Abstract
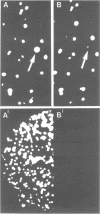
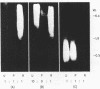
The major portion of the eukaryotic genome consists of various categories of repetitive DNA sequences which have been studied with respect to their base compositions, organizations, copy numbers, transcription and species specificities; their biological roles, however, are still unclear. A novel quality of a highly repetitive mouse DNA sequence is described which points to a functional role: All copies (approximately 50,000 per haploid genome) of this DNA sequence reside on genomic Alu I DNA fragments each associated with nuclear polypeptides that are not released from DNA by proteinase K, SDS and phenol extraction. By this quality the repetitive DNA sequence is classified as a member of the sub-set of DNA sequences involved in tight DNA-polypeptide complexes which have been previously shown to be components of the subnuclear structure termed 'nuclear matrix'. From these results it has to be concluded that the repetitive DNA sequence characterized in this report represents or comprises a signal for a large number of site specific attachment points of the mouse genome in the nuclear matrix.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avramova Z., Tsanev R. Stable DNA-protein complexes in eukaryotic chromatin. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jul 20;196(2):437–440. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90704-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodnar J. W., Jones C. J., Coombs D. H., Pearson G. D., Ward D. C. Proteins tightly bound to HeLa cell DNA at nuclear matrix attachment sites. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Sep;3(9):1567–1579. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.9.1567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capesius I., Krauth W., Werner D. Proteinase K-resistant and alkali-stably bound proteins in higher plant DNA. FEBS Lett. 1980 Feb 11;110(2):184–186. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80068-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockerill P. N., Garrard W. T. Chromosomal loop anchorage of the kappa immunoglobulin gene occurs next to the enhancer in a region containing topoisomerase II sites. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):273–282. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90761-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coombs D. H., Robinson A. J., Bodnar J. W., Jones C. J., Pearson G. D. Detection of covalent DNA-protein complexes: the adenovirus DNA-terminal protein complex and HeLa DNA-protein complexes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):741–753. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross-Bellard M., Oudet P., Chambon P. Isolation of high-molecular-weight DNA from mammalian cells. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jul 2;36(1):32–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02881.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennighausen L., Lubon H. Interaction of protein with DNA in vitro. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:721–735. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52076-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek W. R., Schmid C. W. Repetitive sequences in eukaryotic DNA and their expression. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:813–844. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.004121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keppel F. Transcribed human ribosomal RNA genes are attached to the nuclear matrix. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jan 5;187(1):15–21. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90402-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirov N., Djondjurov L., Tsanev R. Nuclear matrix and transcriptional activity of the mouse alpha-globin gene. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 15;180(3):601–614. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90029-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krauth W., Werner D. Analysis of the most tightly bound proteins in eukaryotic DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Oct 25;564(3):390–401. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(79)90030-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käs E., Chasin L. A. Anchorage of the Chinese hamster dihydrofolate reductase gene to the nuclear scaffold occurs in an intragenic region. J Mol Biol. 1987 Dec 20;198(4):677–692. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90209-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu X., Kopun M., Werner D. Cell cycle phase-specific cDNA libraries reflecting phase-specific gene expression of Ehrlich ascites cells growing in vivo. Exp Cell Res. 1988 Jan;174(1):199–214. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(88)90155-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto L. H. Enrichment of satellite DNA on the nuclear matrix of bovine cells. Nature. 1981 Dec 3;294(5840):481–482. doi: 10.1038/294481a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirkovitch J., Mirault M. E., Laemmli U. K. Organization of the higher-order chromatin loop: specific DNA attachment sites on nuclear scaffold. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):223–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90208-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuer-Nitsche B., Werner D. Sub-set characteristics of DNA sequences involved in tight DNA/polypeptide complexes and their homology to nuclear matrix DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Aug 31;147(1):335–339. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80126-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuer B., Plagens U., Werner D. Phosphodiester bonds between polypeptides and chromosomal DNA. J Mol Biol. 1983 Feb 25;164(2):213–235. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90076-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuer B., Werner D. Screening of isolated DNA for sequences released from anchorage sites in nuclear matrix. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jan 5;181(1):15–25. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90321-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pietras D. F., Bennett K. L., Siracusa L. D., Woodworth-Gutai M., Chapman V. M., Gross K. W., Kane-Haas C., Hastie N. D. Construction of a small Mus musculus repetitive DNA library: identification of a new satellite sequence in Mus musculus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Oct 25;11(20):6965–6983. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.20.6965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plagens U. Effect of salt-treatment on manually isolated polytene chromosomes from Chironomus tentans. Chromosoma. 1978 Aug 21;68(1):1–19. doi: 10.1007/BF00330369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S. V., Mantieva V. L., Georgiev G. P. DNA adjacent to attachment points of deoxyribonucleoprotein fibril to chromosomal axial structure is enriched in reiterated base sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Dec;5(12):4737–4751. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.12.4737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rest R., Müller M., Werner D. Disintegration of nucleoskeletal elements by metrizamide/2 M salt isopyknic centrifugation. Exp Cell Res. 1986 Nov;167(1):144–156. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(86)90212-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner D., Chanpu S., Müller M., Spiess E., Plagens U. Antibodies to the most tightly bound proteins in eukaryotic DNA. Formation of immuno-complexes with 'nuclear matrix' components. Exp Cell Res. 1984 Apr;151(2):384–395. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(84)90389-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner D., Rest R. Radiolabelling of DNA/polypeptide complexes in isolated bulk DNA and in residual nuclear matrix DNA by nick-translation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Aug 31;147(1):340–345. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80127-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]