Abstract
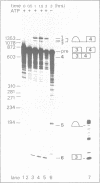
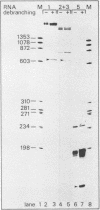
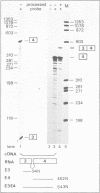
To study splice site selection in alternative RNA processing we used the human Calcitonin/CGRP-I (CALC-I) gene. Expression of the CALC-I gene in thyroid C-cells results predominantly in calcitonin (CT) mRNA (containing exons 1 to 4) whereas CGRP-I mRNA (containing exons 1,2,3,5 and 6) is the exclusive product in particular nerve cells. We previously reported that a model precursor RNA containing the exon 3 to exon 5 region is predominantly processed into CGRP-I mRNA in vitro using nuclear extracts of three different cell types. To study CT specific processing in Hela cell nuclear extracts we have used precursor RNAs corresponding to the exon 3 to exon 4 region containing only CT specific processing signals. The results revealed the usage of a uridine residue 23 nucleotides upstream of the 3' splice site as the major site of lariat formation in CT specific splicing. The implications of this finding for the alternative, tissue specific processing of the CALC-I pre-mRNA and for branch point selection in general are discussed.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aebi M., Hornig H., Padgett R. A., Reiser J., Weissmann C. Sequence requirements for splicing of higher eukaryotic nuclear pre-mRNA. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):555–565. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90620-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aebi M., Hornig H., Weissmann C. 5' cleavage site in eukaryotic pre-mRNA splicing is determined by the overall 5' splice region, not by the conserved 5' GU. Cell. 1987 Jul 17;50(2):237–246. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90219-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amara S. G., Evans R. M., Rosenfeld M. G. Calcitonin/calcitonin gene-related peptide transcription unit: tissue-specific expression involves selective use of alternative polyadenylation sites. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):2151–2160. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.2151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arenas J., Hurwitz J. Purification of a RNA debranching activity from HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 25;262(9):4274–4279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ares M., Jr U2 RNA from yeast is unexpectedly large and contains homology to vertebrate U4, U5, and U6 small nuclear RNAs. Cell. 1986 Oct 10;47(1):49–59. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90365-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bindereif A., Green M. R. An ordered pathway of snRNP binding during mammalian pre-mRNA splicing complex assembly. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2415–2424. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02520.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black D. L., Chabot B., Steitz J. A. U2 as well as U1 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins are involved in premessenger RNA splicing. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):737–750. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90270-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bovenberg R. A., van de Meerendonk W. P., Baas P. D., Steenbergh P. H., Lips C. J., Jansz H. S. Model for alternative RNA processing in human calcitonin gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 25;14(22):8785–8803. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.22.8785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crenshaw E. B., 3rd, Russo A. F., Swanson L. W., Rosenfeld M. G. Neuron-specific alternative RNA processing in transgenic mice expressing a metallothionein-calcitonin fusion gene. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):389–398. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90291-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domdey H., Apostol B., Lin R. J., Newman A., Brody E., Abelson J. Lariat structures are in vivo intermediates in yeast pre-mRNA splicing. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):611–621. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90468-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edbrooke M. R., Parker D., McVey J. H., Riley J. H., Sorenson G. D., Pettengill O. S., Craig R. K. Expression of the human calcitonin/CGRP gene in lung and thyroid carcinoma. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):715–724. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03688.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frendewey D., Keller W. Stepwise assembly of a pre-mRNA splicing complex requires U-snRNPs and specific intron sequences. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):355–367. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80131-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freyer G. A., Arenas J., Perkins K. K., Furneaux H. M., Pick L., Young B., Roberts R. J., Hurwitz J. In vitro formation of a lariat structure containing a G2'-5'G linkage. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 25;262(9):4267–4273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerke V., Steitz J. A. A protein associated with small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles recognizes the 3' splice site of premessenger RNA. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):973–984. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90812-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabowski P. J., Padgett R. A., Sharp P. A. Messenger RNA splicing in vitro: an excised intervening sequence and a potential intermediate. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):415–427. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90372-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabowski P. J., Seiler S. R., Sharp P. A. A multicomponent complex is involved in the splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):345–353. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80130-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R. Pre-mRNA splicing. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:671–708. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.003323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmuth K., Barta A. In vitro processing of the human growth hormone primary transcript. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 11;15(17):7005–7025. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.17.7005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmuth K., Barta A. Unusual branch point selection in processing of human growth hormone pre-mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2011–2020. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornig H., Aebi M., Weissmann C. Effect of mutations at the lariat branch acceptor site on beta-globin pre-mRNA splicing in vitro. Nature. 1986 Dec 11;324(6097):589–591. doi: 10.1038/324589a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höppener J. W., Steenbergh P. H., Slebos R. J., Visser A., Lips C. J., Jansz H. S., Bechet J. M., Lenoir G. M., Born W., Haller-Brem S. Expression of the second calcitonin/calcitonin gene-related peptide gene in Ewing sarcoma cell lines. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987 Apr;64(4):809–817. doi: 10.1210/jcem-64-4-809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller E. B., Noon W. A. Intron splicing: a conserved internal signal in introns of animal pre-mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7417–7420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Maniatis T., Ruskin B., Green M. R. Normal and mutant human beta-globin pre-mRNAs are faithfully and efficiently spliced in vitro. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):993–1005. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90049-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krämer A., Keller W., Appel B., Lührmann R. The 5' terminus of the RNA moiety of U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles is required for the splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):299–307. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90551-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamond A. I., Konarska M. M., Grabowski P. J., Sharp P. A. Spliceosome assembly involves the binding and release of U4 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):411–415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langford C. J., Klinz F. J., Donath C., Gallwitz D. Point mutations identify the conserved, intron-contained TACTAAC box as an essential splicing signal sequence in yeast. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):645–653. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90344-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leff S. E., Evans R. M., Rosenfeld M. G. Splice commitment dictates neuron-specific alternative RNA processing in calcitonin/CGRP gene expression. Cell. 1987 Feb 13;48(3):517–524. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90202-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leff S. E., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Complex transcriptional units: diversity in gene expression by alternative RNA processing. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1091–1117. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Reed R. The role of small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles in pre-mRNA splicing. Nature. 1987 Feb 19;325(6106):673–678. doi: 10.1038/325673a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M., Pettersson I., Hinterberger M., Karmas A., Steitz J. A. The U1 small nuclear RNA-protein complex selectively binds a 5' splice site in vitro. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):509–518. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90432-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson K. K., Green M. R. Splice site selection and ribonucleoprotein complex assembly during in vitro pre-mRNA splicing. Genes Dev. 1988 Mar;2(3):319–329. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.3.319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble J. C., Pan Z. Q., Prives C., Manley J. L. Splicing of SV40 early pre-mRNA to large T and small t mRNAs utilizes different patterns of lariat branch sites. Cell. 1987 Jul 17;50(2):227–236. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90218-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Grabowski P. J., Konarska M. M., Seiler S., Sharp P. A. Splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1119–1150. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Hardy S. F., Sharp P. A. Splicing of adenovirus RNA in a cell-free transcription system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5230–5234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Konarska M. M., Aebi M., Hornig H., Weissmann C., Sharp P. A. Nonconsensus branch-site sequences in the in vitro splicing of transcripts of mutant rabbit beta-globin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8349–8353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Konarska M. M., Grabowski P. J., Hardy S. F., Sharp P. A. Lariat RNA's as intermediates and products in the splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Science. 1984 Aug 31;225(4665):898–903. doi: 10.1126/science.6206566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R., Siliciano P. G., Guthrie C. Recognition of the TACTAAC box during mRNA splicing in yeast involves base pairing to the U2-like snRNA. Cell. 1987 Apr 24;49(2):229–239. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90564-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R., Maniatis T. A role for exon sequences and splice-site proximity in splice-site selection. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):681–690. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90343-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R., Maniatis T. Intron sequences involved in lariat formation during pre-mRNA splicing. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90064-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez J. R., Pikielny C. W., Rosbash M. In vivo characterization of yeast mRNA processing intermediates. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90467-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld M. G., Mermod J. J., Amara S. G., Swanson L. W., Sawchenko P. E., Rivier J., Vale W. W., Evans R. M. Production of a novel neuropeptide encoded by the calcitonin gene via tissue-specific RNA processing. Nature. 1983 Jul 14;304(5922):129–135. doi: 10.1038/304129a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Green M. R. An RNA processing activity that debranches RNA lariats. Science. 1985 Jul 12;229(4709):135–140. doi: 10.1126/science.2990042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Greene J. M., Green M. R. Cryptic branch point activation allows accurate in vitro splicing of human beta-globin intron mutants. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):833–844. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80064-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Krainer A. R., Maniatis T., Green M. R. Excision of an intact intron as a novel lariat structure during pre-mRNA splicing in vitro. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):317–331. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90553-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Zamore P. D., Green M. R. A factor, U2AF, is required for U2 snRNP binding and splicing complex assembly. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):207–219. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90509-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt P., Gattoni R., Keohavong P., Stévenin J. Alternative splicing of E1A transcripts of adenovirus requires appropriate ionic conditions in vitro. Cell. 1987 Jul 3;50(1):31–39. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90659-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A. Splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Science. 1987 Feb 13;235(4790):766–771. doi: 10.1126/science.3544217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steenbergh P. H., Höppener J. W., Zandberg J., Visser A., Lips C. J., Jansz H. S. Structure and expression of the human calcitonin/CGRP genes. FEBS Lett. 1986 Dec 1;209(1):97–103. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81091-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tazi J., Alibert C., Temsamani J., Reveillaud I., Cathala G., Brunel C., Jeanteur P. A protein that specifically recognizes the 3' splice site of mammalian pre-mRNA introns is associated with a small nuclear ribonucleoprotein. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):755–766. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90518-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeitlin S., Efstratiadis A. In vivo splicing products of the rabbit beta-globin pre-mRNA. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):589–602. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90466-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang Y., Weiner A. M. A compensatory base change in U1 snRNA suppresses a 5' splice site mutation. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):827–835. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]