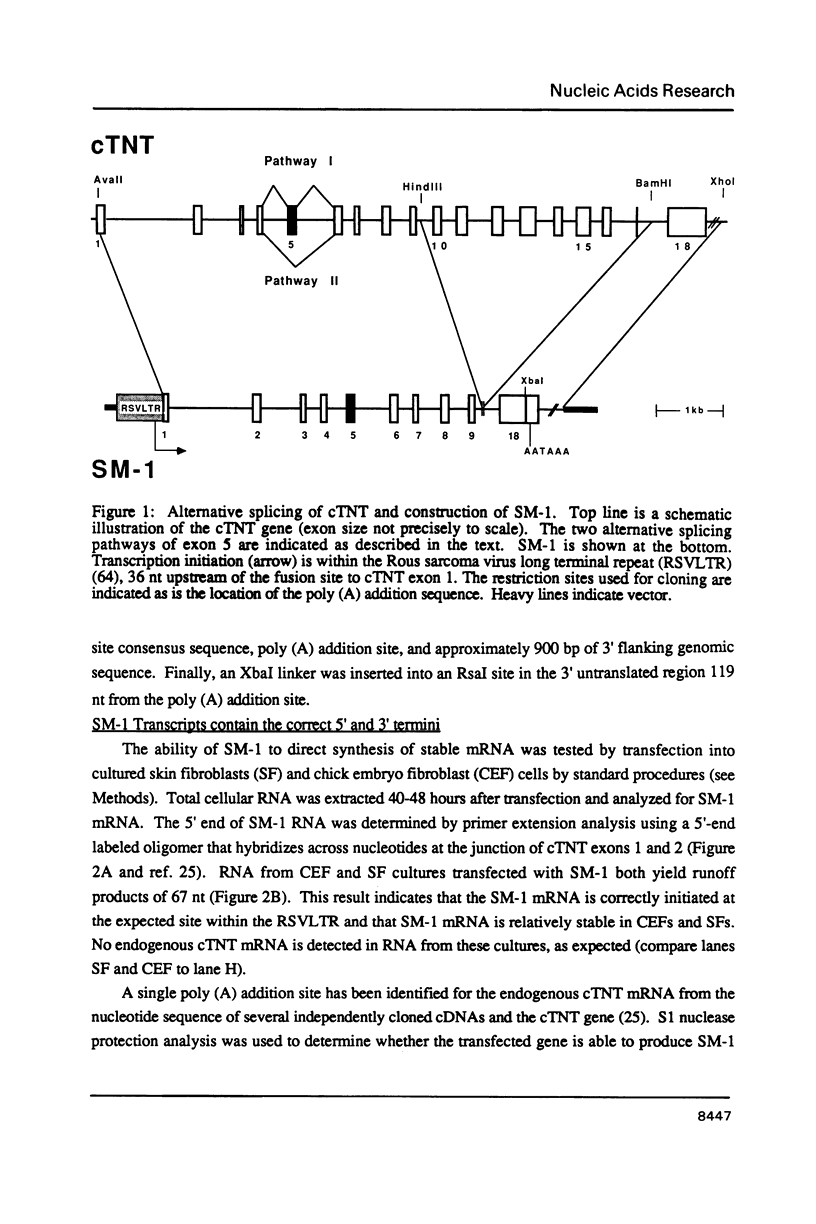
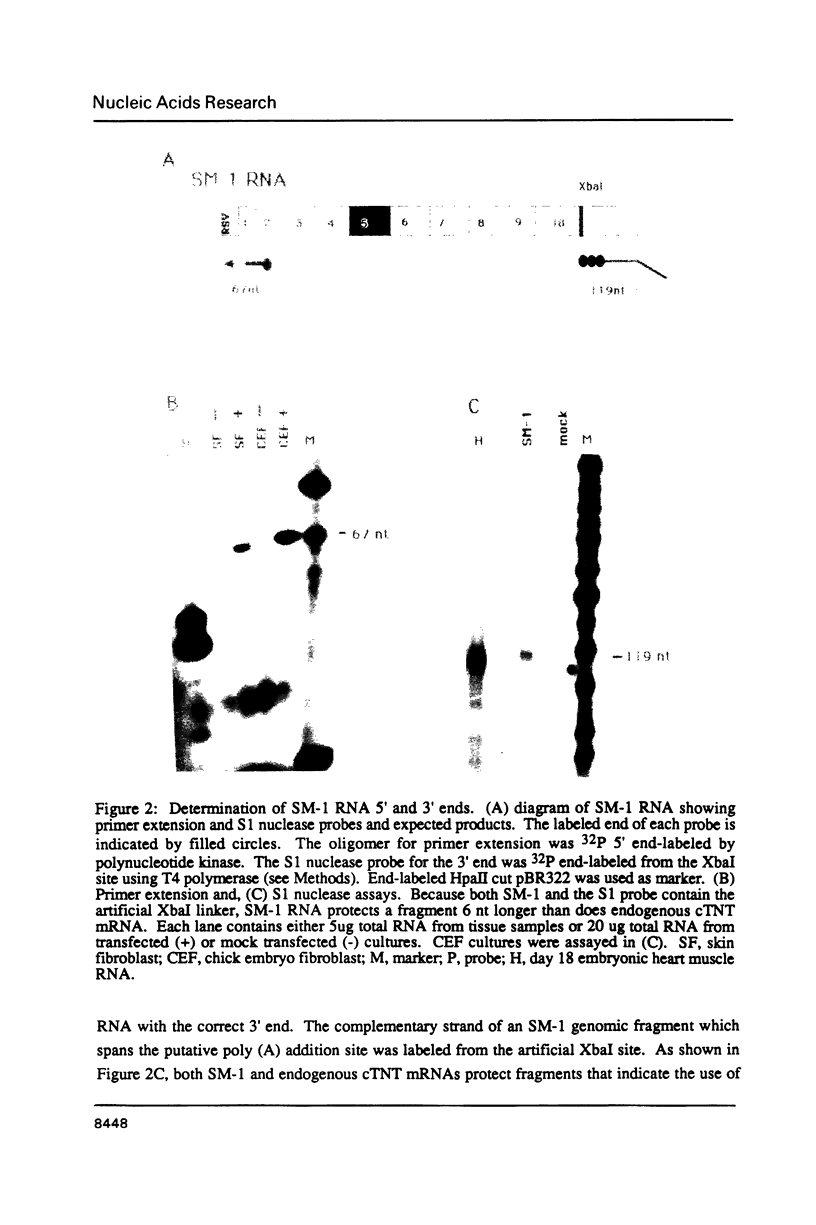
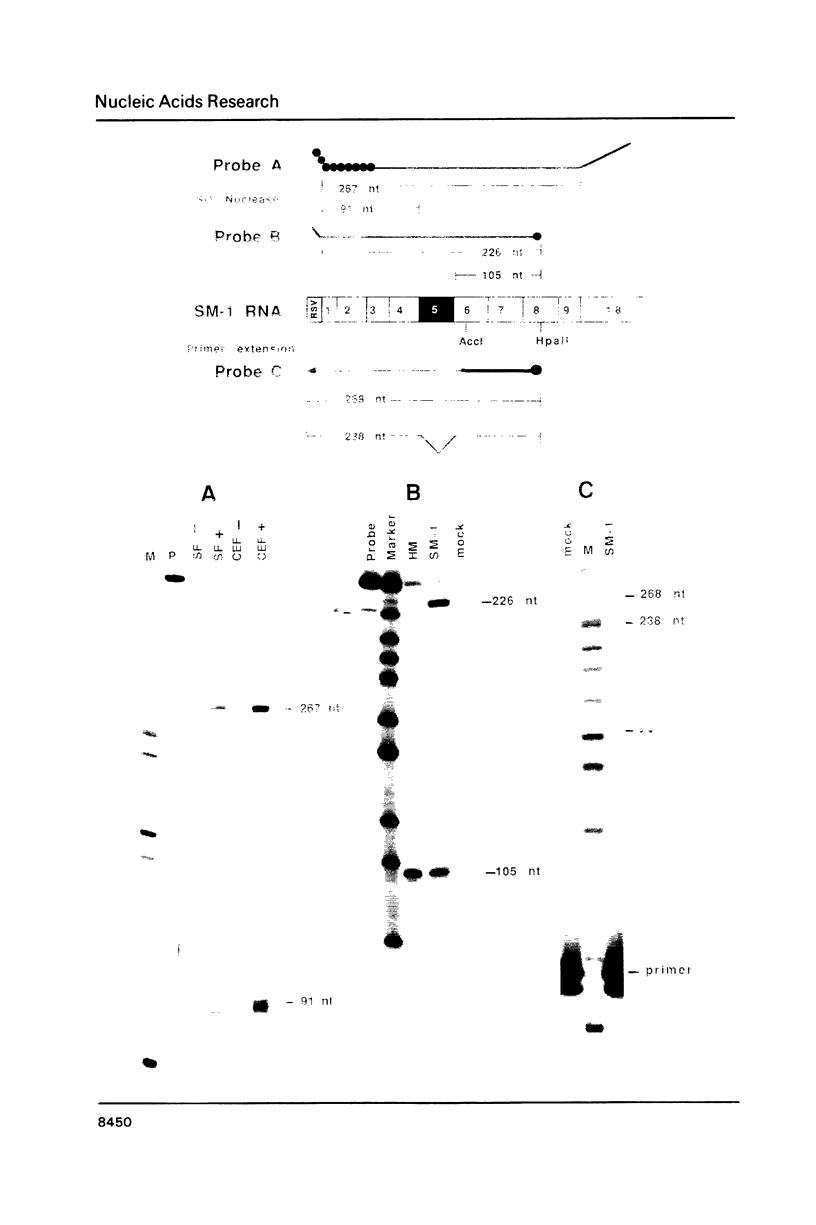
Abstract
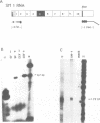
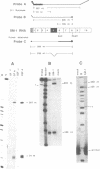
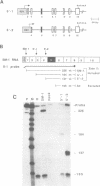
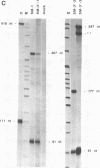
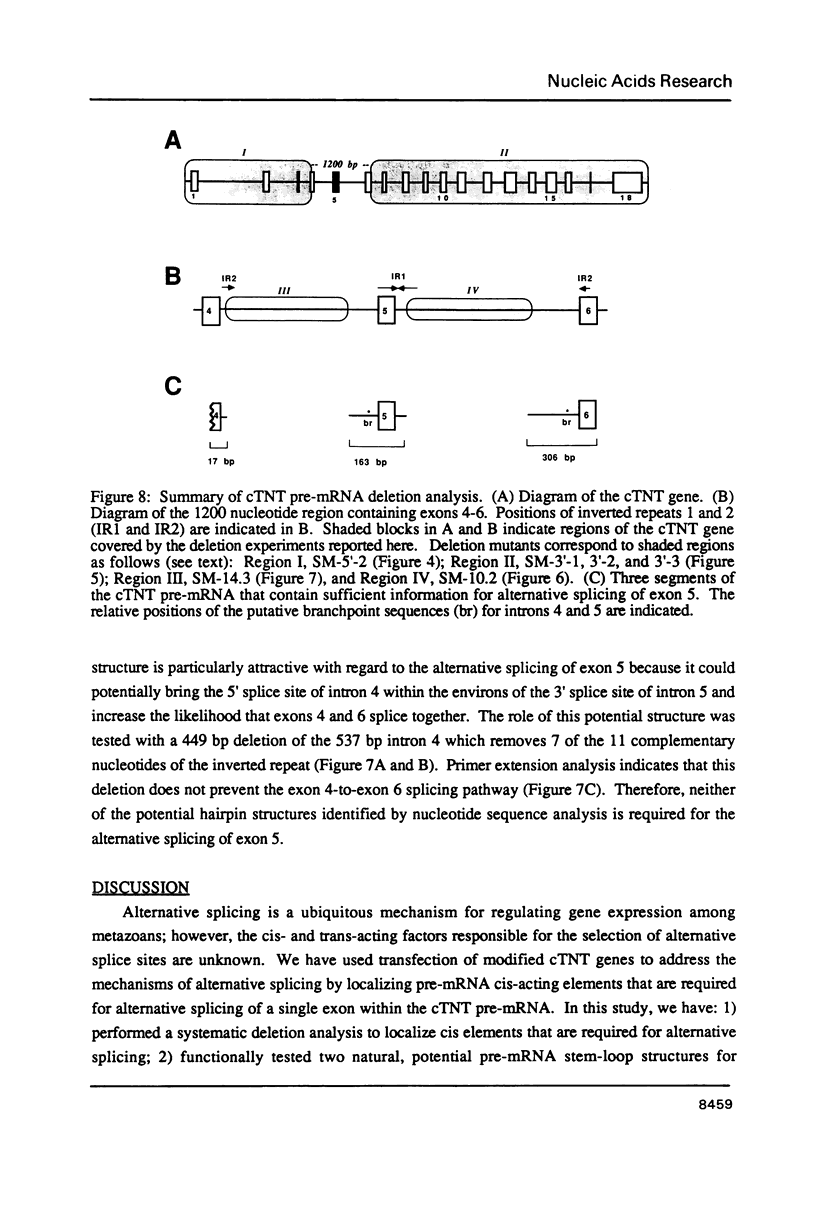
The cardiac troponin T (cTNT) pre-mRNA splices 17 exons contiguously but alternatively splices (includes or excludes) the fifth exon. Because both alternative splice products are processed from the same pre-mRNA species, the cTNT pre-mRNA must contain cis-acting sequences which specify exon 5 as an alternative exon. A cTNT minigene (SM-1) transfected into cultured cells produces mRNAs both including and excluding exon 5. The junctions of exons 4-5-6 and 4-6 in the cTNT minigene mRNAs are identical to those of endogenous cTNT mRNAs and no other exons are alternatively spliced. Thus, the SM-1 pre-mRNA is correctly alternatively spliced in transfected cells. To circumscribe the pre-mRNA regions which are required for the alternative nature of exon 5, we have constructed a systematic series of deletion mutants of SM-1. Transfection of this series demonstrates that a 1200 nt pre-mRNA region containing exons 4, 5, and 6 is sufficient to direct alternative splicing of exon 5. Within this region are two relatively large inverted repeats which potentially sequester the alternative exon via intramolecular base-pairing. Such sequestration of an alternative exon is consistent with models which propose pre-mRNA conformation as being determinative for alternative splicing of some pre-mRNAs. However, deletion mutants which remove the majority of each of the inverted repeats retain the ability to alternatively splice exon 5 demonstrating that neither is required for cTNT alternative splice site selection. Taken together, deletion analysis has limited cis elements required for alternative splicing to three small regions of the pre-mRNA containing exons 4, 5, and 6. In addition, the cTNT minigene pre-mRNA expresses both alternative splice products in a wide variety of cultured non-muscle cells as well as in cultured striated muscle cells, although expression of the cTNT pre-mRNA is normally restricted to striated muscle. This indicates that cis elements involved in defining the cTNT exon 5 as an alternative exon do not require muscle-specific factors in trans to function.
Full text
PDF















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Behlke M. A., Loh D. Y. Alternative splicing of murine T-cell receptor beta-chain transcripts. Nature. 1986 Jul 24;322(6077):379–382. doi: 10.1038/322379a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benyajati C., Place A. R., Wang N., Pentz E., Sofer W. Deletions at intervening sequence splice sites in the alcohol dehydrogenase gene of Drosophila. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 25;10(22):7261–7272. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.22.7261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein S. I., Hansen C. J., Becker K. D., Wassenberg D. R., 2nd, Roche E. S., Donady J. J., Emerson C. P., Jr Alternative RNA splicing generates transcripts encoding a thorax-specific isoform of Drosophila melanogaster myosin heavy chain. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2511–2519. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitbart R. E., Andreadis A., Nadal-Ginard B. Alternative splicing: a ubiquitous mechanism for the generation of multiple protein isoforms from single genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:467–495. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.002343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitbart R. E., Nadal-Ginard B. Complete nucleotide sequence of the fast skeletal troponin T gene. Alternatively spliced exons exhibit unusual interspecies divergence. J Mol Biol. 1986 Apr 5;188(3):313–324. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90157-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitbart R. E., Nadal-Ginard B. Developmentally induced, muscle-specific trans factors control the differential splicing of alternative and constitutive troponin T exons. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):793–803. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90617-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitbart R. E., Nguyen H. T., Medford R. M., Destree A. T., Mahdavi V., Nadal-Ginard B. Intricate combinatorial patterns of exon splicing generate multiple regulated troponin T isoforms from a single gene. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):67–82. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90062-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R., Bass B. L. Biological catalysis by RNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:599–629. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper T. A., Ordahl C. P. A single cardiac troponin T gene generates embryonic and adult isoforms via developmentally regulated alternate splicing. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 15;260(20):11140–11148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper T. A., Ordahl C. P. A single troponin T gene regulated by different programs in cardiac and skeletal muscle development. Science. 1984 Nov 23;226(4677):979–982. doi: 10.1126/science.6095446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham B. A., Hemperly J. J., Murray B. A., Prediger E. A., Brackenbury R., Edelman G. M. Neural cell adhesion molecule: structure, immunoglobulin-like domains, cell surface modulation, and alternative RNA splicing. Science. 1987 May 15;236(4803):799–806. doi: 10.1126/science.3576199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutscher S. L., Bhat B. M., Pursley M. H., Cladaras C., Wold W. S. Novel deletion mutants that enhance a distant upstream 5' splice in the E3 transcription unit of adenovirus 2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Aug 26;13(16):5771–5788. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.16.5771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edlind T. D., Cooley T. E., Ihler G. M. A conserved base pairing involving an alternative splice site of SV40 and polyoma late RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8566–8566. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards R. H., Selby M. J., Rutter W. J. Differential RNA splicing predicts two distinct nerve growth factor precursors. 1986 Feb 27-Mar 5Nature. 319(6056):784–787. doi: 10.1038/319784a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eperon L. P., Estibeiro J. P., Eperon I. C. The role of nucleotide sequences in splice site selection in eukaryotic pre-messenger RNA. Nature. 1986 Nov 20;324(6094):280–282. doi: 10.1038/324280a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forbes D. J., Kirschner M. W., Caput D., Dahlberg J. E., Lund E. Differential expression of multiple U1 small nuclear RNAs in oocytes and embryos of Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):681–689. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90263-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fornwald J. A., Kuncio G., Peng I., Ordahl C. P. The complete nucleotide sequence of the chick a-actin gene and its evolutionary relationship to the actin gene family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jul 10;10(13):3861–3876. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.13.3861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freier S. M., Kierzek R., Jaeger J. A., Sugimoto N., Caruthers M. H., Neilson T., Turner D. H. Improved free-energy parameters for predictions of RNA duplex stability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9373–9377. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. Y., Manley J. L. Factors influencing alternative splice site utilization in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):738–748. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garfinkel L. I., Davidson N. Developmentally regulated expression of a truncated myosin light-chain 1F/3F gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3826–3829. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Merlino G. T., Willingham M. C., Pastan I., Howard B. H. The Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat is a strong promoter when introduced into a variety of eukaryotic cells by DNA-mediated transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6777–6781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helfman D. M., Cheley S., Kuismanen E., Finn L. A., Yamawaki-Kataoka Y. Nonmuscle and muscle tropomyosin isoforms are expressed from a single gene by alternative RNA splicing and polyadenylation. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3582–3595. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez N., Weiner A. M. Formation of the 3' end of U1 snRNA requires compatible snRNA promoter elements. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):249–258. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90447-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S. H., Greenhouse J. J., Petropoulos C. J., Sutrave P. Adaptor plasmids simplify the insertion of foreign DNA into helper-independent retroviral vectors. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3004–3012. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3004-3012.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson A. P., Seow H. F., Holmes N., Drickamer K., Parham P. Clathrin light chains contain brain-specific insertion sequences and a region of homology with intermediate filaments. Nature. 1987 Mar 12;326(6109):154–159. doi: 10.1038/326154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedes D. H., Steitz J. A. Accurate 5' splice-site selection in mouse kappa immunoglobulin light chain premessenger RNAs is not cell-type-specific. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):7928–7932. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.7928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller E. B., Noon W. A. Intron splicing: a conserved internal signal in introns of animal pre-mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7417–7420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury G., Gruss P., Dhar R., Lai C. J. Processing and expression of early SV40 mRNA: a role for RNA conformation in splicing. Cell. 1979 Sep;18(1):85–92. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90356-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leff S. E., Evans R. M., Rosenfeld M. G. Splice commitment dictates neuron-specific alternative RNA processing in calcitonin/CGRP gene expression. Cell. 1987 Feb 13;48(3):517–524. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90202-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leff S. E., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Complex transcriptional units: diversity in gene expression by alternative RNA processing. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1091–1117. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund E., Kahan B., Dahlberg J. E. Differential control of U1 small nuclear RNA expression during mouse development. Science. 1985 Sep 20;229(4719):1271–1274. doi: 10.1126/science.2412294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mardon H. J., Sebastio G., Baralle F. E. A role for exon sequences in alternative splicing of the human fibronectin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 12;15(19):7725–7733. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.19.7725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin-Zanca D., Hughes S. H., Barbacid M. A human oncogene formed by the fusion of truncated tropomyosin and protein tyrosine kinase sequences. 1986 Feb 27-Mar 5Nature. 319(6056):743–748. doi: 10.1038/319743a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Gavis E. R., Kingsbury R., Axel R. Analysis of transcriptional regulatory signals of the HSV thymidine kinase gene: identification of an upstream control region. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):385–398. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90057-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munroe S. H. Secondary structure of splice sites in adenovirus mRNA precursors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 26;12(22):8437–8456. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.22.8437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabeshima Y., Fujii-Kuriyama Y., Muramatsu M., Ogata K. Alternative transcription and two modes of splicing results in two myosin light chains from one gene. Nature. 1984 Mar 22;308(5957):333–338. doi: 10.1038/308333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H., Kazazian H. H., Jr, Antonarakis S. E., Goff S. C., Boehm C. D., Sexton J. P., Waber P. G., Giardina P. J. Linkage of beta-thalassaemia mutations and beta-globin gene polymorphisms with DNA polymorphisms in human beta-globin gene cluster. Nature. 1982 Apr 15;296(5858):627–631. doi: 10.1038/296627a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUBIN H. Interactions between Newcastle disease virus (NDV), antibody and cell. Virology. 1957 Dec;4(3):533–562. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(57)90085-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R., Maniatis T. Intron sequences involved in lariat formation during pre-mRNA splicing. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90064-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinach F. C., MacLeod A. R. Tissue-specific expression of the human tropomyosin gene involved in the generation of the trk oncogene. Nature. 1986 Aug 14;322(6080):648–650. doi: 10.1038/322648a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Krainer A. R., Maniatis T., Green M. R. Excision of an intact intron as a novel lariat structure during pre-mRNA splicing in vitro. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):317–331. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90553-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schejter E. D., Segal D., Glazer L., Shilo B. Z. Alternative 5' exons and tissue-specific expression of the Drosophila EGF receptor homolog transcripts. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1091–1101. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90709-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiki M., Hikikoshi A., Taniguchi T., Yoshida M. Expression of the pX gene of HTLV-I: general splicing mechanism in the HTLV family. Science. 1985 Jun 28;228(4707):1532–1534. doi: 10.1126/science.2990031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shtivelman E., Lifshitz B., Gale R. P., Roe B. A., Canaani E. Alternative splicing of RNAs transcribed from the human abl gene and from the bcr-abl fused gene. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):277–284. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90450-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sisodia S. S., Cleveland D. W., Sollner-Webb B. A combination of RNase H and S1 nuclease circumvents an artefact inherent to conventional S1 analysis of RNA splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 11;15(5):1995–2011. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.5.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sisodia S. S., Sollner-Webb B., Cleveland D. W. Specificity of RNA maturation pathways: RNAs transcribed by RNA polymerase III are not substrates for splicing or polyadenylation. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3602–3612. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solnick D. Alternative splicing caused by RNA secondary structure. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):667–676. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90239-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solnick D., Lee S. I. Amount of RNA secondary structure required to induce an alternative splice. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3194–3198. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somasekhar M. B., Mertz J. E. Exon mutations that affect the choice of splice sites used in processing the SV40 late transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Aug 12;13(15):5591–5609. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.15.5591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton L. W., Bishop J. M. Alternative processing of RNA transcribed from NMYC. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4266–4272. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svensson C., Akusjärvi G. Defective RNA splicing in the absence of adenovirus-associated RNAI. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4690–4694. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R., Orkin S. H., Maniatis T. Specific transcription and RNA splicing defects in five cloned beta-thalassaemia genes. Nature. 1983 Apr 14;302(5909):591–596. doi: 10.1038/302591a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vibe-Pedersen K., Kornblihtt A. R., Baralle F. E. Expression of a human alpha-globin/fibronectin gene hybrid generates two mRNAs by alternative splicing. EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2511–2516. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02165.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring R. B., Davies R. W. Assessment of a model for intron RNA secondary structure relevant to RNA self-splicing--a review. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):277–291. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieringa B., Hofer E., Weissmann C. A minimal intron length but no specific internal sequence is required for splicing the large rabbit beta-globin intron. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):915–925. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90426-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeitlin S., Efstratiadis A. In vivo splicing products of the rabbit beta-globin pre-mRNA. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):589–602. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90466-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis: a simple method using two oligonucleotide primers and a single-stranded DNA template. DNA. 1984 Dec;3(6):479–488. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1984.3.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vegvar H. E., Lund E., Dahlberg J. E. 3' end formation of U1 snRNA precursors is coupled to transcription from snRNA promoters. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):259–266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90448-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]