Abstract
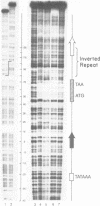
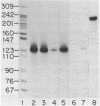
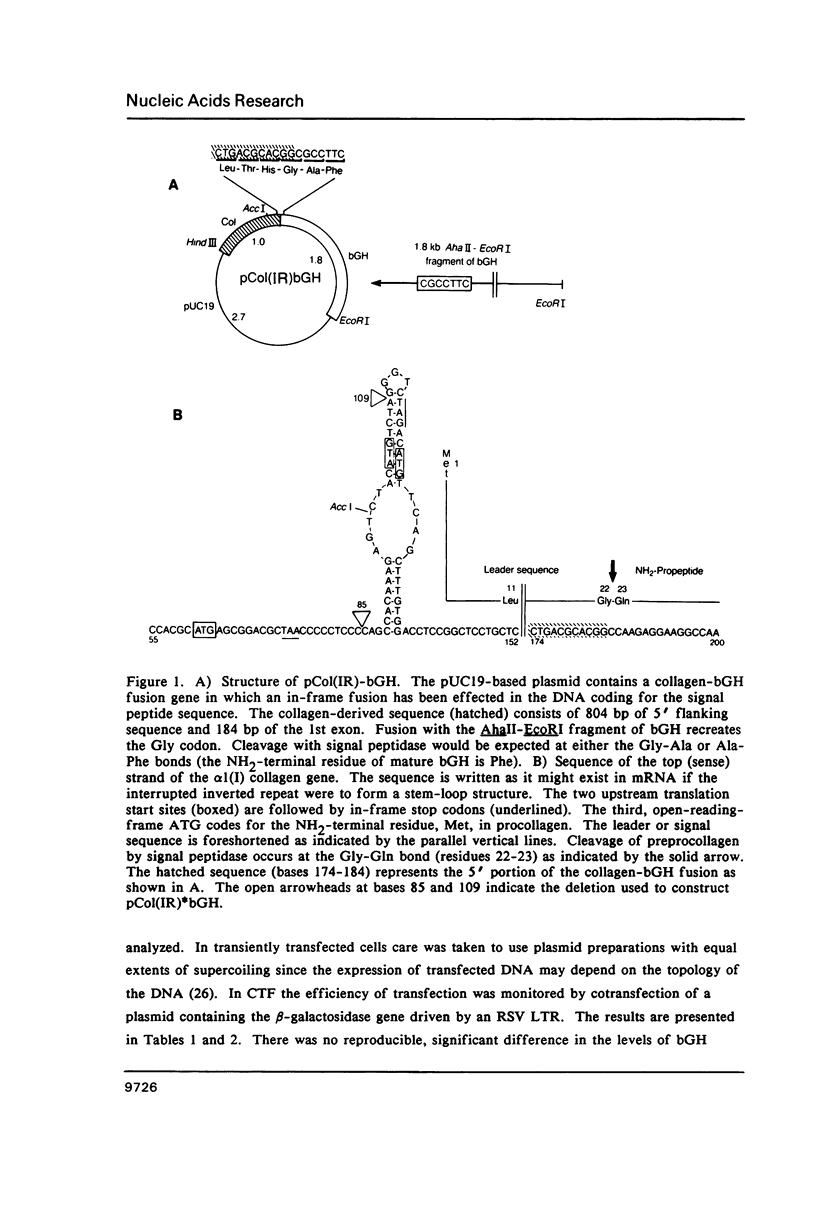
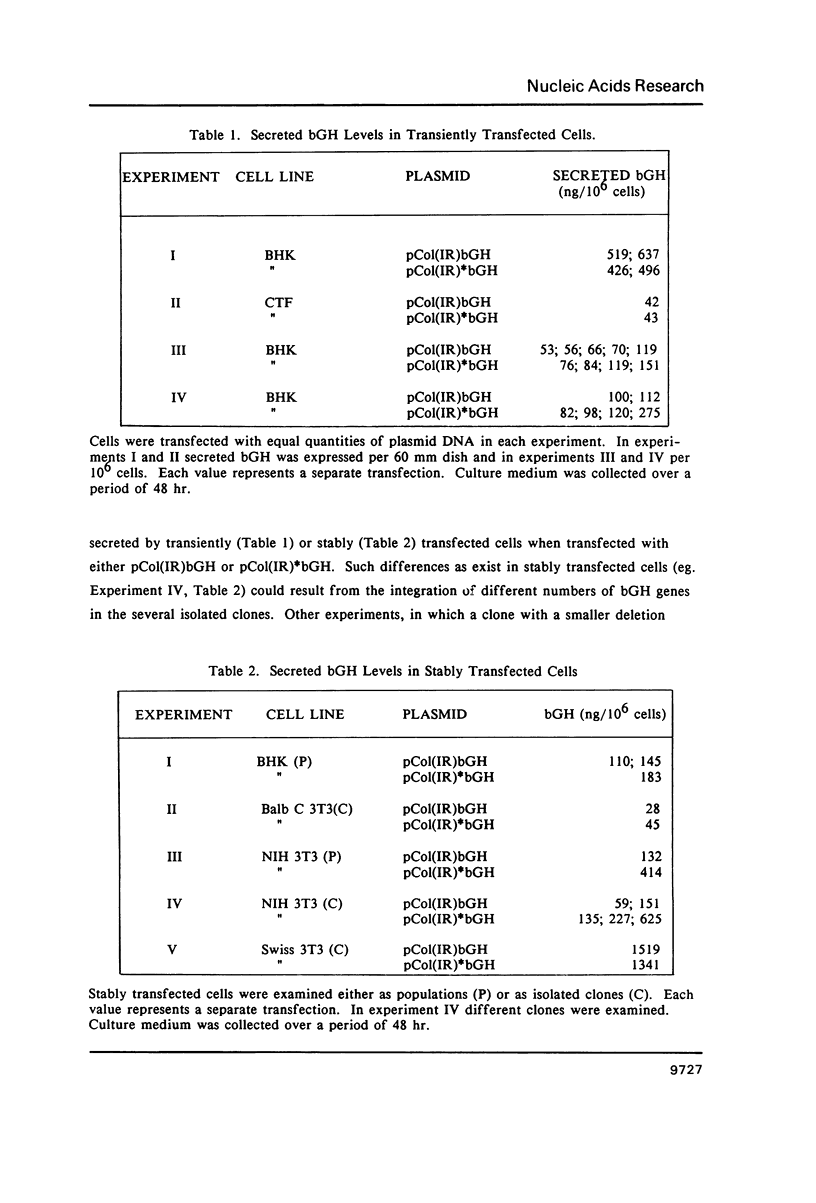
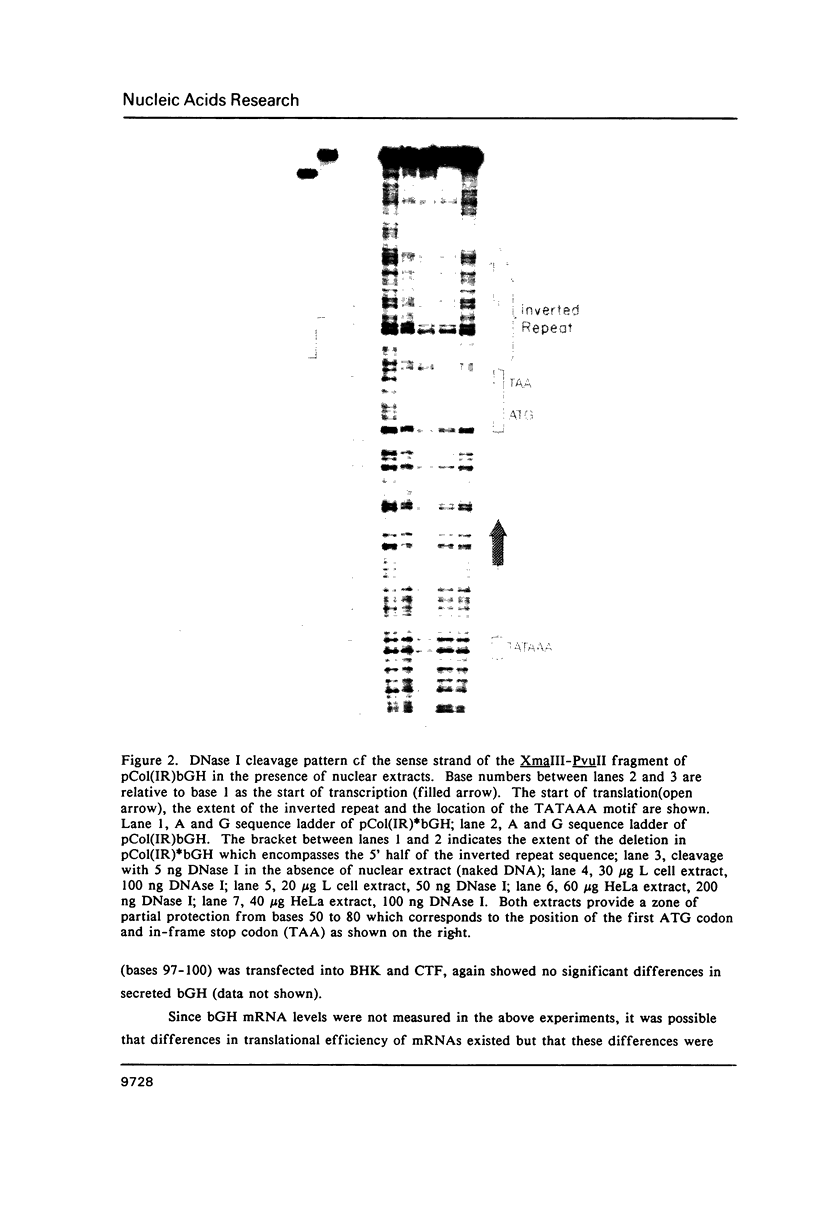
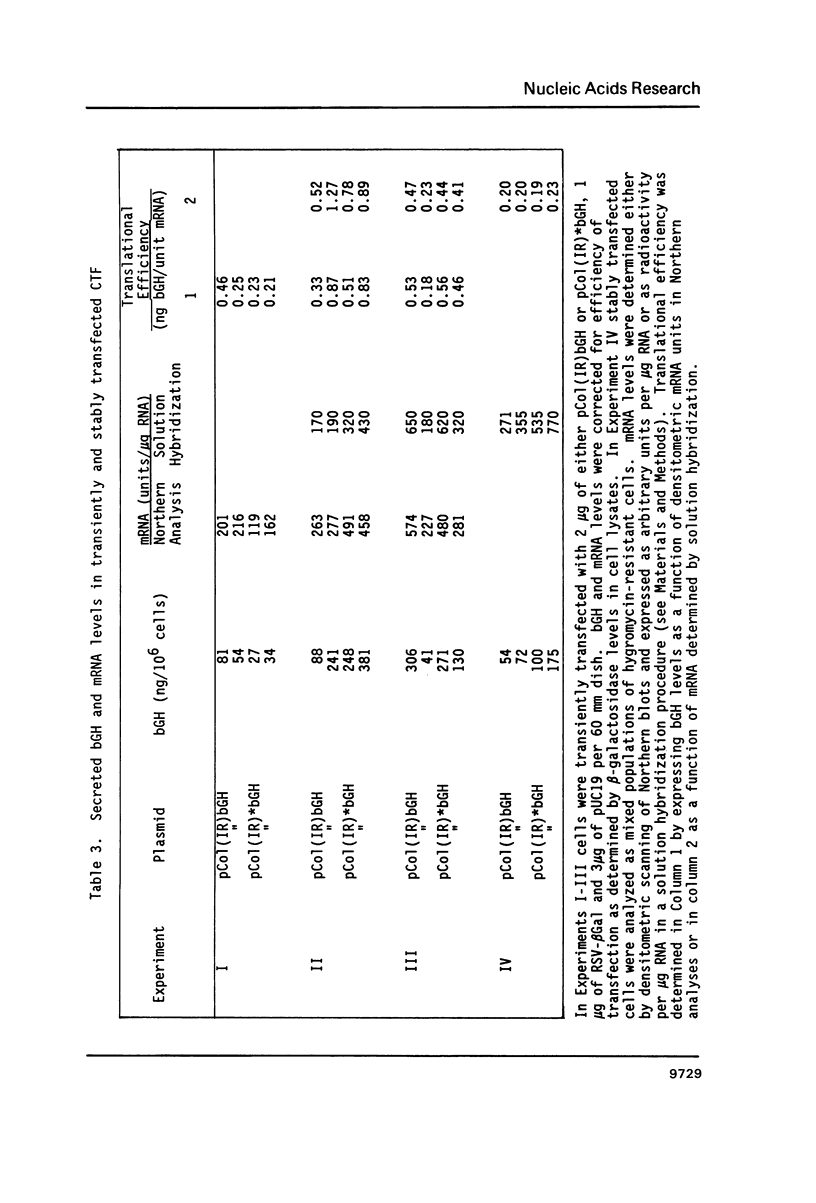
An inverted repeat sequence, extending from the 5' untranslated region of the first exon through the translation initiation codon, is highly conserved in the alpha 1(I), alpha 2(I) and alpha 1(III) collagen genes of mammals and birds. It has been suggested that this sequence functions in translational control of collagen gene expression. When the upstream axis of the dyad of symmetry was deleted, the efficiency of translation of transcripts from a human alpha 1(I) collagen-bovine growth hormone fusion gene was unchanged in either transiently or stably transfected cells. Furthermore, mRNA levels were not affected when the same deletion was transferred to a collagen-human growth hormone fusion gene in which the collagen sequence retained the first intron. Examination of human alpha 1(I) DNA, extending from the start of transcription to the start of translation, by the DNAse I protection procedure revealed evidence for protein binding to a sequence just upstream of the inverted repeat sequence but not to the inverted repeat itself. Our studies therefore indicate that this highly conserved DNA sequence does not function generally in translational or transcriptional control of type I procollagen synthesis.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allebach E. S., Boettiger D., Pacifici M., Adams S. L. Control of types I and II collagen and fibronectin gene expression in chondrocytes delineated by viral transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):1002–1008. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.1002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Augereau P., Chambon P. The mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer: effect on transcription in vitro and binding of proteins present in HeLa and lymphoid B cell extracts. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1791–1797. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04428.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aycock R. S., Raghow R., Stricklin G. P., Seyer J. M., Kang A. H. Post-transcriptional inhibition of collagen and fibronectin synthesis by a synthetic homolog of a portion of the carboxyl-terminal propeptide of human type I collagen. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 25;261(30):14355–14360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein P., McKay J., Morishima J. K., Devarayalu S., Gelinas R. E. Regulatory elements in the first intron contribute to transcriptional control of the human alpha 1(I) collagen gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8869–8873. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein P., McKay J. The first intron of the alpha 1(I) collagen gene contains several transcriptional regulatory elements. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 5;263(4):1603–1606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu M. L., de Wet W., Bernard M., Ramirez F. Fine structural analysis of the human pro-alpha 1 (I) collagen gene. Promoter structure, AluI repeats, and polymorphic transcripts. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2315–2320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson L. A., de Wet W., Di Liberto M., Weil D., Ramirez F. Analysis of the promoter region and the N-propeptide domain of the human pro alpha 2(I) collagen gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 May 24;13(10):3427–3438. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.10.3427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finer M. H., Aho S., Gerstenfeld L. C., Boedtker H., Doty P. Unusual DNA sequences located within the promoter region and the first intron of the chicken pro-alpha 1(I) collagen gene. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 25;262(27):13323–13332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Focht R. J., Adams S. L. Tissue specificity of type I collagen gene expression is determined at both transcriptional and post-transcriptional levels. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1843–1852. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freier S. M., Kierzek R., Jaeger J. A., Sugimoto N., Caruthers M. H., Neilson T., Turner D. H. Improved free-energy parameters for predictions of RNA duplex stability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9373–9377. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geballe A. P., Spaete R. R., Mocarski E. S. A cis-acting element within the 5' leader of a cytomegalovirus beta transcript determines kinetic class. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):865–872. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90068-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldenberg R., Fine R. E. Generalized inhibition of cell-free translation by the amino-terminal propeptide of chick type I procollagen. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Nov 13;826(2-3):101–107. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(85)90114-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon D. F., Quick D. P., Erwin C. R., Donelson J. E., Maurer R. A. Nucleotide sequence of the bovine growth hormone chromosomal gene. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1983 Nov;33(1):81–95. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(83)90058-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harbers K., Kuehn M., Delius H., Jaenisch R. Insertion of retrovirus into the first intron of alpha 1(I) collagen gene to embryonic lethal mutation in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1504–1508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentze M. W., Rouault T. A., Caughman S. W., Dancis A., Harford J. B., Klausner R. D. A cis-acting element is necessary and sufficient for translational regulation of human ferritin expression in response to iron. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6730–6734. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hörlein D., McPherson J., Goh S. H., Bornstein P. Regulation of protein synthesis: translational control by procollagen-derived fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6163–6167. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohno K., Sullivan M., Yamada Y. Structure of the promoter of the rat type II procollagen gene. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 10;260(7):4441–4447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Influences of mRNA secondary structure on initiation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2850–2854. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Selection of initiation sites by eucaryotic ribosomes: effect of inserting AUG triplets upstream from the coding sequence for preproinsulin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 11;12(9):3873–3893. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.9.3873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liau G., Mudryj M., de Crombrugghe B. Identification of the promoter and first exon of the mouse alpha 1 (III) collagen gene. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3773–3777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu C. C., Simonsen C. C., Levinson A. D. Initiation of translation at internal AUG codons in mammalian cells. Nature. 1984 May 3;309(5963):82–85. doi: 10.1038/309082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller P. P., Hinnebusch A. G. Multiple upstream AUG codons mediate translational control of GCN4. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):201–207. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90384-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Larin Z., Maniatis T. Detection of single base substitutions by ribonuclease cleavage at mismatches in RNA:DNA duplexes. Science. 1985 Dec 13;230(4731):1242–1246. doi: 10.1126/science.4071043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunez A. M., Kohno K., Martin G. R., Yamada Y. Promoter region of the human pro-alpha 1(II)-collagen gene. Gene. 1986;44(1):11–16. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90037-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto T., Wong-Staal F. Demonstration of virus-specific transcriptional activator(s) in cells infected with HTLV-III by an in vitro cell-free system. Cell. 1986 Oct 10;47(1):29–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90363-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paglia L., Wilczek J., de Leon L. D., Martin G. R., Hörlein D., Müller P. Inhibition of procollagen cell-free synthesis by amino-terminal extension peptides. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 30;18(22):5030–5034. doi: 10.1021/bi00589a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peabody D. S., Berg P. Termination-reinitiation occurs in the translation of mammalian cell mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2695–2703. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peabody D. S. Translation initiation at an ACG triplet in mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 25;262(24):11847–11851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J., Sonenberg N. Photochemical cross-linking of cap binding proteins to eucaryotic mRNAs: effect of mRNA 5' secondary structure. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):3222–3230. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.3222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piette J., Kryszke M. H., Yaniv M. Specific interaction of cellular factors with the B enhancer of polyoma virus. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2675–2685. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03987.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen C. A., Sodroski J. G., Goh W. C., Dayton A. I., Lippke J., Haseltine W. A. Post-transcriptional regulation accounts for the trans-activation of the human T-lymphotropic virus type III. Nature. 1986 Feb 13;319(6054):555–559. doi: 10.1038/319555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi P., de Crombrugghe B. Formation of a type I collagen RNA dimer by intermolecular base-pairing of a conserved sequence around the translation initiation site. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 11;15(21):8935–8956. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.21.8935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt A., Yamada Y., de Crombrugghe B. DNA sequence comparison of the regulatory signals at the 5' end of the mouse and chick alpha 2 type I collagen genes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7411–7415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selden R. F., Howie K. B., Rowe M. E., Goodman H. M., Moore D. D. Human growth hormone as a reporter gene in regulation studies employing transient gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;6(9):3173–3179. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.9.3173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stepp M. A., Kindy M. S., Franzblau C., Sonenshein G. E. Complex regulation of collagen gene expression in cultured bovine aortic smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 15;261(14):6542–6547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolstoshev P., Berg R. A., Rennard S. I., Bradley K. H., Trapnell B. C., Crystal R. G. Procollagen production and procollagen messenger RNA levels and activity in human lung fibroblasts during periods of rapid and stationary growth. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 25;256(6):3135–3140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolstoshev P., Haber R., Trapnell B. C., Crystal R. G. Procollagen messenger RNA levels and activity and collagen synthesis during the fetal development of sheep lung, tendon, and skin. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 25;256(18):9672–9679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Cheng P. F., Conrad K. Expression of transfected DNA depends on DNA topology. Cell. 1986 Jul 4;46(1):115–122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90865-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiestner M., Krieg T., Hörlein D., Glanville R. W., Fietzek P., Müller P. K. Inhibiting effect of procollagen peptides on collagen biosynthesis in fibroblast cultures. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):7016–7023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wildeman A. G., Sassone-Corsi P., Grundström T., Zenke M., Chambon P. Stimulation of in vitro transcription from the SV40 early promoter by the enhancer involves a specific trans-acting factor. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3129–3133. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02269.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. H., Donovan C. B., Wu G. Y. Evidence for pretranslational regulation of collagen synthesis by procollagen propeptides. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 15;261(23):10482–10484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada Y., Mudryj M., de Crombrugghe B. A uniquely conserved regulatory signal is found around the translation initiation site in three different collagen genes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):14914–14919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]