Abstract
The title compound, C14H19N3O3, was synthesized by the reaction of 3-methoxypropionitrile, tert-butyl bromoacetate and ethoxymethylenemalononitrile. In the crystal, N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds link the molecules into chains propagating along the b axis.
Related literature
For a related structure, see: Wang et al. (2007 ▶). For applications of pyridines, see: Spurr (1995 ▶). For background to the synthesis of highly substituted pyridines, see: Chun et al. (2009 ▶, 2011 ▶). 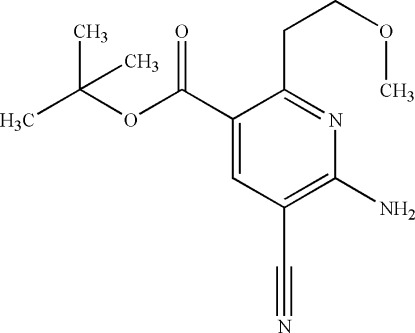
Experimental
Crystal data
C14H19N3O3
M r = 277.32
Monoclinic,

a = 10.1155 (4) Å
b = 15.2482 (5) Å
c = 19.4882 (6) Å
β = 99.853 (3)°
V = 2961.59 (18) Å3
Z = 8
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.09 mm−1
T = 130 K
0.35 × 0.30 × 0.30 mm
Data collection
Agilent Xcalibur Eos diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2010 ▶) T min = 0.902, T max = 1.000
5419 measured reflections
2608 independent reflections
2094 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.020
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.040
wR(F 2) = 0.100
S = 1.05
2608 reflections
191 parameters
4 restraints
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.16 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.22 e Å−3
Data collection: CrysAlis PRO (Agilent, 2010 ▶); cell refinement: CrysAlis PRO; data reduction: CrysAlis PRO; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: OLEX2 (Dolomanov et al., 2009 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: OLEX2.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812014328/cv5269sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812014328/cv5269Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812014328/cv5269Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2—H2A⋯O3i | 0.88 (1) | 2.25 (1) | 3.0186 (18) | 146 (2) |
| N2—H2B⋯O1i | 0.88 (1) | 2.00 (1) | 2.8427 (18) | 159 (2) |
Symmetry code: (i)  .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Yin Ping, Fang Bo and Fochon Pharma, Inc.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Pyridines can be found in many natural products and biologically active compounds (Spurr, 1995). Thus, the synthesis of highly substituted pyridines has attracted much attention (Chun et al. 2009, 2011). We synthesized the title compound (I). Herein we present its crystal structure.
In (I) (Fig. 1), all bond lengths and angles are normal and comparable with those observed in the related compound methyl 6-amino-5-cyano-4-(4-fluorophenyl)-2-methylpyridine-3-carboxylate (Wang et al., 2007).
In the crystal structure of (I), intermolecular N—H···O hydrogen bonds (Table 1) link the molecules into chains propagated along the b axis.
Experimental
A mixture of zinc powder (0.65 g) and 3-methoxypropionitrile (0.85 g) in tetrahydrofuran (10 ml) was refluxed, then tert-Butyl bromoacetate (1.95 g) was added dropwise. Keep stirring under reflux for 1 h. Ethoxymethylenemalononitrile (1.22 g) was added, the reaction mixture was stirred under reflux for 2 h to afford the title compound (I) (Chun et al. 2009, 2011). Single crystals were grown by slow evaporation of a solution of Pet: EtOAc=5:1 at room temperature.
Refinement
C-bound H atoms were positioned geometrically (C—H 0.95–0.99 Å), and were refined using a riding model, with Uiso(H) = 1.2–1.5 Ueq (C). N-bound H atoms were located in a difference map and refined freely with Uiso(H) = 1.2 Ueq(N).
Figures
Fig. 1.

The molecular structure of the title compound. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
Crystal data
| C14H19N3O3 | Dx = 1.244 Mg m−3 |
| Mr = 277.32 | Melting point: 404.16 K |
| Monoclinic, C2/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.7107 Å |
| a = 10.1155 (4) Å | Cell parameters from 2258 reflections |
| b = 15.2482 (5) Å | θ = 2.9–29.1° |
| c = 19.4882 (6) Å | µ = 0.09 mm−1 |
| β = 99.853 (3)° | T = 130 K |
| V = 2961.59 (18) Å3 | Block, colourless |
| Z = 8 | 0.35 × 0.30 × 0.30 mm |
| F(000) = 1184 |
Data collection
| Agilent Xcalibur Eos diffractometer | 2608 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: Enhance (Mo) X-ray Source | 2094 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.020 |
| Detector resolution: 16.0874 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 25.0°, θmin = 2.9° |
| ω scans | h = −12→11 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2010) | k = −18→10 |
| Tmin = 0.902, Tmax = 1.000 | l = −15→23 |
| 5419 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.040 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.100 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.05 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0438P)2 + 1.1844P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2608 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 191 parameters | Δρmax = 0.16 e Å−3 |
| 4 restraints | Δρmin = −0.22 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.21160 (13) | 0.04640 (8) | 0.29380 (6) | 0.0402 (3) | |
| O2 | 0.12016 (10) | 0.02438 (7) | 0.38946 (5) | 0.0280 (3) | |
| O3 | 0.33430 (10) | −0.04292 (7) | 0.12374 (6) | 0.0296 (3) | |
| N1 | 0.17189 (12) | −0.23015 (8) | 0.25819 (6) | 0.0241 (3) | |
| N2 | 0.16078 (15) | −0.36625 (9) | 0.30598 (8) | 0.0322 (4) | |
| H2A | 0.1613 (17) | −0.4024 (9) | 0.3412 (8) | 0.039* | |
| H2B | 0.1820 (17) | −0.3884 (10) | 0.2674 (7) | 0.039* | |
| N3 | 0.11844 (14) | −0.34153 (10) | 0.48130 (7) | 0.0367 (4) | |
| C1 | 0.15937 (14) | −0.27913 (10) | 0.31410 (8) | 0.0237 (4) | |
| C2 | 0.14474 (14) | −0.24020 (10) | 0.37841 (8) | 0.0233 (4) | |
| C3 | 0.14728 (14) | −0.15014 (10) | 0.38336 (8) | 0.0230 (4) | |
| H3 | 0.1386 | −0.1227 | 0.4261 | 0.028* | |
| C4 | 0.16250 (13) | −0.09908 (10) | 0.32599 (8) | 0.0218 (3) | |
| C5 | 0.17249 (13) | −0.14259 (10) | 0.26322 (8) | 0.0219 (3) | |
| C6 | 0.16804 (14) | −0.00242 (11) | 0.33331 (8) | 0.0250 (4) | |
| C7 | 0.13015 (15) | −0.29497 (11) | 0.43634 (8) | 0.0263 (4) | |
| C8 | 0.11812 (17) | 0.11866 (10) | 0.40839 (9) | 0.0303 (4) | |
| C9 | 0.0559 (2) | 0.11529 (13) | 0.47372 (11) | 0.0529 (6) | |
| H9A | 0.0480 | 0.1749 | 0.4913 | 0.079* | |
| H9B | 0.1128 | 0.0802 | 0.5092 | 0.079* | |
| H9C | −0.0334 | 0.0886 | 0.4629 | 0.079* | |
| C10 | 0.25917 (19) | 0.15437 (14) | 0.42359 (11) | 0.0505 (5) | |
| H10A | 0.2974 | 0.1550 | 0.3806 | 0.076* | |
| H10B | 0.3143 | 0.1171 | 0.4583 | 0.076* | |
| H10C | 0.2575 | 0.2142 | 0.4417 | 0.076* | |
| C11 | 0.03036 (19) | 0.16861 (12) | 0.35095 (10) | 0.0459 (5) | |
| H11A | 0.0773 | 0.1751 | 0.3112 | 0.069* | |
| H11B | 0.0104 | 0.2268 | 0.3680 | 0.069* | |
| H11C | −0.0536 | 0.1364 | 0.3363 | 0.069* | |
| C12 | 0.18509 (14) | −0.09710 (11) | 0.19592 (8) | 0.0247 (4) | |
| H12A | 0.1426 | −0.0385 | 0.1950 | 0.030* | |
| H12B | 0.1367 | −0.1315 | 0.1563 | 0.030* | |
| C13 | 0.33020 (14) | −0.08676 (11) | 0.18746 (8) | 0.0252 (4) | |
| H13A | 0.3796 | −0.0524 | 0.2268 | 0.030* | |
| H13B | 0.3732 | −0.1451 | 0.1873 | 0.030* | |
| C14 | 0.46425 (17) | −0.04423 (13) | 0.10532 (10) | 0.0417 (5) | |
| H14A | 0.4621 | −0.0133 | 0.0611 | 0.063* | |
| H14B | 0.4923 | −0.1051 | 0.1004 | 0.063* | |
| H14C | 0.5280 | −0.0152 | 0.1418 | 0.063* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0612 (8) | 0.0263 (7) | 0.0407 (7) | −0.0069 (6) | 0.0305 (6) | −0.0014 (6) |
| O2 | 0.0394 (6) | 0.0213 (6) | 0.0262 (6) | −0.0012 (5) | 0.0138 (5) | −0.0030 (5) |
| O3 | 0.0326 (6) | 0.0331 (7) | 0.0258 (6) | −0.0025 (5) | 0.0128 (4) | 0.0028 (5) |
| N1 | 0.0260 (7) | 0.0240 (7) | 0.0236 (7) | −0.0005 (6) | 0.0082 (5) | −0.0018 (6) |
| N2 | 0.0477 (9) | 0.0228 (8) | 0.0300 (8) | 0.0015 (7) | 0.0177 (7) | −0.0008 (7) |
| N3 | 0.0444 (9) | 0.0367 (9) | 0.0296 (8) | −0.0065 (7) | 0.0077 (6) | 0.0051 (7) |
| C1 | 0.0204 (8) | 0.0241 (8) | 0.0274 (8) | 0.0001 (6) | 0.0065 (6) | −0.0001 (7) |
| C2 | 0.0225 (8) | 0.0249 (8) | 0.0235 (8) | 0.0001 (6) | 0.0066 (6) | 0.0007 (7) |
| C3 | 0.0207 (8) | 0.0274 (8) | 0.0216 (8) | 0.0005 (6) | 0.0060 (6) | −0.0013 (7) |
| C4 | 0.0185 (7) | 0.0245 (8) | 0.0231 (8) | 0.0004 (6) | 0.0059 (6) | −0.0003 (7) |
| C5 | 0.0164 (7) | 0.0253 (8) | 0.0249 (8) | −0.0001 (6) | 0.0062 (6) | 0.0010 (7) |
| C6 | 0.0241 (8) | 0.0274 (9) | 0.0248 (8) | −0.0003 (7) | 0.0078 (6) | −0.0009 (7) |
| C7 | 0.0282 (9) | 0.0258 (9) | 0.0259 (9) | −0.0014 (7) | 0.0071 (7) | −0.0029 (8) |
| C8 | 0.0399 (9) | 0.0211 (8) | 0.0324 (9) | −0.0023 (7) | 0.0132 (7) | −0.0071 (8) |
| C9 | 0.0851 (15) | 0.0328 (11) | 0.0507 (13) | −0.0069 (10) | 0.0392 (11) | −0.0133 (10) |
| C10 | 0.0487 (12) | 0.0491 (12) | 0.0533 (13) | −0.0149 (10) | 0.0076 (9) | −0.0227 (11) |
| C11 | 0.0542 (12) | 0.0304 (10) | 0.0526 (12) | 0.0095 (9) | 0.0080 (9) | −0.0036 (10) |
| C12 | 0.0259 (8) | 0.0268 (9) | 0.0219 (8) | −0.0008 (7) | 0.0052 (6) | −0.0002 (7) |
| C13 | 0.0304 (9) | 0.0246 (8) | 0.0223 (8) | 0.0020 (7) | 0.0094 (6) | 0.0022 (7) |
| C14 | 0.0431 (11) | 0.0426 (11) | 0.0470 (11) | 0.0023 (9) | 0.0290 (8) | 0.0050 (10) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—C6 | 1.2072 (18) | C8—C10 | 1.508 (2) |
| O2—C6 | 1.3342 (17) | C8—C11 | 1.510 (2) |
| O2—C8 | 1.4852 (19) | C9—H9A | 0.9800 |
| O3—C13 | 1.4170 (18) | C9—H9B | 0.9800 |
| O3—C14 | 1.4209 (18) | C9—H9C | 0.9800 |
| N1—C1 | 1.3447 (19) | C10—H10A | 0.9800 |
| N1—C5 | 1.339 (2) | C10—H10B | 0.9800 |
| N2—H2A | 0.880 (12) | C10—H10C | 0.9800 |
| N2—H2B | 0.883 (12) | C11—H11A | 0.9800 |
| N2—C1 | 1.338 (2) | C11—H11B | 0.9800 |
| N3—C7 | 1.149 (2) | C11—H11C | 0.9800 |
| C1—C2 | 1.417 (2) | C12—H12A | 0.9900 |
| C2—C3 | 1.377 (2) | C12—H12B | 0.9900 |
| C2—C7 | 1.432 (2) | C12—C13 | 1.513 (2) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C13—H13A | 0.9900 |
| C3—C4 | 1.392 (2) | C13—H13B | 0.9900 |
| C4—C5 | 1.410 (2) | C14—H14A | 0.9800 |
| C4—C6 | 1.481 (2) | C14—H14B | 0.9800 |
| C5—C12 | 1.508 (2) | C14—H14C | 0.9800 |
| C8—C9 | 1.515 (2) | ||
| C6—O2—C8 | 121.51 (12) | H9A—C9—H9B | 109.5 |
| C13—O3—C14 | 112.44 (12) | H9A—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| C5—N1—C1 | 119.64 (13) | H9B—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| H2A—N2—H2B | 117.1 (16) | C8—C10—H10A | 109.5 |
| C1—N2—H2A | 121.9 (11) | C8—C10—H10B | 109.5 |
| C1—N2—H2B | 119.3 (11) | C8—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| N1—C1—C2 | 121.50 (14) | H10A—C10—H10B | 109.5 |
| N2—C1—N1 | 116.81 (14) | H10A—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| N2—C1—C2 | 121.69 (15) | H10B—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C1—C2—C7 | 119.56 (14) | C8—C11—H11A | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 118.44 (14) | C8—C11—H11B | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—C7 | 121.99 (14) | C8—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.8 | H11A—C11—H11B | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 120.32 (14) | H11A—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.8 | H11B—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 117.88 (14) | C5—C12—H12A | 109.3 |
| C3—C4—C6 | 119.12 (13) | C5—C12—H12B | 109.3 |
| C5—C4—C6 | 123.00 (14) | C5—C12—C13 | 111.75 (12) |
| N1—C5—C4 | 122.18 (14) | H12A—C12—H12B | 107.9 |
| N1—C5—C12 | 113.27 (13) | C13—C12—H12A | 109.3 |
| C4—C5—C12 | 124.55 (14) | C13—C12—H12B | 109.3 |
| O1—C6—O2 | 123.89 (15) | O3—C13—C12 | 108.60 (12) |
| O1—C6—C4 | 124.35 (14) | O3—C13—H13A | 110.0 |
| O2—C6—C4 | 111.76 (13) | O3—C13—H13B | 110.0 |
| N3—C7—C2 | 177.52 (17) | C12—C13—H13A | 110.0 |
| O2—C8—C9 | 101.62 (13) | C12—C13—H13B | 110.0 |
| O2—C8—C10 | 110.20 (14) | H13A—C13—H13B | 108.4 |
| O2—C8—C11 | 109.60 (13) | O3—C14—H14A | 109.5 |
| C10—C8—C9 | 111.25 (16) | O3—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| C10—C8—C11 | 112.31 (16) | O3—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C11—C8—C9 | 111.34 (16) | H14A—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| C8—C9—H9A | 109.5 | H14A—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C8—C9—H9B | 109.5 | H14B—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C8—C9—H9C | 109.5 | ||
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | −1.8 (2) | C4—C5—C12—C13 | 93.76 (17) |
| N1—C1—C2—C7 | 179.27 (13) | C5—N1—C1—N2 | −179.37 (13) |
| N1—C5—C12—C13 | −86.09 (16) | C5—N1—C1—C2 | 0.9 (2) |
| N2—C1—C2—C3 | 178.53 (14) | C5—C4—C6—O1 | −18.0 (2) |
| N2—C1—C2—C7 | −0.4 (2) | C5—C4—C6—O2 | 162.63 (13) |
| C1—N1—C5—C4 | 1.0 (2) | C5—C12—C13—O3 | −179.41 (12) |
| C1—N1—C5—C12 | −179.11 (12) | C6—O2—C8—C9 | 179.74 (14) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.7 (2) | C6—O2—C8—C10 | −62.23 (19) |
| C1—C2—C7—N3 | −3 (4) | C6—O2—C8—C11 | 61.86 (18) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 1.2 (2) | C6—C4—C5—N1 | 177.67 (13) |
| C2—C3—C4—C6 | −178.59 (13) | C6—C4—C5—C12 | −2.2 (2) |
| C3—C2—C7—N3 | 178 (100) | C7—C2—C3—C4 | 179.59 (13) |
| C3—C4—C5—N1 | −2.1 (2) | C8—O2—C6—O1 | −0.6 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—C12 | 178.08 (12) | C8—O2—C6—C4 | 178.73 (12) |
| C3—C4—C6—O1 | 161.74 (15) | C14—O3—C13—C12 | −169.39 (13) |
| C3—C4—C6—O2 | −17.62 (19) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N2—H2A···O3i | 0.88 (1) | 2.25 (1) | 3.0186 (18) | 146 (2) |
| N2—H2B···O1i | 0.88 (1) | 2.00 (1) | 2.8427 (18) | 159 (2) |
Symmetry code: (i) −x+1/2, y−1/2, −z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: CV5269).
References
- Agilent (2010). CrysAlis PRO Agilent Technologies, Yarnton, England.
- Chun, Y. S., Lee, J. H., Kim, J. H., Ko, Y. O. & Lee, S. G. (2011). Org. Lett. 13, 6390–6393. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Chun, Y. S., Ryu, K. Y., Ko, Y. O., Hong, J. Y., Hong, J., Shin, H. & Lee, S. G. (2009). J. Org. Chem. 74, 7556–7558. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K. & Puschmann, H. (2009). J. Appl. Cryst. 42, 339–341.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spurr, P. R. (1995). Tetrahedron Lett. 36, 2745–2748.
- Wang, Q., Zhou, D., Li, C., Shao, Q. & Tu, S. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, o4220.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812014328/cv5269sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812014328/cv5269Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812014328/cv5269Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report


