Abstract
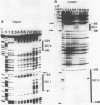
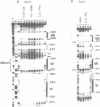
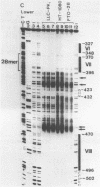
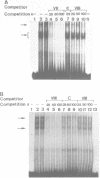
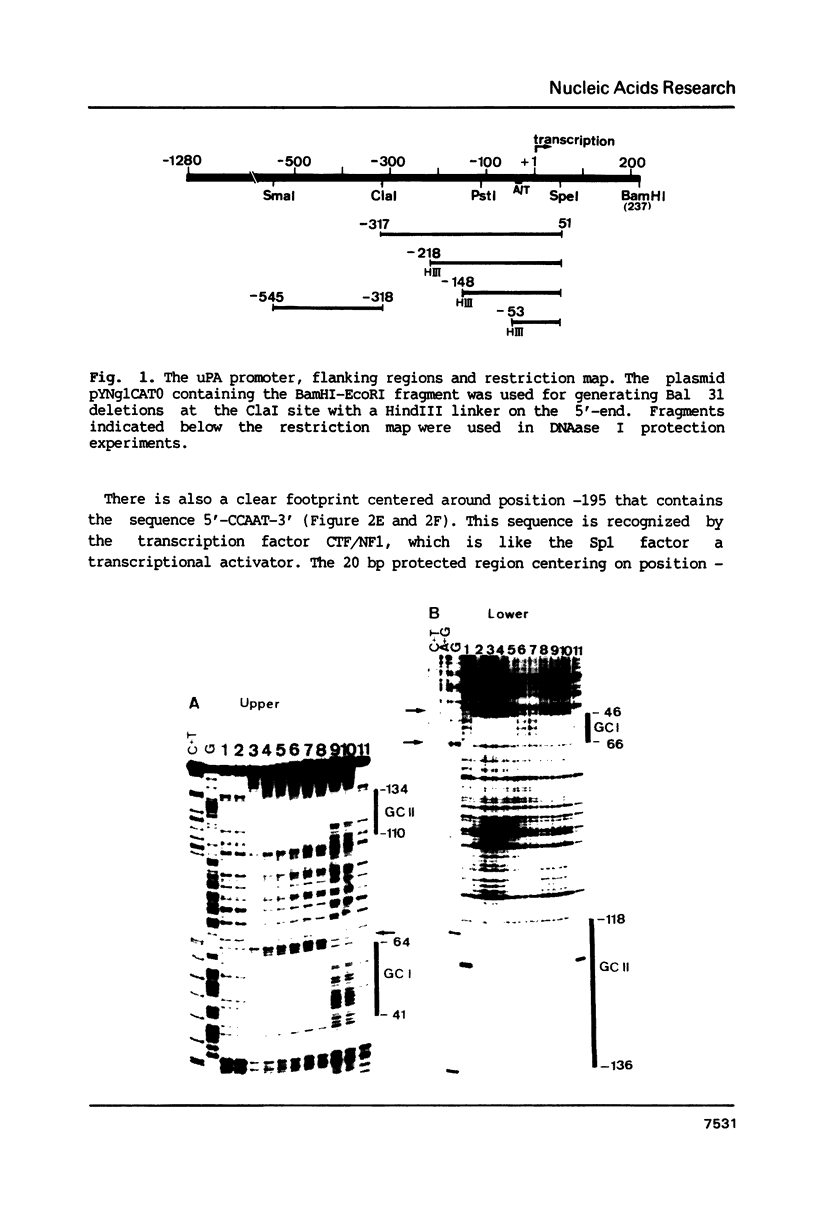
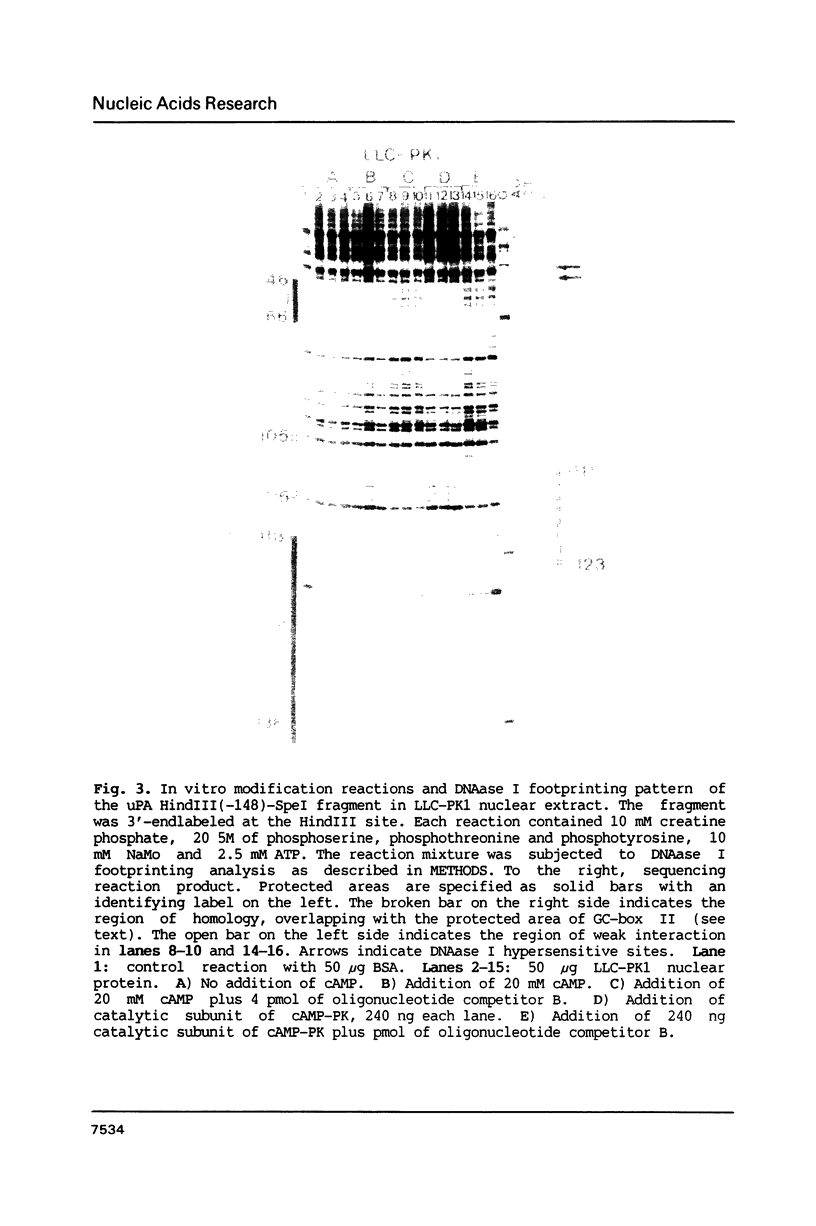
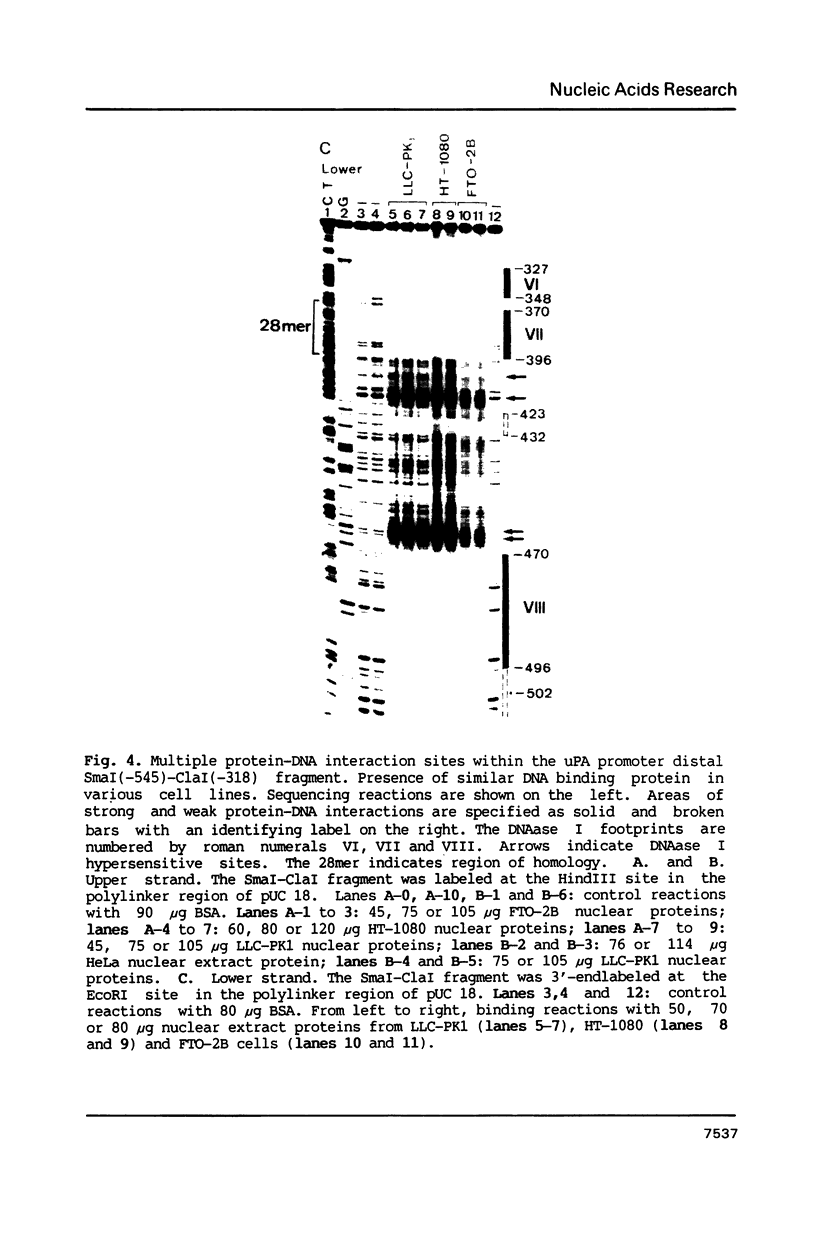
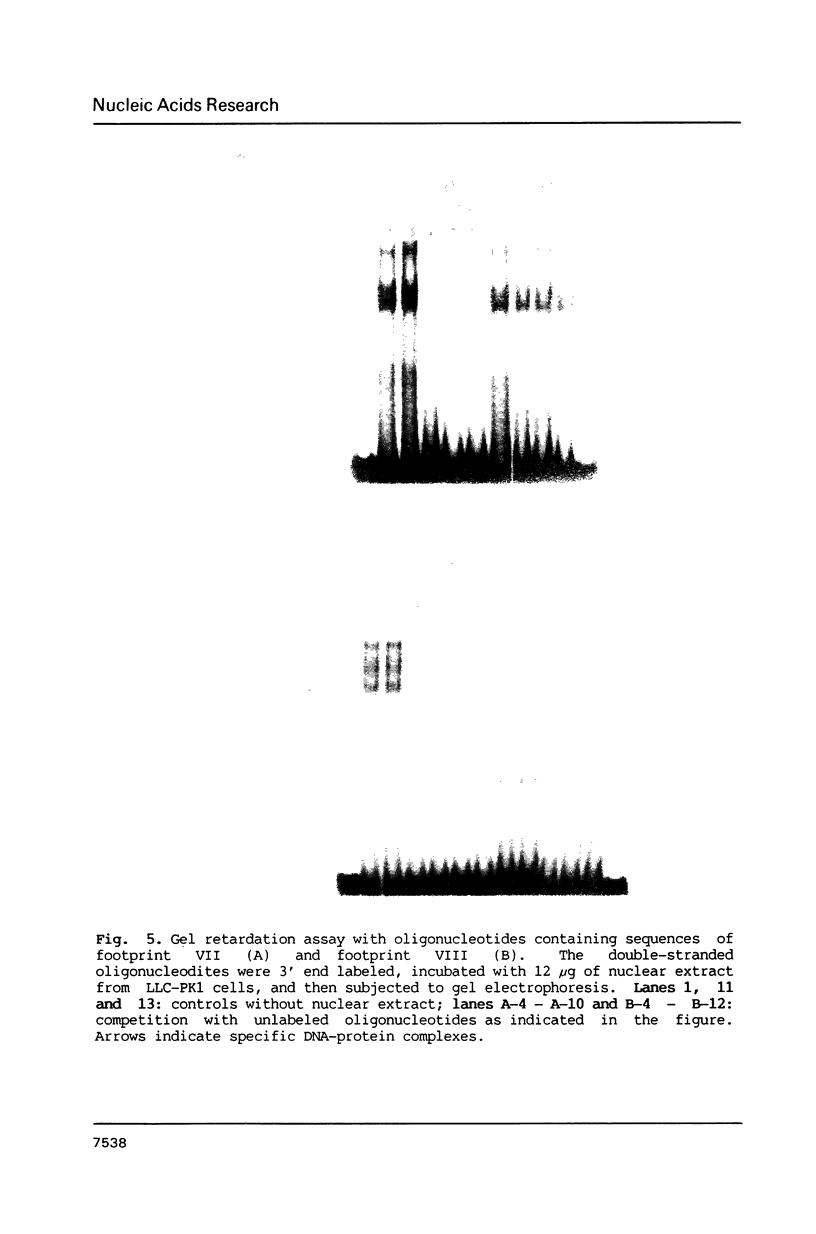
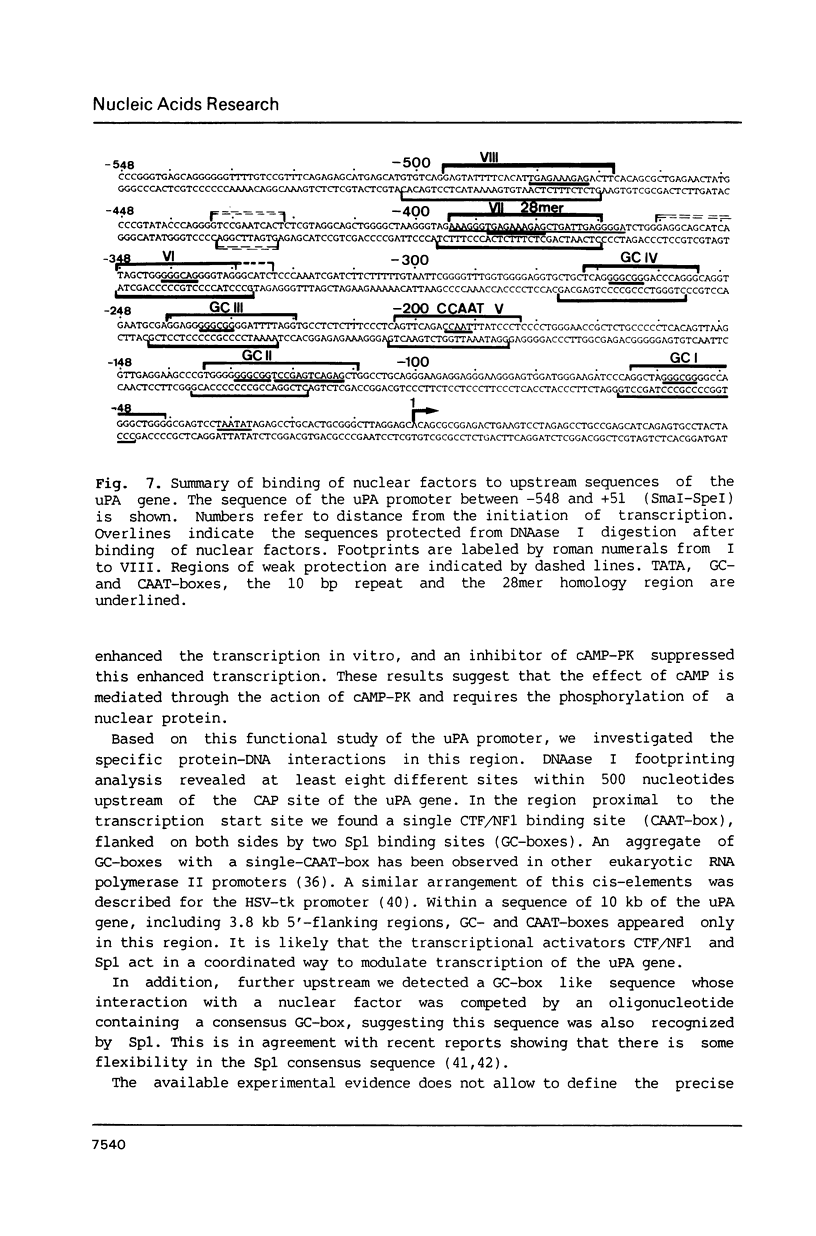
To characterize proteins that bind to the cyclic AMP inducible promoter of the urokinase-type plasminogen activator gene, we performed a DNAase I footprinting analysis. Within 500 nucleotides upstream of the transcription start site we found eight protected regions due to at least four different binding proteins. Among these is a single binding site for the transcription factor CTF/NF1, which is flanked on each side by two conserved binding sites for the transcription factor Sp1. A region at -380, which shares a similarity with sequences observed in the corresponding regions of other cyclic AMP regulated genes, was protected. This binding site contains a sequence of ten nucleotides which is repeated further upstream at -480 and also protected against DNAase I digestion. Comparisons of extracts from four different cell lines revealed that all DNA binding factors are present in nuclei of uPA expressing and nonexpressing cells. Mechanism underlying hormonal regulation of the gene is discussed.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altus M. S., Pearson D., Horiuchi A., Nagamine Y. Inhibition of protein synthesis in LLC-PK1 cells increases calcitonin-induced plasminogen-activator gene transcription and mRNA stability. Biochem J. 1987 Mar 1;242(2):387–392. doi: 10.1042/bj2420387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailly A., Le Page C., Rauch M., Milgrom E. Sequence-specific DNA binding of the progesterone receptor to the uteroglobin gene: effects of hormone, antihormone and receptor phosphorylation. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3235–3241. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04634.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beavo J. A., Bechtel P. J., Krebs E. G. Preparation of homogeneous cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase(s) and its subunits from rabbit skeletal muscle. Methods Enzymol. 1974;38:299–308. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)38046-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker P. B., Gloss B., Schmid W., Strähle U., Schütz G. In vivo protein-DNA interactions in a glucocorticoid response element require the presence of the hormone. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):686–688. doi: 10.1038/324686a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker P. B., Ruppert S., Schütz G. Genomic footprinting reveals cell type-specific DNA binding of ubiquitous factors. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):435–443. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90639-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen B., Steinberg J., Laemmli U. K., Weintraub H. The detection of DNA-binding proteins by protein blotting. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):1–20. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collen D. On the regulation and control of fibrinolysis. Edward Kowalski Memorial Lecture. Thromb Haemost. 1980 Jun 18;43(2):77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comb M., Birnberg N. C., Seasholtz A., Herbert E., Goodman H. M. A cyclic AMP- and phorbol ester-inducible DNA element. 1986 Sep 25-Oct 1Nature. 323(6086):353–356. doi: 10.1038/323353a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danø K., Andreasen P. A., Grøndahl-Hansen J., Kristensen P., Nielsen L. S., Skriver L. Plasminogen activators, tissue degradation, and cancer. Adv Cancer Res. 1985;44:139–266. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayer J. M., Vassalli J. D., Bobbitt J. L., Hull R. N., Reich E., Krane S. M. Calcitonin stimulates plasminogen activator in porcine renal tubular cells: LLC-PK1. J Cell Biol. 1981 Oct;91(1):195–200. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.1.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degen J. L., Estensen R. D., Nagamine Y., Reich E. Induction and desensitization of plasminogen activator gene expression by tumor promoters. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12426–12433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch P. J., Jameson J. L., Habener J. F. Cyclic AMP responsiveness of human gonadotropin-alpha gene transcription is directed by a repeated 18-base pair enhancer. Alpha-promoter receptivity to the enhancer confers cell-preferential expression. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 5;262(25):12169–12174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. The promoter-specific transcription factor Sp1 binds to upstream sequences in the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90210-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granelli-Piperno A., Vassalli J. D., Reich E. Secretion of plasminogen activator by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Modulation by glucocorticoids and other effectors. J Exp Med. 1977 Dec 1;146(6):1693–1706. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.6.1693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofstetter P., Kikinis Z., Altus M. S., Pearson D., Nagamine Y. A new genetic approach for studying hormonal regulation of urokinase-type plasminogen activator gene expression in LLC-PK1 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4535–4541. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Kadonaga J. T., Luciw P. A., Tjian R. Activation of the AIDS retrovirus promoter by the cellular transcription factor, Sp1. Science. 1986 May 9;232(4751):755–759. doi: 10.1126/science.3008338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Kadonaga J. T., Rosenfeld P. J., Kelly T. J., Tjian R. A cellular DNA-binding protein that activates eukaryotic transcription and DNA replication. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):79–89. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90358-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Yamamoto K. R., Tjian R. Two distinct transcription factors bind to the HSV thymidine kinase promoter in vitro. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):559–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killary A. M., Fournier R. E. A genetic analysis of extinction: trans-dominant loci regulate expression of liver-specific traits in hepatoma hybrid cells. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):523–534. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90507-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mak T. W., Rutledge G., Sutherland D. J. Androgen-dependent fibrinolytic activity in a murine mammary carcinoma (Shionogi SC-115 cells) in vitro. Cell. 1976 Feb;7(2):223–226. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90021-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markus G., Camiolo S. M., Kohga S., Madeja J. M., Mittelman A. Plasminogen activator secretion of human tumors in short-term organ culture, including a comparison of primary and metastatic colon tumors. Cancer Res. 1983 Nov;43(11):5517–5525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medcalf R. L., Van den Berg E., Schleuning W. D. Glucocorticoid-modulated gene expression of tissue- and urinary-type plasminogen activator and plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 and 2. J Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;106(3):971–978. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.3.971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miskimins W. K., Roberts M. P., McClelland A., Ruddle F. H. Use of a protein-blotting procedure and a specific DNA probe to identify nuclear proteins that recognize the promoter region of the transferrin receptor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):6741–6744. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.6741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montminy M. R., Sevarino K. A., Wagner J. A., Mandel G., Goodman R. H. Identification of a cyclic-AMP-responsive element within the rat somatostatin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6682–6686. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins D. E., Rohrlich S. T. The role of proteinases in cellular invasiveness. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Dec 29;695(3-4):177–214. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(83)90011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagamine Y., Pearson D., Altus M. S., Reich E. cDNA and gene nucleotide sequence of porcine plasminogen activator. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 21;12(24):9525–9541. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.24.9525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagamine Y., Reich E. Gene expression and cAMP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4606–4610. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagamine Y., Sudol M., Reich E. Hormonal regulation of plasminogen activator mRNA production in porcine kidney cells. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1181–1190. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90301-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa J., von der Ahe D., Pearson D., Hemmings B. A., Shibahara S., Nagamine Y. Transcriptional regulation of a plasminogen activator gene by cyclic AMP in a homologous cell-free system. Involvement of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase in transcriptional control. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 15;263(5):2460–2468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ossowski L., Reich E. Antibodies to plasminogen activator inhibit human tumor metastasis. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):611–619. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90093-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson H., Reeves B., Brown R., Hall A., Furth M., Bos J., Jones P., Marshall C. Activated N-ras controls the transformed phenotype of HT1080 human fibrosarcoma cells. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):803–812. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90103-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saksela O., Hovi T., Vaheri A. Urokinase-type plasminogen activator and its inhibitor secreted by cultured human monocyte-macrophages. J Cell Physiol. 1985 Jan;122(1):125–132. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041220119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinomiya T., Scherer G., Schmid W., Zentgraf H., Schütz G. Isolation and characterization of the rat tyrosine aminotransferase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1346–1350. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short J. M., Wynshaw-Boris A., Short H. P., Hanson R. W. Characterization of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) promoter-regulatory region. II. Identification of cAMP and glucocorticoid regulatory domains. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9721–9726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C., Van der Westhuyzen D. R., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S., Russell D. W. Three direct repeats and a TATA-like sequence are required for regulated expression of the human low density lipoprotein receptor gene. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10773–10779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassalli J. D., Hamilton J., Reich E. Macrophage plasminogen activator: modulation of enzyme production by anti-inflammatory steroids, mitotic inhibitors, and cyclic nucleotides. Cell. 1976 Jun;8(2):271–281. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90011-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Weinstein I. B. Tumour promotor induces plasminogen activator. Nature. 1976 Jan 22;259(5540):232–233. doi: 10.1038/259232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willmann T., Beato M. Steroid-free glucocorticoid receptor binds specifically to mouse mammary tumour virus DNA. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):688–691. doi: 10.1038/324688a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wynshaw-Boris A., Lugo T. G., Short J. M., Fournier R. E., Hanson R. W. Identification of a cAMP regulatory region in the gene for rat cytosolic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP). Use of chimeric genes transfected into hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):12161–12169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von der Ahe D., Renoir J. M., Buchou T., Baulieu E. E., Beato M. Receptors for glucocorticosteroid and progesterone recognize distinct features of a DNA regulatory element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2817–2821. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]