Abstract
A multiple approach to the study of RNA secondary structure is described which provides for the independent drawing of structures using base-pairing lists, for the generation of local structures in the form of hairpins, and for the generation of global structures by both Monte Carlo and dynamic programming methodologies. User-adjustable parameters provide for limiting the size of hairpin loops, bulges and inner loops, and constraints can be imposed relative to position-dependent base pairing.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dumas J. P., Ninio J. Efficient algorithms for folding and comparing nucleic acid sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 11;10(1):197–206. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.1.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez H. M. An RNA folding rule. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):323–334. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salser W. Globin mRNA sequences: analysis of base pairing and evolutionary implications. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 2):985–1002. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
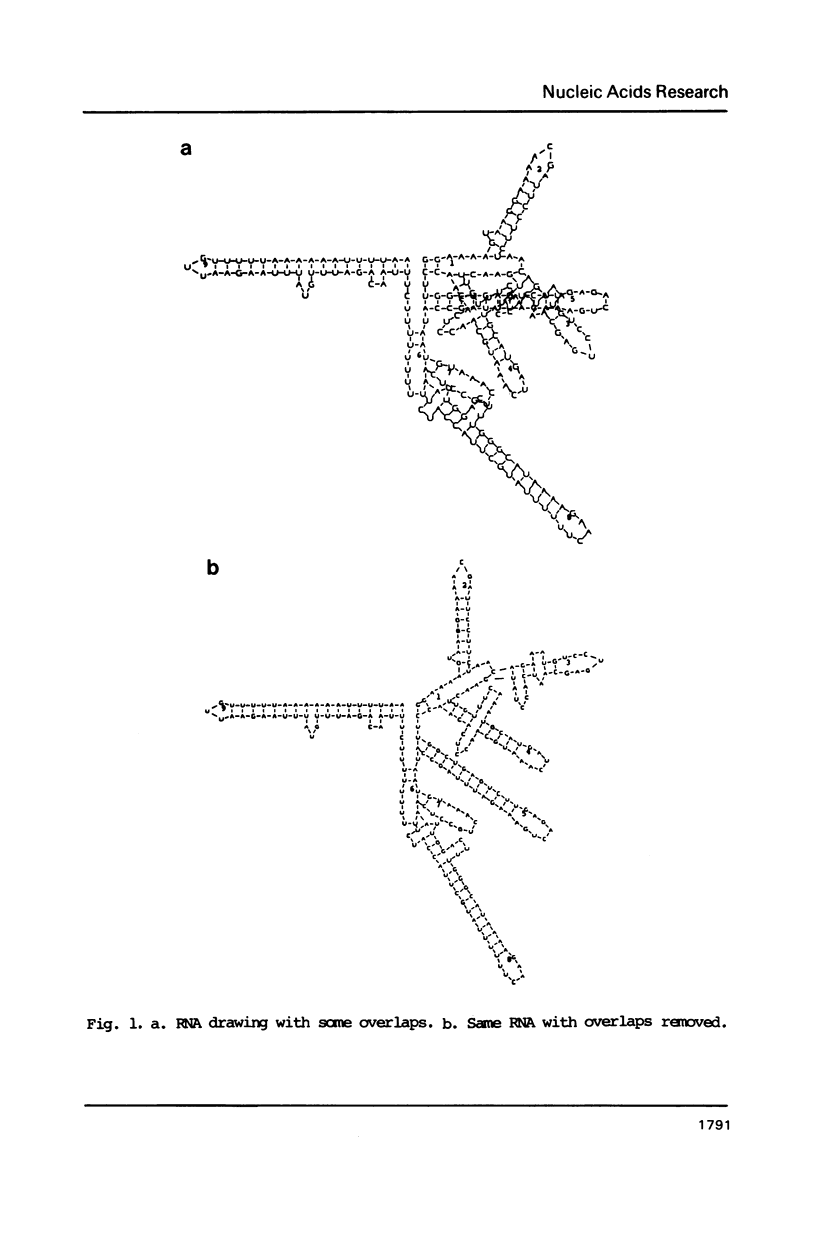
- Shapiro B. A., Maizel J., Lipkin L. E., Currey K., Whitney C. Generating non-overlapping displays of nucleic acid secondary structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):75–88. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studnicka G. M., Rahn G. M., Cummings I. W., Salser W. A. Computer method for predicting the secondary structure of single-stranded RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3365–3387. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker M., Stiegler P. Optimal computer folding of large RNA sequences using thermodynamics and auxiliary information. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):133–148. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



