Abstract
Background
Acute lower respiratory tract infections (ALRI) commonly result in fatal outcomes in the young children of Papua New Guinea (PNG). However, comprehensive studies of the viral aetiology of ALRI have not been conducted in PNG for almost 30 years.
Objectives
To determine the viruses associated with ALRI among children living in the PNG highlands using sensitive molecular detection techniques.
Study design
Pernasal swabs were collected routinely between 1 week and 18 months of age and also during episodes of ALRI, as part of a neonatal pneumococcal conjugate vaccine trial. A tandem multiplex real-time PCR assay was used to test for a comprehensive range of respiratory viruses in samples collected from 221 young children. Picornavirus typing was supported by DNA sequence analysis.
Results
Recognized pathogenic respiratory viruses were detected in 198/273 (73%) samples collected from children with no evidence of ALRI and 69/80 (86%) samples collected during ALRI episodes. Human rhinoviruses (HRV) species A, B and C were detected in 152 (56%) samples from non-ALRI children and 50 (63%) samples collected during ALRI episodes. Partial structural region sequences for two new species C rhinoviruses were added to the GenBank database. ALRI was associated with detection of adenovirus species B (p < 0.01) or C (p < 0.05), influenza A (p < 0.0001) or respiratory syncytial virus (p < 0.0001). Multiple viruses were detected more often during ALRI episodes (49%) than when children displayed no symptoms of ALRI (18%) (p < 0.0001).
Conclusions
The burden of infection with respiratory viruses remains significant in young children living in the PNG highlands.
Abbreviations: PNG, Papua New Guinea; ALRI, acute lower respiratory tract infection; HRV, human rhinovirus; HEV, human enterovirus; PCV, pneumococcal conjugate vaccine; STGGB, skim milk-tryptone-glucose-glycerin-broth; HAdV, human adenovirus; HBoV, human bocavirus; HCoV, human coronavirus; PIV, parainfluenza virus; PyV, polyomavirus; RSV, respiratory syncytial virus; MS2, MS2 RNA coliphage; EHV, equine herpesvirus; HMPV, human metapneumovirus; URTI, upper respiratory tract infection; UTR, untranslated region
Keywords: ALRI, Papua New Guinea, Co-infections, Multiplex PCR, Human rhinoviruses
1. Background
Acute lower respiratory infections (ALRI) are the leading cause of death in children, accounting for approximately two million deaths worldwide annually.1 Currently there is limited information on the role of many of the respiratory viruses in lower respiratory tract infections in children. This is particularly true in developing countries where this knowledge is critically important in improving the management and prevention of childhood respiratory infections. Children in the highlands of Papua New Guinea (PNG) suffer an average of 4.3 ALRIs by the age of 18 months.2 Previous studies of respiratory viral infection in young children in PNG relied on the detection of viral antigens by immunofluorescence and traditional cell culture techniques.3, 4 Compared with nucleic acid detection tests, such techniques lack sensitivity for the detection of many respiratory viruses, particularly the recently described human coronaviruses, respiratory polyomaviruses, bocavirus and rhinovirus C.5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 Furthermore, since a number of these viruses have been detected commonly in the respiratory tract of asymptomatic children in developed countries, their pathogenicity is uncertain.11, 12, 13, 14, 15
2. Objectives
We undertook a PCR-based study to identify and characterize respiratory viruses associated with ALRI in young PNG children.
3. Study design
A randomized trial of neonatal 7-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV) was conducted in the Asaro Valley, Eastern Highlands Province, PNG between May 2005 and March 2009.16 As part of this trial, pernasal swabs (rayon-tipped, metal shaft swabs) were collected routinely at 1, 2, 3, 4 weeks and 3, 9 and 18 months of age, and also when children presented with symptoms of ALRI. ALRI was defined as cough with raised respiratory rate (≥60/min at age <1 month, ≥50/min at age 1 to <12 months and ≥40/min at age ≥12 months) in accordance with local recommendations17 based on World Health Organization criteria.18 During the course of the vaccine trial, 1888 pernasal swabs were collected from 319 young children. Swabs were collected into 1 mL of skim milk-tryptone-glucose-glycerin-broth (STGGB)19 and stored at −80 °C. A limited number of those samples collected between January 2006 and August 2008 were shipped to Perth, Western Australia for viral studies. Those samples included 80 from young children with ALRI and 273 from children with no evidence of ALRI. Multiple samples from separate presentations were included from 95 of the 221 young children represented in the study. ALRI and non-ALRI samples were matched for gender, PCV group, age, season of birth and collection date. It was not possible to identify an asymptomatic control group due to the high prevalence of upper respiratory tract symptoms such as rhinorrhoea in this population.2
Nucleic acid was extracted from a 200 μL volume of clinical sample20, 21 and tested for a comprehensive range of respiratory viruses using a tandem multiplex real-time PCR assay20 that detects human adenovirus (HAdV) species B-D; human bocavirus (HBoV); coronaviruses (HCoV) OC43, 229E, HKU1 and NL63; influenza viruses A, B and C; parainfluenzaviruses (PIV) 1–4; KI and WU polyomaviruses (PyV); respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) types A and B; and the MS2 RNA coliphage (MS2) and equine herpes virus 4 (EHV) added to the sample lysis buffer as extraction, amplification and inhibition controls.22, 23 Negative controls were included between every 5 clinical samples and treated as samples for the completion of the assays. Additional PCR assays were directed at the matrix gene of human metapneumovirus (HMPV) and the 5′UTR of picornaviruses,24, 25, 26 and products confirmed by sequence analysis. Further genetic characterization of rhinovirus (HRV) species utilized PCR primers directed at the VP1 and VP4/2 regions of the genome.27, 28, 29
3.1. Statistical analyses
Data were analyzed using the Yates-corrected Chi-square test and p-values <0.05 were considered statistically significant.
4. Results
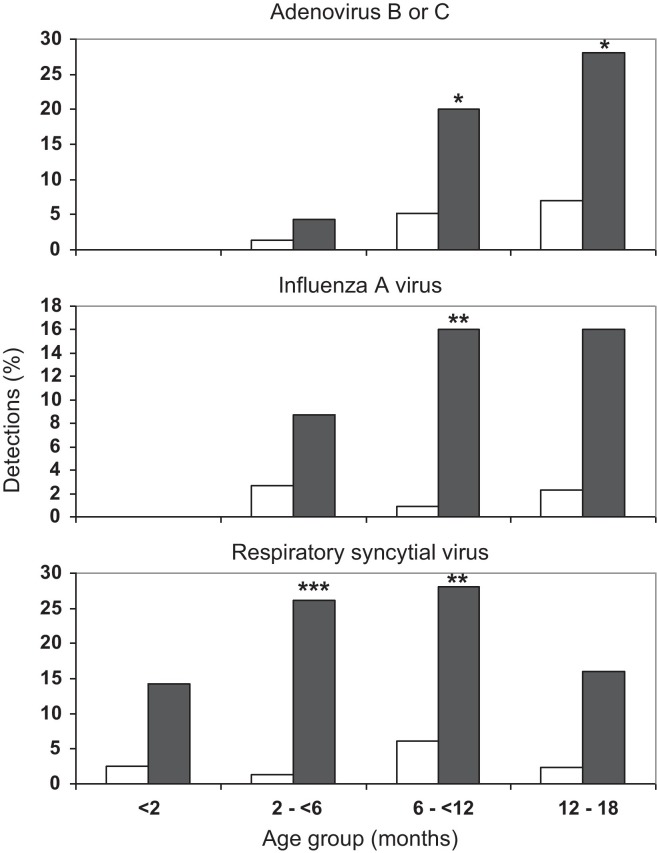
Pernasal swabs (n = 80) were collected from children with an ALRI of 0–24 days’ duration at time of sample collection (median = 3.0 days). A further 273 samples were collected from children with no ALRI symptoms at the time of specimen collection or within one week of that sample collection. These yielded an extensive range of respiratory viruses (Table 1 ). Adenovirus (p < 0.01), influenza A (p < 0.0001) and RSV (p < 0.0001) were associated with ALRI, but significant adenovirus associations were confined to species B (p < 0.01) and C (p < 0.05). When analyzed by age (Fig. 1 ), the association between RSV and ALRI was significant in 2- to <12-month-age groups (p < 0.0005–0.005), adenovirus B or C and ALRI (p < 0.05) in the 6–18 month age groups and influenza A and ALRI (p < 0.005) in the 6- to <12-month-age group.
Table 1.
Viruses detected in pernasal swabs from young children in PNG with and without clinical symptoms of acute lower respiratory tract infection (ALRI).
| Virus detected | non-ALRI (n = 273) | ALRI (n = 80) | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No detections (%) | No detections (%) | ||||
| Any virus | 223 | (82) | 72 | (90) | 0.111 |
| Any recognized pathogenic virusa | 198 | (73) | 69 | (86) | 0.018 |
| Adenovirus B–D | 18 | (6.6) | 14 | (17.5) | 0.006 |
| Adenovirus B | 7 | (2.6) | 8 | (10.0) | 0.010 |
| Adenovirus C | 3 | (1.1) | 5 | (6.2) | 0.022 |
| Adenovirus D | 9 | (3.3) | 1 | (1.2) | 0.557 |
| Bocavirus | 53 | (19.4) | 18 | (22.5) | 0.655 |
| Coronavirus | 31 | (11.4) | 11 | (13.8) | 0.700 |
| Coronavirus-229E | 2 | (0.7) | 0 | (0.0) | – |
| Coronavirus-HKU1 | 6 | (2.2) | 3 | (3.8) | 0.710 |
| Coronavirus-NL63 | 18 | (6.6) | 3 | (3.8) | 0.498 |
| Coronavirus-OC43 | 5 | (1.8) | 5 | (6.2) | 0.087 |
| Enterovirus | 20 | (7.3) | 1 | (1.2) | 0.080 |
| Human metapneumovirus | 1 | (0.4) | 3 | (3.8) | 0.056 |
| Influenza A virus | 4 | (1.5) | 10 | (12.5) | <0.0001 |
| Influenza B virus | 1 | (0.4) | 2 | (2.5) | 0.256 |
| Influenza C virus | 1 | (0.4) | 0 | (0.0) | – |
| Parainfluenza virus 1–4 | 14 | (5.1) | 8 | (10.0) | 0.186 |
| Rhinovirus (HRV) | 152 | (55.7) | 50 | (62.5) | 0.369 |
| HRV-A | 70 | (25.6) | 27 | (33.8) | 0.198 |
| HRV-B | 16 | (5.9) | 2 | (2.5) | 0.361 |
| HRV-C | 56 | (20.5) | 18 | (22.5) | 0.820 |
| Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) | 10 | (3.7) | 18 | (22.5) | <0.0001 |
| RSV A | 8 | (2.9) | 14 | (17.5) | <0.0001 |
| RSV B | 2 | (0.7) | 6 | (7.5) | 0.002 |
| KI polyoma virus | 4 | (1.5) | 0 | (0.0) | 0.612 |
| WU polyoma virus | 75 | (28.2) | 16 | (20.0) | 0.189 |
Number (%) samples in which particular virus was detected.
p Value: Chi-square with Yates’correction (in bold font when significant).
Any recognized pathogenic respiratory virus does not include bocavirus or polyomaviruses.
Fig. 1.
The detection (%) of adenovirus type B or C, influenza virus A and respiratory syncytial virus in children grouped by age (months) with no ALRI symptoms □ (n = 273) and during ALRI episodes ■ (n = 80). Significant associations with disease are marked *p < 0.05, **p < 0.005, ***p < 0.0005.
There was no evidence of an ALRI disease association for bocavirus or the KI and WU polyomaviruses, which were detected in 53 (19%), 4 (1.5%) and 75 (28%) of non-ALRI samples and 18 (22.5%), 0 and 16 (20%) samples from children during episodes of ALRI, respectively.
Picornaviruses were detected in 61.5% of samples, mainly HRV species A and C based on 5′UTR sequencing (Fig. 2 ), including 13 mixed picornavirus infections. Adequate capsid gene sequences were obtained for 150 of the samples: 146 partial VP4/VP2 sequences and 76 partial VP1 sequences. These matched the 5′UTR results for 67 samples with HRV-A, 9 with HRV-B, 48 with HRV-C, 11 with HEV and 13 with mixed picornavirus species. One picornavirus was unable to be assigned to a species as the 5′UTR matched best with HRV-B, the VP1 sequence with HRV-A and the VP2/4 with HEV. Limited sample volume and lack of virus isolates prevented further sequence analysis of these samples. There was no association of picornavirus detection with ALRI when analyzed overall or by individual species (Fig. 2).
Fig. 2.
Picornaviruses detected (%) in samples collected from young children in the absence of ALRI □ (n = 273) and during ALRI episodes ■ (n = 80). HRV, human rhinovirus; HEV, human enterovirus.
Two new species C rhinoviruses were detected from non-ALRI patients and designated as HRV-C47 and HRV-C48 by the Picornaviridae Study Group (http://www.picornastudygroup.com/types/enterovirus/hrv-c.htm). VP1 and VP4/2 coding region sequences were deposited in GenBank under accession numbers JF519760–JF519763.
Sequential samples separated by 0.5–13 months (mean = 4.9 months), were available for 95 children. For one child, HCoV-OC43 was detected in consecutive samples separated by 17 weeks. The later sample was collected when the child had an ALRI and also contained HRV-A and RSV-B. A further 41 children had rhinoviruses detected in consecutive samples. However, except for one child with HRV-A12 detected in two samples collected 3 months apart, all had different HRV types in the different samples.
Multiple viruses were detected in 53/80 (66.2%) ALRI samples and 115/273 (42.2%) non-ALRI samples (p = 0.0002). Combinations that only included viruses shown to be individually pathogenic were detected in 39/80 (48.8%) of ALRI samples and 50/273 (18.3%) of non-ALRI samples (p < 0.0001). In contrast, combinations that only contained HBoV, PyV, HRV, HEV or adenovirus D showed no association with ALRI. The viruses significantly associated with ALRI, namely RSV, influenza A, adenovirus B and adenovirus C, were detected as mixed infections with any other virus in 19/273 (7.0%) of the non-ALRI cases and 29/80 (36.3%) of the ALRI samples (p < 0.0001).
5. Discussion
Influenza A, RSV, adenovirus B and adenovirus C were all common and significant contributors to ALRI in children in PNG. In contrast, the rhinoviruses, bocavirus and respiratory polyomaviruses were not associated with ALRI. For the other pathogens the numbers were too low to draw any conclusions. Mixed infections were also more likely to be associated with ALRI than were single infections, and this effect was strongest when it was a combination of two viruses that individually also showed a significant association with ALRI.
Although only a few sequential samples from individual children were investigated, the same virus was detected from the same child on only two occasions. Conversely, numerous unique rhinoviruses were detected in sequential samples from 41 children. This suggests that the children of PNG are infected with a variety of different respiratory viruses rather than chronic colonization with a particular viral species.
The high rate of respiratory virus detection (>80% of all participants) and the frequent multiple carriage (66% of ALRI and 42% of non-ALRI children) exceeds the detection rates of the most recent study in this setting, conducted almost 30 years ago. In that study virus detection rates of 65% and 43% in nasopharyngeal secretions of children with or without ALRI respectively, were reported with mixed infections in 37% of both healthy and sick children.4 However, fewer viruses were sought (measles, adenovirus, RSV, influenza viruses A and B, parainfluenza types 1 and 3) and cell culture or viral antigens were used for detection. Other studies of ALRI using traditional diagnostic methods have also found low rates in Gambian infants (49% of pneumonia cases and in 19% of the controls),30 and Nigerian children (50% of pneumonia cases, with multiple viral pathogens detected in 16%).31
Studies using PCR in children with symptomatic respiratory disease detect viruses in 44–92% of patients depending on the cohort size and the range of respiratory agents investigated, and multiple viruses in 2–20% of samples.29, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37 A case–control study of Nepalese children aged 2–35 months, reported virus detection rate of 36.5% in pneumonia cases and 7.1% in controls, but excluded rhinoviruses, adenoviruses or coronaviruses.38 In rural Kenya respiratory viruses were detected in 56% of children hospitalized with severe pneumonia, 44% with mild upper respiratory tract infections (URTI) and 28% of controls, but did not include picornaviruses.39 In the same study multiple viruses were detected in 9.7% of samples from children with pneumonia, 6.2% from those with URTI and 1.8% from controls. They found that only RSV, either alone or in combination with other viruses, was significantly associated with either URTI or pneumonia, unlike our study which also found significant associations of influenza A, ADV-B and ADV-C with ALRI. The differences may reflect the lower incidence of these viruses in their population, being 5.8% and 3.8% compared with 12.5% and 17.5% respectively for influenza A and adenoviruses in our study. Furthermore, as they did not speciate their adenoviruses and as we found that only some ADV species were significantly associated with ALRI, it is possible that differences in species distributions may have affected the observed disease association.
Our assay detected some viruses (HBoV, KIPyV and WUPyV) that have uncertain roles as respiratory tract pathogens. We found no association between these viruses and ALRI in this study. Even with exclusion of these viruses, detection rates of potential viral pathogens remained high (86% in children with ALRI and 73% in non-ALRI children), and multiple virus detection rates were 49% for ALRI and 18% for non-ALRI.
The anticipated association of rhinoviruses with ALRI in this population40, 41, 42 was not supported when analyzed either as a group or as individual species. Similarly, other viruses detected were not shown to be associated with ALRI. Only RSV, influenza A, adenovirus B and adenovirus C were significantly associated with ALRI and were detected as mixed infections with any other virus in 7.0% of the non-ALRI cases and 36.3% of the ALRI samples. Since these results are consistent with previous studies using traditional detection methods, this suggests that the newer nucleic acid detection methods do not detect additional significant respiratory pathogens, at least for lower respiratory tract disease. This emphasizes the importance of both accurate characterization and speciation of the viruses, and the inclusion of control populations. There are also data to indicate that measuring viral loads, although technically difficult, may assist in assigning significance.43
A limitation of this study was that we could not exclude children with an upper respiratory tract infection (URTI) since nasal discharge is almost universal in this population.2 Therefore, while many of the viruses detected in this study did not show any association with ALRI, we could not determine whether they may have contributed to URTI. We also recognize that pernasal swabs will miss some lower respiratory tract viral infections, but it would have been both impractical and unethical to obtain bronchial lavage samples from this population.
In the current study, the picornavirus PCR targeted the relatively conserved 5′UTR region of the genome and tentative species and group typing was made using sequence information from that region. As there has been controversy regarding the reliability of rhinovirus speciation using 5′UTR sequences rather than structural gene regions,44, 45 we also attempted sequencing of VP1 and VP4 capsid genes. Partial sequence was obtained for 150/217 samples and, while assignment of particular types requires structural gene sequence information, the discrimination between HRV A, B and C species correlated well with the 5′UTR results.
Two new picornavirus types, HRV-C47 and HRV-C48, were detected in single patients without ALRI but disease associations could not be assessed.
6. Conclusions
There is a high burden of infection with respiratory viruses in the children of the PNG highlands, with mixed infections common, particularly in children with ALRI. The association between ALRI and the detection of adenoviruses, influenza A virus or RSV, suggests that these viruses have a significant health impact. This is important in informing decisions about the value of influenza vaccination in children and emphasizing the importance of infection control measures to prevent spread of these viruses within health care and community settings.
Funding
This work was supported by an International Collaborative Research Grant Scheme grant from the Wellcome Trust and Australian National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) (071613/Z/03/Z). DL received funding from a past (353514) and current NHMRC Program grant (572742) and project Grant (572590).
Competing interests
None.
Ethical approval
Ethical approval to conduct the study was obtained from the Medical Research Advisory Committee of PNG and from the Princess Margaret Hospital Committee for Children Ethics in Perth, Australia.
Acknowledgements
We thank the parents and guardians of the study children, and those involved in specimen collection and collation including Celestine Aho, Agnes Javati, Mildred Lai, Audrey Michael, Pioto Namuigi, Christine Opa, Gerard Saleu and Janet Totave.
References
- 1.Bryce J., Boschi-Pinto C., Shibuya K., Black R.E. WHO estimates of the causes of death in children. Lancet. 2005;365(9465):1147–1152. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)71877-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Smith T., Lehmann D., Coakley C., Spooner V., Alpers M. Relationships between growth and acute lower-respiratory infections in children aged less than 5 y in a highland population of Papua New Guinea. Am J Clin Nutr. 1991;53(4):963–970. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/53.4.963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lehmann D.M., Michael A.M., Omena M.M., Clegg A.M., Lupiwa T.M., Sanders R.C.P. Bacterial and viral etiology of severe infection in children less than three months old in the highlands of Papua New Guinea. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1999;18(10):S42–S49. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199910001-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Phillips P., Lehmann D., Spooner V., Barker J., Tulloch S., Sungu M. Viruses associated with acute lower respiratory tract infections in children from the eastern highlands of Papua New Guinea (1983–1985) SE Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 1990;21(3):373–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Lee W.-M., Kiesner C., Pappas T., Lee I., Grindle K., Jartti T. A diverse group of previously unrecognized human rhinoviruses are common causes of respiratory illnesses in infants. PLoS ONE. 2007;2(10):e966. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Allander T., Tammi M., Eriksson M., Bjerkner A., Tivel-Lindell A. Cloning of a human parvovirus by molecular screening of respiratory tract samples. Proc Nat Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(36):12891–12896. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0504666102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Van Der Hoek L., Pyrc K., Jebbink M.F., Vermeulen-Oost W., Berkhout R.J.M., Wolthers K.C. Identification of a new human coronavirus. Nat Med. 2004;10(4):368–373. doi: 10.1038/nm1024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Woo P.C.Y., Lau S.K.P., Chu C.-M., Chan K.-H., Tsoi H.-W., Huang Y. Characterization and complete genome sequence of a novel coronavirus, coronavirus HKU1, from patients with pneumonia. J Virol. 2005;79(2):884–895. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.2.884-895.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Gaynor A.M., Nissen M.D., Whiley D.M., Mackay I.M., Lambert S.B., Guang W. Identification of a novel polyomavirus from patients with acute respiratory tract infections. PLoS Pathogens. 2007;3(5):e64. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.0030064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Allander T., Andreasson K., Gupta S., Bjerkner A., Bogdanovic G., Persson MaA Identification of a third human polyomavirus. J Virol. 2007;81(8):4130–4136. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00028-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Jartti T., Lee W.M., Pappas T., Evans M., Lemanske R.F., Gern J.E. Serial viral infections in infants with recurrent respiratory illnesses. Eur Respir J. 2008;32:314–320. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00161907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Singleton R.J., Bulkow L.R., Miernyk K., Debyle C., Pruitt L., Hummel K.B. Viral respiratory infections in hospitalized and community control children in Alaska. J Med Virol. 2010;82(7):1282–1290. doi: 10.1002/jmv.21790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Christensen A., Nordbø S.A., Krokstad S., Rognlien A.G.W., Døllner H. Human bocavirus in children: mono-detection, high viral load and viraemia are associated with respiratory tract infection. J Clin Virol. 2010;49(3):158–162. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2010.07.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Norja P., Ubillos I., Templeton K., Simmonds P. No evidence for an association between infections with WU and KI polyomaviruses and respiratory disease. J Clin Virol. 2007;40(4):307–311. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2007.09.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Wattier R.L., Vazquez M., Weibel C., Shapiro E.D., Ferguson D., Landry M.L. Role of human polyomaviruses in respiratory tract disease in young children. Emerg Infect Dis. 2008;14(11):1766–1768. doi: 10.3201/eid1411.080394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Phuanukoonnon S, Reeder JC, Pomat WS, Van Den Biggelaar AHJ, Holt PG, Saleu G, et al. A neonatal pneumococcal conjugate vaccine trial in Papua New Guinea: Study population, methods and operational challenges. PNG Med J53(3–4); in press. [PubMed]
- 17.Shann F., Biddulph J., Duke T. second ed. PNG Department of Health; Port Moresby: 2003. Paediatrics for doctors in Papua New Guinea. A guide for doctors providing health services for children. [Google Scholar]
- 18.World Health Organization. WHO recommended surveillance standards; 1999. Available from: http://www.who.int/csr/resources/publications/surveillance/WHO_CDS_CSR_ISR_99_2_EN [accessed 12.10.11].
- 19.Turner P., Po L., Turner C., Goldblatt D., Nosten F. Detection of respiratory viruses by PCR assay of nasopharyngeal swabs stored in skim milk-tryptone-glucose-glycerol transport medium. J Clin Microbiol. 2011;49(6):2311–2313. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00224-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Chidlow G., Harnett G., Shellam G., Smith D. An economical tandem multiplex real-time PCR technique for the detection of a comprehensive range of respiratory pathogens. Viruses. 2009;1(1):42–56. doi: 10.3390/v1010042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Chidlow G., Harnett G., Williams S., Levy A., Speers D., Smith D.W. Duplex real-time reverse transcriptase PCR assays for rapid detection and identification of pandemic (H1N1) 2009 and seasonal influenza A/H1, A/H3, and B viruses. J Clin Microbiol. 2010;48(3):862–866. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01435-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Dreier J., Stormer M., Kleesiek K. Use of bacteriophage MS2 as an internal control in viral reverse transcription-PCR assays. J Clin Microbiol. 2005;43(9):4551–4557. doi: 10.1128/JCM.43.9.4551-4557.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Druce J., Catton M., Chibo D., Minerds K., Tyssen D., Kostecki R. Utility of a multiplex PCR assay for detecting herpesvirus DNA in clinical samples. J Clin Microbiol. 2002;40(5):1728–1732. doi: 10.1128/JCM.40.5.1728-1732.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Hyypia T., Auvinen P., Maaronen M. Polymerase chain reaction for human picornaviruses. J Gen Virol. 1989;70(Pt 12):3261–3268. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-12-3261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Ireland D.C., Kent J., Nicholson K.G. Improved detection of rhinoviruses in nasal and throat swabs by seminested RT-PCR. J Med Virol. 1993;40(2):96–101. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890400204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Gama R.E., Hughes P.J., Bruce C.B., Stanway G. Polymerase chain reaction amplification of rhinovirus nucleic acids from clinical material. Nucl Acids Res. 1988;16(19):9346. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.19.9346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ledford R.M., Patel N.R., Demenczuk T.M., Watanyar A., Herbertz T., Collett M.S. VP1 sequencing of all human rhinovirus serotypes: Insights into genus phylogeny and susceptibility to antiviral capsid-binding compounds. J Virol. 2004;78(7):3663–3674. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.7.3663-3674.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Mcintyre C.L., Mcwilliam Leitch E.C., Savolainen-Kopra C., Hovi T., Simmonds P. Analysis of genetic diversity and sites of recombination in human rhinovirus species C. J Virol. 2010;84(19):10297–10310. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00962-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Coiras M.T., Aguilar J.C., García M.L., Casas I., Pérez-Breña P. Simultaneous detection of fourteen respiratory viruses in clinical specimens by two multiplex reverse transcription nested-PCR assays. J Med Virol. 2004;72(3):484–495. doi: 10.1002/jmv.20008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Forgie I.M., O’Neill K.P., Lloyd-Evans N., Leinonen M., Campbell H., Whittle H.C. Etiology of acute lower respiratory tract infections in Gambian children: I. Acute lower respiratory tract infections in infants presenting at the hospital. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1991;10(1):33–41. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199101000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Johnson A.F., Osinusi K.F., Aderele W.F., Gbadero D.F., Olaleye O.P., Adeyemi-Doro F.F. Etiologic agents and outcome determinants of community-acquired pneumonia in urban children: a hospital-based study. J Nat Med Assoc. 2008;100(4):370. doi: 10.1016/s0027-9684(15)31269-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Franz A., Adams O., Willems R., Bonzel L., Neuhausen N., Schweizer-Krantz S. Correlation of viral load of respiratory pathogens and co-infections with disease severity in children hospitalized for lower respiratory tract infection. J Clin Virol. 2010;48(4):239–245. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2010.05.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Jin Y., Song J.-R., Xie Z.-P., Gao H.-C., Yuan X.-H., Xu Z.-Q. Prevalence and clinical characteristics of human CoV-HKU1 in children with acute respiratory tract infections in China. J Clin Virol. 2010;49(2):126–130. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2010.07.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Boivin G., Cote S., Dery P., De Serres G., Bergeron M.G. Multiplex real-time PCR assay for detection of influenza and human respiratory syncytial viruses. J Clin Microbiol. 2004;42(1):45–51. doi: 10.1128/JCM.42.1.45-51.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Freymuth F., Vabret A., Cuvillon-Nimal D., Simon S., Dina J., Legrand L. Comparison of multiplex PCR assays and conventional techniques for the diagnostic of respiratory virus infections in children admitted to hospital with an acute respiratory illness. J Med Virol. 2006;78(11):1498–1504. doi: 10.1002/jmv.20725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Lam W.Y., Yeung A.C.M., Tang J.W., Ip M., Chan E.W.C., Hui M. Rapid multiplex nested PCR for detection of respiratory viruses. J Clin Microbiol. 2007;45(11):3631–3640. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00280-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Wang W., Ren P., Sheng J., Mardy S., Yan H., Zhang J. Simultaneous detection of respiratory viruses in children with acute respiratory infection using two different multiplex reverse transcription-PCR assays. J Virol Methods. 2009;162(1–2):40–45. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2009.07.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Mathisen M., Strand T.A., Valentiner-Branth P., Chandyo R.K., Basnet S., Sharma B.N. Respiratory viruses in Nepalese children with and without pneumonia: a case–control study. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2010;29(8):731–735. doi: 10.1097/INF.0b013e3181d9bcce. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Berkley J.A., Munywoki P.M., Ngama M., Kazungu S., Abwao J., Bett A. Viral etiology of severe pneumonia among Kenyan infants and children. JAMA. 2010;303(20):2051–2057. doi: 10.1001/jama.2010.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Ruuskanen O., Lahti E., Jennings L., Murdoch D. Viral pneumonia. Lancet. 2011;377(9773):1264. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)61459-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Hayden F.G. Rhinovirus and the lower respiratory tract. Rev Med Virol. 2004;14(1):17–31. doi: 10.1002/rmv.406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Louie J.K., Roy-Burman A., Guardia-Labar L., Boston E.J., Kiang D., Padilla T. Rhinovirus associated with severe lower respiratory tract infections in children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2009;28(4):337–339. doi: 10.1097/INF.0b013e31818ffc1b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Jansen R.R., Wieringa J., Koekkoek S.M., Visser C.E., Pajkrt D., Molenkamp R. Frequent detection of respiratory viruses without symptoms: toward defining clinically relevant cutoff values. J Clin Microbiol. 2011;49(7):2631–2636. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02094-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Savolainen-Kopra C., Blomqvist S., Smura T., Roivainen M., Hovi T., Kiang D. 5′ noncoding region alone does not unequivocally determine genetic type of human rhinovirus strains. J Clin Microbiol. 2009;47(4):1278–1280. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02130-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Palmenberg A.C., Spiro D., Kuzmickas R., Wang S., Djikeng A., Rathe J.A. Sequencing and analyses of all known human rhinovirus genomes reveal structure and evolution. Science. 2009;324(5923):55–59. doi: 10.1126/science.1165557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]