Abstract
Supercoiled plasmid DNA is the substrate for initiation of pUB110 replication, and - by inference - for binding of its initiator protein (RepU) to the plasmid replication origin (oriU) in vivo. No hairpin structure is required for RepU-oriU recognition. RepH (the pC194 replication initiation protein) failed to initiate replication in trans at oriU. The nucleotides that determine the specificity of the replication initiation process are located within oriU but termination is unefficient. Therefore the segment that forms the full recognition signal for termination is probably located 3' of the oriU recognition sequence. Two overlapping domains, one for initiation and one required for termination, compose the leading strand replication origin of plasmid pUB110.
Full text
PDF















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alonso J. C., Tailor R. H. Initiation of plasmid pC194 replication and its control in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Dec;210(3):476–484. doi: 10.1007/BF00327200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alonso J. C., Tailor R. H., Lüder G. Characterization of recombination-deficient mutants of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jul;170(7):3001–3007. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.7.3001-3007.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alonso J. C., Trautner T. A. A gene controlling segregation of the Bacillus subtilis plasmid pC194. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;198(3):427–431. doi: 10.1007/BF00332934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alonso J. C., Viret J. F., Tailor R. H. Plasmid maintenance in Bacillus subtilis recombination-deficient mutants. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Jun;208(1-2):349–352. doi: 10.1007/BF00330464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baas P. D. Mutational analysis of the bacteriophage phi X174 replication origin. J Mol Biol. 1987 Nov 5;198(1):51–61. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90457-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benham C. J. Torsional stress and local denaturation in supercoiled DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3870–3874. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dotto G. P., Horiuchi K., Zinder N. D. Initiation and termination of phage f1 plus-strand synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7122–7126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., Mizuuchi K., O'Dea M. H., Itoh T., Tomizawa J. I. Nalidixic acid resistance: a second genetic character involved in DNA gyrase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4772–4776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gros M. F., te Riele H., Ehrlich S. D. Rolling circle replication of single-stranded DNA plasmid pC194. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3863–3869. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02724.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn J., Dubnau D. Analysis of plasmid deletional instability in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jun;162(3):1014–1023. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.3.1014-1023.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James A. A., Morrison P. T., Kolodner R. Genetic recombination of bacterial plasmid DNA. Analysis of the effect of recombination-deficient mutations on plasmid recombination. J Mol Biol. 1982 Sep 25;160(3):411–430. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90305-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan S. A., Carleton S. M., Novick R. P. Replication of plasmid pT181 DNA in vitro: requirement for a plasmid-encoded product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4902–4906. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koepsel R. R., Khan S. A. Cleavage of single-stranded DNA by plasmid pT181-encoded RepC protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 May 26;15(10):4085–4097. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.10.4085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koepsel R. R., Murray R. W., Khan S. A. Sequence-specific interaction between the replication initiator protein of plasmid pT181 and its origin of replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5484–5488. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koepsel R. R., Murray R. W., Rosenblum W. D., Khan S. A. Purification of pT181-encoded repC protein required for the initiation of plasmid replication. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 15;260(14):8571–8577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koepsel R. R., Murray R. W., Rosenblum W. D., Khan S. A. The replication initiator protein of plasmid pT181 has sequence-specific endonuclease and topoisomerase-like activities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):6845–6849. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.6845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacey R. W., Chopra I. Genetic studies of a multi-resistant strain of Staphylococcus aureus. J Med Microbiol. 1974 May;7(2):285–297. doi: 10.1099/00222615-7-2-285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohman T. M., Overman L. B. Two binding modes in Escherichia coli single strand binding protein-single stranded DNA complexes. Modulation by NaCl concentration. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3594–3603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
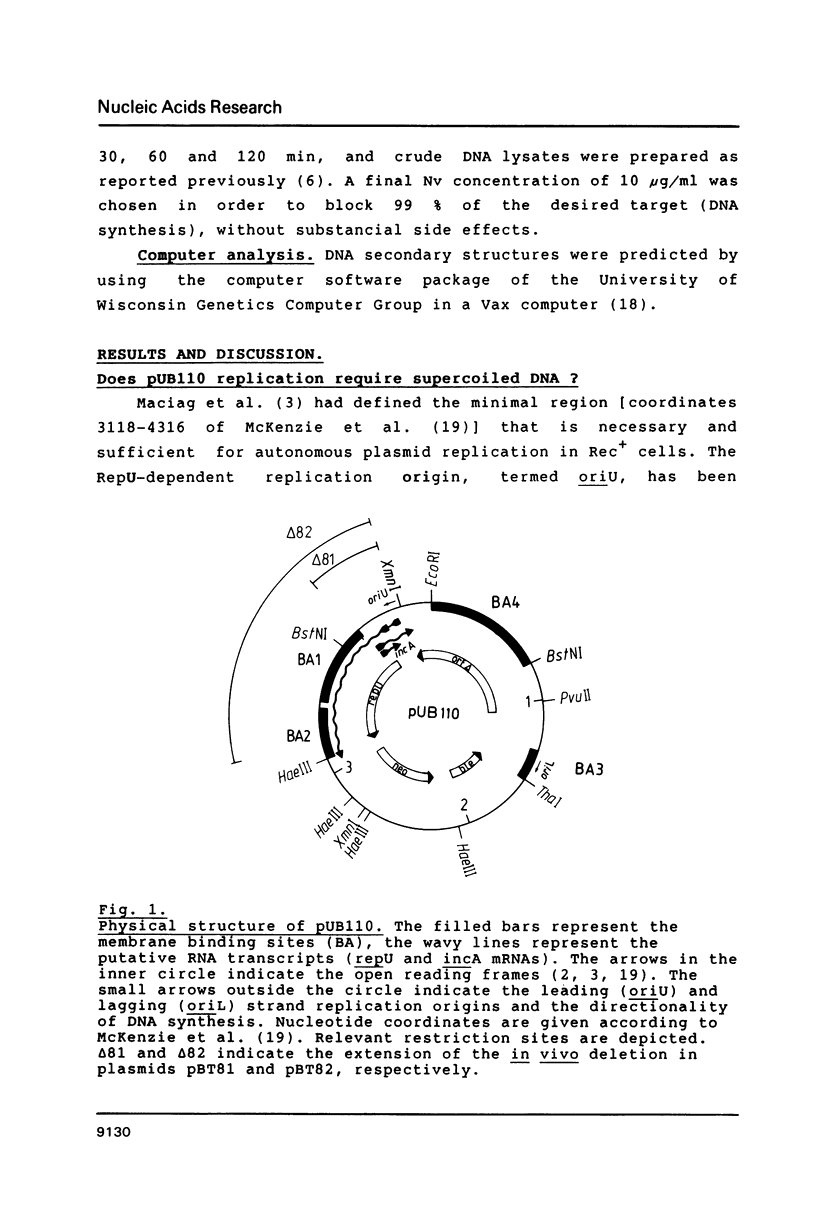
- Maciag I. E., Viret J. F., Alonso J. C. Replication and incompatibility properties of plasmid pUB110 in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 May;212(2):232–240. doi: 10.1007/BF00334690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majumder S., Novick R. P. Intermediates in plasmid pT181 DNA replication. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 11;16(7):2897–2912. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.7.2897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie T., Hoshino T., Tanaka T., Sueoka N. The nucleotide sequence of pUB110: some salient features in relation to replication and its regulation. Plasmid. 1986 Mar;15(2):93–103. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(86)90046-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel B., Ehrlich S. D. Illegitimate recombination occurs between the replication origin of the plasmid pC194 and a progressing replication fork. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3691–3696. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04701.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller R. E., Ano T., Imanaka T., Aiba S. Complete nucleotide sequences of Bacillus plasmids pUB110dB, pRBH1 and its copy mutants. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Jan;202(1):169–171. doi: 10.1007/BF00330534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottländer E., Trautner T. A. Genetic and transfection studies with B, subtilis phage SP 50. I. Phage mutants with restricted growth on B. subtilis strain 168. Mol Gen Genet. 1970;108(1):47–60. doi: 10.1007/BF00343184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
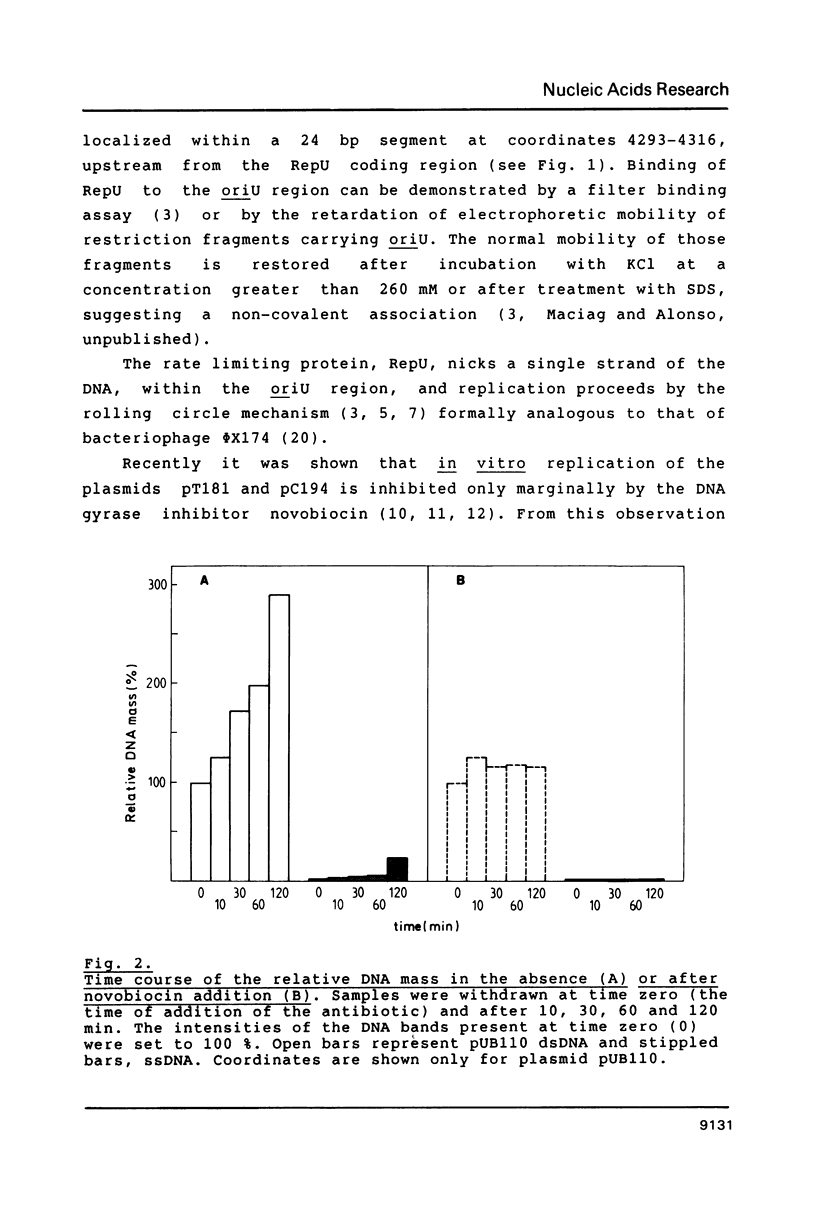
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarachu A. N., Alonso J. C., Grau O. Novobiocin blocks the shutoff of SPO1 early transcription. Virology. 1980 Aug;105(1):13–18. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90151-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semon D., Movva N. R., Smith T. F., el Alama M., Davies J. Plasmid-determined bleomycin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Plasmid. 1987 Jan;17(1):46–53. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(87)90007-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheehy R. J., Novick R. P. Studies on plasmid replication. V Replicative intermediates. J Mol Biol. 1975 Apr 5;93(2):237–253. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90130-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
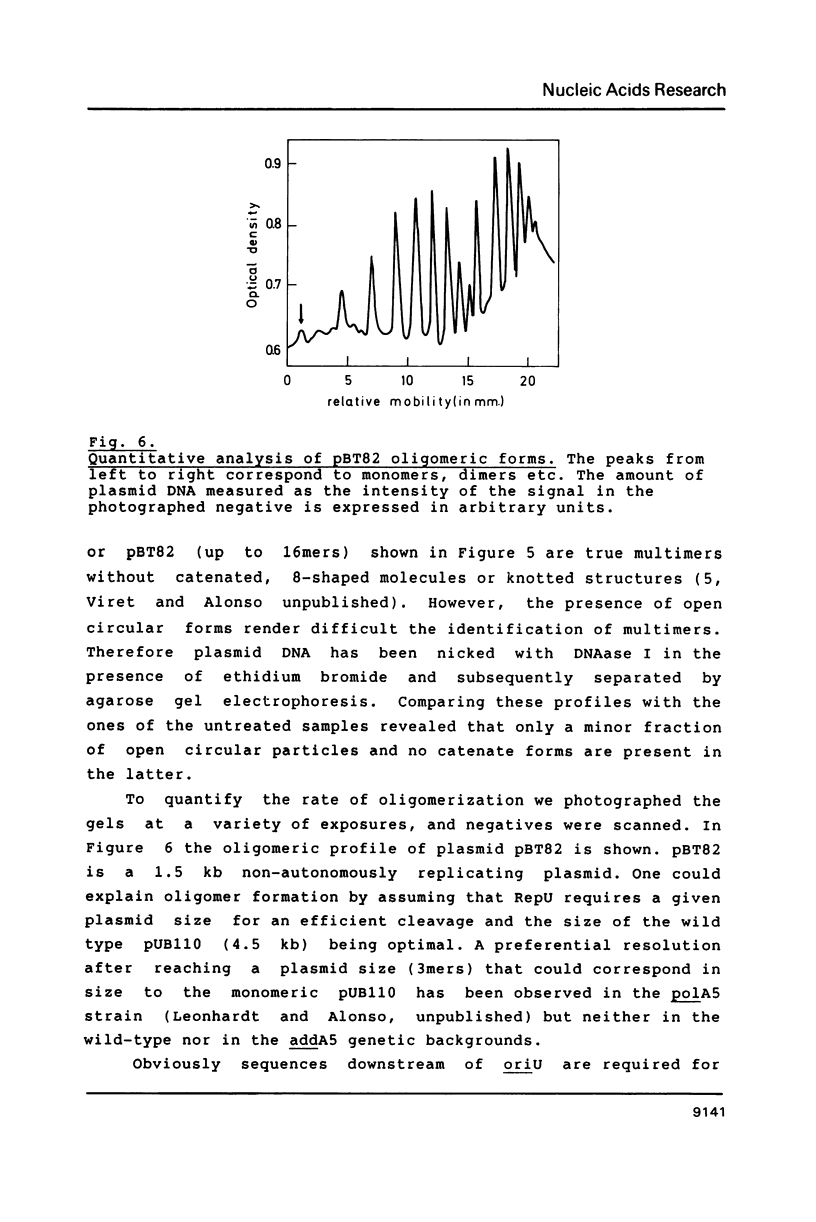
- Tinoco I., Jr, Borer P. N., Dengler B., Levin M. D., Uhlenbeck O. C., Crothers D. M., Bralla J. Improved estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 14;246(150):40–41. doi: 10.1038/newbio246040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viret J. F., Alonso J. C. A DNA sequence outside the pUB110 minimal replicon is required for normal replication in Bacillus subtilis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 25;16(10):4389–4406. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.10.4389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viret J. F., Alonso J. C. Generation of linear multigenome-length plasmid molecules in Bacillus subtilis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 25;15(16):6349–6367. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.16.6349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren G. J., Clark A. J. Sequence-specific recombination of plasmid ColE1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6724–6728. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winston S., Sueoka N. DNA-membrane association is necessary for initiation of chromosomal and plasmid replication in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2834–2838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- del Solar G., Diaz R., Espinosa M. Replication of the streptococcal plasmid pMV158 and derivatives in cell-free extracts of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Mar;206(3):428–435. doi: 10.1007/BF00428882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- te Riele H., Michel B., Ehrlich S. D. Single-stranded plasmid DNA in Bacillus subtilis and Staphylococcus aureus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2541–2545. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Mansfeld A. D., van Teeffelen H. A., Fluit A. C., Baas P. D., Jansz H. S. Effect of SSB protein on cleavage of single-stranded DNA by phi X gene A protein and A* protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 25;14(4):1845–1861. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.4.1845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]