Abstract
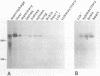
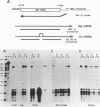
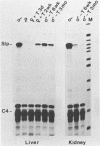
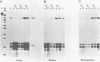
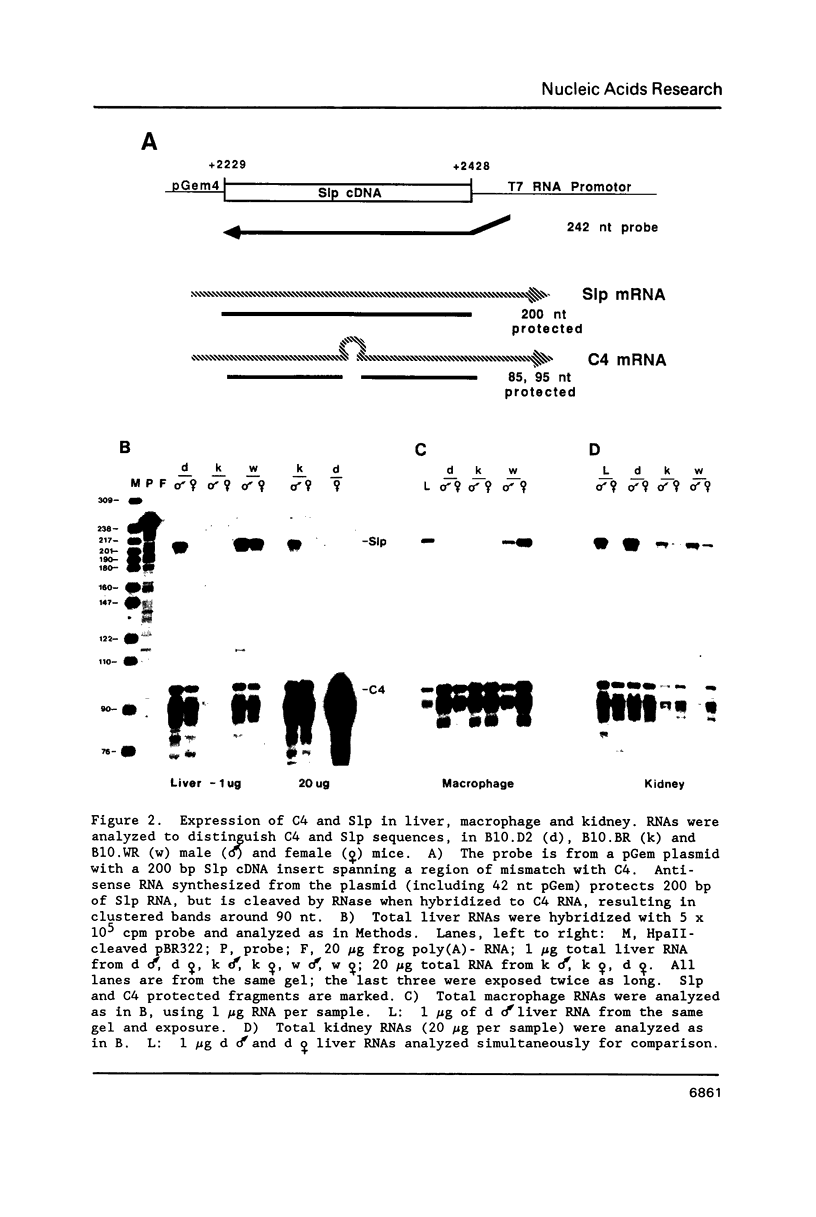
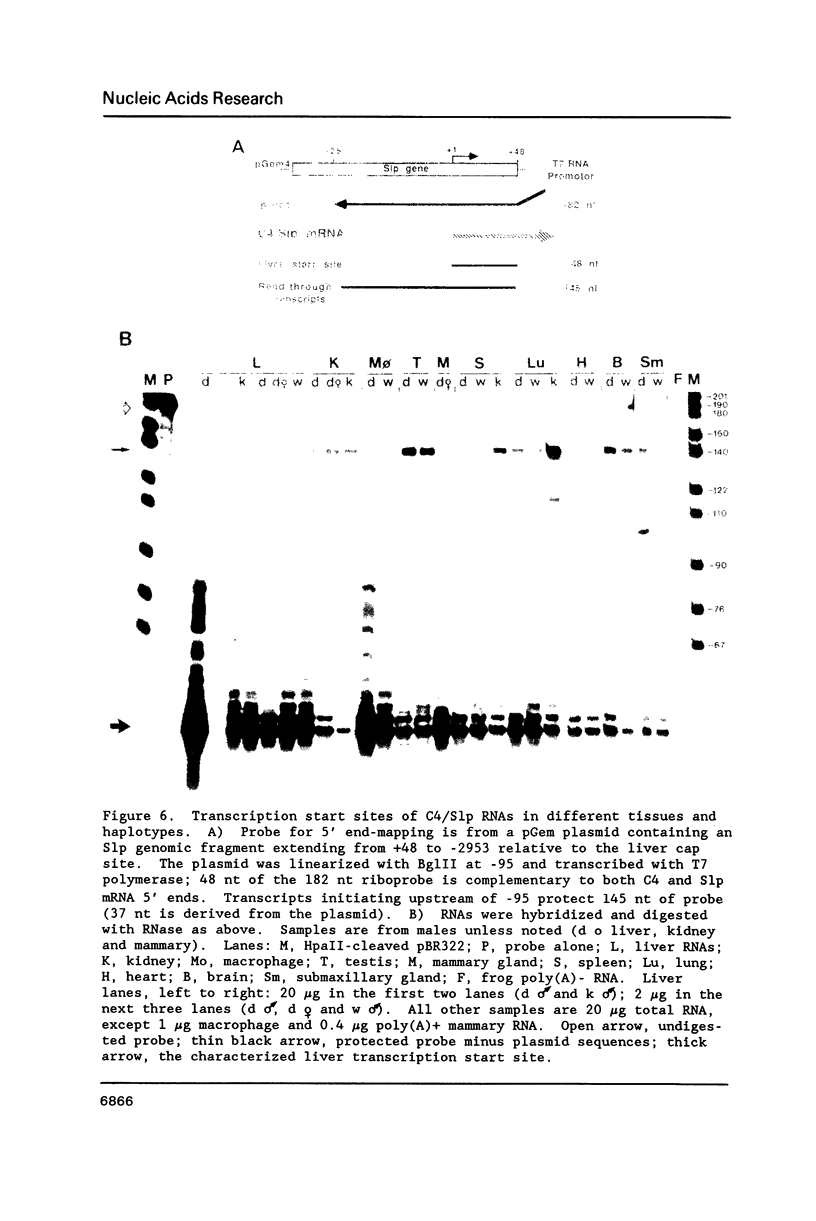
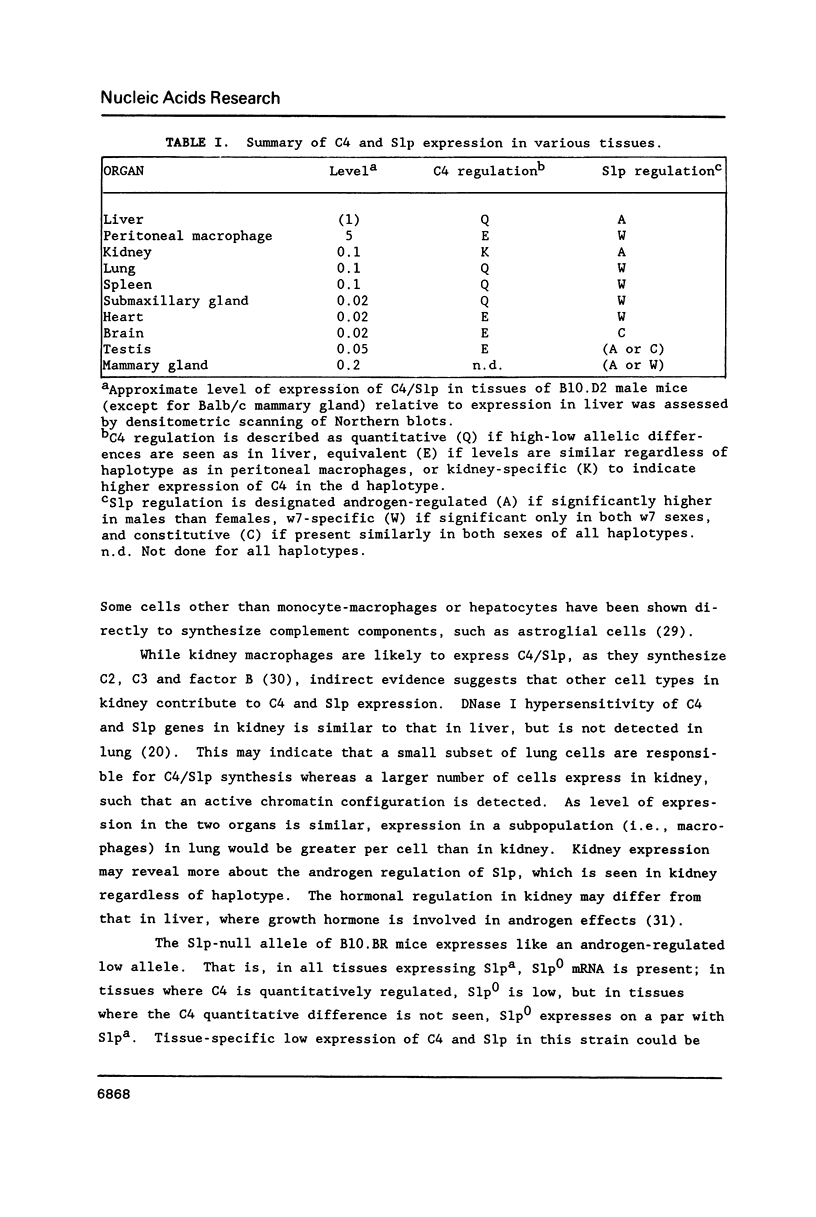
C4 and Slp are highly homologous mouse genes that differ in function and regulation. Allelic variants exist in quantitative regulation of C4 and in hormonal regulation of Slp. We have examined expression in several tissues, including liver and peritoneal macrophages which are the major sites of synthesis, using a probe that allows direct comparison of C4 and Slp mRNAs. Correctly-sized and initiated RNA, within an order of magnitude of liver levels, is found in mammary gland, lung, spleen, and kidney; lower levels are detectable in testis, brain, heart and submaxillary gland. By comparing expression in congenic mouse strains differing in C4 and Slp loci, regulation of these genes is seen to vary in different tissues. This provides a well-defined genetic system in which to examine cis-acting sequences and trans-acting factors that result in tissue-specific patterns of gene regulation.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alpert S. E., Auerbach H. S., Cole F. S., Colten H. R. Macrophage maturation: differences in complement secretion by marrow, monocyte, and tissue macrophages detected with an improved hemolytic plaque assay. J Immunol. 1983 Jan;130(1):102–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown L. J., Shreffler D. C. Female expression of the H-2-linked sex-limited protein (Slp) due to non-H-2 genes. Immunogenetics. 1980;10(1):19–29. doi: 10.1007/BF01561549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cathala G., Savouret J. F., Mendez B., West B. L., Karin M., Martial J. A., Baxter J. D. A method for isolation of intact, translationally active ribonucleic acid. DNA. 1983;2(4):329–335. doi: 10.1089/dna.1983.2.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaplin D. D., Woods D. E., Whitehead A. S., Goldberger G., Colten H. R., Seidman J. G. Molecular map of the murine S region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6947–6951. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole F. S., Auerbach H. S., Goldberger G., Colten H. R. Tissue-specific pretranslational regulation of complement production in human mononuclear phagocytes. J Immunol. 1985 Apr;134(4):2610–2616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colten H. R. Biosynthesis of complement. Adv Immunol. 1976;22:67–118. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60548-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falus A., Beuscher H. U., Auerbach H. S., Colten H. R. Constitutive and IL 1-regulated murine complement gene expression is strain and tissue specific. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 1;138(3):856–860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira A., Eichinger D., Nussenzweig V. The murine sex-limited protein (Slp): reassessment of its sex limitation. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1506–1508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen T. H., Shreffler D. C. Characterization of a constitutive variant of the murine serum protein allotype, Slp. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 Pt 1):1507–1513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemenway C., Kalff M., Stavenhagen J., Walthall D., Robins D. Sequence comparison of alleles of the fourth component of complement (C4) and sex-limited protein (Slp). Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 25;14(6):2539–2554. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.6.2539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemenway C., Robins D. M. DNase I-hypersensitive sites associated with expression and hormonal regulation of mouse C4 and Slp genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4816–4820. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loreni F., Stavenhagen J., Kalff M., Robins D. M. A complex androgen-responsive enhancer resides 2 kilobases upstream of the mouse Slp gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2350–2360. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lévi-Strauss M., Mallat M. Primary cultures of murine astrocytes produce C3 and factor B, two components of the alternative pathway of complement activation. J Immunol. 1987 Oct 1;139(7):2361–2366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelson J., Ferreira A., Nussenzweig V. cis-Interacting genes in the S region of the murine major histocompatibility complex. Nature. 1981 Jan 22;289(5795):306–308. doi: 10.1038/289306a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama K., Nonaka M., Yokoyama S., Yeul Y. D., Pattanakitsakul S. N., Takahashi M. Recombination of two homologous MHC class III genes of the mouse (C4 and Slp) that accounts for the loss of testosterone dependence of sex-limited protein expression. J Immunol. 1987 Jan 15;138(2):620–627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newell S. L., Shreffler D. C., Atkinson J. P. Biosynthesis of C4 by mouse peritoneal macrophages. I. Characterization of an in vitro culture system and comparison of C4 synthesis by "low" vs "high" C4 strains. J Immunol. 1982 Aug;129(2):653–659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonaka M., Kimura H., Yeul Y. D., Yokoyama S., Nakayama K., Takahashi M. Identification of the 5'-flanking regulatory region responsible for the difference in transcriptional control between mouse complement C4 and Slp genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7883–7887. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonaka M., Takahashi M., Natsuume-Sakai S., Nonaka M., Tanaka S., Shimizu A., Honjo T. Isolation of cDNA clones specifying the fourth component of mouse complement and its isotype, sex-limited protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6822–6826. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norstedt G., Palmiter R. Secretory rhythm of growth hormone regulates sexual differentiation of mouse liver. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):805–812. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90030-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata R. T., Sepich D. S. Genes for murine fourth complement component (C4) and sex-limited protein (Slp) identified by hybridization to C4- and Slp-specific cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4908–4911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata R. T., Sepich D. S. Murine sex-limited protein: complete cDNA sequence and comparison with murine fourth complement component. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):4239–4244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passmore H. C., Hansen T. H. Genetic control of the immune response to the H-2 associated Slp alloantigen in the mouse. J Immunol. 1975 Apr;114(4):1139–1142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa P. A., Sepich D. S., Robins D. M., Ogata R. T. Constitutive expression of Slp genes in mouse strain B10.WR directed by C4 regulatory sequences. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 1;139(5):1568–1577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders D., Edidin M. Sites of localization and synthesis of Ss protein in mice. J Immunol. 1974 Jun;112(6):2210–2218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shreffler D. C., Atkinson J. P., Chan A. C., Karp D. R., Killion C. C., Ogata R. T., Rosa P. A. The C4 and Slp genes of the complement region of the murine H-2 major histocompatibility complex. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1984 Sep 6;306(1129):395–403. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1984.0100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stavenhagen J., Loreni F., Hemenway C., Kalff M., Robins D. M. Molecular genetics of androgen-dependent and -independent expression of mouse sex-limited protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1716–1724. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whaley K. Biosynthesis of the complement components and the regulatory proteins of the alternative complement pathway by human peripheral blood monocytes. J Exp Med. 1980 Mar 1;151(3):501–516. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.3.501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinn K., DiMaio D., Maniatis T. Identification of two distinct regulatory regions adjacent to the human beta-interferon gene. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):865–879. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90544-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]