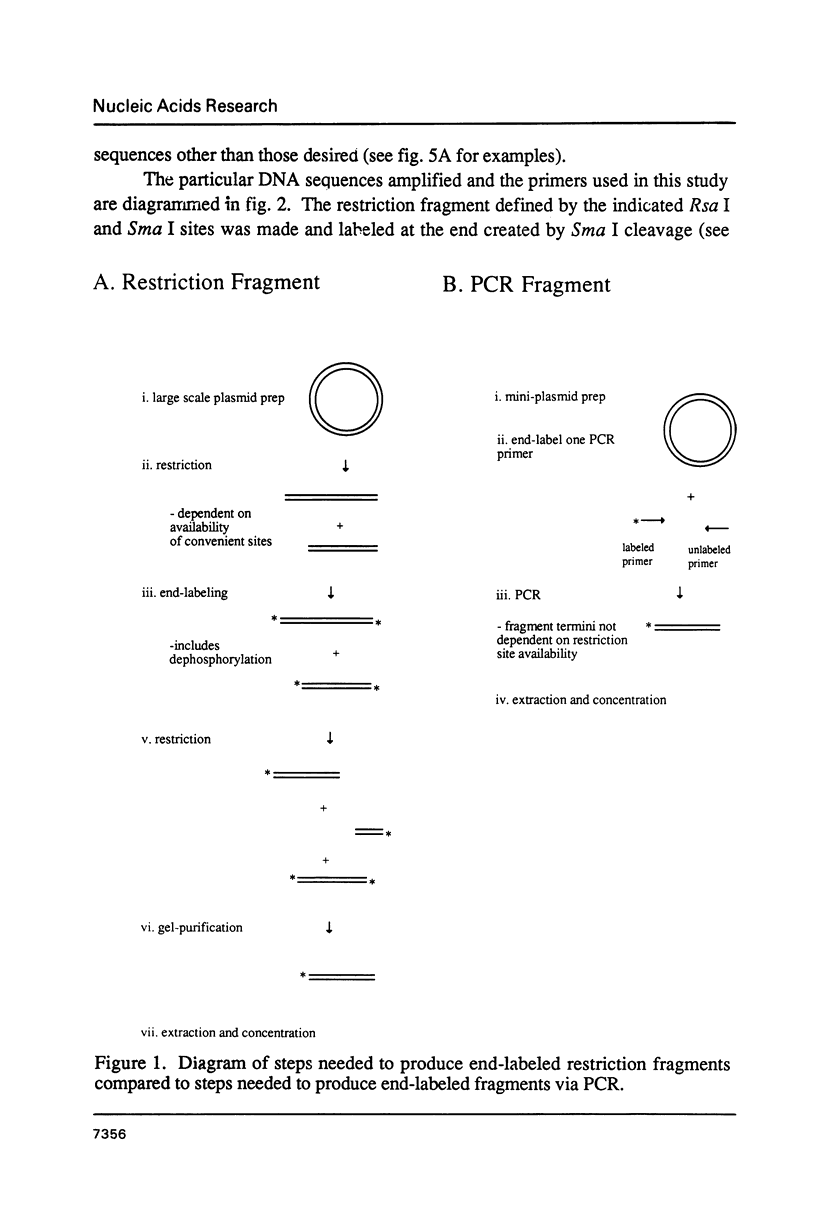
Abstract
Specific, end-labeled DNA fragments can be simply and rapidly prepared using the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Such fragments are suitable for use in DNase I protection footprint assays, chemical sequencing reactions, and for the production and analysis of paused RNA polymerase transcription complexes. Moreover, a general means of introducing a specific mutation at any position along the length of such PCR-generated fragments is described. These procedures, which can circumvent the need for large-scale phage or plasmid growths, preparative gel-electrophoresis and the screening of molecular clones, can facilitate the rapid study of sequence-specific interactions of proteins and DNA. A rapid means of removing excess oligonucleotide primers from completed PCRs is also described.
Full text
PDF





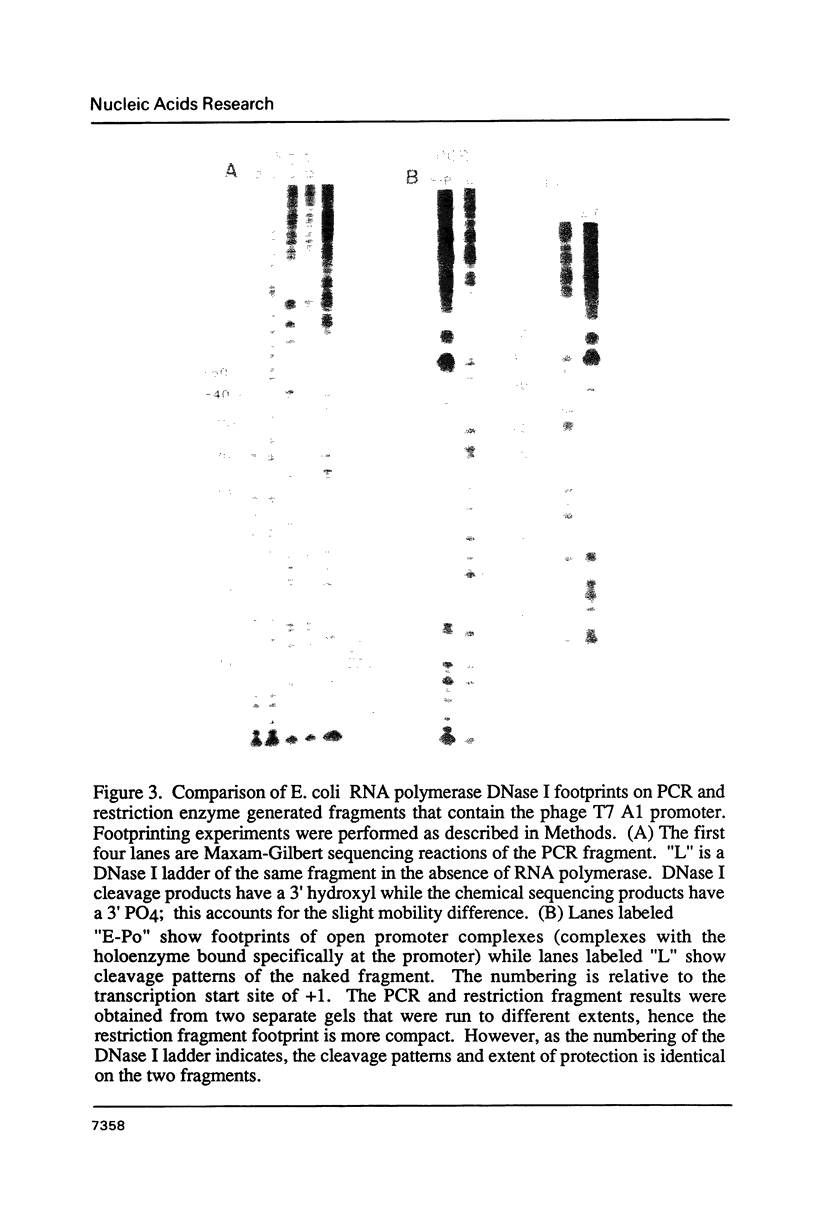

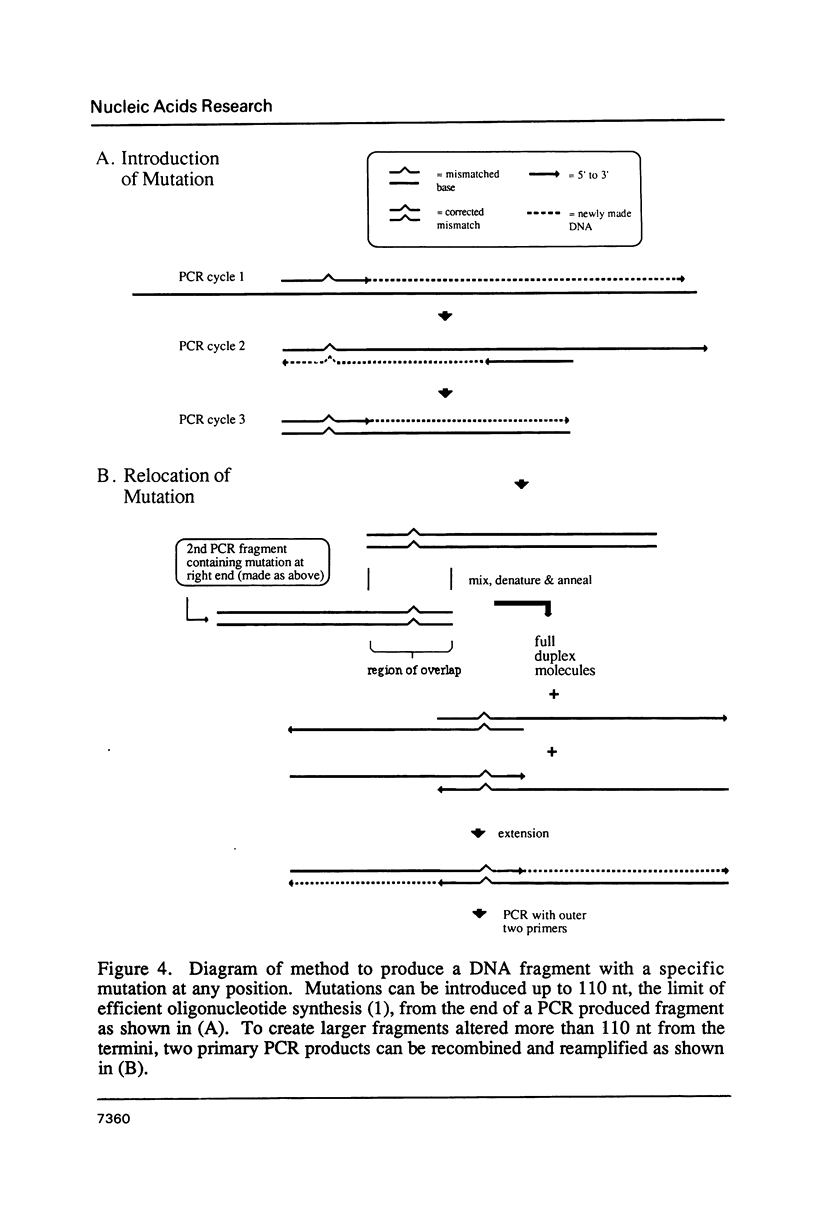

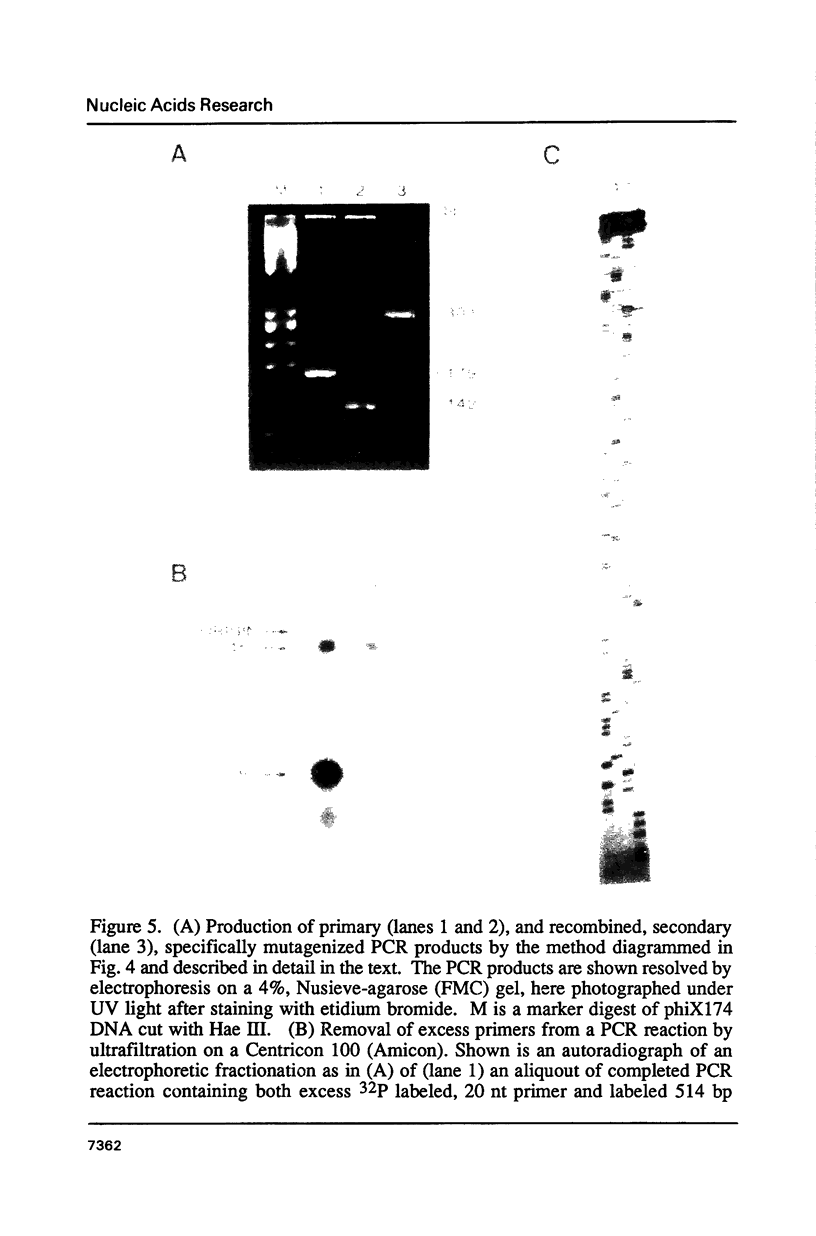





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Briggs M. R., Kadonaga J. T., Bell S. P., Tjian R. Purification and biochemical characterization of the promoter-specific transcription factor, Sp1. Science. 1986 Oct 3;234(4772):47–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3529394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bujard H., Gentz R., Lanzer M., Stueber D., Mueller M., Ibrahimi I., Haeuptle M. T., Dobberstein B. A T5 promoter-based transcription-translation system for the analysis of proteins in vitro and in vivo. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:416–433. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55028-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Nucleotide sequence from the genetic left end of bacteriophage T7 DNA to the beginning of gene 4. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jun 5;148(4):303–330. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90178-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez N., Wiggs J., Chamberlin M. J. A simple procedure for resolution of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase holoenzyme from core polymerase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Aug;182(2):404–408. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90521-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi R., von Beroldingen C. H., Sensabaugh G. F., Erlich H. A. DNA typing from single hairs. Nature. 1988 Apr 7;332(6164):543–546. doi: 10.1038/332543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keohavong P., Kat A. G., Cariello N. F., Thilly W. G. DNA amplification in vitro using T4 DNA polymerase. DNA. 1988 Jan-Feb;7(1):63–70. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin J. R., Krummel B., Chamberlin M. J. Isolation and properties of transcribing ternary complexes of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase positioned at a single template base. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jul 5;196(1):85–100. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90512-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullis K. B., Faloona F. A. Specific synthesis of DNA in vitro via a polymerase-catalyzed chain reaction. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:335–350. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharf S. J., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A. Direct cloning and sequence analysis of enzymatically amplified genomic sequences. Science. 1986 Sep 5;233(4768):1076–1078. doi: 10.1126/science.3461561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz A., Galas D. J. The interaction of RNA polymerase and lac repressor with the lac control region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jan;6(1):111–137. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.1.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U. RNA polymerase unwinds an 11-base pair segment of a phage T7 promoter. Nature. 1979 Jun 14;279(5714):651–652. doi: 10.1038/279651a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straney D. C., Crothers D. M. Intermediates in transcription initiation from the E. coli lac UV5 promoter. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):449–459. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90175-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wosnick M. A., Barnett R. W., Vicentini A. M., Erfle H., Elliott R., Sumner-Smith M., Mantei N., Davies R. W. Rapid construction of large synthetic genes: total chemical synthesis of two different versions of the bovine prochymosin gene. Gene. 1987;60(1):115–127. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90219-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrischnik L. A., Higuchi R. G., Stoneking M., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N., Wilson A. C. Length mutations in human mitochondrial DNA: direct sequencing of enzymatically amplified DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 26;15(2):529–542. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.2.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]