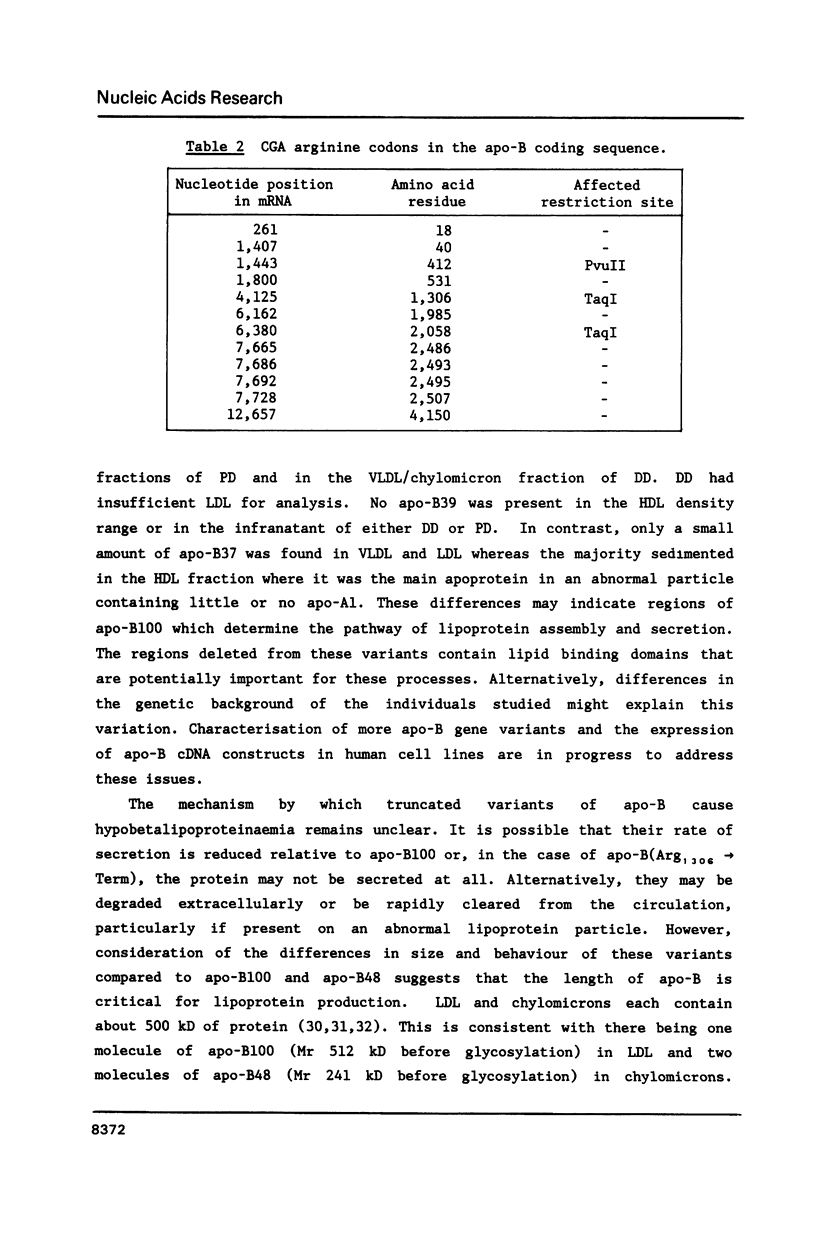
Abstract
Familial hypobetalipoproteinaemia is a rare autosomal dominant disorder in which levels of apo-B-containing plasma lipoproteins are approximately half-normal in heterozygotes and virtually absent in homozygotes. Here we describe mutations of the apo-B gene that cause two different truncated variants of apo-B in unrelated individuals with hypobetalipoproteinaemia. One variant, apo-B(His1795----Met-Trp-Leu-Val-Thr-Term) is predicted to be 1799 amino acids long and arises from deletion of a single nucleotide (G) from leucine codon 1794. This protein was found at low levels in very low density and low density lipoprotein fractions in the blood. The second, shorter variant, apo-B(Arg1306----Term), is caused by mutation of a CpG dinucleotide in arginine codon 1306 converting it to a stop codon and predicting a protein of 1305 residues. The product of this allele could not be detected in the circulation. The differences in size and behaviour of these two variants compared to apo-B100 or apo-B48 point to domains that may be important for the assembly, secretion or stability of apo-B-containing lipoproteins.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhattacharya S., Redgrave T. G. The content of apolipoprotein B in chylomicron particles. J Lipid Res. 1981 Jul;22(5):820–828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardin A. D., Witt K. R., Chao J., Margolius H. S., Donaldson V. H., Jackson R. L. Degradation of apolipoprotein B-100 of human plasma low density lipoproteins by tissue and plasma kallikreins. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8522–8528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. H., Habib G., Yang C. Y., Gu Z. W., Lee B. R., Weng S. A., Silberman S. R., Cai S. J., Deslypere J. P., Rosseneu M. Apolipoprotein B-48 is the product of a messenger RNA with an organ-specific in-frame stop codon. Science. 1987 Oct 16;238(4825):363–366. doi: 10.1126/science.3659919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper D. N., Youssoufian H. The CpG dinucleotide and human genetic disease. Hum Genet. 1988 Feb;78(2):151–155. doi: 10.1007/BF00278187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deckelbaum R. J., Shipley G. G., Small D. M. Structure and interactions of lipids in human plasma low density lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 25;252(2):744–754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dullaart R. P., Speelberg B., Schuurman H. J., Milne R. W., Havekes L. M., Marcel Y. L., Geuze H. J., Hulshof M. M., Erkelens D. W. Epitopes of apolipoprotein B-100 and B-48 in both liver and intestine. Expression and evidence for local synthesis in recessive abetalipoproteinemia. J Clin Invest. 1986 Nov;78(5):1397–1404. doi: 10.1172/JCI112727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elovson J., Jacobs J. C., Schumaker V. N., Puppione D. L. Molecular weights of apoprotein B obtained from human low-density lipoprotein (apoprotein B-PI) and from rat very low density lipoprotein (apoprotein B-PIII). Biochemistry. 1985 Mar 12;24(6):1569–1578. doi: 10.1021/bi00327a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glickman R. M., Green P. H., Lees R. S., Lux S. E., Kilgore A. Immunofluorescence studies of apolipoprotein B in intestinal mucosa. Absence in abetalipoproteinemia. Gastroenterology. 1979 Feb;76(2):288–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., EDER H. A., BRAGDON J. H. The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1345–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI103182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardman D. A., Gustafson A., Schilling J. W., Donaldson V. H., Kane J. P. Scission of human apolipoprotein B-100 by kallikrein: characterization of the cleavage site. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jun 13;137(2):821–825. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)91153-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi K., Hospattankar A. V., Law S. W., Meglin N., Cortright J., Brewer H. B., Jr Human apolipoprotein B (apoB) mRNA: identification of two distinct apoB mRNAs, an mRNA with the apoB-100 sequence and an apoB mRNA containing a premature in-frame translational stop codon, in both liver and intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1772–1776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knott T. J., Pease R. J., Powell L. M., Wallis S. C., Rall S. C., Jr, Innerarity T. L., Blackhart B., Taylor W. H., Marcel Y., Milne R. Complete protein sequence and identification of structural domains of human apolipoprotein B. Nature. 1986 Oct 23;323(6090):734–738. doi: 10.1038/323734a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel L. M., Smith K. D., Boyer S. H., Borgaonkar D. S., Wachtel S. S., Miller O. J., Breg W. R., Jones H. W., Jr, Rary J. M. Analysis of human Y-chromosome-specific reiterated DNA in chromosome variants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1245–1249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lackner K. J., Monge J. C., Gregg R. E., Hoeg J. M., Triche T. J., Law S. W., Brewer H. B., Jr Analysis of the apolipoprotein B gene and messenger ribonucleic acid in abetalipoproteinemia. J Clin Invest. 1986 Dec;78(6):1707–1712. doi: 10.1172/JCI112766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy E., Marcel Y. L., Milne R. W., Grey V. L., Roy C. C. Absence of intestinal synthesis of apolipoprotein B-48 in two cases of abetalipoproteinemia. Gastroenterology. 1987 Nov;93(5):1119–1126. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90577-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W., Innerarity T. L., Rall S. C., Jr, Weisgraber K. H. Plasma lipoproteins: apolipoprotein structure and function. J Lipid Res. 1984 Dec 1;25(12):1277–1294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milne R. W., Blanchette L., Théolis R., Jr, Weech P. K., Marcel Y. L. Monoclonal antibodies distinguish between lipid-dependent and reversible conformational states of human apolipoprotein B. Mol Immunol. 1987 May;24(5):435–447. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(87)90017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell L. M., Wallis S. C., Pease R. J., Edwards Y. H., Knott T. J., Scott J. A novel form of tissue-specific RNA processing produces apolipoprotein-B48 in intestine. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):831–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90510-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. C., Mann D. A. Rapid transfer of DNA from agarose gels to nylon membranes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7207–7221. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. S., Gregg R. E., Law S. W., Monge J. C., Grant S. M., Higuchi K., Triche T. J., Jefferson J., Brewer H. B., Jr Homozygous hypobetalipoproteinemia: a disease distinct from abetalipoproproteinemia at the molecular level. J Clin Invest. 1988 Feb;81(2):590–595. doi: 10.1172/JCI113357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. The human apolipoprotein genes. Oxf Surv Eukaryot Genes. 1987;4:168–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang C. Y., Chen S. H., Gianturco S. H., Bradley W. A., Sparrow J. T., Tanimura M., Li W. H., Sparrow D. A., DeLoof H., Rosseneu M. Sequence, structure, receptor-binding domains and internal repeats of human apolipoprotein B-100. Nature. 1986 Oct 23;323(6090):738–742. doi: 10.1038/323738a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S. G., Bertics S. J., Curtiss L. K., Dubois B. W., Witztum J. L. Genetic analysis of a kindred with familial hypobetalipoproteinemia. Evidence for two separate gene defects: one associated with an abnormal apolipoprotein B species, apolipoprotein B-37; and a second associated with low plasma concentrations of apolipoprotein B-100. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jun;79(6):1842–1851. doi: 10.1172/JCI113026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S. G., Bertics S. J., Curtiss L. K., Witztum J. L. Characterization of an abnormal species of apolipoprotein B, apolipoprotein B-37, associated with familial hypobetalipoproteinemia. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jun;79(6):1831–1841. doi: 10.1172/JCI113025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S. G., Peralta F. P., Dubois B. W., Curtiss L. K., Boyles J. K., Witztum J. L. Lipoprotein B37, a naturally occurring lipoprotein containing the amino-terminal portion of apolipoprotein B100, does not bind to the apolipoprotein B,E (low density lipoprotein) receptor. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16604–16611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]