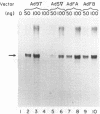
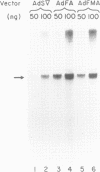
Abstract
Nuclear factor I (NFI) is a site-specific DNA binding protein required for the replication of adenovirus DNA in vitro and in vivo. We have examined the effect of natural and synthetic binding sites for NFI (FIB sites) on RNA synthesis in HeLa whole cell extracts. The natural binding site used is the 26bp FIB-2 site previously isolated from the human genome. When present upstream of the TATA box of the adenovirus major late promoter, the FIB-2 site stimulates RNA synthesis 3 to 5-fold. This stimulation occurs with either orientation of the FIB-2 site. A point mutation in FIB-2 that decreases NFI binding at least 100-fold reduces, but does not completely abolish, the stimulation of transcription. A number of synthetic binding sites for NFI were tested for the ability to increase RNA synthesis. The strongest binding sites stimulated transcription the most, while the weakest sites had the least effect. These studies strongly suggest a role for NFI and cellular FIB sites in the control of RNA synthesis.
Full text
PDF


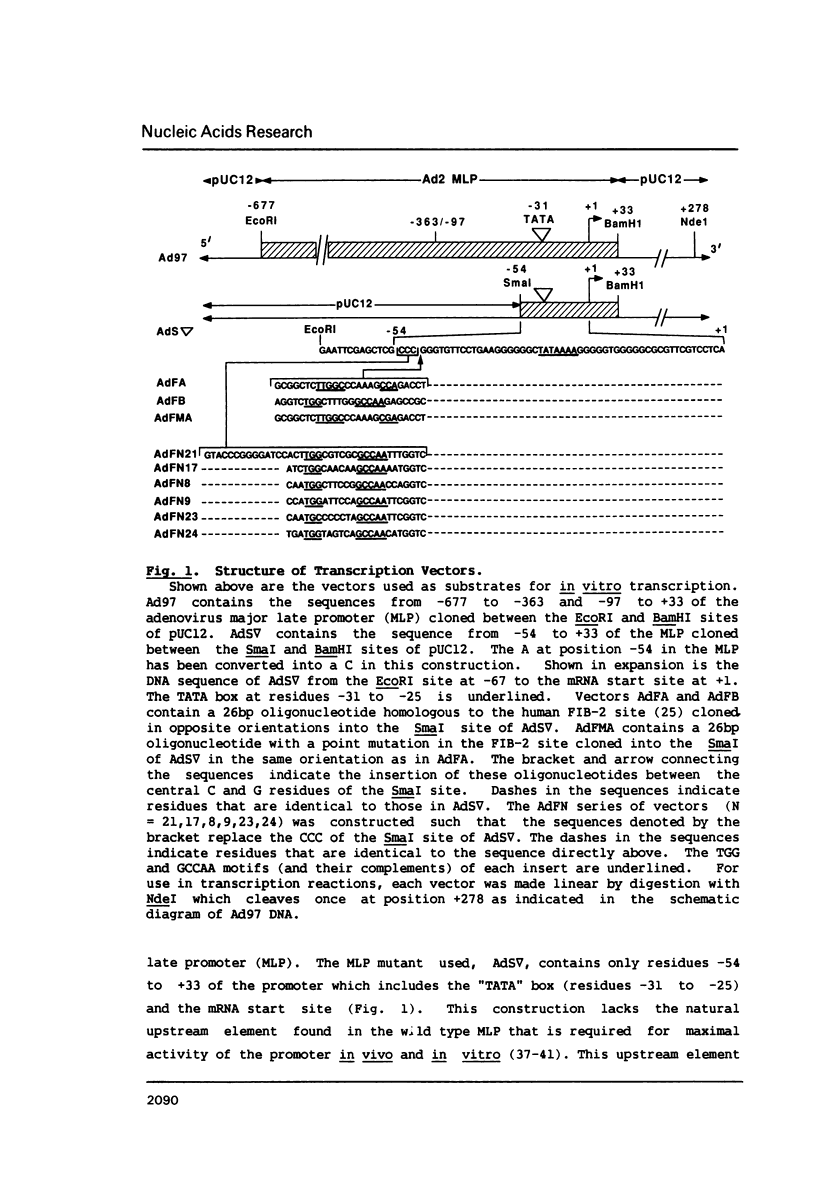


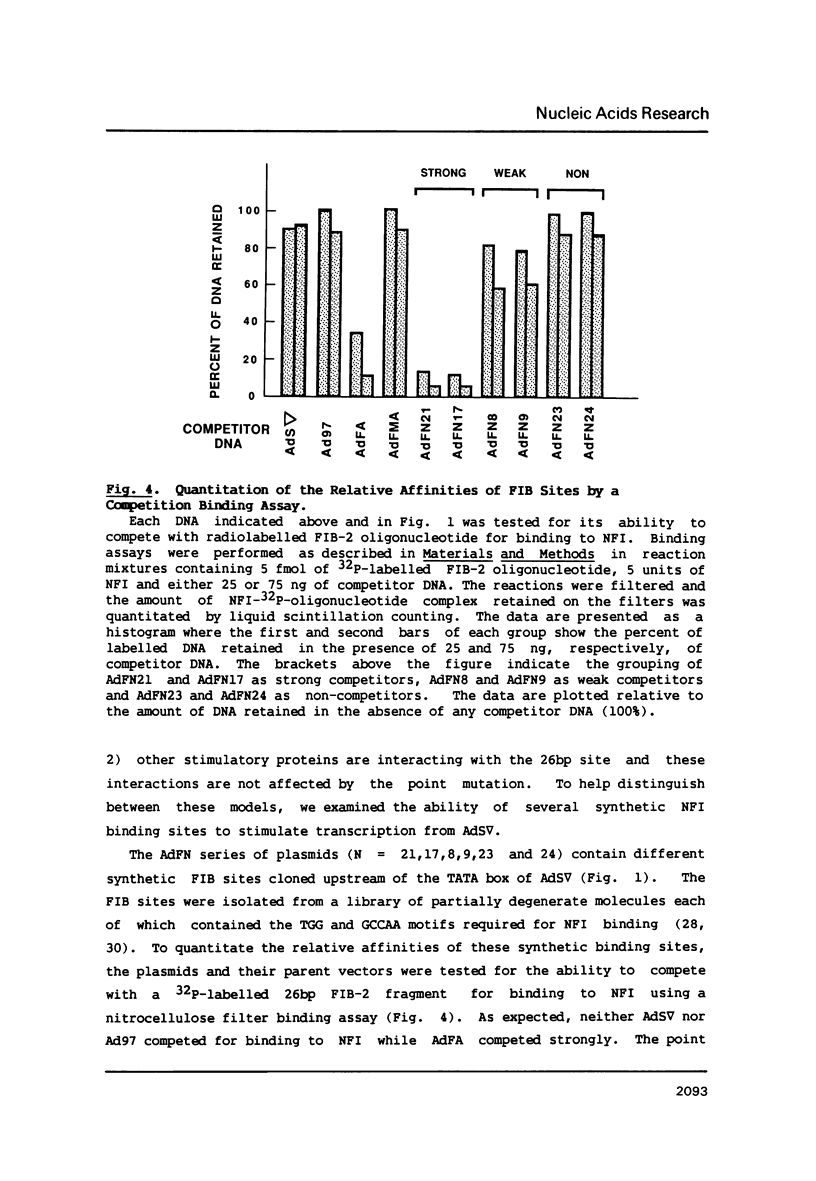





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adhya S., Shneidman P. S., Hurwitz J. Reconstruction of adenovirus replication origins with a human nuclear factor I binding site. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 5;261(7):3339–3346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerji J., Rusconi S., Schaffner W. Expression of a beta-globin gene is enhanced by remote SV40 DNA sequences. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):299–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90413-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barberis A., Superti-Furga G., Busslinger M. Mutually exclusive interaction of the CCAAT-binding factor and of a displacement protein with overlapping sequences of a histone gene promoter. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):347–359. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90489-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgmeyer U., Nowock J., Sippel A. E. The TGGCA-binding protein: a eukaryotic nuclear protein recognizing a symmetrical sequence on double-stranded linear DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 25;12(10):4295–4311. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.10.4295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chodosh L. A., Carthew R. W., Sharp P. A. A single polypeptide possesses the binding and transcription activities of the adenovirus major late transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4723–4733. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochran M. D., Weissmann C. Modular structure of the beta-globin and the TK promoters. EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2453–2459. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02155.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen R. B., Sheffery M., Kim C. G. Partial purification of a nuclear protein that binds to the CCAAT box of the mouse alpha 1-globin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;6(3):821–832. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.3.821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Control of eukaryotic messenger RNA synthesis by sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):774–778. doi: 10.1038/316774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves B. J., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Homologous recognition of a promoter domain common to the MSV LTR and the HSV tk gene. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):565–576. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90266-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronostajski R. M., Adhya S., Nagata K., Guggenheimer R. A., Hurwitz J. Site-specific DNA binding of nuclear factor I: analyses of cellular binding sites. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):964–971. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronostajski R. M. Analysis of nuclear factor I binding to DNA using degenerate oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 25;14(22):9117–9132. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.22.9117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronostajski R. M., Nagata K., Hurwitz J. Isolation of human DNA sequences that bind to nuclear factor I, a host protein involved in adenovirus DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4013–4017. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronostajski R. M. Site-specific DNA binding of nuclear factor I: effect of the spacer region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 24;15(14):5545–5559. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.14.5545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guggenheimer R. A., Stillman B. W., Nagata K., Tamanoi F., Hurwitz J. DNA sequences required for the in vitro replication of adenovirus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):3069–3073. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.3069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay R. T. The origin of adenovirus DNA replication: minimal DNA sequence requirement in vivo. EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):421–426. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03645.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennighausen L., Fleckenstein B. Nuclear factor 1 interacts with five DNA elements in the promoter region of the human cytomegalovirus major immediate early gene. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1367–1371. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04368.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennighausen L., Siebenlist U., Danner D., Leder P., Rawlins D., Rosenfeld P., Kelly T., Jr High-affinity binding site for a specific nuclear protein in the human IgM gene. Nature. 1985 Mar 21;314(6008):289–292. doi: 10.1038/314289a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. E., Hope I. A., Macke J. P., Struhl K. Saturation mutagenesis of the yeast his3 regulatory site: requirements for transcriptional induction and for binding by GCN4 activator protein. Science. 1986 Oct 24;234(4775):451–457. doi: 10.1126/science.3532321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeang K. T., Rawlins D. R., Rosenfeld P. J., Shero J. H., Kelly T. J., Hayward G. S. Multiple tandemly repeated binding sites for cellular nuclear factor 1 that surround the major immediate-early promoters of simian and human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1559–1570. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1559-1570.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Kadonaga J. T., Rosenfeld P. J., Kelly T. J., Tjian R. A cellular DNA-binding protein that activates eukaryotic transcription and DNA replication. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):79–89. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90358-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jove R., Manley J. L. In vitro transcription from the adenovirus 2 major late promoter utilizing templates truncated at promoter-proximal sites. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8513–8521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovesdi I., Satake M., Furukawa K., Reichel R., Ito Y., Nevins J. R. A factor discriminating between the wild-type and a mutant polyomavirus enhancer. Nature. 1987 Jul 2;328(6125):87–89. doi: 10.1038/328087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leegwater P. A., van Driel W., van der Vliet P. C. Recognition site of nuclear factor I, a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein from HeLa cells that stimulates adenovirus DNA replication. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1515–1521. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03811.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan J., Shenk T. In vivo identification of sequence elements required for normal function of the adenovirus major late transcriptional control region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 11;14(15):6327–6335. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Fire A., Cano A., Sharp P. A., Gefter M. L. DNA-dependent transcription of adenovirus genes in a soluble whole-cell extract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3855–3859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto N. G., Moncollin V., Wintzerith M., Hen R., Egly J. M., Chambon P. Stimulation of in vitro transcription by the upstream element of the adenovirus-2 major late promoter involves a specific factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 11;12(23):8779–8799. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.23.8779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncollin V., Miyamoto N. G., Zheng X. M., Egly J. M. Purification of a factor specific for the upstream element of the adenovirus-2 major late promoter. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2577–2584. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04537.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskaluk C., Bastia D. The E2 "gene" of bovine papillomavirus encodes an enhancer-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1215–1218. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata K., Guggenheimer R. A., Enomoto T., Lichy J. H., Hurwitz J. Adenovirus DNA replication in vitro: identification of a host factor that stimulates synthesis of the preterminal protein-dCMP complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6438–6442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata K., Guggenheimer R. A., Hurwitz J. Specific binding of a cellular DNA replication protein to the origin of replication of adenovirus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6177–6181. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowock J., Borgmeyer U., Püschel A. W., Rupp R. A., Sippel A. E. The TGGCA protein binds to the MMTV-LTR, the adenovirus origin of replication, and the BK virus enhancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 25;13(6):2045–2061. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.6.2045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruijn G. J., van Driel W., van der Vliet P. C. Nuclear factor III, a novel sequence-specific DNA-binding protein from HeLa cells stimulating adenovirus DNA replication. Nature. 1986 Aug 14;322(6080):656–659. doi: 10.1038/322656a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawlins D. R., Rosenfeld P. J., Wides R. J., Challberg M. D., Kelly T. J., Jr Structure and function of the adenovirus origin of replication. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):309–319. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90327-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld P. J., O'Neill E. A., Wides R. J., Kelly T. J. Sequence-specific interactions between cellular DNA-binding proteins and the adenovirus origin of DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):875–886. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider R., Gander I., Müller U., Mertz R., Winnacker E. L. A sensitive and rapid gel retention assay for nuclear factor I and other DNA-binding proteins in crude nuclear extracts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 11;14(3):1303–1317. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.3.1303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaul Y., Ben-Levy R., De-Medina T. High affinity binding site for nuclear factor I next to the hepatitis B virus S gene promoter. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1967–1971. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04451.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Hennighausen L., Battey J., Leder P. Chromatin structure and protein binding in the putative regulatory region of the c-myc gene in Burkitt lymphoma. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):381–391. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90368-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sive H. L., Roeder R. G. Interaction of a common factor with conserved promoter and enhancer sequences in histone H2B, immunoglobulin, and U2 small nuclear RNA (snRNA) genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6382–6386. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staudt L. M., Singh H., Sen R., Wirth T., Sharp P. A., Baltimore D. A lymphoid-specific protein binding to the octamer motif of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Oct 16;323(6089):640–643. doi: 10.1038/323640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang K., Pearson G. D. Adenovirus sequences required for replication in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 25;13(14):5173–5187. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.14.5173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Wasylyk C., Augereau P., Chambon P. The SV40 72 bp repeat preferentially potentiates transcription starting from proximal natural or substitute promoter elements. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):503–514. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90470-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wides R. J., Challberg M. D., Rawlins D. R., Kelly T. J. Adenovirus origin of DNA replication: sequence requirements for replication in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):864–874. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vries E., van Driel W., Tromp M., van Boom J., van der Vliet P. C. Adenovirus DNA replication in vitro: site-directed mutagenesis of the nuclear factor I binding site of the Ad2 origin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 11;13(13):4935–4952. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.13.4935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vries E., van Driel W., van den Heuvel S. J., van der Vliet P. C. Contactpoint analysis of the HeLa nuclear factor I recognition site reveals symmetrical binding at one side of the DNA helix. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):161–168. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04734.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]