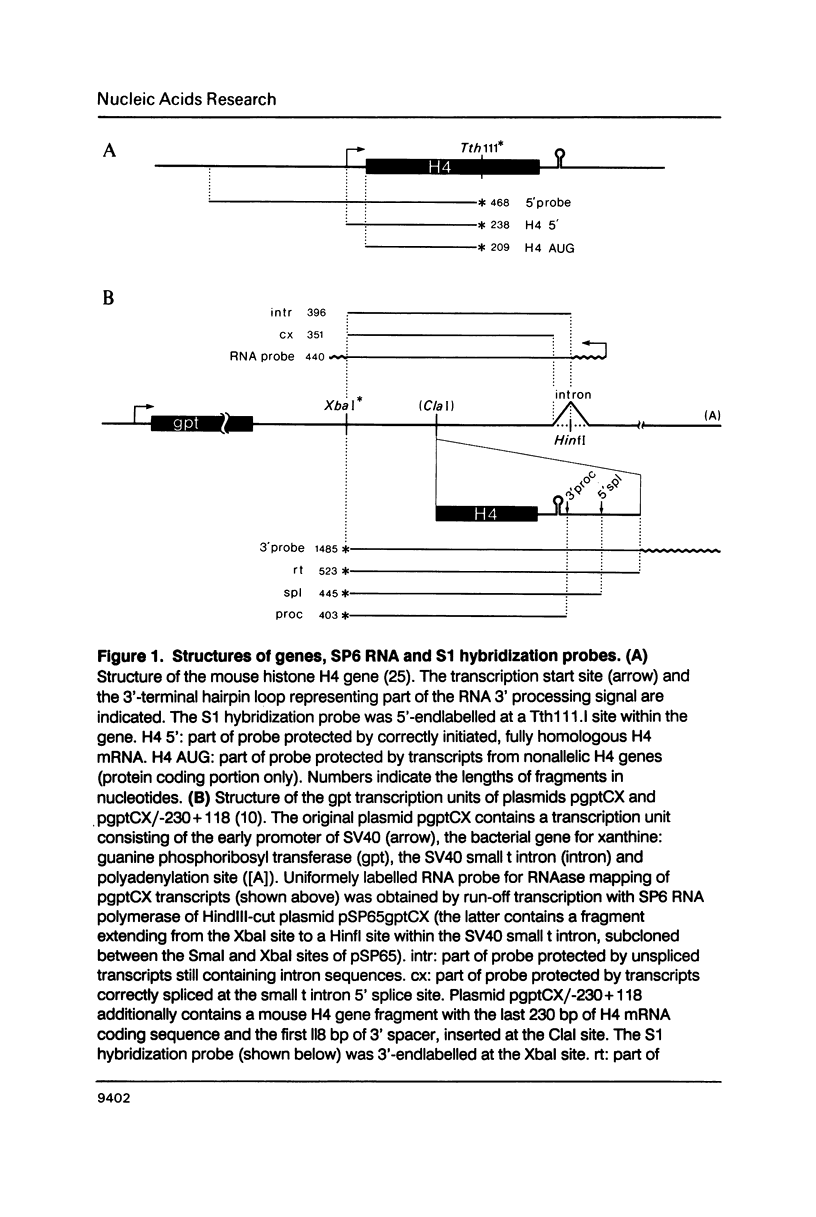
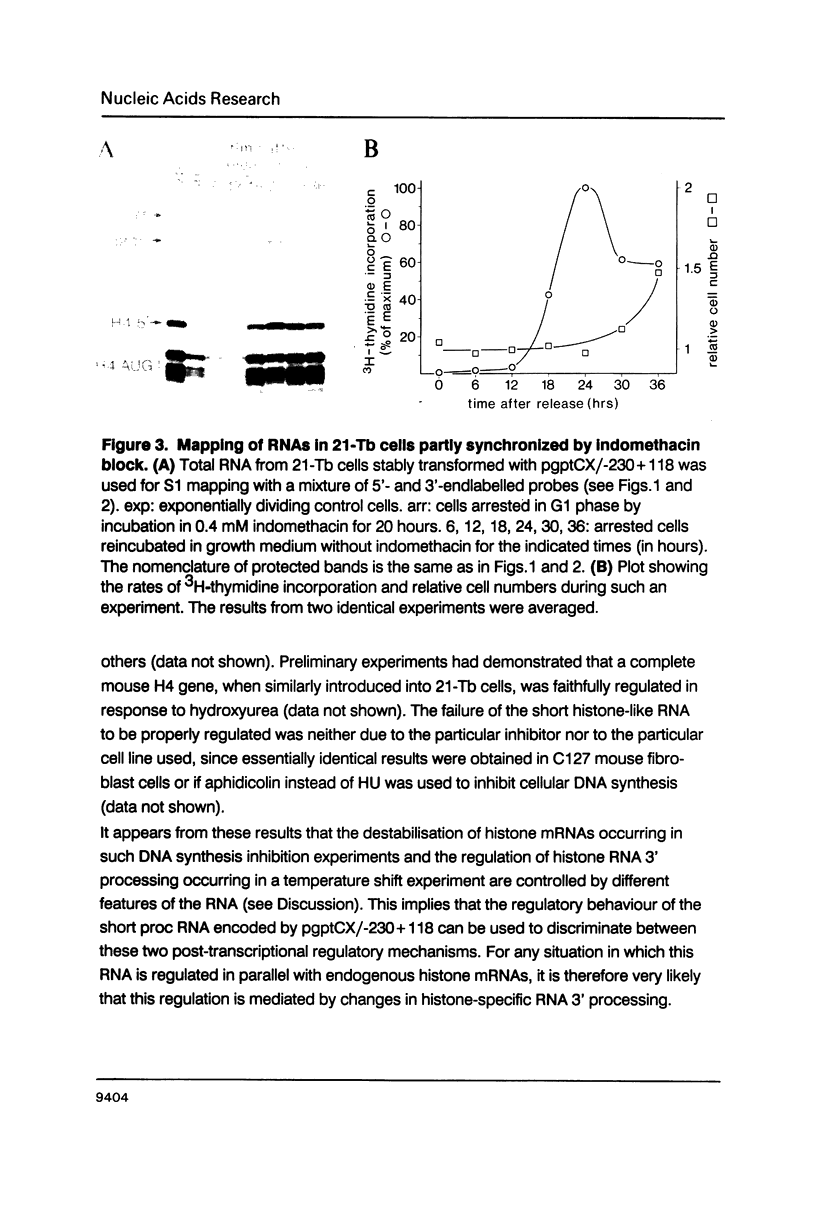
Abstract
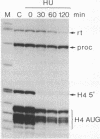
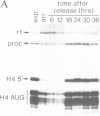
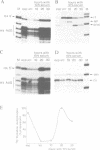
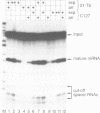
A short histone-like fusion RNA, generated when the RNA 3' processing signal from a mouse histone H4 gene is inserted into a heterologous transcription unit, becomes correctly down-regulated in G1-arrested cells of a temperature-sensitive mouse mastocytoma cell cycle mutant (21-Tb; Stauber et al., EMBO J. 5, 3297-3303 [1986]), due to a specific deficiency in histone RNA processing (Lüscher and Schümperli, EMBO J. 6, 1721-1726 [1987]). In contrast, inhibitors of DNA synthesis, known to stimulate histone mRNA degradation, have little or no effect on the fusion RNA. This RNA can therefore be used to discriminate between regulation by RNA 3' processing and RNA stability, respectively. The fusion RNA is also faithfully regulated in 21-Tb cells arrested in G1 phase by the drug indomethacin or in C127 mouse fibroblasts during a serum starvation experiment. Moreover, nuclear extracts from serum-starved C127 cells show a specific deficiency in a heat-labile component of the histone RNA processing apparatus, similar to that previously observed for temperature-arrested 21-Tb cells. These results suggest that RNA 3' processing is a major determinant for the response of histone mRNA levels to changes in cell proliferation.
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Artishevsky A., Wooden S., Sharma A., Resendez E., Jr, Lee A. S. Cell-cycle regulatory sequences in a hamster histone promoter and their interactions with cellular factors. 1987 Aug 27-Sep 2Nature. 328(6133):823–827. doi: 10.1038/328823a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumbach L. L., Stein G. S., Stein J. L. Regulation of human histone gene expression: transcriptional and posttranscriptional control in the coupling of histone messenger RNA stability with DNA replication. Biochemistry. 1987 Sep 22;26(19):6178–6187. doi: 10.1021/bi00393a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer B. M., Kruth H. S., Vaughan M., Beaven M. A. Arrest of cultured cells in the G1 phase of the cell cycle by indomethacin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1979 Jul;210(1):106–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnstiel M. L., Busslinger M., Strub K. Transcription termination and 3' processing: the end is in site! Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):349–359. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capasso O., Bleecker G. C., Heintz N. Sequences controlling histone H4 mRNA abundance. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1825–1831. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02437.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalton S., Wells J. R. A gene-specific promoter element is required for optimal expression of the histone H1 gene in S-phase. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):49–56. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02782.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher C., Heintz N., Roeder R. G. Purification and characterization of OTF-1, a transcription factor regulating cell cycle expression of a human histone H2b gene. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):773–781. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90100-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gick O., Krämer A., Keller W., Birnstiel M. L. Generation of histone mRNA 3' ends by endonucleolytic cleavage of the pre-mRNA in a snRNP-dependent in vitro reaction. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1319–1326. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04362.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gick O., Krämer A., Vasserot A., Birnstiel M. L. Heat-labile regulatory factor is required for 3' processing of histone precursor mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8937–8940. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves R. A., Marzluff W. F. Rapid reversible changes in the rate of histone gene transcription and histone mRNA levels in mouse myeloma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;4(2):351–357. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.2.351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves R. A., Pandey N. B., Chodchoy N., Marzluff W. F. Translation is required for regulation of histone mRNA degradation. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):615–626. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90240-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaBella F., Sive H. L., Roeder R. G., Heintz N. Cell-cycle regulation of a human histone H2b gene is mediated by the H2b subtype-specific consensus element. Genes Dev. 1988 Jan;2(1):32–39. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.1.32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine B. J., Chodchoy N., Marzluff W. F., Skoultchi A. I. Coupling of replication type histone mRNA levels to DNA synthesis requires the stem-loop sequence at the 3' end of the mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6189–6193. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowy D. R., Rands E., Scolnick E. M. Helper-independent transformation by unintegrated Harvey sarcoma virus DNA. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):291–298. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.291-298.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüscher B., Schümperli D. RNA 3' processing regulates histone mRNA levels in a mammalian cell cycle mutant. A processing factor becomes limiting in G1-arrested cells. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1721–1726. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02423.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüscher B., Stauber C., Schindler R., Schümperli D. Faithful cell-cycle regulation of a recombinant mouse histone H4 gene is controlled by sequences in the 3'-terminal part of the gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4389–4393. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marzluff W. F., Pandey N. B. Multiple regulatory steps control histone mRNA concentrations. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Feb;13(2):49–52. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90027-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan R. C., Berg P. Selection for animal cells that express the Escherichia coli gene coding for xanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2072–2076. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osley M. A., Gould J., Kim S., Kane M. Y., Hereford L. Identification of sequences in a yeast histone promoter involved in periodic transcription. Cell. 1986 May 23;45(4):537–544. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90285-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandey N. B., Marzluff W. F. The stem-loop structure at the 3' end of histone mRNA is necessary and sufficient for regulation of histone mRNA stability. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4557–4559. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peltz S. W., Ross J. Autogenous regulation of histone mRNA decay by histone proteins in a cell-free system. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4345–4356. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt T. Transcription termination and the regulation of gene expression. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:339–372. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.002011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plumb M., Stein J., Stein G. Coordinate regulation of multiple histone mRNAs during the cell cycle in HeLa cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2391–2410. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaer J. C., Schindler R. The requirement of mammalian cell cultures for serum proteins. Growth-promoting activity of pepsin-digested serum albumin in different media. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Sep 19;147(1):154–161. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(67)90098-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schümperli D. Multilevel regulation of replication-dependent histone genes. Trends Genet. 1988 Jul;4(7):187–191. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90074-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiler-Tuyns A., Birnstiel M. L. Structure and expression in L-cells of a cloned H4 histone gene of the mouse. J Mol Biol. 1981 Oct 5;151(4):607–625. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90426-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiler-Tuyns A., Paterson B. M. Cell cycle regulation of a mouse histone H4 gene requires the H4 promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1048–1054. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sive H. L., Heintz N., Roeder R. G. Regulation of human histone gene expression during the HeLa cell cycle requires protein synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2723–2734. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stauber C., Lüscher B., Eckner R., Lötscher E., Schümperli D. A signal regulating mouse histone H4 mRNA levels in a mammalian cell cycle mutant and sequences controlling RNA 3' processing are both contained within the same 80-bp fragment. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3297–3303. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04643.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stimac E., Groppi V. E., Jr, Coffino P. Inhibition of protein synthesis stabilizes histone mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):2082–2090. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.2082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver R. F., Weissmann C. Mapping of RNA by a modification of the Berk-Sharp procedure: the 5' termini of 15 S beta-globin mRNA precursor and mature 10 s beta-globin mRNA have identical map coordinates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1175–1193. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R. Biochemical transfer of single-copy eucaryotic genes using total cellular DNA as donor. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):725–731. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90254-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann A., Schaer J. C., Muller D. E., Schneider J., Miodonski-Maculewicz N. M., Schindler R. Formation of mast cell granules in cell cycle mutants of an undifferentiated mastocytoma line: evidence for two different states of reversible proliferative quiescence. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;96(6):1756–1760. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.6.1756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]