Abstract
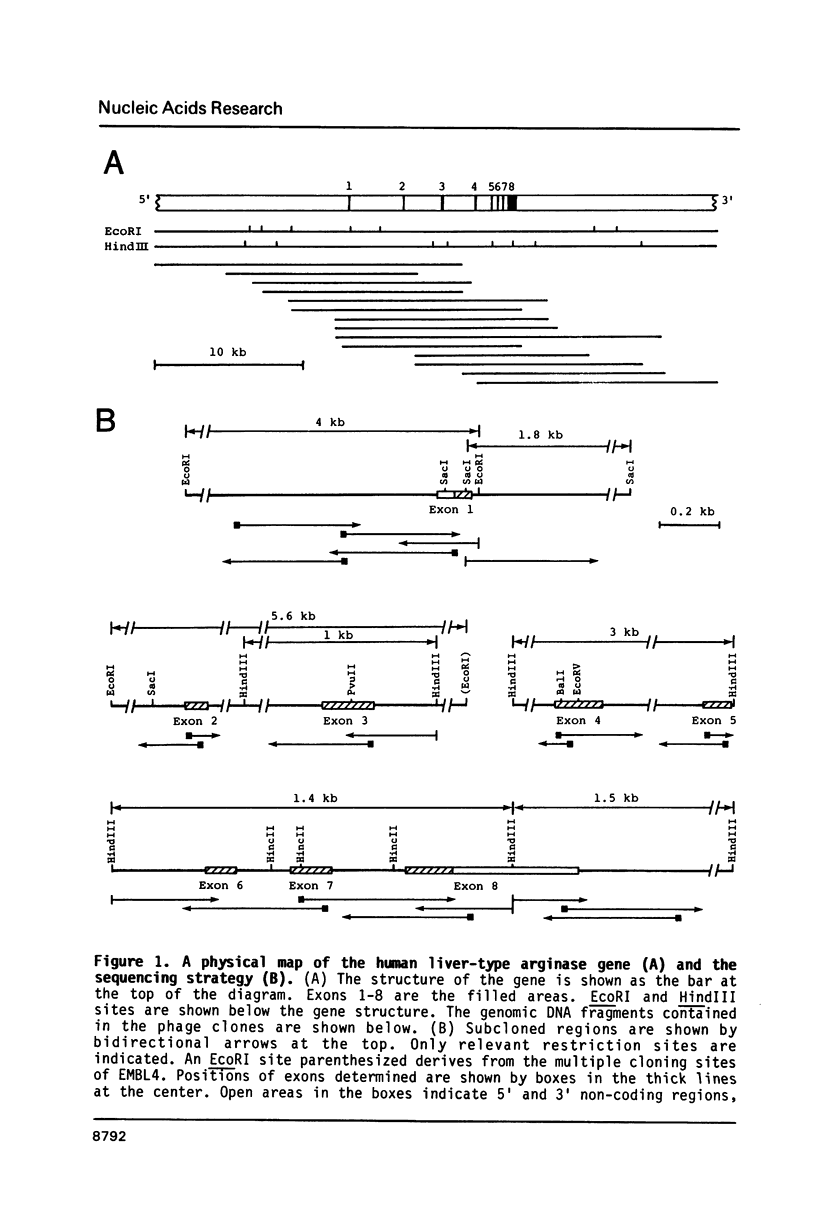
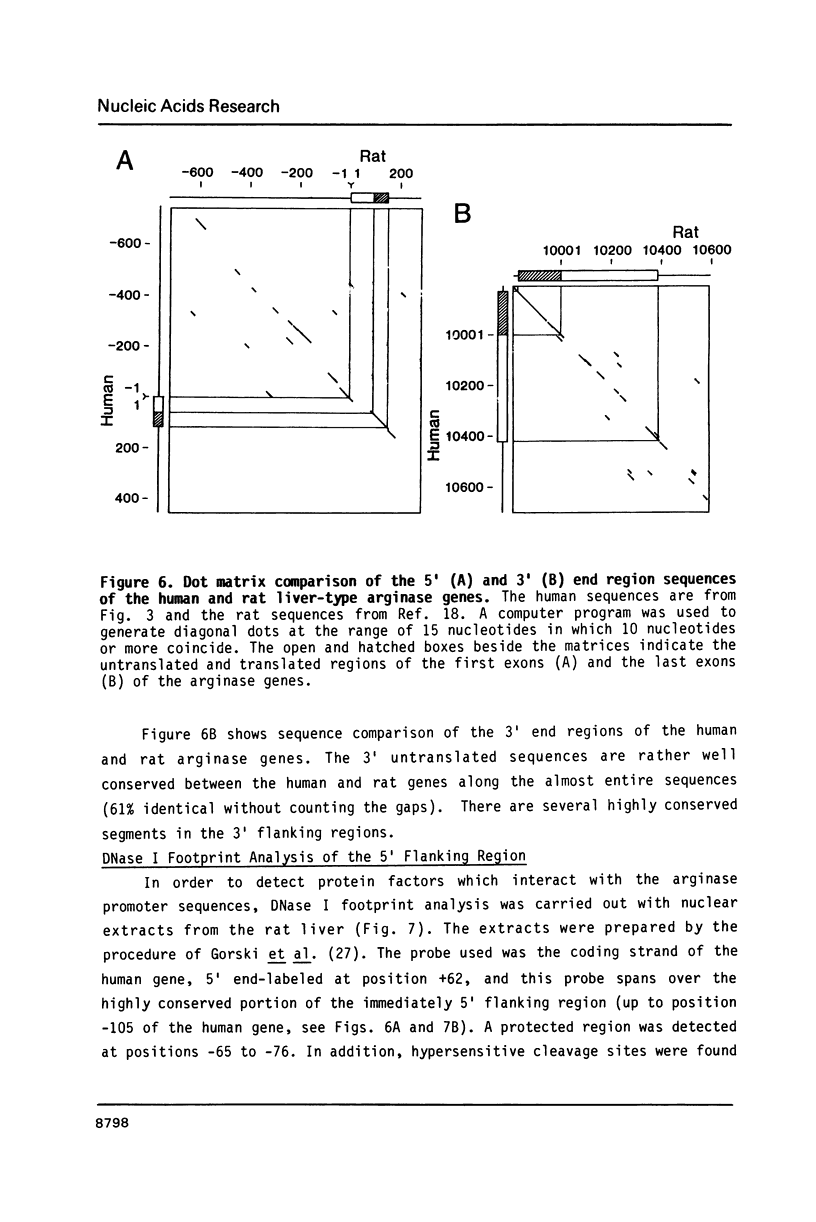
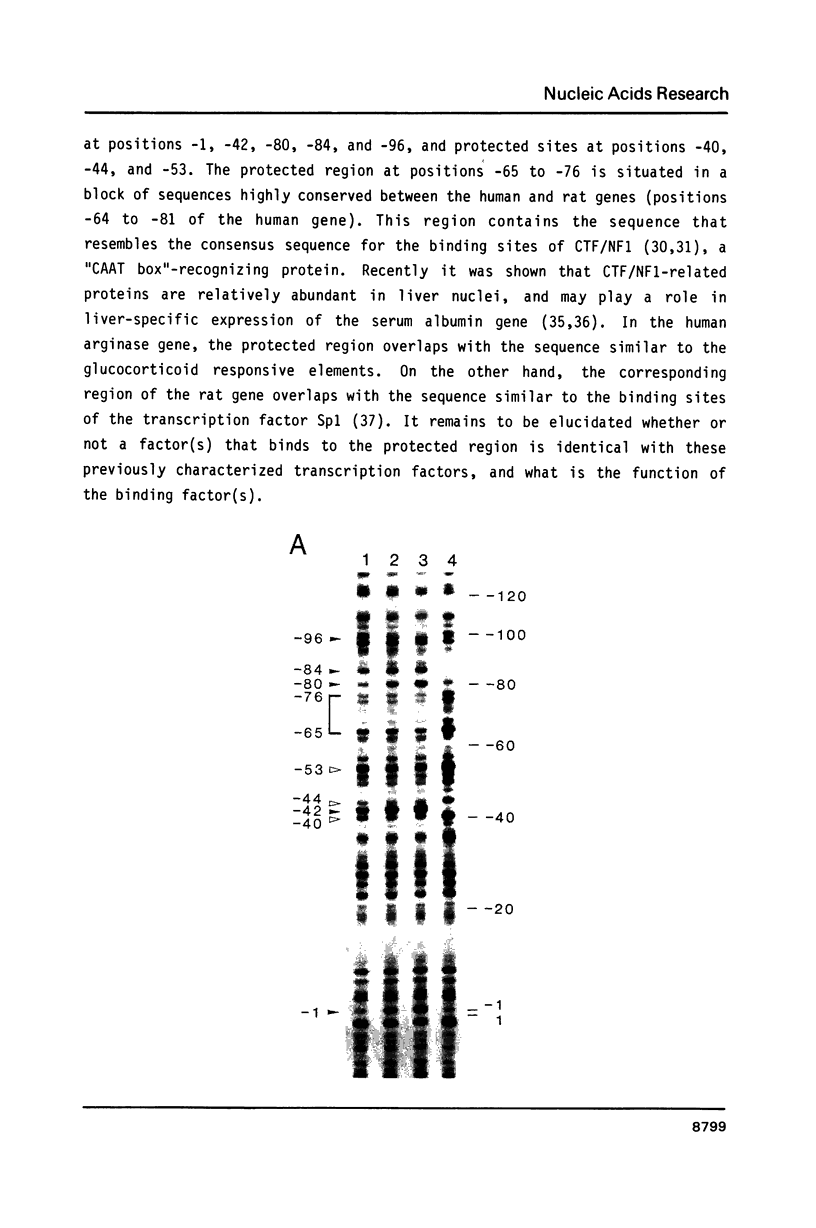
The gene for human liver-type arginase (EC 3.5.3.1), a urea cycle enzyme, was cloned and the structure was determined. This gene is 11.5 kilobases long and is split into 8 exons. The cap site was determined by nuclease S1 mapping and primer extension. A "TATA box"-like sequence is located 28 bases upstream from the cap site, and a sequence similar to the binding sites of the transcription factor CTF/NF1, a "CAAT box"-binding protein, is located 72 bases upstream. In the 5' end region, sequences resembling the glucocorticoid responsive elements, the cAMP responsive elements, and the enhancer core sequences are present. The immediately 5' flanking region of the human gene up to position -105 is 84% identical with the corresponding segment of the rat gene. In this region of the human gene, one DNase I-protected area and several hypersensitive cleavage sites were detected by footprint analysis, using nuclear extracts from the rat liver. The protected area contains the sequence similar to the binding sites of CTF/NF1 and also overlaps with the sequence resembling the glucocorticoid responsive elements.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agarwal K. L., Brunstedt J., Noyes B. E. A general method for detection and characterization of an mRNA using an oligonucleotide probe. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):1023–1028. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cereghini S., Raymondjean M., Carranca A. G., Herbomel P., Yaniv M. Factors involved in control of tissue-specific expression of albumin gene. Cell. 1987 Aug 14;50(4):627–638. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90036-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freytag S. O., Beaudet A. L., Bock H. G., O'Brien W. E. Molecular structure of the human argininosuccinate synthetase gene: occurrence of alternative mRNA splicing. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):1978–1984. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebhardt R., Mecke D. Permissive effect of dexamethasone on glucagon induction of urea-cycle enzymes in perifused primary monolayer cultures of rat hepatocytes. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jun;97(1):29–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13082.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass R. D., Knox W. E. Arginase isozymes of rat mammary gland, liver, and other tissues. J Biol Chem. 1973 Aug 25;248(16):5785–5789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski K., Carneiro M., Schibler U. Tissue-specific in vitro transcription from the mouse albumin promoter. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):767–776. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90519-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haraguchi Y., Takiguchi M., Amaya Y., Kawamoto S., Matsuda I., Mori M. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of cDNA for human liver arginase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(2):412–415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.2.412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hata A., Tsuzuki T., Shimada K., Takiguchi M., Mori M., Matsuda I. Structure of the human ornithine transcarbamylase gene. J Biochem. 1988 Feb;103(2):302–308. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Sakaki Y. Dideoxy sequencing method using denatured plasmid templates. Anal Biochem. 1986 Feb 1;152(2):232–238. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90403-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzfeld A., Raper S. M. The heterogeneity of arginases in rat tissues. Biochem J. 1976 Feb 1;153(2):469–478. doi: 10.1042/bj1530469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jantzen H. M., Strähle U., Gloss B., Stewart F., Schmid W., Boshart M., Miksicek R., Schütz G. Cooperativity of glucocorticoid response elements located far upstream of the tyrosine aminotransferase gene. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):29–38. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90752-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jinno Y., Matuo S., Nomiyama H., Shimada K., Matsuda I. Novel structure of the 5' end region of the human argininosuccinate synthetase gene. J Biochem. 1985 Nov;98(5):1395–1403. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Kadonaga J. T., Rosenfeld P. J., Kelly T. J., Tjian R. A cellular DNA-binding protein that activates eukaryotic transcription and DNA replication. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):79–89. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90358-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENNAN A. L., COHEN P. P. Ammonia detoxication in liver from humans. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1961 Jan;106:170–173. doi: 10.3181/00379727-106-26274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamoto S., Amaya Y., Murakami K., Tokunaga F., Iwanaga S., Kobayashi K., Saheki T., Kimura S., Mori M. Complete nucleotide sequence of cDNA and deduced amino acid sequence of rat liver arginase. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 5;262(13):6280–6283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamoto S., Amaya Y., Oda T., Kuzumi T., Saheki T., Kimura S., Mori M. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of cDNA for arginase of rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 May 14;136(3):955–961. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90425-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagacé M., Howell B. W., Burak R., Lusty C. J., Shore G. C. Rat carbamyl-phosphate synthetase I gene. Promoter sequence and tissue-specific transcriptional regulation in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10415–10418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamers W. H., Mooren P. G., De Graaf A., Charles R. Perinatal development of the liver in rat and spiny mouse. Its relation to altricial and precocial timing of birth. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jan 15;146(2):475–480. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08675.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtsteiner S., Wuarin J., Schibler U. The interplay of DNA-binding proteins on the promoter of the mouse albumin gene. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):963–973. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90583-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin R. C., Snodgrass P. J., Rabier D. Induction of urea cycle enzymes by glucagon and dexamethasone in monolayer cultures of adult rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5061–5067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montminy M. R., Sevarino K. A., Wagner J. A., Mandel G., Goodman R. H. Identification of a cyclic-AMP-responsive element within the rat somatostatin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6682–6686. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori M., Miura S., Tatibana M., Cohen P. P. Cell-free translation of carbamyl phosphate synthetase I and ornithine transcarbamylase messenger RNAs of rat liver. Effect of dietary protein and fasting on translatable mRNA levels. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):4127–4132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris S. M., Jr, Moncman C. L., Rand K. D., Dizikes G. J., Cederbaum S. D., O'Brien W. E. Regulation of mRNA levels for five urea cycle enzymes in rat liver by diet, cyclic AMP, and glucocorticoids. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 Jul;256(1):343–353. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90455-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyunoya H., Broglie K. E., Widgren E. E., Lusty C. J. Characterization and derivation of the gene coding for mitochondrial carbamyl phosphate synthetase I of rat. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 5;260(16):9346–9356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtake A., Takiguchi M., Shigeto Y., Amaya Y., Kawamoto S., Mori M. Structural organization of the gene for rat liver-type arginase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 15;263(5):2245–2249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T. Protein-DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:293–321. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld P. J., Kelly T. J. Purification of nuclear factor I by DNA recognition site affinity chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):1398–1408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHIMKE R. T. Adaptive characteristics of urea cycle enzymes in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1962 Feb;237:459–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer S. E., Veres G., Caskey C. T. The genetic structure of mouse ornithine transcarbamylase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 25;16(4):1593–1601. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.4.1593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skrzypek-Osiecka I., Robin Y., Porembska Z. Purification of rat kidney arginases A1 and A4 and their subcellular distribution. Acta Biochim Pol. 1983;30(1):83–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparkes R. S., Dizikes G. J., Klisak I., Grody W. W., Mohandas T., Heinzmann C., Zollman S., Lusis A. J., Cederbaum S. D. The gene for human liver arginase (ARG1) is assigned to chromosome band 6q23. Am J Hum Genet. 1986 Aug;39(2):186–193. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector E. B., Rice S. C., Cederbaum S. D. Immunologic studies of arginase in tissues of normal human adult and arginase-deficient patients. Pediatr Res. 1983 Dec;17(12):941–944. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198312000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takiguchi M., Murakami T., Miura S., Mori M. Structure of the rat ornithine carbamoyltransferase gene, a large, X chromosome-linked gene with an atypical promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6136–6140. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiher H., König M., Gruss P. Multiple point mutations affecting the simian virus 40 enhancer. Science. 1983 Feb 11;219(4585):626–631. doi: 10.1126/science.6297005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]