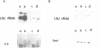Abstract
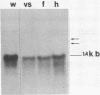
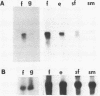
A cDNA clone that encodes the large subunit of mitochondrial ribosomal RNA (LSU rRNA) from the liver fluke F. hepatica was isolated and characterized. This RNA molecule is polyadenylated at the 3' end and represents 10% of the poly A+RNA in adult F. hepatica. Fluke LSU rRNA has significant sequence homology to mosquito mitochondria LSU rRNA and is more closely related to the mitochondrial rRNA of hermaphroditic than dioecious trematodes. Mitochondrial DNA constitutes approximately 10% of the total cellular DNA of adult flukes. This percentage is lower in non-embryonated eggs as are the levels of LSU rRNA indicating eggs have lower metabolic activity. Analysis of transcription and the number of mitochondrial genomes in S. mansoni shows that the LSU rRNA is more abundant in females than in males. Restriction endonuclease analysis of the fluke mitochondrial LSU rRNA genes suggests the presence of heterogeneous repeated copies in the mitochondrial genome or heterogeneity among individual genomes of mitochondria.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bogenhagen D., Clayton D. A. The number of mitochondrial deoxyribonucleic acid genomes in mouse L and human HeLa cells. Quantitative isolation of mitochondrial deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 25;249(24):7991–7995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feagin J. E., Jasmer D. P., Stuart K. Developmentally regulated addition of nucleotides within apocytochrome b transcripts in Trypanosoma brucei. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):337–345. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90286-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg D. A. Isolation and partial characterization of the Drosophila alcohol dehydrogenase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5794–5798. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Weaver D., Baltimore D., Costantini F. Introduction of a mu immunoglobulin gene into the mouse germ line: specific expression in lymphoid cells and synthesis of functional antibody. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):647–658. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90259-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HsuChen C. C., Kotin R. M., Dubin D. T. Sequences of the coding and flanking regions of the large ribosomal subunit RNA gene of mosquito mitochondria. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Oct 25;12(20):7771–7785. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.20.7771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lie K. J., Basch P. F. The life history of Echinostoma paraensei sp. n. (Trematoda: Echinostomatidae). J Parasitol. 1967 Dec;53(6):1192–1199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd G. M. Energy metabolism and its regulation in the adult liver fluke Fasciola hepatica. Parasitology. 1986 Aug;93(Pt 1):217–248. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000049957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANSOUR T. E. Studies on the carbohydrate metabolism of the liver fluke Fasciola hepatica. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Aug;34:456–464. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90298-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy W. J., Watkins K. P., Agabian N. Identification of a novel Y branch structure as an intermediate in trypanosome mRNA processing: evidence for trans splicing. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):517–525. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90616-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton R. E., Boothroyd J. C. Evidence for trans splicing in trypanosomes. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):527–535. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90617-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurita M., Bieber D., Ringold G., Mansour T. E. Cloning and characterization of a female genital complex cDNA from the liver fluke Fasciola hepatica. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2340–2344. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]