Abstract
Much attention has focused on the dramatic expansion of the forebrain, particularly the neocortex, as the neural substrate of cognitive evolution. However, though relatively small, the cerebellum contains about four times more neurons than the neocortex. I show that commonly used comparative measures such as neocortex ratio underestimate the contribution of the cerebellum to brain evolution. Once differences in the scaling of connectivity in neocortex and cerebellum are accounted for, a marked and general pattern of correlated evolution of the two structures is apparent. One deviation from this general pattern is a relative expansion of the cerebellum in apes and other extractive foragers. The confluence of these comparative patterns, studies of ape foraging skills and social learning, and recent evidence on the cognitive neuroscience of the cerebellum, suggest an important role for the cerebellum in the evolution of the capacity for planning, execution and understanding of complex behavioural sequences—including tool use and language. There is no clear separation between sensory–motor and cognitive specializations underpinning such skills, undermining the notion of executive control as a distinct process. Instead, I argue that cognitive evolution is most effectively understood as the elaboration of specialized systems for embodied adaptive control.
Keywords: brain, neocortex, cerebellum, evolution, cognition, language
1. Introduction
The idea that there was likely to have been a wide variety of selection pressures on cognitive abilities, and a corresponding variety of neural evolutionary responses [1–3], has been rather lost in the current enthusiasm for monolithic explanations for the evolution of large brains, including social intelligence [4], behavioural flexibility [5] and general intelligence [6,7]. These general explanations are associated with the search for a single comparative brain measure that best reflects cognitive ability, such as neocortex ratio [8,9], ‘executive brain’ ratio [10,11] and even whole brain size [12,13]. A relatively strong correlation between the putatively critical behavioural variable and a particular comparative brain measure is sometimes taken to suggest that the measure identified does indeed most effectively capture the neurological basis of cognitive evolution [8,13].
Empirically, there is a problem with this approach: comparative studies have not produced a single, unified picture of the relationship between such measures and behaviours. Healy & Rowe [14, p. 456] summarized the picture as one of a ‘bewildering array of correlations between brain size and behavioural traits’, a picture which shows little sign of resolving. For example, while Dunbar & Shultz [9] argue that the central aspect of primate brain evolution is the correlation between neocortex size and social group size, Reader et al. [11] find that neocortex and ‘executive brain’ size correlate strongly with a composite measure of general intelligence that cuts across the social/non-social domain, and that this composite measure does not correlate with social group size.
There are also theoretical reasons to question the underlying assumption that intelligence evolved in a unitary way and can in principle be measured by a single, ideal comparative brain measure. First, which measure achieves the strongest correlation with a putatively important aspect of behaviour should not be the sine qua non for deciding how to measure cognitive evolution. Indeed, it is circular to argue that a particular measure is ideal because it most strongly supports a hypothesis. Second, organisms are subject to a wide variety of challenges. For example, they may be aquatic or terrestrial; they may be active at night or by day; they may be more or less social; they may graze on abundant plants, search for rare fruits, or hunt for prey; they may learn complex songs; they may store food and recover it by memory. Each of these and other dimensions of behavioural ecology has been shown to correlate with the brain size and/or with a specific and relevant aspect of brain structure [14–20]. And studies of phylogenetic variation in the brain structure of mammals and birds indicate not one or two dimensions of variation but many [21–24].
A further problem is that critical assumptions underlying the use of brain size indices remain largely untested. The volume of a brain region is potentially related to cognitive capacities to the extent that it correlates with more functionally meaningful variables such as numbers of neurons and synapses. Recent works suggest that the relationship between volume and neuron number or density varies between taxonomic groups and between brain structures [25,26]. Such variability potentially presents problems for inferring functional consequences from relative size measures such as volumetric ratios between one structure and another. Here I examine the consequences of volumetric ratios for relative numbers of neurons in the neocortex and cerebellum, and I argue that an excessive emphasis on the neocortex has obscured important patterns in brain evolution and led to an unwarranted neglect of the cerebellum. I then re-examine phylogenetic correlates of neocortex and cerebellum size.
In the light of these results, I develop a synthesis of the comparative, anatomical and functional neuroscience data. This synthesis stresses the unity of sensory–motor and cognitive evolution. Classically, distinctions are made between cognition, as a process of interpreting and integrating information about the outside world, the perceptual information that this process is about, and the motor commands that represent the output of cognitive processes [27]. More recently, these distinctions have been broken down by the recognition that cognition is best conceived as a set of processes mediating the adaptive control of bodies in environments: the concept of embodied cognition [28–33]. This perspective suggests that ‘a key aspect of human cognition is … the adaptation of sensory-motor brain mechanisms to serve new roles in reason and language, while retaining their original function as well.’ [34, p. 456]. Here I argue that understanding brain evolution both contributes to and is benefited by this perspective.
2. Methods
I use phylogenetic comparative analyses of brain component volumes and neuron numbers to test hypotheses about the evolutionary determinants and cognitive consequences of brain structure evolution. Analyses include broad patterns of brain evolution across mammalian orders and more focused analyses of behavioural correlates within primates. In the absence of direct observation of evolutionary processes, phylogenetic comparative analysis provides a powerful technique for investigating evolutionary patterns and processes [35] such as correlated trait evolution. A variety of methods now exist, but the underlying rationale of each is that combining information on phylogenetic relationships among species with data on their phenotypic traits allows one to statistically model the evolution of those traits along the branches of the tree representing their relationships [35]. To assess how different brain and behavioural traits evolved in relation to one another, I used phylogenetic generalized least squares, which incorporates phylogeny into statistical models [36–38]. Further details of this method and data used are provided in the electronic supplementary material. Results are presented in the context of discussion of a series of key questions, and embedded where appropriate to the discussion rather than consolidated in a single results section.
3. Is the neocortex the ‘intelligent’ bit of the brain?
The brain structure most often identified with ‘higher’ cognitive functions is the neocortex [39], having been described, for example, as ‘the crowning achievement of evolution and the biological substrate of human mental prowess’ [40]. The assumption that the neocortex is the place to look for evidence about cognitive evolution drives much comparative research and even the selection of regions of interest in the study of fossil hominin endocasts [41].
Why this focus on the neocortex? One reason is undoubtedly the simple observation that it is disproportionately large in large-brained species. In small-brained mammals such as shrews the neocortex comprises as little as 15 per cent of brain volume, whereas in monkeys the corresponding figure is about 65–75 per cent and in humans it is about 80 per cent [42,43]. The correlation between brain size and neocortical proportion (or ratio) may, however, have more to do with allometric scaling than with cognitive selection pressures. Cortical proportions are generally high in large-bodied species such as sea lions (66%) [44], camels (71%) [45] and sperm whales (87%) [45]. Whilst it might be tempting to speculate on the hitherto unappreciated intelligence of these species, the most parsimonious explanation is that they are just large animals. Indeed, controlling for phylogenetic effects, there is a strong correlation between body size and proportion of the brain that is neocortex (phylogenetic least squares (PGLS); λ = 0.92, t = 14.23, p < 0.0001). There is no such correlation for the cerebellum (λ = 0.93, t = 1.25, p = 0.21).
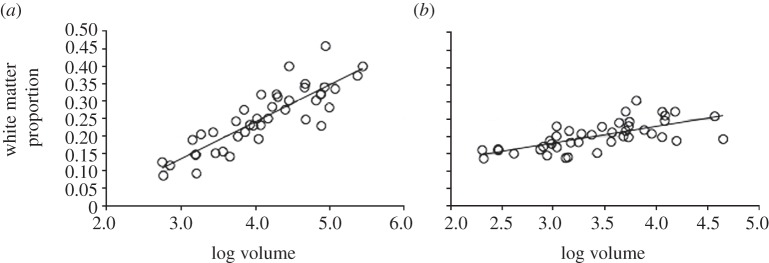
Why does the cortex balloon in proportional size as body size (and overall brain size) increase? Apparently because of a need to devote increasing brain space to making cortical connections: larger cortices are increasingly made up of white rather than grey matter (figure 1a, see also [46,47]). In the cerebellum, there is a much less steep increase in white matter volume with overall size (figure 1b; and see [47]). Hence connectivity scales in different ways in these two structures.
Figure 1.
White matter proportion increases more steeply with size in neocortex than in cerebellum. The proportion of volume of (a) neocortex and (b) cerebellum that is white matter, plotted against volume of each structure (mm3). The graphs plot data for the same species and the PGLS slopes are significantly different (see text).
The reasons for this difference in white versus grey matter scaling presumably relate to the basic connectional architecture of the mammalian brain. Much of the neocortical white matter consists of fibres that make long-range connections, in which increases in axon diameter and myelination are necessary to preserve processing speed over longer conduction distances in larger brains [48,49]. The relative ballooning of the neocortex in large (and large-brained) animals may therefore be driven by allometric connectional constraints rather than by any special cognitive selection pressures. One implication is that the ratio measures of relative brain structure size used commonly in comparative studies, such as neocortex ratio [8], ‘executive’ brain ratio [7,10,11] and ‘cerebrotype’ [50] conflate allometric scaling with selection on specific brain regions. A volumetric ratio between neocortex and other structures potentially underestimates selection on non-cortical (e.g. cerebellar) functions.
The striking variation in the proportional size of the mammalian neocortex cannot therefore be simplistically read as reflecting selection specifically on cortical functions. This is further emphasized by the lack of correspondence between volumetric ratios and numbers of neurons. In stark contrast to the way that cortical volume proportion scales up with brain size, cortical neuron number proportion is unrelated to brain size [26] and unrelated to cortical volume proportion [25]. Similarly, the ratio of cortical to cerebellar volumes is uncorrelated with the ratio of cortical to cerebellar neurons (PGLS; λ = 0.63, t2,23 = 1.13, p = 0.27), casting doubt on the functional significance of volumetric ratios. Neuron density decreases as brain size increases in both neocortex (PGLS: λ = 0.83, slope = −0.23, t2,23 = 4.55, p < 0.0002) and cerebellum (PGLS: λ = 0.76, slope = −0.04, t = 2.43, p = 0.02), but the decline is significantly steeper in the neocortex (difference in PGLS coefficients: t = 3.92, p = 0.0008). The same is true when neuron densities of the two structures are related to their volumes rather than to overall brain size (t = 2.86, p = 0.009). Hence, the increase in neocortical volume proportion with brain size is traded off against a steeper decrease in neuron density.
Evidently there are different scaling constraints on each structure. Figure 2 illustrates the markedly different patterns of cross-species variability in proportional volumes and proportional neuron numbers, as well as the much larger number of neurons in the cerebellum than in the neocortex of all species. These results question both the validity of volumetric ratios as useful measures of information-processing capacity and the justification based on their variability across species for the near-exclusive focus of comparative studies on the neocortex.
Figure 2.
Contrast in the pattern of variation in the proportion of the brain composed of neocortex versus cerebellum when expressed as (a) volume proportion and (b) proportional number of neurons. Dark bars represent cortical proportions and light bars denote cerebellar proportions.
As pervasive as the assumption that neocortical expansion underpinned the evolution of ‘higher’ cognition is the assumption that it was the frontal lobes in particular that expanded most. Comparative data are relatively sparse, and most attention has focused on whether human frontal lobes are relatively large compared with their size in other primates [51–60]. The question has until recently remained unresolved, largely because of confusion over whether the proportional size or the size relative to allometric scaling provides the most useful measure. Because frontal lobe volume, like overall neocortex volume but to an even greater extent, scales hyper-allometrically, human frontal areas are large as a proportion of brain or neocortex size [53,54,59,60]. However, there is no more reason to think that proportional or absolute volume is a good measure of functional specialization for the frontal lobes than there is to believe it for the neocortex as a whole. Recent allometric analyses reveal that, although absolute and proportional frontal region size increased rapidly in hominins, this change was associated with size increase in other areas and whole brain size, rather than with specialization for enlarged frontal lobes specifically [57,61–63]. Consistent with allometric effects, neuron densities are particularly low in human frontal cortex [58]. Interestingly, there is stronger evidence for relative enlargement of temporal lobe structures [64,65]. This does not suggest that the frontal lobes were unimportant in cognitive evolution, just that their importance needs to be interpreted in terms of the areas with which they connect and with which they have co-evolved, including the cerebellum [61,62].
4. Cerebella comes to the ball: relative expansion and co-variation of neocortex and cerebellum
Although allometric scaling explains much of the variation in proportional neocortex size, it does not explain all of it. After taking scaling against other brain structures into account, primates have relatively large neocortices [23], and a relatively high density of cortical neurons [48]. However, the cerebellum is also larger [66] and contains more neurons in primates compared to other mammals (figure 3). This conjoint expansion of the two structures early in primate evolution reflects a general evolutionary trend for the two structures to evolve together, in primates in particular [23,26,62,67], and more generally during mammalian evolution (figure 4).
Figure 3.

Difference in relative numbers of neurons in (a) the neocortex and (b) cerebellum of primates (open circles) compared to other mammals (filled circles). Controlling for numbers of neurons in the rest of the brain, the difference between primates and non-primates is significant for neocortex (PGLS; λ = 0.86, t3,23 = 3.43, p = 0.002) and cerebellum (PGLS; λ = 0.76, t3,23 = 4.54, p = 0.0002). The effect is stronger for cerebellar neurons and the primate–non-primate difference in cerebellar neurons is still near-significant after controlling for neocortical neurons (PGLS; λ = 0.61, t4,23 = 2.02, p = 0.06).
Figure 4.

Correlated evolution of neocortex and cerebellum size in mammals. Neocortex size and cerebellum size are positively correlated after controlling for phylogenetic effects and volume of other brain regions (PGLS, neocortex volume regressed on volume of cerebellum controlling for volume of the rest of the brain; λ = 0.97, t3,298 = 8.85, p < 0.0001).
There are three compelling aspects of the evidence for correlated evolution of the neocortex and cerebellum. First, it is apparent after accounting for variability in the size of other brain structures, discounting the possibility that it is a reflection of some global allometric or developmental constraint acting across the whole brain. Second, there is a striking correspondence between the patterns of correlated evolution among specific components of the cortico-cerebellar system and their anatomical connectivity, down to the level of individual nuclei [62,67]. Third, it is evident not just in terms of volumes, but also in two independent data sets on numbers and densities of neurons (figure S1 in the electronic supplementary material).
The linkage between neocortical and cerebellar expansion suggests that both contributed significantly to brain size evolution. Indeed, a phylogenetic analysis reveals that, controlling for body mass, mammalian brain size is positively and independently correlated with both neocortex and cerebellum, and also that there is a significant interaction between the effects of the two structures on brain size (PGLS, brain mass regressed on: body mass, t = 8.47, p < 0.0001; neocortex, t = 19.73, p < 0.0001; cerebellum, t = 12.35, p < 0.0001; interaction between neocortex and cerebellum, t = 4.04, p < 0.0001; λ = 0.92, n = 298 mammal species). The combination of significant main and interaction effects suggests that the evolution of brain size was a product of both independent and co-ordinated size change of neocortex and cerebellum.
Previous work demonstrated a strong association between relative neocortex size and visual specialization in non-human primates [19,20,48]. Is the pattern of cortico-visual evolution confounded by cortico-cerebellar evolution? Further analysis suggests not: neocortex volume is significantly and independently correlated with volumes of both visual thalamus (LGN) and cerebellum, after accounting for variation in other brain structures (PGLS, neocortex volume regressed on volumes of cerebellum, LGN and rest of the brain; λ = 0.87, r2 = 0.98; LGN, t4,42 = 3.46, p = 0.001; cerebellum, t4,42 = 4.20, p = 0.0002). The same pattern is found after subtracting primary visual area V1 from total neocortex volume (λ = 0.89, r2 = 0.98, n = 42; LGN, t4,42 = 2.82, p = 0.008; cerebellum, t4,42 = 4.26, p = 0.0001), emphasizing that extra-striate cortex is not ‘non-visual’ [68]. The latter point is important, as different scaling trends for V1 and non-V1 against brain size have been misinterpreted as evidence against the visual specialization hypothesis [59]. In summary, variation in primate neocortex size is strongly related to the evolution both of visual structures and the cerebellum.
Several comparative studies suggest that cerebellar expansion, specifically involving the lateral cerebellum, was especially marked in apes [69–71]. It therefore seems that the cerebellum—modestly concealed beneath the volumetrically dominating neocortex, and largely ignored—may be the Cinderella of the study of brain evolution. This conclusion is reinforced by growing evidence that ascribing to it the task of basic chores in adaptive neural processes has also been a mistake.
5. Cognitive implications
It has long been known that the cerebellum is involved in sensory–motor control and learning of motor skills [72,73]. The relative expansion of the cerebellum in primates together with stereopsis and elaboration of the visual system [19,20,68] presumably underpins primates' fine visuo-motor control and manual dexterity. For example, smooth-pursuit eye-movements in primates are based on a unique cortico-cerebellar pathway that evolved together with foveal vision [74].
However, in the past 10 years or so considerable evidence has accumulated that the cerebellum has a broader role than previously recognized, including emotion [75,76], non-motor associative learning [77], working memory and mental rehearsal [77,78], verbal working memory and other language functions [76,78–81], spatial and episodic memory [79,81,82], event prediction [83], empathy and predicting others' actions [84–87], imitation [88], planning and decision-making [79,89,90], individual variation in cognitive performance [91], and cognitive developmental disorders including autism [80,92].
Some have argued that the case for cognitive functions of the cerebellum remains unproven [72,93]. The details of this debate are beyond the scope of this paper, but three general points can be made. First, although some studies have been criticized for failure to control for eye movements [93], the overall weight of evidence of many clinical and functional imaging studies indicates cerebellar involvement in a wide variety of cognitive processes [94]. Second, the cerebellum and neocortex are massively interconnected [78,90], and these connections involve many cortical areas, again suggesting a wide range of functions. Third, the distinction between sensory–motor control and cognition is arbitrary and an impediment to understanding brain function and evolution. Dissolving this distinction makes the debate on the cerebellum one about the range of its functions rather than a question of whether or not it has cognitive functions.
The classical view of cortico-cerebellar connections was that the cerebellum collected sensory information and returned it to primary motor cortex for the generation of movements [90]. However, it is now known that all major cortical regions, i.e. beyond motor cortex and including frontal and prefrontal areas, have reciprocal connections with the cerebellum. These cortico-cerebellar loops form multiple, independent anatomical modules which are architecturally quite uniform [90,95]. This anatomical uniformity together with functional data suggests basic similarities in the computations performed in different functional domains by different cortico-cerebellar modules [95,96]. These computations act as internal models or simulations of cortical processes that continuously update and error-correct responses, based on a comparison of actual and expected inputs, and they underlie a wide range of behavioural control processes [89,95,96]. Thus, internal models generated by the cerebellum guide behaviour in different domains. Direct control of behaviour, prediction of its consequences and reasoning about it may be mediated by similar cortico-cerebellar computations, with functional differences determined by which specific cortico-cerebellar modules are activated and their connectivity with other systems. Simulations computed ‘offline’ (as in the planning of sequences of behaviour), and those generated by observing other individuals (allowing prediction of their behaviour), are widely considered to be ‘cognitive’, or ‘executive’ processes. However, essentially the same kinds of computation appear to underlie sensory–motor and more ‘cognitive’ control processes [95,96], including speech [97].
6. Adaptive neural control processes cut across domains, use similar computations and share circuits
Computational commonality across functional domains with overlapping neural substrates may in fact be a rather generic feature of the brain. For example, social and non-social decision-making activate adjacent brain regions in the anterior cingulate and are mediated by the same computational processes, suggesting that social and non-social cognition may not be as encapsulated or specialized as has been assumed [98]. In another example, social rejection and physical pain activate overlapping brain regions, including somatosensory cortex and cerebellum [99]. Similarly, Shackman et al. [100] argue that cognitive control, negative affect and pain share an overlapping neural substrate and a common computational structure, and suggest the term ‘adaptive control’ as an encompassing term for these processes. Shackman et al. [100] point to the intriguing fact that all three processes activate muscles of the upper face, further emphasizing commonalities across processes traditionally distinguished as ‘executive’ and ‘non-executive’. Here, functional distinctions result from divergent patterns of connection rather than fundamentally different types of computation. Thus, individual brain regions contribute to multiple functional modules, and become secondarily adapted for use in different systems through the evolution of new connections [32,101].
7. Technical skills, cognitive sequencing and language
An adaptive control function in which the cerebellum plays a critical role is the modelling, prediction and organization of sequences of events and behaviours, including sequences involved in tool-making and use, and language comprehension and production [73,77,78,81,90,97,102]. Thus, the cerebellum is involved in learning of procedural sequences, recognition of correct spatial and temporal relations among behaviourally relevant actions, temporal organization of verbal utterances and planning of speech, and mental rehearsal [81]. It also seems to be involved in processing more abstract sequences such as in story comprehension [103].
There is an intriguing confluence between this evidence for cerebellar involvement in the temporal organization, comprehension and learning of sequences, evidence of cerebellar expansion in great apes [69–71], and observations of the facility of these species for extractive foraging and tool use [104], including the flexible recombination of tool components or elements of a problem [105], and for solving problems requiring sensitivity to sequence information [106]. Byrne [107,108] argues that great ape extractive foraging skills are based on iterated, hierarchically organized, multi-stage algorithms for solving ‘syntactical’ problems (problems requiring behaviours to be performed and flexibly recombined in functional sequences), and that they are socially learned, possibly by programme-level imitation [109]. Cerebellar specialization in ancestral great apes may therefore have been a precursor to neural capacities underlying the later development of cumulative cultures of more complex technologies in hominins [110,111].
Parallels between the organization of behavioural sequences in extractive foraging and tool use, on the one hand, and in language processing, on the other hand, may indicate that neural specialization for the first was a pre-adaptation for the second [101,112–114], with gestural communication probably representing an intermediate stage [114]. Indeed, there is overlap in brain areas activated during linguistic processing and other hierarchically organized motor acts such as tool construction [32,101,112,113]. In addition to classical cortical language areas, the cerebellum is activated by speech comprehension tasks [97,101,115]. Hence, language may have been built from pre-existing sensory–motor specializations common to all great apes [101].
8. Technical versus social intelligence and brain evolution
The evidence of cerebellar expansion and involvement in diverse cognitive functions suggests that the well-known link between neocortex size and social group size [8] may not be the only important feature of primate neuro-cognitive evolution; selection on foraging skills may have been important too [70,116]. A new phylogenetic comparative analysis controlling for allometric effects supports this contention (table 1). First, the well-known correlation between neocortex (or brain) size and social group size is recovered, but neocortex size also correlates with foraging skills. Second, cerebellum size also correlates with both types of behavioural variable. Third, there is evidence of an evolutionary brain–behaviour double dissociation; when controlling for the size of other brain structures, cerebellum size correlates markedly more strongly with foraging skill than it does with social group size and more strongly than neocortex size does with foraging skill, whereas for neocortex size the reverse pattern is observed. This is confirmed by analyses of each structure with the other included as a predictor; neocortex size then correlates significantly with social group size (t6,36 = 3.92, p = 0.0005) but not extractive foraging (t6,36 = 1.01, p = 0.32), whereas cerebellum size correlates significantly with extractive foraging (t6,36 = 3.59, p = 0.001) but not social group size (t6,36 = 1.33, p = 0.19). Although these results, together with those showing cerebellum-specific expansion in apes, certainly imply a degree of functional dissociation and independent evolution of the two structures, it is important to emphasize that each structure does correlate with both behavioural variables when not controlling for the other (in line with the evidence of coordinated cortico-cerebellar evolution). Thus, behavioural specializations seem to be based on a combination of both independent and coordinated evolution of individual brain structures.
Table 1.
Phylogenetic generalized least squares analysis of the relationship between volumes of brain components and behavioural variables. Significant associations indicated in bold. In model 1, whole brain size was regressed on body mass, group size and extractive foraging. In models 2 and 3, volumes of the individual brain regions were treated in the same way as in model 1, but the volume of the residual portion of the brain (brain − (neocortex + cerebellum)) was included as a predictor variable. Hence, these results indicate significant relationships between behavioural variables and size variation of neocortex and cerebellum relative to the size of the rest of the brain.
| model | model 1. | model 2. | model 3. |
|---|---|---|---|
| parameter | whole brain size t4,42, p-value | neocortex t4,42, p-value | cerebellum t4,42, p-value |
| body mass | 18.0, <0.0001 | 0.95, 0.35 | 3.12, 0.003 |
| volume of residual brain portion | — | 12.37, <0.0001 | 8.93, <0.0001 |
| group size | 3.47, 0.001 | 5.55, <0.0001 | 2.64, 0.012 |
| extractive foraging | 2.73, 0.01 | 2.07, 0.045 | 3.58, 0.0009 |
| λ | >0.99 | >0.99 | >0.99 |
| model summary | |||
| maximized log-likelihood | 38.7 | 33.6 | 65.2 |
| adjusted R2 | 0.92 | 0.98 | 0.99 |
Primate tool use frequently occurs in the context of extractive forging and involves similarly complex, organized sequences of behaviours [113]. Fewer species are recorded as using tools than using extractive foraging [7]. Nevertheless, broadly similar results are obtained for tool use. Controlling for body size, and residual brain volume, cerebellum size correlates with tool use (t5,36 = 2.04, p = 0.050) but not social group size (t6,36 = 1.47, p = 0.15), while neocortex size correlates with social group size (t6,36 = 3.98, p = 0.0003) but not tool use (t6,36 = 0.71, p = 0.48).
9. Co-evolution of social and technical intelligence
The debate about whether it was selection on social or technical intelligence that drove the evolution of brain size and cognitive capacities has increasingly appeared to be resolved in favour of the former [8,9]. Based on the evidence presented above, and in common with some other recent authors [33,108,112–114], I suggest not only that selection pressures on both social and technical skills were important, but also that they interacted with one another during human evolution. The theoretical argument is elaborated by Barrett et al. [33], who persuasively argue that the social and physical environment form mutually reinforcing feedback loops.
Specialization for technical intelligence seems particularly relevant to aspects of great ape behaviour. Great apes do not live in particularly large groups, but they are adept at extractive foraging and tool use, and at learning these skills by observation of others [104,105,113]. The capacities to perform such behaviours, and to learn them by observing others, may be intrinsically linked. Byrne [112] argues that both depend on ‘behaviour parsing’: the capacity to segment and mentally organize a sequence of acts into its subroutines based on the statistical regularities among the observed acts. This capacity is likely to have its origin in foraging skills: the relative lack of physiological adaptations for digesting high-fibre plant material in apes compared to Old World monkeys would have put a premium on extraction of more nutritious resources from hard or tough shells, spiny plants, termite mounds and other challenging defences. Once, however, the capacity to parse action sequences was established, it could have been secondarily adapted for use in the social domain, forming a basis for the prediction of conspecifics' behaviour [108–112].
10. Embodied simulation and social understanding
A sensory–motor origin of socio-cognitive capacities, and a linkage between the ability to execute complex behavioural sequences and to perceive and decode them when observing others, both fit with data indicating that the neural systems activated during a particular behaviour are also activated when observing the same behaviour performed by another individual [117]. It may therefore be that simulating the neural states underlying behaviours contributes to understanding them during observation. For example, the recognition of emotional expressions is disrupted by transcranial magnetic stimulation of somatosensory cortex, implying that activation of the system for producing expressions contributes to decoding them [118]. Computational work also supports the idea that simulation may provide a direct link between sensory–motor control and social understanding [119], and there are close computational parallels between motor control and control of social interactions [120].
Although most work on embodied social simulation has focused on the activity of ‘mirror neurons’ localised to a few cortical regions, such mirror-like properties are likely to be a function of the way that neurons are embedded in more distributed neural networks involved in sensory–motor processing [121–124], and experimental evidence now implicates the cerebellum [85–87,90,125,126]. The ‘mirror neuron system’ may thus not be a functionally specialized neural circuit restricted to a few cortical areas, nor an adaptation evolved specifically for action understanding, and as such may not merit the term ‘system’ [121]. Instead, mirroring may be a rather general adaptive property of neural systems with the right architecture for forming associations between one's own and others' actions, and may be phylogenetically widespread [127].
Damasio and Meyer [123] outline in broad form a model of mirror neurons based on ‘retro-activation’, the key to which is a neural architecture in which anterior association areas send signals back to visual cortex (and even to the visual thalamus). The comparatively large size and great complexity of primate visual and visuo-motor systems, including numerous reciprocal connections between anterior and posterior visual areas, and between these areas and association areas in frontal and temporal cortices [68,128], may therefore have implications for primate social cognition without necessarily having evolved primarily as an adaptation for it. However, an interesting question is then whether, once a sensory–motor system has mirroring potential, this potential is exploited by further evolutionary adaptive strengthening of critical connections in more social species, or perhaps inhibited in species or domains of behaviour where mirroring would be disadvantageous (for example, mirroring of subordinate expressions in dominance interactions).
11. Conclusions
The search for a single ideal comparative brain measure that captures the neural basis of cognitive evolution is likely to be more obfuscatory than illuminating, because different selection pressures have acted on different neural systems at different times. Whilst there are general patterns, such as the tendency of neocortex and cerebellum to evolve together, there are also significant deviations from such trends, such as visual pathway expansion in primates, and cerebellar expansion in apes. Gross brain size and composite brain indices or ratios therefore conflate different neural adaptations and mask important evolutionary patterns. To understand the neural bases of cognitive evolution, appropriate statistical, phylogenetic analyses that tease apart the variation associated with different neural systems and due to different selection pressures will therefore be more useful than composite indices.
Any account of human neuro-cognitive evolution needs to explain why there are so many neurons in the cerebellum. The answer suggested here, based on converging comparative and experimental evidence, is that the cerebellum and cortico-cerebellar networks are key components of systems enabling the control, organization and comprehension of complex sequences involved in both technical and social intelligence, and, ultimately, language. These proposals agree with Sterelny's [114] scenario for language evolution which suggests that the control of motor sequences involved in ape foraging skills provided a cognitive platform for gestural communication and thence ultimately syntax and language, and with Fitch's [101] proposal that motor control and hierarchical action planning systems were secondarily adapted for syntax.
The evidence presented here suggests that sensory–motor and cognitive evolution are not dissociable. In common with Barrett [33], I argue that there is no need to postulate a distinct set of ‘cognitive’ processes to fill the supposed gap between sensory reception and motor output. Even ‘offline’ and seemingly abstract cognitive processes, such as number representation and metaphor, appear to be ‘body based’ [31,129], and many allegedly abstract, centralized cognitive processes recruit distributed sensory–motor systems that evolved to control bodily movement [31]. By extension, cognitive evolution is to be understood as the elaboration of embodied control systems, rather than of a disembodied reasoning device [28,30]. As a corollary, there is no ‘intelligent’, ‘executive’ or indeed ‘Fodorian’ [130] bit of the brain that holds the key to cognitive evolution. Instead, the evolution of large brains was associated with the elaboration of sensory–motor mechanisms for the adaptive control of bodies in their environments.
Acknowledgements
I thank Celia Heyes, Russell Gray, Kim Sterelny, Eva Jablonka, Alison Gopnik, Arthur Robson, Matthew Rushworth and Nick Shea for many useful discussions, Simon Reader for access to extractive foraging and tool use data from ref. 7, and Andy Whiten, Dick Byrne and two anonymous referees for additional comments on the manuscript.
References
- 1.Harvey P. H., Krebs J. R. 1990. Comparing brains. Science 249, 140–146 10.1126/science.2196673 (doi:10.1126/science.2196673) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Shettleworth S. J. 1998. Cognition, evolution, and behavior. New York, NY: Oxford University Press [Google Scholar]
- 3.Striedter G. F. 2005. Principles of brain evolution. Sunderland, MA: Sinauer. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Dunbar R. I. M., Shultz S. 2007. Evolution in the social brain. Science 317, 1344–1347 10.1126/science.1145463 (doi:10.1126/science.1145463) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Sol D. 2009. Revisiting the cognitive buffer hypothesis for the evolution of large brains. Biol. Lett. 5, 130–133 10.1098/rsbl.2008.0621 (doi:10.1098/rsbl.2008.0621) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Lefebvre L., Sol D. 2008. Brains, lifestyles and cognition: are there general trends? Brain Behav. Evol. 72, 135–144 10.1159/000151473 (doi:10.1159/000151473) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Reader S. M., Hager Y., Laland K. N. 2011. The evolution of primate general and cultural intelligence. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 366, 1017–1027 10.1098/rstb.2010.0342 (doi:10.1098/rstb.2010.0342) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Dunbar R. I. M. 1998. The social brain hypothesis. Evol. Anthrop. 6, 178–190 (doi:10.1002/(SICI)1520-6505(1998)6:5<178::AID-EVAN5>3.0.CO;2-8) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Dunbar R. I. M., Shultz S. 2007. Understanding primate brain evolution. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 362, 649–658 10.1098/rstb.2006.2001 (doi:10.1098/rstb.2006.2001) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Keverne E. B., Martel F. L., Nevison C. M. 1996. Primate brain evolution: genetic and functional considerations. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 263, 689–696 10.1098/rspb.1996.0103 (doi:10.1098/rspb.1996.0103) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Reader S. M., Laland K. N. 2002. Social intelligence, innovation, and enhanced brain size in primates. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 99, 4436–4441 10.1073/pnas.062041299 (doi:10.1073/pnas.062041299) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lefebvre L., Reader S. M., Sol D. 2004. Brains, innovations and evolution in birds and primates. Brain Behav. Evol. 63, 233–246 10.1159/000076784 (doi:10.1159/000076784) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Deaner R. O., Isler K., Burkhart J., van Schaik C. P. 2007. Overall brain size, and not encephalization quotient, best predicts cognitive ability across non-human primates. Brain Behav. Evol. 70, 115–124 10.1159/000102973 (doi:10.1159/000102973) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Healy S. D., Rowe C. 2007. A critique of comparative studies of brain size. Proc. R. Soc. B 274, 453–464 10.1098/rspb.2006.3748 (doi:10.1098/rspb.2006.3748) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Krebs J. R. 1990. Food-storing birds: adaptive specialization in brain and behaviour? Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B 329, 153–160 10.1098/rstb.1990.0160 (doi:10.1098/rstb.1990.0160) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Barton R. A., Dean P. 1993. Comparative evidence indicating neural specialization for predatory behaviour in mammals. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 254, 63–68 10.1098/rspb.1993.0127 (doi:10.1098/rspb.1993.0127) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Devoogd T. J., Krebs J. R., Healy S. D., Purvis A. 1993. Relations between song repertoire size and the volume of brain nuclei related to song: comparative evolutionary analyses amongst oscine birds. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 254, 75–82 10.1098/rspb.1993.0129 (doi:10.1098/rspb.1993.0129) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Barton R. A., Purvis A., Harvey P. H. 1995. Evolutionary radiation of visual and olfactory brain systems in primates, bats and insectivores. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B 348, 381–392 10.1098/rstb.1995.0076 (doi:10.1098/rstb.1995.0076) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Barton R. A. 1998. Visual specialisation and brain evolution in primates. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 265, 1933–1937 10.1098/rspb.1998.0523 (doi:10.1098/rspb.1998.0523) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Barton R. A. 2004. Binocularity and brain evolution in primates. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 101, 10 113–10 115 10.1073/pnas.0401955101 (doi:10.1073/pnas.0401955101) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Iwaniuk A. N., Hurd P. L. 2005. The evolution of cerebrotypes in birds. Brain Behav. Evol. 65, 215–230 10.1159/000084313 (doi:10.1159/000084313) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Shumway C. A. 2010. The evolution of complex brains and behaviors in African cichlid fishes. Curr. Zool. 56, 144–156 [Google Scholar]
- 23.Barton R. A., Harvey P. H. 2000. Mosaic evolution of brain structure in mammals. Nature 405, 1055–1058 10.1038/35016580 (doi:10.1038/35016580) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.De Winter W., Oxnard C. E. 2001. Evolutionary radiations and convergences in the structural organization of mammalian brains. Nature 409, 710–714 10.1038/35055547 (doi:10.1038/35055547) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Herculano-Houzel S. 2009. The human brain in numbers: a linearly scaled-up primate brain. Front Neurosci. 3, 31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Herculano-Houzel S. 2010. Coordinated scaling of cortical and cerebellar numbers of neurons. Front. Neuroanat. 4, 12 10.3389/fnana.2010.00012 (doi:10.3389/fnana.2010.00012) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Fodor J. 1983. The modularity of mind. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press [Google Scholar]
- 28.Damasio A. 1994. Descartes’ error: emotion, reason, and the human brain. New York, NY: Putnam [Google Scholar]
- 29.Chiel H. J., Beer R. D. 1997. The brain has a body: adaptive behavior emerges from interactions of nervous system, body and environment. Trends Neurosci. 20, 553–557 10.1016/S0166-2236(97)01149-1 (doi:10.1016/S0166-2236(97)01149-1) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Clark A. 1997. Being there: putting brain, body, and world together again. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press [Google Scholar]
- 31.Wilson M. 2002. Six views of embodied cognition. Psychol. Bull. Rev. 9, 625–636 10.3758/BF03196322 (doi:10.3758/BF03196322) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Anderson M. L. 2010. Neural reuse: a fundamental organizational principle of the brain. Behav. Brain Sci. 33, 245–313 10.1017/S0140525X10000853 (doi:10.1017/S0140525X10000853) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Barrett L., Henzi S. P., Lusseau D. 2012. Taking sociality seriously: the structure of multi-dimensional social networks as a source of information for individuals. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 367, 2108–2118 10.1098/rstb.2012.0113 (doi:10.1098/rstb.2012.0113) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Gallese V., Lakoff G. 2005. The brain's concepts: the role of the sensory-motor system in conceptual knowledge. Cogn. Neuropsychol. 22, 455–479 10.1080/02643290442000310 (doi:10.1080/02643290442000310) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Nunn C. L. 2011. The comparative approach in evolutionary anthropology and biology. Chicago, IL: Chicago University Press [Google Scholar]
- 36.Pagel M. 1999. The maximum likelihood approach to reconstructing ancestral character states of discrete characters on phylogenies. Syst. Biol. 48, 612–622 10.1080/106351599260184 (doi:10.1080/106351599260184) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Rohlf F. J. 2001. Comparative methods for the analysis of continuous variables: geometric interpretations. Evolution 55, 2143–2160 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Freckleton R. P., Harvey P. H., Pagel M. 2002. Phylogenetic analysis and comparative data: a test and review of evidence. Am. Nat. 160, 712–726 10.1086/343873 (doi:10.1086/343873) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Lui J. H., Hansen D. V., Kriegstein A. R. 2011. Development and evolution of the human neocortex. Cell 146, 18–36 10.1016/j.cell.2011.06.030 (doi:10.1016/j.cell.2011.06.030) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Rakic P. 2009. Evolution of the neocortex: a perspective from developmental biology. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 724–735 10.1038/nrn2719 (doi:10.1038/nrn2719) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Carlson K. J., Stout D., Jashashvili T., de Ruiter D. J., Tafforeau P., Carlson K., Berger L. R. 2011. The endocast of MH1, Australopithecus sediba. Science 333, 1402–1407 10.1126/science.1203922 (doi:10.1126/science.1203922) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Stephan H., Frahm H. D., Baron G. 1981. New and revised data on volumes of brain structures in insectivores and primates. Folia Primatol. 35, 1–29 10.1159/000155963 (doi:10.1159/000155963) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Stephan H., Baron G., Frahm H. D. 1991. Comparative brain research in mammals, vol. 1. Insectivores. New York, NY: Springer [Google Scholar]
- 44.Bush E. C., Allman J. M. 2004. The scaling of frontal cortex size in primates and carnivores. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 101, 3962–3966 10.1073/pnas.0305760101 (doi:10.1073/pnas.0305760101) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Mangold-Wirz K. 1966. Cerebralisation Und Ontogenesemodus Bei Eutherien. Acta Anat. 63, 449 10.1159/000142809 (doi:10.1159/000142809) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Zhang K., Sejnowski T. J. 2000. A universal scaling law between gray matter and white matter of cerebral cortex. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 97, 5621–5626 10.1073/pnas.090504197 (doi:10.1073/pnas.090504197) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Bush E. C., Allman J. M. 2003. The scaling of white matter to grey matter in cerebellum and neocortex. Brain Behav. Evol. 61, 1–5 10.1159/000068880 (doi:10.1159/000068880) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Barton R. A. 2006. Primate brain evolution: integrating comparative, neurophysiological and ethological data. Evol. Anthrop. 15, 224–236 10.1002/evan.20105 (doi:10.1002/evan.20105) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Wang S-H., Shultz J. R., Burish M. J., Harrison K. H., Hof P. R., Towns L. C., Wagers M. W., Wyatt K. D. 2008. Functional trade-offs in white matter axonal scaling. J. Neurosci. 28, 4047–4056 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5559-05.2008 (doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5559-05.2008) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Clark D. A., Mitra P. P., Wang S. S. H. 2001. Scalable architecture in mammalian brains. Nature 411, 189–193 10.1038/35075564 (doi:10.1038/35075564) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Brodmann K. 1912. Neue Ergebnisse uber die vergleichende histologische Lokalisation der Grosshirnrinde mit besonderer Berücksichtigung des Stirnhirns Anat. Anzeiger 41, 157–216 [Google Scholar]
- 52.Blinkov S. M., Glezer I. I. 1968. Das Zentralnervensystem in Zahlen und Tabellen. Jena, Germany: Fischer [Google Scholar]
- 53.Rilling J. K. 2006. Human and non-human primate brains: are they allometrically scaled versions of the same design? Evol. Anthrop. 15, 65–77 10.1002/evan.20095 (doi:10.1002/evan.20095) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Semendeferi K., Lu A., Schenker N., Damasio H. 2002. Humans and great apes share a large frontal cortex. Nat. Neurosci. 5, 272–276 10.1038/nn814 (doi:10.1038/nn814) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Schoenemann P. T., Sheehan M. J., Glotzer L. D. 2005. Prefrontal white matter volume is disproportionately larger in humans than in other primates. Nat. Neurosci. 8, 242–252 10.1038/nn1394 (doi:10.1038/nn1394) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Sherwood C. C., Holloway R. L., Semendeferi K., Hof P. R. 2005. Is prefrontal white matter enlargement a human evolutionary specialization? Nat. Neurosci. 8, 537–538 10.1038/nn0505-537 (doi:10.1038/nn0505-537) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Smaers J. B., Steele J., Case C. R., Cowper A., Amunts K., Zilles K. 2011. Primate prefrontal cortex evolution: human brains are the extreme of a lateralized ape trend. Brain Behav. Evol. 77, 67–78 10.1159/000323671 (doi:10.1159/000323671) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Semendeferi K., Teffer K., Buxhoeveden D. P., Park M. S., Bludau S., Amunts K., Travis K., Buckwalte J. 2011. Spatial organization of neurons in the frontal pole sets humans apart from great apes. Cereb. Cortex 21, 1485–1497 10.1093/cercor/bhq191 (doi:10.1093/cercor/bhq191) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Dunbar R. I. M., Shultz S. 2007. Understanding primate brain evolution. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 362, 649–658 10.1098/rstb.2006.2001 (doi:10.1098/rstb.2006.2001) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Semendeferi K., Armstrong E., Schleicher A., Zilles K., Van Hoesen G. W. 2001. Prefrontal cortex in humans and apes: a comparative study of area 10. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 114, 224–241 (doi:10.1002/1096-8644(200103)114:3<224::AID-AJPA1022>3.0.CO;2-I) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Balsters J. H., Cussans E., Diedrichsen J., Phillips K. A., Preuss T. M., Rilling J. K., Ramnani N. 2009. Evolution of the cerebellar cortex: the selective expansion of prefrontal-projecting cerebellar lobules. NeuroImage 49, 2045–2052 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.10.045 (doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.10.045) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Smaers J. B., Steele J., Zilles K. 2011. Modeling the evolution of cortico-cerebellar systems in primates. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 1225, 176–190 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2011.06003.x (doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2011.06003.x) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Barton R. A., Venditti C. Submitted. Human frontal lobes are not disproportionately expanded. Nat. Neurosci. [Google Scholar]
- 64.Rilling J. K., Seligman R. A. 2002. A quantitative morphometric comparative analysis of the primate temporal lobe. J. Hum. Evol. 42, 505–533 10.1006/jhev.2001.0537 (doi:10.1006/jhev.2001.0537) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Barger N., Stefanacci L., Semendeferi K. 2007. A comparative volumetric analysis of the amygdaloid complex and basolateral division in the human and ape brain. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 134, 392–403 10.1002/ajpa.20684 (doi:10.1002/ajpa.20684) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Barton R. A. 2000. Ecological and social factors in primate brain evolution. In On the move: how and why animals travel in groups (eds Boinski S., Garber P.), pp. 204–237 Chicago, IL: Chicago University Press [Google Scholar]
- 67.Whiting B., Barton R. A. 2003. The evolution of the cortico-cerebellar complex in primates: anatomical connections predict patterns of correlated evolution. J. Hum. Evol. 44, 3–10 10.1016/S0047-2484(02)00162-8 (doi:10.1016/S0047-2484(02)00162-8) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.van Essen D. C., Anderson C. H., Felleman D. J. 1992. Information processing in the primate visual system: an integrated systems perspective. Science 255, 419–423 10.1126/science.1734518 (doi:10.1126/science.1734518) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Rilling J. K., Insel T. R. 1998. Evolution of the cerebellum in primates: differences in relative volume among monkeys, apes and humans. Brain Behav. Evol. 52, 308–314 10.1159/000006575 (doi:10.1159/000006575) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.MacLeod C. E., Zilles K., Schleicher A., Rilling J. K., Gibson K. R. 2003. Expansion of the neocerebellum in Hominoidea. J. Hum. Evol. 44, 401–429 10.1016/S0047-2484(03)00028-9 (doi:10.1016/S0047-2484(03)00028-9) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Barton R. A., Venditti C. In revision. Explosive evolution of the cerebellum in humans and other great apes. Curr. Biol. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Glickstein M., Doron K. 2008. Cerebellum: connections and functions. Cerebellum 7, 589–594 10.1007/s12311-008-0074-4 (doi:10.1007/s12311-008-0074-4) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Habas C. 2010. Functional imaging of the deep cerebellar nuclei: a review. Cerebellum 9, 22–28 10.1007/s12311-009-0119-3 (doi:10.1007/s12311-009-0119-3) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Thier P., Ilg U. J. 2005. The neural basis of smooth-pursuit eye movements. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 15, 645–652 10.1016/j.conb.2005.10.013 (doi:10.1016/j.conb.2005.10.013) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Colibazzi T., et al. 2010. Neural systems subserving valence and arousal during the experience of induced emotions. Emotion 10, 377–389 10.1037/a0018484 (doi:10.1037/a0018484) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Tavano A., Borgatti R. 2010. Evidence for a link among cognition, language and emotion in cerebellar malformations. Cortex 46, 907–918 10.1016/j.cortex.2009.07.017 (doi:10.1016/j.cortex.2009.07.017) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Bellebaum C., Daum I. 2011. Mechanisms of cerebellar involvement in associative learning. Cortex 47, 128–136 10.1016/j.cortex.2009.07.016 (doi:10.1016/j.cortex.2009.07.016) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Leiner H. C. 2010. Solving the mystery of the human cerebellum. Neuropsychol. Rev. 20, 229–235 10.1007/s11065-010-9140-z (doi:10.1007/s11065-010-9140-z) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Schmahmann J. D., Sherman J. C. 1998. The cerebellar cognitive affective syndrome. Brain 121, 561–579 10.1093/brain/121.4.561 (doi:10.1093/brain/121.4.561) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Steinlin M. 2008. Cerebellar disorders in childhood: cognitive problems. Cerebellum 7, 607–610 10.1007/s12311-008-0083-3 (doi:10.1007/s12311-008-0083-3) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Leggio M. G., Chiricozzi F. R., Clausi S., Tedesco A. M., Molinari M. 2011. The neuropsychological profile of cerebellar damage: the sequencing hypothesis. Cortex 47, 137–144 10.1016/j.cortex.2009.08.011 (doi:10.1016/j.cortex.2009.08.011) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Rochefort C., Arabo A., André M., Poucet B., Save E., Rondi-Reig L. 2011. Cerebellum shapes hippocampal spatial code. Science 334, 385–389 10.1126/science.1207403 (doi:10.1126/science.1207403) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Forster S. E., Brown J. W. 2011. Medial prefrontal cortex predicts and evaluates the timing of action outcomes. NeuroImage 55, 253–265 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.11.035 (doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.11.035) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Ramnani N., Miall C. R. 2004. A system in the human brain for predicting the actions of others. Nat. Neurosci. 7, 85 10.1038/nn1168 (doi:10.1038/nn1168) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Gazzola V., Keyser C. 2009. The observation and execution of actions share motor and somatosensory voxels in all tested subjects: single-subject analyses of unsmoothed fMRI data. Cereb. Cortex 19, 1239–1255 10.1093/cercor/bhn181 (doi:10.1093/cercor/bhn181) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Schulte-Ruther M., Markowitsch H. J., Fink G. R., Piefke M. 2007. Mirror neuron and theory of mind mechanisms involved in face-to-face interactions: a functional magnetic resonance imaging approach to empathy. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 19, 1354–1372 10.1162/jocn.2007.19.8.1354 (doi:10.1162/jocn.2007.19.8.1354) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Singer T., Seymour B., O'Doherty J., Kaube H., Dolan R. J., Frith C. D. 2004. Empathy for pain involves affective but not sensory components of pain. Science 303, 1157–1162 10.1126/science.1093535 (doi:10.1126/science.1093535) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Jackson P. L., Meltzoff A. N., Decety J. 2005. Neural circuits involved in imitation and perspective-taking. NeuroImage 31, 429–439 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2005.11.026 (doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2005.11.026) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Ito M. 2008. Control of mental activities by internal models in the cerebellum. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 9, 304–313 10.1038/nrn2332 (doi:10.1038/nrn2332) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Strick P. L., Dum R. P., Fiez J. A. 2009. Cerebellum and nonmotor function. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 32, 413–434 10.1146/annurev.neuro.31.060407.125606 (doi:10.1146/annurev.neuro.31.060407.125606) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Hogan M. J., Staff R. T., Bunting B. P., Murray A. D., Ahearn T. S., Deary I. J., Whalley L. J. 2011. Cerebellar brain volume accounts for variance in cognitive performance in older adults. Cortex 47, 441–450 10.1016/j.cortex.2010.01.001 (doi:10.1016/j.cortex.2010.01.001) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Shukla D. K., Keehn B., Lincoln A. J., Muller R. A. 2010. White matter compromise of callosal and subcortical fiber tracts in children with autism spectrum disorder: a diffusion tensor imaging study. J. Am. Acad. Child Adol. Psych. 49, 1269–1278 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Glickstein M., Sultan F., Voogd J. 2008. Functional localization in the cerebellum. Cortex 47, 59–80 10.1016/j.cortex.2009.09.001 (doi:10.1016/j.cortex.2009.09.001) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Beaton A., Mariën P. 2010. Language, cognition and the cerebellum: grappling with an enigma. Cortex 46, 811–820 10.1016/j.cortex.2010.02.005 (doi:10.1016/j.cortex.2010.02.005) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Ramnani N. 2006. The primate cortico-cerebellar system: anatomy and function. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 7, 511 10.1038/nrn1953 (doi:10.1038/nrn1953) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Ito M. 1993. Movement and thought: identical control mechanisms by the cerebellum. Trends Neurosci. 16, 448–450 10.1016/0166-2236(93)90073-U (doi:10.1016/0166-2236(93)90073-U) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Hickok G. 2012. Computational neuroanatomy of speech production. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 13, 135–145 10.1038/nrg3118 (doi:10.1038/nrg3118) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Behrens T. E., Hunt L. T., Rushworth M. F. 2009. The computation of social behavior. Science 324, 1160–1164 10.1126/science.1169694 (doi:10.1126/science.1169694) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Krossa E., Bermana M. G., Mischel W., Smith E. E., Wager T. D. 2011. Social rejection shares somatosensory representations with physical pain. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 108, 6270–6275 10.1073/pnas.1102693108 (doi:10.1073/pnas.1102693108) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Shackman A. J., Salomons T. V., Slagter H. A., Fox A. S., Winter J. J., Davidson R. J. 2011. The integration of negative affect, pain and cognitive control in the cingulate cortex. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 12, 154–167 10.1038/nrn2994 (doi:10.1038/nrn2994) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Fitch W. T. 2011. The evolution of syntax: an exaptationist perspective. Front. Evol. Neurosci. 3, 9 10.3389/fnevo.2011.00009 (doi:10.3389/fnevo.2011.00009) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Imamizu H., Miyauchi S., Tamada T., Sasaki Y., Takino R., Putz B., Yoshioko T., Kawato M. 2000. Human cerebellar activity reflecting an acquired internal model of a new tool. Nature 403, 192–195 10.1038/35003194 (doi:10.1038/35003194) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Mar R. A. 2011. The neural bases of social cognition and story comprehension. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 62, 103–134 10.1146/annurev-psych-120709-145406 (doi:10.1146/annurev-psych-120709-145406) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Whiten A., Goodall J., McGrew W. C., Nishida T., Reynolds V., Sugiyama Y., Tutin C. E., Wrangham R. W., Boesch C. 1999. Cultures in chimpanzees. Nature 399, 682–685 10.1038/21415 (doi:10.1038/21415) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Whiten A., Suddendorf T. 2007. Great ape cognition and the evolutionary roots of human imagination. Proc. Br. Acad. 147, 31–59 10.5871/bacad/9780197264195.001.0001 (doi:10.5871/bacad/9780197264195.001.0001) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Endress A. D., Carden S., Versace E., Hauser M. D. 2010. The apes’ edge: positional learning in chimpanzees and humans. Anim. Cogn. 13, 483–495 10.1007/s10071-009-0299-8 (doi:10.1007/s10071-009-0299-8) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Byrne R. W. 1999. Object manipulation and skill organization in the complex food preparation of mountain gorillas. In The mentality of gorillas and orangutans (eds Parker S. T., Mitchell R. W., Miles H. L.), pp. 147–159 Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press; 10.1017/CBO9780511542305.007 (doi:10.1017/CBO9780511542305.007) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Byrne R. W., Bates L. A. 2010. Primate social cognition: uniquely primate, uniquely social, or just unique? Neuron 65, 815–830 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.03.010 (doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2010.03.010) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Byrne R. W., Hobaiter C., Klailova M. 2011. Local traditions in gorilla manual skill: evidence for observational learning of behavioral organization. Anim. Cogn. 14, 683–693 10.1007/s10071-011-0403-8 (doi:10.1007/s10071-011-0403-8) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Byrne R. W. 2007. Culture in great apes: using intricate complexity in feeding skills to trace the evolutionary origin of human technical prowess. Phil. Trans. R.. Soc. B 362, 577–585 10.1098/rstb.2006.1996 (doi:10.1098/rstb.2006.1996) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Stout D., Toth N., Schick K., Chaminade T. 2008. Neural correlates of Early Stone Age toolmaking: technology, language and cognition in human evolution. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B. 363, 1939–1949 10.1098/rstb.2008.0001 (doi:10.1098/rstb.2008.0001) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Byrne R. W. 2006. Parsing behaviour. A mundane origin for an extraordinary ability? In The roots of human sociality (eds Levinson S., Enfield N.), pp. 478–505 Oxford, UK: Berg. [Google Scholar]
- 113.Stout D., Passingham R., Frith C., Apel J., Chaminade T. 2011. Technology, expertise and social cognition in human evolution. Eur. J. Neurosci. 33, 1328–1338 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2011.07619.x (doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2011.07619.x) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Sterelny K. 2012. Language, gesture, skill: the coevolutionary foundations of language. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 367, 2141–2151 10.1098/rstb.2012.0116 (doi:10.1098/rstb.2012.0116) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Londei A., D'Ausilio A., Basso D., Sestieri C., Del Gratta C., Romani G. L., Belardinelli M. O. 2010. Sensory-motor brain network connectivity for speech comprehension. Hum. Brain Mapp. 4, 567–580 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Gibson K. R. 1986. Cognition, brain size and the extraction of embedded food resources. In Primate ontogeny, cognition and social behaviour. (eds Else J. G., Lee P. C.), pp. 93–103 Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press [Google Scholar]
- 117.Gallese V. 2009. Motor abstraction: a neuroscientific account of how action goals and intentions are mapped and understood. Psychol. Res. 73, 486–498 10.1007/s00426-009-0232-4 (doi:10.1007/s00426-009-0232-4) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Pitcher D., Garrido L., Walsh V., Duchaine B. C. 2008. Transcranial magnetic stimulation disrupts the perception and embodiment of facial expressions. J. Neurosci. 28, 8929–8933 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1450-08.2008 (doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1450-08.2008) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Oztop E., Wolpert D., Kawato M. 2005. Mental state inference using visual control parameters. Cog. Brain Res. 22, 129–151 10.1016/j.cogbrainres.2004.08.004 (doi:10.1016/j.cogbrainres.2004.08.004) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Wolpert D. M., Doya K., Kawato M. 2003. A unifying computational framework for motor control and social interaction. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B. 358, 593–602 10.1098/rstb.2002.1238 (doi:10.1098/rstb.2002.1238) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Heyes C. M. 2010. Where do mirror neurons come from? Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 34, 575–583 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2009.11.007 (doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2009.11.007) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Keysers C., Perrett D. I. 2004. Demystifying social cognition: a Hebbian perspective. Trends Cogn. Sci. 8, 501–507 10.1016/j.tics.2004.09.005 (doi:10.1016/j.tics.2004.09.005) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Damasio A., Meyer K. 2008. Behind the looking-glass. Nature 454, 167–168 10.1038/454167a (doi:10.1038/454167a) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Gallese V. 2008. Mirror neurons and the social nature of language: the neural exploitation hypothesis. Soc. Neurosci. 3, 317–333 10.1080/17470910701563608 (doi:10.1080/17470910701563608) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Peeters R., Simone L., Nelissen K., Fabbri-Destro M., Vanduffel W., Rizzolatti G., Orban G. A. 2009. The representation of tool use in humans and monkeys: common and uniquely human features. J. Neurosci. 29, 11 523–11 539 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Kana R. K., Wadsworth H. M., Travers B. G. 2011. A systems level analysis of the mirror neuron hypothesis and imitation impairments in autism spectrum disorders. Neurosc. Biobehav. Rev. 35, 894–902 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2010.10.007 (doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2010.10.007) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Bonini L., Ferrari P. F. 2011. Evolution of mirror systems: a simple mechanism for complex cognitive functions. Ann. NY Acad Sci. 1225, 166–175 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2011.06002.x (doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2011.06002.x) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Young M. P. 2000. The architecture of visual cortex and inferential processes in vision. Spat. Vis. 13, 137–146 10.1163/156856800741162 (doi:10.1163/156856800741162) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Santana E., de Vega M. 2011. Metaphors are embodied, and so are their literal counterparts. Front. Psychol. 2, 90 10.3389/fpsyg.2011.00090 (doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2011.00090) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Bolhuis J. J., Brown G. R., Richardson R. C., Laland K. N. 2011. Darwin in mind: new opportunities for evolutionary psychology. PLoS Biol. 9, e1001109 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001109 (doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1001109) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]