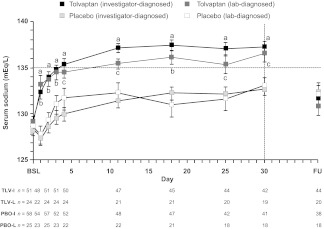
Figure 2.
Serum sodium levels in SIADH patients during treatment with tolvaptan or placebo in the SALT trials. Investigator-diagnosed patients received a primary diagnosis of SIADH from the investigator; lab-diagnosed patients received a primary diagnosis of SIADH from the investigator and had a urine sodium concentration >20 mEq/L during the first day of treatment.
ap < .0001, tolvaptan (investigator-diagnosed) versus placebo (investigator-diagnosed).
bp < .001, tolvaptan (lab-diagnosed) versus placebo (lab-diagnosed).
cp < .029, tolvaptan (lab-diagnosed) versus placebo (lab-diagnosed).
Error bars are ± standard error of the mean.
Abbreviations: BSL, baseline; FU, 7-day follow-up visit; PBO-I, placebo (investigator-diagnosed); PBO-L, placebo (lab-diagnosed), TLV-I; tolvaptan (investigator-diagnosed); TLV-L, tolvaptan (lab-diagnosed); SALT, Study of Ascending Levels of Tolvaptan in Hyponatremia; SIADH, syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone.
Reproduced with permission from Verbalis JG, Adler S, Schrier RW et al. Efficacy and safety of oral tolvaptan therapy in patients with the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion. Eur J Endocrinol 2011;164:725–732. ©Society of the European Journal of Endocrinology (2011).