was performed. HeLa cells showed statistically significant differences, with reduction of RANTES, MCP-3, CXCL2 and CXCL3 expression, but these decreases were under twofold (supplementary material Fig. S1). From these results, we estimate that Stn modulated chemokine production. Taken together, these results indicate that Stn is not associated with the virulence of Salmonella (i.e. invasion in the host cells, survival in macrophages, enterotoxicity), but that Stn does affect chemokine release.
Characterization of the Δstn mutant to estimate the function of Stn
To evaluate Stn function, we characterized the phenotypes of the Δstn mutant, including growth under different culture conditions (e.g. pH, temperature, growth in the presence of acid or H2O2), motility on a soft agar and antibiotic resistance. No difference was found between these strains (data not shown).
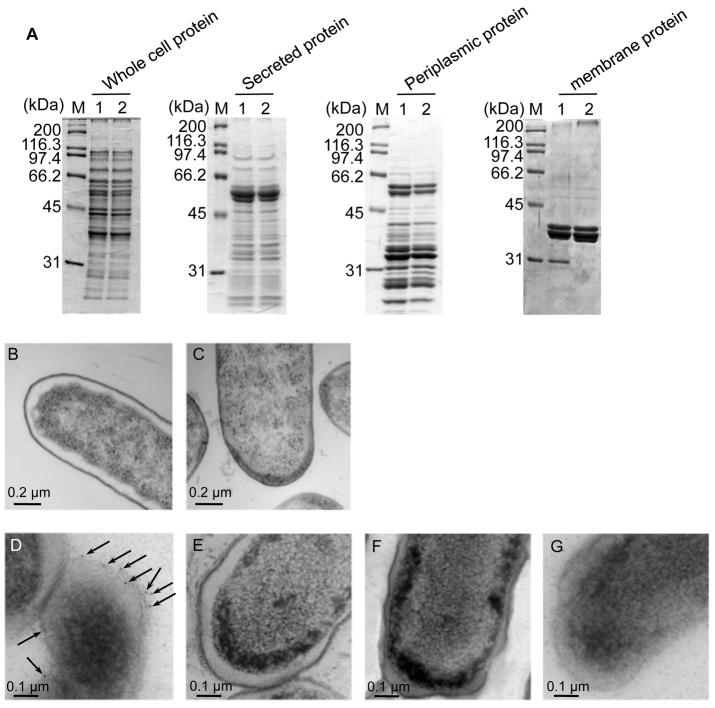
We next analyzed the Salmonella membrane protein fraction by SDS-PAGE. A protein signal was missing in the Δstn fraction and this missing protein was identified as the outer membrane protein A (OmpA) (Fig. 2A). To determine whether Stn regulates the expression of ompA, we quantified ompA mRNA at mid-log phase by real-time PCR. The transcriptional level of ompA in the Δstn mutant was almost the same as in wild type (Fig. 3). In addition, we also did not observe statistically significant differences in the transcription of another four membrane protein genes (ompC, lpp, lamB and ompW) between wild type and the Δstn mutant (Fig. 3). These results indicate that Stn does not affect expression of membrane protein genes, including ompA, and that OmpA localization or levels in the Δstn mutant might differ compared with that of the wild-type strain.
Fig. 2.
Regulation of OmpA localization by Stn. (A) SDS-PAGE of prepared protein fractions. Proteins were loaded on 10% gel in each lane as follows: 10 μg of whole cell protein fraction, 5 μg of secreted protein fraction, 10 μg of periplasmic protein fraction and 5 μg of total membrane protein fraction. Gel was stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue R-250. M, protein marker; lane 1, wild type; lane 2, Δstn. (B,C) Transmission electron microscopic image of wild-type (B) and Δstn mutant (C) cells in ultrathin sections (magnification: 12,000×). Bacteria were cultured in LB medium at 37°C for 16 hours. (D–G) Immunogold labeling of OmpA using anti-OmpA antibody (magnification: 20,000×). Bacteria were cultured on LB agar plates at 37°C for 16 hours. D, wild-type strain; E, Δstn; F, ΔompA; G, wild type using normal mouse serum for control reaction. Arrows indicate the gold particles.
Fig. 3.
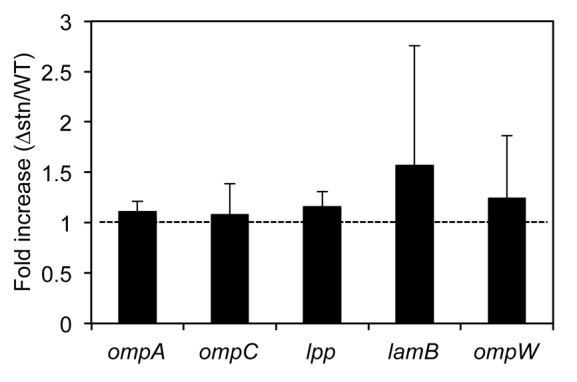
Quantification of mRNA levels associated with the membrane protein genes in Salmonella. Bacteria were cultured in LB medium until mid-log phase (OD600=0.8). Fold change in the mRNA levels from the Δstn versus the parent strain was measured by quantitative real-time PCR. mRNA levels were normalized to 16S rRNA levels. Data are expressed as means ± s.d. values of five independent experiments.
OmpA is a major outer membrane protein of Gram-negative bacteria, including Salmonella, and is associated with many cellular functions (Chai and Foulds, 1997). We next investigated the membrane of Salmonella strains by electron microscopy. Indeed, we found that the Δstn mutant had a different pole structure from a wild-type strain. The Δstn strain also had a very thin periplasmic space compared with a wild-type strain (Fig. 2B,C). From these results, we concluded that Stn might regulate membrane integrity by its interaction with OmpA. We next analyzed OmpA localization by immunogold staining using anti-OmpA antibody. In wild-type strains, we detected OmpA signals in the membrane region, whereas the Δstn mutant did not show evidence of the protein (Fig. 2D,E). To verify this result, we also constructed the ompA gene-deleted mutant (ΔompA) and carried out the immunogold staining analysis. As expected, we could not find signals in the ΔompA mutant (Fig. 2F). These results indicate that Stn affects OmpA localization in the membrane region.
Stn interacts with OmpA
As shown in Fig. 2, lack of Stn affects membrane integrity and the localization of OmpA in the outer membrane. From these results, we hypothesized that Stn might interact with OmpA directly to control the localization of OmpA in the outer membrane of Salmonella. To test the hypothesis that OmpA interacts with purified recombinant Stn (named TF-Stn), we carried out far-western blotting. Using purified recombinant OmpA and TF-Stn proteins, we found that membrane OmpA interacted with soluble TF-Stn, which was used as a probe (Fig. 4B). By contrast, a control reaction using TF-tag did not generate a specific signal with OmpA (Fig. 4A). Thus, this result suggests that Stn interacts with OmpA directly, and that it might facilitate the proper localization of OmpA in the organism.
Fig. 4.
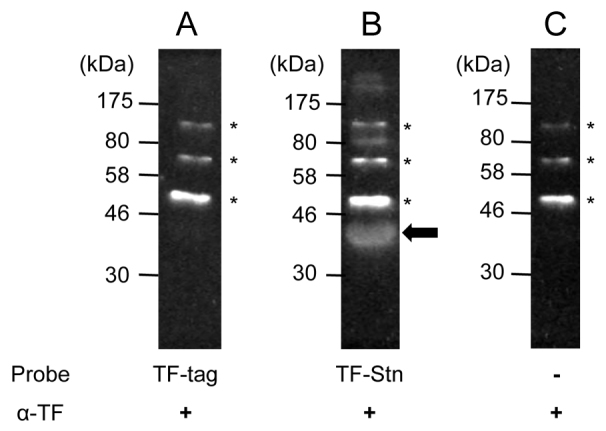
Interaction between Stn and OmpA. OmpA (1 μg/reaction) was separated by SDS-PAGE and transferred to PVDF membranes, which were soaked in the presence of purified TF-tag (10 μg; A) or purified TF-Stn (10 μg; B), and also in the absence of probe (C) at 4°C for 16 hours. Interaction of TF-Stn and OmpA was detected with anti-TF antibody. Asterisks indicate the non-specific signals with anti-TF antibody and arrow is the specific signal that formed as a result of the OmpA-Stn complex. Panel C was performed as a control reaction for the verification of antibody quality. TF, trigger factor-tag used as a negative control.
DISCUSSION
Although it has been reported that Salmonella produces an agent responsible for enterotoxic activity, little information concerning this factor is available (Finkelstein et al., 1983; Molina and Peterson, 1980). That factor has not been identified thus far. Chopra et al. have shown that Stn from Salmonella typhimurium strain Q1 exhibits enterotoxic and cytotoxic activities (Chopra et al., 1999). Furthermore, they also noted that the deduced amino acid sequence of Stn (amino acid residues 127–142) shows some similarity to the active site of cholera toxin (CT) and heat-labile enterotoxin (LT) ADP-ribosyltransferases (Chopra et al., 1994). Therefore, they proposed that Stn could be a key factor in acute gastroenteritis and diarrhea and could contribute to Salmonella virulence. However, other research groups reported that Stn is not associated with Salmonella virulence, e.g. enterotoxicity, cytotoxic activity (Lindgren et al., 1996; Watson et al., 1998; Wallis et al., 1999). As mentioned above, the functions of Stn are still debated, but it is interesting to note that the stn gene is distributed only in Salmonella species (Dinjus et al., 1997; Makino et al., 1999; Moore and Feist, 2007; Lee et al., 2009). From this point of view, it is possible that Stn might play a role in unique or special functions of Salmonella. We therefore proposed that biological activities of Stn are important to Salmonella virulence, especially acute gastroenteritis.
In this study, we examined the functions of Stn using the Δstn mutant to verify whether Stn is involved in Salmonella virulence. As shown in Fig. 1, we could not find any differences of virulence phenotypes between the wild type and Δstn. In addition, we could not detect the R-S-EXE triad motif, which is essential for the ADP-ribosyltransferase of CT and LT (Harford et al., 1989; Laing et al., 2011), in the deduced amino acid sequence of Stn (Fig. 5). On the basis of these data, we think that Stn is not an ADP-ribosyltransferase and does not function as a virulence factor of Salmonella.
Fig. 5.
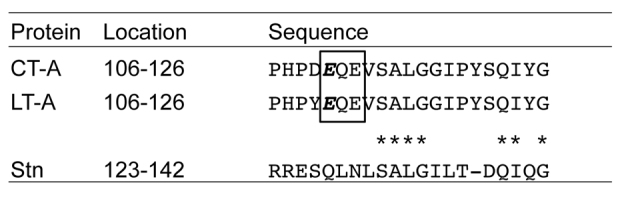
Sequence alignment of partial Stn and each of the A subunits of CT and LT. Amino acid sequences of Stn, CT (CT-A) and LT (LT-A) were derived from S. typhimurium strain Q1, Vibrio cholerae El Tor strain N16961, and enterotoxigenic E. coli strain H10407, respectively (Chopra et al., 1994; Heidelberg et al., 2000; Crossman et al., 2010). Asterisks represent the identical amino acid residues in Stn compared with those of CT and LT. Box and italic letters indicate the conserved motif and catalytic amino acid for ADP-ribosyltransferase of CT and LT (Laing et al., 2011).
Previous studies concerning Stn function have been focused on its effect in infected host cells (Chopra et al., 1994; Chopra et al., 1999). By contrast, in this study, we investigated unknown functions of Stn in Salmonella. We attempted to estimate the functions of Stn from its deduced amino acid sequence. It is noteworthy that Stn protein has no homology with other proteins (data not shown). We characterized the Δstn mutant and showed that Stn might affect membrane integrity via regulation of OmpA localization. OmpA is generally synthesized in the cytoplasm in a precursor form with a signal sequence and is translocated into the periplasmic space or outer membrane. Previous studies have indicated that the requirements for translocation of OmpA include the signal sequence and correct protein conformation (Freudl et al., 1985; Freudl et al., 1990). It has been speculated that Stn is located in the cytoplasm, because Stn lacks a typical signal sequence and transmembrane region. Thus, we hypothesize that interaction between Stn and OmpA contributes to the conservation of OmpA protein conformation and might facilitate OmpA translocation into the outer membrane. It is noteworthy that Stn is predicted to be a highly basic protein [isoelectric point (pI) is over 11], whereas OmpA in Salmonella is predicted to be a slightly acidic protein (pI 5.6). Consequently, charge difference might contribute to the interaction between Stn and OmpA. Further detailed studies on the interaction between Stn and OmpA are needed to verify the function of this proposed complex.
Our observations give new insight into Stn function in bacterial cells. Stn might participate in the maintenance or membrane integrity of this bacterium. We are currently underway analyzing the detailed molecular mechanisms by which Stn regulates membrane integrity.
METHODS
Bacteria
Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis strain 171, a clinical isolate from Thailand, was used as a standard strain in this study. Bacteria were routinely cultured in Luria-Bertani (LB) medium at 37°C.
Construction of deletion mutants
Deletion mutant strains were constructed as described previously (Kodama et al., 2002). In brief, a DNA fragment of the stn gene was generated by PCR using primers stn-1 (5′-GGATCCGATTGAGCGCTTTAATCTCC-3′) and stn-4 (5′-CTGCAGATCACTCATAGCAACCCTGG-3′) after the preparation of PCR products using primers stn-1 and stn-2 (5′-ATCAGCGTTATCAGCATTGAGGGTAAAGGC-3′), and stn-3 (5′-GCCTTTACCCTCAATGCTGATAACGCTGAT-3′) and stn-4, respectively. A DNA fragment of the ompA gene was amplified by PCR using primers omp-1 (5′-CTGCAGAGTTTCCAACTACGTTGTAG-3′) and omp-4 (5′-GCATGCATGCCACGCAAATGACCACG-3′) after the preparation of PCR products using primers omp-1 and omp-2 (5′-AACTTCGATCTCTACAGCGTACCAGGTGTT-3′), and omp-3 (5′-AACACCTGGTACGCTGTAGAGATCGAAGTT-3′) and omp-4, respectively. The PCR products generated using primers stn-1 and stn-4, and omp-1 and omp-4, were cloned into the suicide vector pYAK1, and cloned plasmid was transfected into Escherichia coli strain SM10λpir. After conjugation and disruption by homologous recombination, candidates were confirmed by PCR using primers stn-1 and stn-4 or omp-1 and omp-4, respectively. Resulting mutant strains for the stn and ompA genes were named Δstn and ΔompA, respectively.
Preparation of recombinant proteins
The stn gene was amplified by PCR using primers stn-F (5′-GGATCCTTGTTAATCCTGTTGTCTCG-3′) and stn-R (5′-GTCGACTTACTGGCGTTTTTTTGGCA-3′). PCR product was cloned into pCold TF (TaKaRa Bio) and the plasmid construct was transfected into E. coli BL21(DE3). Recombinant Stn was expressed in LB medium supplemented with 50 μg/ml ampicillin and 1% glucose at 30°C; 0.5 mM isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) was added to induced toxin expression. A fusion protein was generated with the trigger factor (TF)-tag sequence at the N-terminus of Stn (named TF-Stn).
The ompA gene was amplified by PCR using primers omp-F (5′-CGCATGCGCTCCGAAAGATAACAC-3′) and omp-R (5′-TAAGCTTTTAAGCCTGCGGCTGAGTTAC-3′). PCR product was cloned into pQE30 (QIAGEN) and the plasmid construct was transfected into E. coli M15[pREP4]. Recombinant OmpA was expressed in LB medium, supplemented with 100 μg/ml ampicillin, 25 μg/ml kanamycin and 1% glucose at 25°C, by addition of 1 mM IPTG.
Recombinant proteins were purified by Ni Sepharose 6 Fast Flow (GE Healthcare), according to the manufacturer’s instructions, under non-denatured (for Stn) and denatured (for OmpA) conditions, with or without 4M urea, respectively.
Preparation of protein fractions
To perform the protein profiles of Δstn cells, we prepared four different protein fractions as follows. To prepare the whole cell protein fraction, bacteria were cultured in LB medium at 37°C for 16 hours with shaking. After washing the bacteria once with PBS and resuspension in 1× loading buffer (10% glycerol, 62.5 mM Tris-HCl, pH 6.8, 2% sodium dodecyl sulfate, 0.01 mg/ml bromophenol blue, 5% β-mercaptoethanol), bacterial cells were disrupted by heat for 10 minutes and insoluble proteins were removed by centrifugation at 20,000 g, 4°C for 10 minutes. To prepare the secreted protein fraction, bacteria were cultured in LB medium at 37°C for 20 hours and proteins were precipitated from the supernatant using trichloroacetic acid (final concentration: 5%) at 4°C for 16 hours followed by centrifugation for 1 hour at 20,000 g, 4°C. Pellet was washed twice with ice-cold acetone and neutralized with 1 M Tris-HCl (pH 8.0). The periplasmic protein fraction and membrane protein fraction were prepared as previously described (Sittka et al., 2007).
The concentration of each protein fraction was calculated using a Pierce 660 nm Protein Assay Kit with Ionic Detergent Compatibility Reagent (Thermo Scientific).
Amino acid sequence analysis
Proteins (10 μg/lane) were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE and a target protein was excised from the gel. Amino acid sequence was determined by an Agilent 1100 LC/MSD Trap XCT (Agilent Technologies). Protein identification was performed using the Spectrum Mill MS Proteomics Workbench, with a Swiss-Prot protein database search (Ichihara et al., 2006).
Far-western blotting
Interaction between Stn and OmpA was analyzed by far-western blotting (Nambu and Kutsukake, 2000). OmpA (1 μg) was loaded on 10% SDS-PAGE and transferred onto a polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membrane (Millipore). Binding of TF-Stn (10 μg) was performed in TBST buffer (10 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 0.15 M NaCl, 0.5% Tween 20) containing 5% skim milk for 16 hours at 4°C. Signals were generated using anti-TF antibody (TaKaRa Bio) and anti-mouse IgG antibody (Zymed) with ECL Western Blotting Detection Reagents (GE Healthcare), and visualized by LAS-1000 (Fujifilm).
Invasion assay
Invasion assays were performed as previously reported (Sittka et al., 2007). HeLa cells (5×105 cells/well in a 12-well plate) were cultured at 37°C under 5% CO2 for 18 hours in modified Eagle’s medium (Sigma-Aldrich) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS; Nichirei Biosciences), 2 mM glutamine. Bacteria were added at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 10 and centrifuged at 300 g for 10 minutes to synchronize the infection, followed by incubation at 37°C for 1 hour. After infection, cells were washed with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS; pH 7.4) and incubated further for 1 hour at 37°C with 100 μg/ml gentamicin. Invaded bacteria were counted on LB agar plates.
Survival assay
Survival assays were performed as described previously (Schwan et al., 2000; Ge et al., 2010). In brief, differentiation of U937 cells (5×105 cells/well) was induced in RPMI-1640 medium (Sigma-Aldrich) supplemented with 10% FBS, 100 μg/ml of gentamicin and 10 nM phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (Merck) for 18 hours. Medium was then replaced with fresh RPMI-1640 medium, supplemented with 10% FBS. Before use, medium was replaced again with fresh culture medium and incubation continued at 37°C, 5% CO2 for 1 hour. Bacteria were added at an MOI of 10 and incubation continued at 37°C for 10 minutes. After incubation, cells were washed with PBS and incubated at 37°C, 5% CO2 until 2 hours post infection with 100 μg/ml gentamicin. At 2 hours post infection, medium was replaced with fresh culture medium containing 10 μg/ml gentamicin, and incubation continued until 8 or 24 hours post infection. Infected cells were washed with PBS and lysed with PBS containing 0.1% Triton X-100. Viable bacteria were counted on LB agar plates.
Electron microscopy and immunostaining of OmpA
Salmonella morphology was examined by transmission electron microscopy. Bacteria were cultured in LB medium at 37°C for 16 hours and collected by centrifugation (300 g, 10 minutes). Bacteria were fixed in 2% glutaraldehyde buffer (pH 7.4) containing 0.02 M sodium cacodylate, 0.6% NaCl and 0.02% ruthenium red. After fixation in 1.5% osmium tetroxide containing 0.02 M sodium cacodylate and 0.6% NaCl, bacterial cells were dehydrated in ethanol and were saturated with Quetol 653. The sections were prepared by Ultra microtone (Leica Microsystems) and stained with uranyl acetate and citrate.
Immunogold labeling was performed as previously described (Ichinose et al., 2011). In brief, bacteria were cultured on an LB agar plate at 37°C for 16 hours and fixed using 0.2% glutaraldehyde at −80°C. After dehydration, samples were saturated with LR-GOLD resin (Nissin EM) and segments were treated with murine anti-OmpA antibody. Signals were detected using a colloid gold particle conjugated to anti-mouse IgG (10 nm diameter of conjugated gold; BB International).
All specimens for transmission electron microscopy were examined with a JEM-1230 electron microscope (JEOL).
Assay for Salmonella enterotoxicity
Salmonella enterotoxicity assays were performed as described previously, with some modifications (Chopra et al., 1999; Kajikawa et al., 2010). In brief, bacteria were cultured in LB medium at 37°C for 16 hours and washed once with PBS. Prepared bacteria [ca. 1×109 colony forming units (CFU)/loop] were injected into ligated murine ileal loops (C57BL/6 mouse, female, 7-weeks old). At 4 hours after injection, the fluid content of each loop was measured. Activity was expressed as the ratio of the fluid content of the loop (in ml) to its length (in cm).
RNA isolation and quantitative real-time PCR
Total RNA was extracted from infected HeLa cells using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen) and contaminated genomic DNA was removed by DNase I (TaKaRa Bio). cDNA was generated from 1 μg of total RNA using the PrimeScript RT reagent kit and Oligo dT primer (TaKaRa Bio) in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions. The primer sequences for chemokine genes used in this study were described previously (Okuda et al., 2005; Abdallah et al., 2007; Huang et al., 2007; Okuda et al., 2009; Nishihara et al., 2010). The expression levels of each gene were normalized, with GAPDH as an internal control.
Bacteria were cultured in LB medium at 37°C until mid-log phase (OD600=0.8) and total RNA was extracted using TRIzol reagent. cDNA was generated from 1 μg of total RNA using the PrimeScript RT reagent kit and random hexamers (TaKaRa Bio). The primer sequences for membrane protein genes were as follows: ompA (5′-TCCGGAAGTACAGCCAAGC-3′ and 5′-ACCGATACGGTCAGTGAAGC-3′), ompC (5′-ATCAGATTCAGGGCAACCAG-3′ and 5′-TACCACGCTGCTGCATAAAG-3′), lpp (5′-TCTACTCTGCTGGCTGGTTG-3′ and 5′-GTAGCCTGGTTGTCCAGACG-3′), lamB (5′-ACACCTTCAGCAGCCAGAATA-3′ and 5′-GTGAACATCCAGCCGTCTTTC-3′) and ompW (5′-TTACATGGCGACGGACAATA-3′ and 5′-GTTGGCGGTAACAGGTGAAC-3′). All primers were designed from genome sequence of Salmonella enteritidis strain P125109 (Thomson et al., 2008). The expression levels of each gene were normalized, with the 16S rRNA gene as an internal control (Mizusaki et al., 2008).
TRANSLATIONAL IMPACT.
Clinical issue
Food-borne diseases remain a threat despite advances in medical technology. It is well known that Salmonella is a major food-borne pathogen and that it can cause severe clinical symptoms, such as acute gastroenteritis. Previous studies have identified and characterized the activity of several virulence factors in Salmonella, but the molecular mechanisms by which many of them contribute to the development of acute gastroenteritis is still unclear. Stn is considered to be a virulence factor in Salmonella and a candidate for the causative agent of diarrhea because previous work has shown that this factor has enterotoxic activity in a murine ileal loop model. However, the contribution of Stn to virulence is variable in each Salmonella strain, and its molecular mechanism has not been elucidated.
Results
The authors examined the functions of Stn on Salmonella virulence using the Δstn mutant in both in vitro and in vivo models, and found that Stn did not contribute to virulence in these systems. To uncover unidentified functions for Stn, the authors carried out proteomic profiling of total cell membrane proteins. This revealed that the localization of outer membrane protein A (OmpA) was abnormal in the Δstn mutant, thereby affecting membrane morphology and integrity.
Implications and future directions
These results indicate that Stn regulates the localization and levels of OmpA in Salmonella, and that it therefore functions in the maintenance of membrane integrity. Previous studies indicate that OmpA contributes to several cellular functions and is important for the maintenance of bacterial homeostasis. In addition, OmpA has been associated with the virulence of Gram-negative bacteria, and is one of the major proteins towards which host cells mount an immune response. Notably, many studies have shown that among Gram-negative bacteria the stn gene is specific to Salmonella species. Thus, these data not only reveal a functional relationship between Stn and OmpA, but might also provide clues about the generation of host immunity to Salmonella.
Transcripts were quantified by LightCycler (Roche Diagnostics) using SYBR Premix Ex Taq (TaKaRa Bio) in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank Asami Fujii and Kayo Maeda for their technical assistance.
Footnotes
COMPETING INTERESTS
The authors declare that they do not have any competing or financial interests.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
M.N., E.Y., T.H. and H.K. conceived and designed this work. M.N. and E.Y. performed the experiments including all genetic manipulations, proteomic profiles and analysis of the Δstn mutant using cultured mammalian cells. A.I. operated the transmission electron microscope and performed the immunogold labeling. T.S. and A.T. performed the animal experiments. J.K.A. and K.N. conducted the amino acid sequence analysis. M.N., T.H. and H.K. wrote the paper, and J.M. edited this manuscript and provided advice on this work.
FUNDING
This work was supported by the Global Center of Excellence Program on Integrated Global Control Strategy for the Tropical and Emerging Infectious Diseases from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan; by an award from Ohyama Health Foundation (to M.N.); and by the Cooperative Research Grant of NEKKEN, 2011 (to H.K.).
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
Supplementary material for this article is available at http://dmm.biologists.org/lookup/suppl/doi:10.1242/dmm.009324/-/DC1
REFERENCES
- Abdallah B. M., Boissy P., Tan Q., Dahlgaard J., Traustadottir G. A., Kupisiewicz K., Laborda J., Delaisse J. M., Kassem M. (2007). dlk1/FA1 regulates the function of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by modulating gene expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and immune response-related factors. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 7339–7351 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle E. C., Bishop J. L., Grassl G. A., Finlay B. B. (2007). Salmonella: from pathogenesis to therapeutics. J. Bacterial. 189, 1489–1495 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chai T. J., Foulds J. (1997). Purification of protein A, an outer membrane component missing in Escherichia coli K-12 ompA mutants. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 493, 210–215 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra A. K., Peterson J. W., Chart P., Prasad R. (1994). Molecular characterization of an enterotoxin from Salmonella typhimurium. Microb. Pathog. 16, 85–98 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra A. K., Huang J. H., Xu X. J., Burden K., Niesel D. W., Rosenbaum M. W., Popov V. L., Peterson J. W. (1999). Role of Salmonella enterotoxin in overall virulence of the organism. Microb. Pathog. 27, 155–171 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crossman L. C., Chaudhuri R. R., Beatson S. A., Wells T. J., Desvaux M., Cunningham A. F., Petty N. K., Mahon V., Brinkley C., Hobman J. L., et al. (2010). A commensal gone bad: complete genome sequence of the prototypical enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strain H10407. J. Bacteriol. 192, 5822–5831 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinjus U., Hänel I., Müller W., Bauerfeind R., Helmuth R. (1997). Detection of the induction of Salmonella enterotoxin gene expression by contact with epithelial cells with RT-PCR. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 146, 175–179 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A., Marchlewicz B. A., McDonald R. J., Boesman-Finkelstein M. (1983). Isolation and characterization of a cholera-related enterotoxin from Salmonella typhimuirum. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 17, 239–241 [Google Scholar]
- Freudl R., Schwarz H., Klose M., Movva N. R., Henning U. (1985). The nature of information, required for export and sorting, present within the outer membrane protein OmpA of Escherichia coli K-12. EMBO J. 4, 3593–3598 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freudl R., Klose M., Henning U. (1990). Export and sorting of the Escherichia coli outer membrane protein OmpA. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 22, 441–449 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ge S., Danino V., He Q., Hinton J. C. D., Granfors K. (2010). Microarray analysis of response of Salmonella during infection of HLA-B27-transfected human macrophage-like U937 cells. BMC Genomics 11, 456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grassl G. A., Finlay B. B. (2008). Pathogenesis of enteric Salmonella infections. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 24, 22–26 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harford S., Dykes C. W., Hobden A. N., Read M. J., Halliday I. J. (1989). Inactivation of the Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin by in vitro mutagenesis of the A-subunit gene. Eur. J. Biochem. 183, 311–316 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidelberg J. F., Eisen J. A., Nelson W. C., Clayton R. A., Gwinn M. L., Dodson R. J., Haft D. H., Hickey E. K., Peterson J. D., Umayam L., et al. (2000). DNA sequence of both chromosomes of the cholera pathogen Vibrio cholerae. Nature 406, 477–483 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang F., Kao C., Wachi S., Thai P., Ryu J., Wu R. (2007). Requirement for both JAK-mediated PI3K signaling and ACT1/TRAF6/TAK-1 dependent NF-κB activation by IL-17A in enhancing cytokine expression in human airway epithelial cells. J. Immunol. 179, 6504–6513 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichihara T., Akada J. K., Kamei S., Ohshiro S., Sato D., Fujimoto M., Kuramitsu Y., Nakamura K. (2006). A novel approach of protein immobilization for protein chips using an oligo-cysteine tag. J. Proteome Res. 5, 2144–2151 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichinose A., Watanabe K., Senba M., Ahmed K., Ariyoshi K., Matsumoto K. (2011). Demonstration of pneumococcal capsule under immunoelectron microscopy. Acta Med. Nagasaki 56, 1–4 [Google Scholar]
- Kajikawa A., Masuda K., Katoh M., Igimi S. (2010). Adjuvant effects for oral immunization provided by recombinant Lactobacillus casei secreting biologically active murine interleukin-1β. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 17, 43–48 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodama T., Akeda Y., Kono G., Takahashi A., Imura K., Iida T., Honda T. (2002). The EspB protein of enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli interacts directly with α-catenin. Cell. Microbiol. 4, 213–222 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laing S., Unger M., Koch-Nolte F., Haag F. (2011). ADP-ribosylation of arginine. Amino Acids 41, 257–269 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K., Iwata T., Shimizu M., Taniguchi T., Nakadia A., Hirota Y., Hayashidani H. (2009). A novel multiplex PCR assay for Salmonella subspecies identification. J. Appl. Microbiol. 107, 805–811 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindgren S. W., Stojiljkovic I., Heffron F. (1996). Macrophage killing is an essential virulence mechanism of Salmonella typhimurium. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 4197–4201 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino S., Kurazono H., Chongsanguam M., Hayashi H., Cheun H., Suzuki S., Shirahata T. (1999). Establishment of the PCR system specific to Salmonella spp. and its application for the inspection of food and fecal samples. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 61, 1245–1247 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizusaki H., Takaya A., Yamamoto T., Aizawa S. (2008). Signal pathway in salt-activated expression of the Salmonella pathogenicity island 1 type III secretion system in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. J. Bacteriol. 190, 4624–4631 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molina N. C., Peterson J. W. (1980). Cholera toxin-like toxin released by Salmonella species in the presence of mitomycin C. Infect. Immun. 30, 224–230 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M. M., Feist M. D. (2007). Real-time PCR method for Salmonella spp. targeting the stn gene. J. Appl. Microbiol. 102, 516–530 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nambu T., Kutsukake K. (2000). The Salmonella FlgA protein, a putative periplasmic chaperone essential for flagellar P ring formation. Microbiology 146, 1171–1178 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishihara M., Yamada M., Nozaki M., Nakahira K., Yanagihara I. (2010). Transcriptional regulation of the human establishment of cohesion 1 homolog 2 gene. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 393, 111–117 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuda J., Toyotome T., Kataoka N., Ohno M., Abe H., Shimura Y., Seyedarabi A., Pickersgill R., Sasakawa C. (2005). Shigella effector IpaH9.8 binds to a splicing factor U2AF35 to modulate host responses. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 333, 531–539 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuda M., Saio M., Kito Y., Ohe N., Yano H., Yoshimura S., Iwama T., Takami T. (2009). Tumor-associated macrophage/microglia infiltration in human gliomas is correlated with MCP-3, but not MCP-1. Int. J. Oncol. 34, 1621–1627 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwan W. R., Huang X., Hu L., Kopecko D. J. (2000). Differential bacterial survival, replication, and apoptosis-inducing ability of Salmonella serovars within human and murine macrophage. Infect. Immun. 68, 1005–1013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sittka A., Pfeiffer V., Tedin K., Vogel J. (2007). The RNA chaperone Hfq is essential for the virulence of Salmonella typhimurium. Mol. Microbiol. 63, 193–217 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson N. R., Clayton D. J., Windhorst D., Vernikos G., Davidson S., Churcher C., Quail M. A., Stevens M., Jones M. A., Watson M., et al. (2008). Comparative genome analysis of Salmonella Enteritidis PT4 and Salmonella Gallinarum 287/91 provides insights into evolutionary and host adaptation pathways. Genome Res. 18, 1624–1637 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis T. S. M., Wood M., Watson P., Paulin S., Jones M. (1999). Sips, Sops, and SPIs but not stn influence Salmonella enteropathogenesis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 473, 275–280 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson P. R., Galyov E. E., Paulin S. M., Jones P. W., Wallis T. M. (1998). Mutation of invH, but not stn, reduced Salmonella-induced enteritis in cattle. Infect. Immun. 66, 1432–1438 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.