Abstract
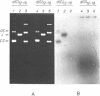
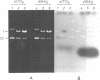
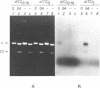
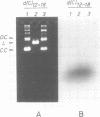
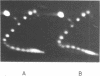
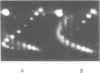
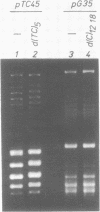
When plasmid DNA duplexes carrying the regular homopurine-homopyrimidine inserts (dGA)n, (dTC)n and (dG)n, (dC)n are preincubated with homologous labeled oligo(dPy) ((dTC)n and (dC)n respectively) at acid pH, the label co-electrophoreses with the duplex DNA. Thus, a very strong complex is formed. Complementary oligo(dPu) does not form a complex under these conditions. No binding is observed for oligo(dPy) with non-homologous inserts as well as with vector plasmids without inserts. The complex is formed equally well with linear, nicked or superhelical DNA. The complex is not detected at pH greater than 6. Complex formation leads to very little, if any, unwinding of the duplex. The observed complex appears to be the Py.Pu.Py triplex consisting of TAT and CGC base-triads with protonated cytosines. Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis patterns show that the presence of homologous oligo(dPy) destabilizes the formation of the H form.
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anshelevich V. V., Vologodskii A. V., Lukashin A. V., Frank-Kamenetskii M. D. Slow relaxational processes in the melting of linear biopolymers: a theory and its application to nucleic acids. Biopolymers. 1984 Jan;23(1):39–58. doi: 10.1002/bip.360230105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnott S., Bond P. J., Selsing E., Smith P. J. Models of triple-stranded polynucleotides with optimised stereochemistry. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Oct;3(10):2459–2470. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.10.2459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantor C. R., Efstratiadis A. Possible structures of homopurine-homopyrimidine S1-hypersensitive sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 12;12(21):8059–8072. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.21.8059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christophe D., Cabrer B., Bacolla A., Targovnik H., Pohl V., Vassart G. An unusually long poly(purine)-poly(pyrimidine) sequence is located upstream from the human thyroglobulin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 25;13(14):5127–5144. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.14.5127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank-Kamenetskii M. DNA chemistry. How the double helix breathes. Nature. 1987 Jul 2;328(6125):17–18. doi: 10.1038/328017a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glikin G. C., Gargiulo G., Rena-Descalzi L., Worcel A. Escherichia coli single-strand binding protein stabilizes specific denatured sites in superhelical DNA. Nature. 1983 Jun 30;303(5920):770–774. doi: 10.1038/303770a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloman W. K., Wiegand R., Hoessli C., Radding C. M. Uptake of homologous single-stranded fragments by superhelical DNA: a possible mechanism for initiation of genetic recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2394–2398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Htun H., Lund E., Dahlberg J. E. Human U1 RNA genes contain an unusually sensitive nuclease S1 cleavage site within the conserved 3' flanking region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7288–7292. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohwi-Shigematsu T., Kohwi Y. Poly(dG)-poly(dC) sequences, under torsional stress, induce an altered DNA conformation upon neighboring DNA sequences. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):199–206. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90024-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen A., Weintraub H. An altered DNA conformation detected by S1 nuclease occurs at specific regions in active chick globin chromatin. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):609–622. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90177-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. S., Johnson D. A., Morgan A. R. Complexes formed by (pyrimidine)n . (purine)n DNAs on lowering the pH are three-stranded. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jul 11;6(9):3073–3091. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.9.3073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyamichev V. I., Mirkin S. M., Frank-Kamenetskii M. D. A pH-dependent structural transition in the homopurine-homopyrimidine tract in superhelical DNA. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1985 Oct;3(2):327–338. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1985.10508420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyamichev V. I., Mirkin S. M., Frank-Kamenetskii M. D. Structure of (dG)n.(dC)n under superhelical stress and acid pH. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1987 Oct;5(2):275–282. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1987.10506393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyamichev V. I., Mirkin S. M., Frank-Kamenetskii M. D. Structures of homopurine-homopyrimidine tract in superhelical DNA. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1986 Feb;3(4):667–669. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1986.10508454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILES H. T. THE STRUCTURE OF THE THREE-STRANDED HELIX, POLY (A+2U). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Jun;51:1104–1109. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.6.1104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mace H. A., Pelham H. R., Travers A. A. Association of an S1 nuclease-sensitive structure with short direct repeats 5' of Drosophila heat shock genes. Nature. 1983 Aug 11;304(5926):555–557. doi: 10.1038/304555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan A. R., Wells R. D. Specificity of the three-stranded complex formation between double-stranded DNA and single-stranded RNA containing repeating nucleotide sequences. J Mol Biol. 1968 Oct 14;37(1):63–80. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickol J. M., Felsenfeld G. DNA conformation at the 5' end of the chicken adult beta-globin gene. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):467–477. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90180-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peck L. J., Wang J. C. Sequence dependence of the helical repeat of DNA in solution. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):375–378. doi: 10.1038/292375a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulleyblank D. E., Haniford D. B., Morgan A. R. A structural basis for S1 nuclease sensitivity of double-stranded DNA. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):271–280. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80122-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarocchi-Landousy M. T., Haas B. L., Guschlbauer W. Interaction of oligoribocytidylates with T7 DNA in neutral and acid media. Biochemistry. 1977 Dec 13;16(25):5414–5420. doi: 10.1021/bi00644a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen C. K. Superhelicity induces hypersensitivity of a human polypyrimidine . polypurine DNA sequence in the human alpha 2-alpha 1 globin intergenic region to S1 nuclease digestion--high resolution mapping of the clustered cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 25;11(22):7899–7910. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.22.7899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M., White R. L., Davis R. W. Hybridization of RNA to double-stranded DNA: formation of R-loops. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2294–2298. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H. A dominant role for DNA secondary structure in forming hypersensitive structures in chromatin. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1191–1203. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90302-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]