Abstract
Alkaline phosphatase (AP) is a key enzyme for phytoplankton to utilize dissolved organic phosphorus (DOP) when dissolved inorganic phosphorus is limited. While three major types of AP and their correspondingly diverse subcellular localization have been recognized in bacteria, little is known about AP in eukaryotic phytoplankton such as dinoflagellates. Here, we isolated a full-length AP cDNA from a latest-diverging dinoflagellate genus Alexandrium, and conducted comparative analyses with homologs from a relatively basal (Amphidinium carterae) and late-diverging (Karenia brevis) lineage of dinoflagellates as well as other eukaryotic algae. New data and previous studies indicate that AP is common in dinoflagellates and most other major eukaryotic groups of phytoplankton. AP sequences are more variable than many other genes studied in dinoflagellates, and are divergent among different eukaryotic phytoplankton lineages. Sequence comparison to the other characterized APs suggests that dinoflagellates and some other eukaryotic phytoplankton possess the putative AP as phoA type, but some other eukaryotic phytoplankton seem to have other types. Phylogenetic analyses based on AP amino acid sequences indicated that the “red-type” eukaryotic lineages formed a monophyletic group, suggesting a common origin of their APs. As different amino acid sequences have been found to predictably determine different spatial distribution in the cells, which may facilitate access to different pools of DOP, existing computational models were adopted to predict the subcellular localizations of putative AP in the three dinoflagellates and other eukaryotic phytoplankton. Results showed different subcellular localizations of APs in different dinoflagellates and other lineages. The linkage between AP sequence divergence, subcellular localization, and ecological niche differentiation requires rigorous experimental verification, and this study now provides a framework for such a future effort.
Keywords: alkaline phosphatase, phosphate limitation, phytoplankton, dinoflagellate, diverse subcellular localization, highly divergent
Introduction
In marine ecosystem, phosphorus (P) is a vital nutrient controlling the growth of phytoplankton thereby affecting primary production (Karl, 2000; Paytan and McLaughlin, 2007). There are two major P reservoirs in the ocean, the dissolved inorganic P (DIP) and dissolved organic P (DOP). DIP is preferable for the growth of phytoplankton; however, its concentration is often so low that it limits phytoplankton growth in marine environments (Benitez-Nelson, 2000; Karl, 2000; Dyhrman et al., 2006; Meseck et al., 2009). In various areas of the open ocean, DIP occurs in nanomolar concentrations (Wu et al., 2000; Thingstad et al., 2005) and has been shown to be a limiting or co-limiting factor of nitrogen fixation (Sañudo-Wilhelmy et al., 2001; Mills et al., 2004) and primary production (Paytan and McLaughlin, 2007). Even in coastal waters, DIP can be stoichiometrically limited by high amounts of nitrogen associated with human activities (Cloern, 2001; Huang et al., 2003; Scavia and Bricker, 2006; Zhang et al., 2007c). Eutrophication with stoichiometric DIP limitation can potentially impose coastal health problems because some harmful algal bloom forming species, such as Alexandrium spp., Dinophysis acuminate, Karlodinium veneficum, and Pseudo-nitzschia multiseries can elevate their toxin production under P-limited conditions (Anderson et al., 2002; John and Flynn, 2002; Fu et al., 2010; Mooney et al., 2010).
To meet the P requirement for growth, different groups of phytoplankton have developed different strategies (Dyhrman et al., 2007). Under P limitation, some phytoplankton species can use DIP that is stored up when DIP is sufficient (Falkner et al., 1998; Ou et al., 2008), while some can lower cellular demand of DIP by using non-phosphorus lipids in the membrane in response to phosphorus scarcity (Van Mooy et al., 2006, 2009), and others maximize DIP uptake efficiency through high affinity P transport systems (Scanlan and Wilson, 1999; Moore et al., 2005; Orchard et al., 2009). Yet, the most important mechanism to cope with DIP deficiency is to hydrolyze various forms of DOP found in the ocean through a battery of enzymes to yield phosphate (Dyhrman et al., 2007). For example, it was found that 30% of primary production is supported by DOP during the boreal spring in the Northern Atlantic subtropical gyre (Mather et al., 2008). Phosphorus esters (∼75%) and phosphonates (∼25%) constitute the two dominant forms of oceanic DOP (Clark et al., 1998; Kolowith et al., 2001). Metabolic pathway analyses based on genome data of cyanobacteria have indicated that some species have the potential to utilize phosphonates to support marine primary production (Dyhrman et al., 2006, 2009; Ilikchyan et al., 2009). However, it is believed that hydrolysis of phosphorus esters by alkaline phosphatase (AP) is the most common mechanism of DOP utilization (Labry et al., 2005; Nicholson et al., 2006; Huang et al., 2007; Duhamel et al., 2010, 2011).
Alkaline phosphatase (EC 3.1.3.1) removes phosphate groups from various types of molecules (e.g., nucleotides, proteins, and alkaloids) and is most effective in an alkaline environment such as seawater (pH typically around 8). Marine bacterial AP has been widely studied and three different forms, phoA, phoX, and phoD, have been recognized (e.g., Luo et al., 2009; Sebastian and Ammerman, 2009; White, 2009). These three forms are localized in different regions of the cell and require different metal ions for active sites to hydrolyze the various phosphorus esters (Luo et al., 2009). AP genes also have been isolated and characterized from some marine cyanobacteria (Ray et al., 1991; Orchard et al., 2009). In contrast, relatively little is known about AP genes in marine eukaryotic phytoplankton. An AP gene (putative phoX) was isolated from the green algae Volvox carteri which was a Ca2+-dependent extracellular phosphatase responding to inorganic phosphate starvation (Hallmann, 1999). From the genome sequence of the freshwater chlorophyte Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, a putative phoX gene was identified which is likely to encode the previously characterized Ca2+-dependent extracellular AP (Quisel et al., 1996; Moseley et al., 2006). An AP gene (ehap1) was isolated and characterized in the haptophyte Emiliania huxleyi (Xu et al., 2006). Putative AP has also been identified from the pelagophyte Aureoumbra lagunensis (Sun et al., 2012). Gene models also predict the presence of AP genes in the genomes of diatoms Thalassiosira pseudonana and Phaeodactylum tricornutum (Armbrust et al., 2004; Bowler et al., 2008), especially a number of putative APs in T. pseudonana (Dyhrman et al., 2012). However, structural features and expression patterns of these putative AP genes remain to be characterized. There has been little evidence of DOP-utilizing proteins in dinoflagellates other than an AP-like protein found in Prorocentrum minimum (Dyhrman and Palenik, 1997) until recent detection of putative AP genes in two dinoflagellate species, Amphidinium carterae (Lin et al., 2011) and Karenia brevis (Morey et al., 2011; Lin et al., 2012).
While low similarity among the AP gene sequences from different organisms was noted, gene sequence divergence and phylogenetic relationships, particularly in relationship to the characterized bacterial APs, have not been examined. Further, in light of the diverse subcellular localizations of the different types of bacterial APs, whether the diverging AP gene sequences in eukaryotic phytoplankton might bear similar cytological and hence ecological significance remains to be explored. To better understand these questions, we isolated a putative AP full-length cDNA from a strain of Alexandrium, the latest-diverging dinoflagellate genus documented so far (John et al., 2003), and compared it with putative APs from the phylogenetically relatively basal and intermediate dinoflagellate species A. carterae and K. brevis (Zhang et al., 2007a), respectively, as well as AP-like sequences identified in other eukaryotic phytoplankton. Sequence variability, phylogenetic relationship, and putatively different subcellular localization of the AP sequences were analyzed.
Materials and Methods
Algal culture and enzyme labeled fluorescence labeling
Alexandrium strain ACHK-NT was kindly provided by the Collection Center of Marine Bacteria and Algae (CCMBA), Xiamen University, China. This strain was originally isolated from Hong Kong and identified as “A. catenella” morphologically. Based on the small subunit ribosomal RNA gene (SSU rDNA) isolated from this strain (unpublished) and phylogenetic analysis guided by information on the intragenomic SSU rDNA variation of “Alexandrium tamarense complex” (Miranda et al., 2012), this strain belongs to Clade IIC, which is exclusively composed of Asian “A. catenella”. The culture was grown in K medium (Keller and Guillard, 1985; Keller et al., 1987) with 0.22 μm-filtered and autoclaved seawater (28 PSU) at 20°C under a L:D = 14 h:10 h photocycle with a photon flux of 100 ± 10 μE s−1 m−2. One million cells were collected during exponential stage by centrifugation, resuspended in Trizol reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) and stored at −80°C for subsequent RNA extraction.
The cells of three different dinoflagellate species (“A. catenella,” A. carterae, and K. brevis) under P limitation in the late stationary growth stage (DIP below detection limit of 0.2 μM in the medium) were collected by centrifugation and the cell pellets were then incubated in 1 mL 70% ethanol for 30 min. The samples were centrifuged and the supernatant was aspirated off. The pellets were incubated in 100 μL 0.22 μm-filtered sterile seawater with ELF®-97 phosphatase substrate (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) in a final concentration of 0.25 mM for 30 min in the dark. The samples were washed three times using sterile seawater and stored in 100 μL sterile seawater in the dark (González-Gil et al., 1998; Ou et al., 2010). The stable green fluorescent precipitates produced in situ by the AP activity and red autofluorescence of the live cells produced by chloroplast were both observed under Nikon 90i epifluorescence microscope (green fluorescence excited by UV, 340–380 nm; Nikon Corporation, Tokyo, Japan).
RNA isolation and cDNA synthesis
Total RNA was extracted as previously reported (Lin et al., 2011) and stored at −80°C. The 1st strand cDNA was synthesized from ∼400 ng of the RNA using M-MLV reverse transcriptase (Promega, Madison, WI, USA) with a modified oligo-dT primer then purified using Zymo DNA Clean and Concentrator (Zymo Research, Orange, CA, USA).
cDNA cloning of the alkaline phosphatase gene fragment and rapid amplification of cDNA ends
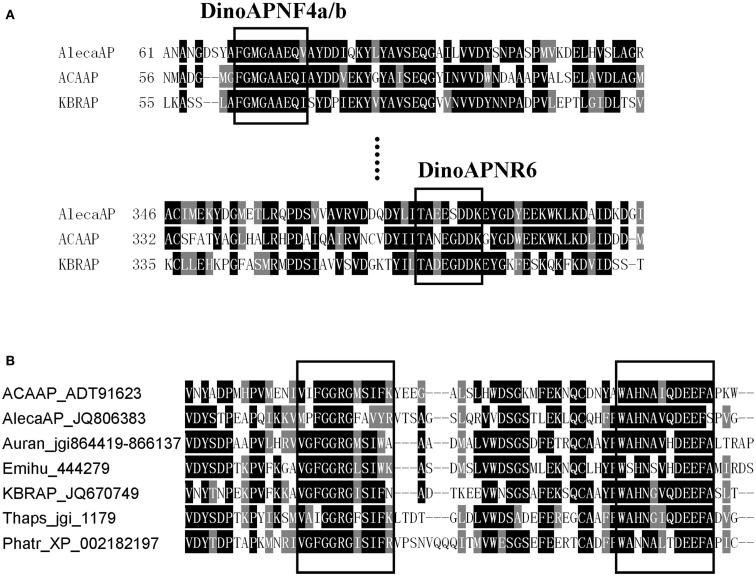
Based on the nucleotide (nt) and amino acid (aa) sequence alignments (see Figure 1) of A. carterae and K. brevis AP genes (Lin et al., 2011, 2012), degenerate primers were designed to obtain AP gene fragments from “A. catenella” under the following PCR conditions: 94°C for 1 min followed by 5 cycles of 95°C for 15 s, 52°C for 30 s, and 72°C for 1 min, and 30 cycles of 95°C for 15 s, 56°C for 30 s, and 72°C for 1 min. Two PCRs were carried out with the 1st PCR performed using forward primer DinoAPNF4a (5′-TTTGGWATGGGWGCMGCRGARCA-3′) paired with reverse primer DinoAPNR6 (5′-CTTRTCRTCRCCTTCRTYMGCKGT-3′). The PCR product was diluted 100 or 1000 fold and used as template for the 2nd (nested) PCR, in which DinoAPNR6 was paired with DinoAPNF4b (5′-GGTATGGGWGCMGCRGARCAGATT-3′) as the primer set. The PCR product with expected size was purified by Zymo DNA Clean and Concentrator (Zymo Research, Orange, CA, USA) and directly sequenced (Invitrogen, Guangzhou, China).
Figure 1.
Comparison of AP conserved regions in dinoflagellates (A) and other eukaryotic phytoplankton (B). (A) Boxed are regions used to design the degenerate primer for amplifying AlecaAP fragment. (B) Example conserved domains (boxed) identified from alignment of amino acid sequences from A. carterae (ACAAP), K. brevis (KBRAP), “A. catenella” (AlecaAP), diatoms Phaeodactylum tricornutum (Phatr) and Thalassiosira pseudonana (Thaps), pelagophyte Aureococcus anophagefferens (Auran), and coccolithophorid Emiliania huxleyi (Emihu). Identical residues are black-shaded while chemically similar ones gray-shaded.
Based on this partial sequence, specific primers were designed for both 5′- and 3′-rapid amplification of cDNA ends (RACE) to obtain the full-length cDNA by nested PCR. In the 5′-RACE, reverse primers AtaapR2 (5′-TGATGGACAAGACGACGATGG-3′, outside) and AtaapR3 (5′-AGTTCACCTTGCCGTTGCTTAC-3′, inside) coupled with forward primer DinoSL (Zhang et al., 2007b) were used in nested PCRs. In the 3′-RACE, forward primers AtaapF3 (5′-GACGACTCCAAGGTGTATGTGAAC-3′, outside) and AtaapF4 (5′-CTGGACATTGCCAGTGGCACGAT-3′, inside) were paired separately with modified oligo-dT primer in nested PCRs. The PCR products obtained from RACE were either directly sequenced, or cloned into a T-vector and several resultant plasmid clones were sequenced as reported (Lin et al., 2012). The sequences obtained were analyzed using Blastx against GenBank non-redundant protein sequences to confirm that the sequences are of the AP gene.
Search of GenBank, JGI genome, and CAMERA metagenomic databases for alkaline phosphatase genes
To recruit as many eukaryotic putative AP genes as possible for phylogenetic analysis, AP sequences of A. carterae and K. brevis were used as queries using basic local alignment search tool (program tblastn) against GenBank database. We also used the keyword search with “alkaline phosphatase” against GenBank database to recruit any reported sequences which were not hit by tblastn search. Furthermore, we searched the completed eukaryotic algal genome datasets at the Joint Genome Institute (JGI) databank using dinoflagellate putative AP sequences as the queries with E-value cutoff set at 1e-3, an e-value commonly used to search for protein homologs (e.g., Rensing et al., 2005; Ueno et al., 2010). In addition, to find AP sequences from the natural plankton assemblages, AP aa sequences of the two dinoflagellates were used as query to tblastn against the Bermuda Atlantic Time-Series Study (BATS) and Hawaii Ocean Time-Series (HOT) 454-sequencing reads as well as Sargasso Sea open reading frame datasets in the Community Cyber infrastructure for Advanced Marine Microbial Ecology Research and Analysis (CAMERA) databank. E-value cutoff was set at 1e-3, and 100 hits were set as the target for retrieval. A previous study showed that BATS water is DIP-poor whereas HOT water contains DIP concentrations which stoichiometrically fit the Redfield ratio (Wu et al., 2000).
Phylogenetic analysis
To examine the relationship between “A. catenella” AP and counterparts from other organisms, deduced aa sequence of the “A. catenella” full-length cDNA was aligned with AP sequences from the representative organisms using ClustalX (Thompson et al., 1997). The environmental sequences retrieved from CAMERA were too short and therefore were not included in the analysis. Sequences of different forms of APs (phoA, phoD, phoX, phoV) from cyanobacteria, a group of organism whose APs have been relatively well studied, were collected and compared with putative dinoflagellate APs (Dino-APs) separately. The phylogenetic analyses were done only to sequences belonging to the same type (phoA) because no reliable alignment could be achieved for a mixed-type dataset. Alignment was performed for each of these datasets using ClustalW1 with default setting (Gapopen 15, Gapext 6.66, Gapdist 8, Maxdiv 40). The alignments were then inspected and corrected manually. Neighbor-joining (NJ) analysis (Saitou and Nei, 1987) was run with 1000 bootstraps, and Bayesian analysis (Hueslenbeck and Ronquist, 2001) was run with model jumping setting for 725,000 generations (two independent runs were performed and the final standard deviation of split frequencies was 0.01), with trees sampled every 100 cycles and the first 25,000 cycles discarded (burn-in).
Computational analysis of major structural features and prediction of alkaline phosphatase subcellular localization
A set of programs were used to spatially characterize the deduced protein. The signal peptide was determined by TargetP V1.1 (Emanuelsson et al., 2000) and SignalP V4.0 (Petersen et al., 2011). GPI-SOM (Fankhauser and Mäser, 2005) and PredGPI (Pierlenoi et al., 2008) were used to locate the glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchor in the deduced protein sequence. TMpred2 was used to predict transmembrane domains.
Four existing bioinformatics models were adopted to predict subcellular localizations of AP in eukaryotic phytoplankton. Interpretable Subcellular Localization Prediction (YLoc; Briesemeister et al., 2010) predicts localization of a protein among nine possible subcompartments of the cell: extracellular space, plasma membrane, cytoplasm, mitochondrion, chloroplast, nucleus, Golgi apparatus, endoplasmic reticulum, and peroxisome. The YLoc+ algorithm in the package was used with plant selected as the target organism. The second program was Euk-mPLoc2.0 (Chou and Shen, 2010), which was designed specifically for predicting subcellular localization of eukaryotic proteins in 22 different compartments (Chou and Shen, 2010), including the nine in YLoc. The other two programs were WoLF PSORT (Horton et al., 2007) and CELLO (Yu et al., 2006). These programs have been used in various studies, such as functional annotation in C. reinhardtii and the subcellular localization prediction of the secretome for fungi (Soanes et al., 2007; Ghamsari et al., 2011; Rai et al., 2012). Because it has not been verified that these models suit APs or other proteins in eukaryotic phytoplankton. We first ran a set of proteins whose locations of functions are known to test the accuracy of the predictions. For AP, we tested a set of APs from the chlorophyte algae V. carteri and C. reinhardtii that are known to be related to phoX, an extracellular AP in bacteria and a homolog from E. huxleyi (EHAP1, GenBank accession number ABI51308) that has been shown to be extracellular (Xu et al., 2006). Included in the test was also AP from humans, whose cell surface distribution has been shown (Cutler et al., 1974). For dinoflagellates, a total of 98 protein sequences were tested, including representative proteins associated with cytoskeleton (actin), light harvesting in the chloroplast (peridinin-chlorophyll a-binding protein or PCP) and cell membrane (rhodopsin), carbon fixation in the chloroplast (ribolose-1, 5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase or Rubisco), and the cell cycle related protein proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), a well-characterized primarily nuclear protein. No model gave 100% correct prediction and no one failed 100% either, and in most cases predictions shared by two or more of these four models were correct (Table S1 in Supplementary Material). Therefore, we decided to use all four models so that the reliability of the predictions could be assessed, with the likelihood of the predicted AP localization ranked according to the number of the models that supported the prediction.
Results
Conservation of alkaline phosphatases in dinoflagellates
After assembling the initial partial AP sequence with the 5′ and 3′ RACE sequences, a full-length cDNA sequence was obtained from “A. catenella,” with an open reading frame of 2,181 bp (GenBank Accession No. JQ806383). Its deduced aa sequence (named as AlecaAP) was used to search against the GenBank protein database and the top two hits were A. carterae (with Expect value [E-value] to be 0.0) and K. brevis (E-value 2e-155), verifying that this is an putative AP cDNA. The AP sequences are moderately conserved among three dinoflagellates (48–52% identitical or 63–66% chemically similar at the aa level) and the overall characteristics are similar (Table 1, Figure 1A). AlecaAP cDNA has a ∼61% G+C content, highest among the three Dino-APs, predicted to encode a protein of 726-aa residues with a molecular mass of 76.6 kDa. Similar to other Dino-APs, AlecaAP also possesses a low pI (4.46), contributed by higher percentage of aspartic acid and glutamic acid residues (6.7 and 5.4%, respectively). A signal peptide was detected with a probability of 0.770 by TargetP 1.1 and confirmed by SignalP V4.0. The GPI anchor located at C-terminus (residues 721–726), which ensures AP to attach to cell membrane, was predicted by GPI-SOM and further confirmed by PredGPI (Table 1).
Table 1.
Comparison of major features of AlecaAP, ACAAP, and KBRAP.
| Gene (protein) | cDNA (bp) | Amino acid | pI | Mw (kDa) | G+C% | Signal peptide* | GPI anchor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| acaap (ACAAP) | 2115 | 704 | 4.31 | 75 | 54 | +, 0.784 | + |
| kbrap (KBRAP) | 2061 | 686 | 4.66 | 72.9 | 49 | +, 0.903 | + |
| aleca-ap (AlecaAP) | 2181 | 726 | 4.48 | 76.6 | 61 | +, 0.770 | + |
*“+” represent “signal peptide = yes” predicted by SignalP V 4.0 (left); “numbers” represent the score predicted by TargetP 1.1.
High divergence of alkaline phosphatase amino acid sequences revealed by phylogenetic analyses
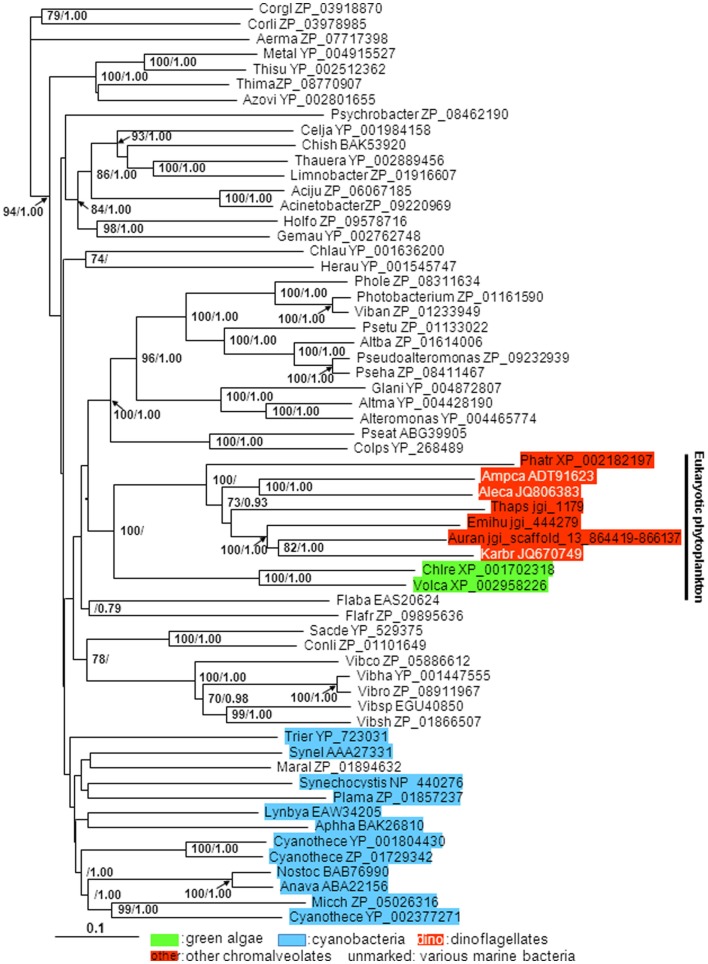
Alkaline phosphatase aa sequences are highly variable among the eukaryotic phytoplankton. No remarkable similarity was observed between the Dino-APs and other well-characterized eukaryotic APs such as EHAP1 from E. huxleyi (Landry et al., 2006; Xu et al., 2006, 2010) or phoX from V. carteri and C. reinhardtii (Hallmann, 1999; Moseley et al., 2006). Nevertheless, tblastn of Dino-APs against E. huxleyi CCMP1516 genome data (JGI) produced several hits with E-value lower than 1e-31. As predicted using TMpred, both the putative Dino-APs and other phytoplankton APs examined all contained 3–7 transmembrane domains. Interestingly, Dino-APs showed 15–30% of aa similarity with the APs from cyanobacteria, including a characterized atypical phoA gene (C-terminal half of the gene) from Synechococcus sp. PCC7942 (Ray et al., 1991; the phoA gene with GenBank accession number AAA27331). Further sequence comparison showed that V. carteri, C. reinhardtii also possessed phoA-like AP genes in addition to the phoX type mentioned above. The putative phoA-like AP sequences from P. tricornutum, T. pseudonana, V. carteri, C. reinhardtii, Aureococcus anophagefferens, cyanobacteria and bacteria share 10–16 conserved domains with Dino-APs (Figure 1B). The phylogenetic tree of phoA-like AP from different organisms showed that all of the eukaryotic phytoplankton APs clustered together, in sister relation to APs from marine bacteria (Figure 2).
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic tree inferred from AP amino acid sequences of eukaryotic phytoplankton, marine bacteria, and cyanobacteria. Shown is neighbor-joining (NJ) tree; Bayesian analysis (BE) tree has similar tree topology albeit with more uneven branch lengths; support of nodes >70% in NJ bootstrap values and >0.70 in Bayesian posterior probability is shown. Color backgrounds indicate the type of organisms which the AP sequence is from. For instance, red background indicates sequences from species whose chloroplasts belong to chromalveolates (“Red-type”), green background indicates sequences from green algae, blue background indicates sequences from cyanobacteria.
Alkaline phosphatase gene sequences from environmental samples
No putative AP sequences were found in the Sargasso Sea ORF, likely due to its relatively small database size. Five significant hits were obtained from HOT and 15 from BATS sharing several conserved regions with Dino-APs. When these retrieved sequences were blasted against GenBank database using blastp, several of them matched bacterial AP as their top hit, giving two HOTS and five BATS sequences as eukaryotic AP as they best matched APs of dinoflagellates or diatoms (Table 2). Given that the metagenomic data were obtained from microbial plankton, the AP genes detected were probably restricted to pico- or nano-plankton. This might explain why so few sequences of AP genes were found and partially why none were found from the Sargasso Sea ORF dataset.
Table 2.
BLASTP result of CAMERA datasets.
| Sampling site | Clone ID | Hit organisms* | E-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| HOTS | HF_READ_03392351/accession=HF_READ_03392351 | Thaps, Ampca, Phatr | −9 to −13 |
| HOTS | HF_READ_03392351/accession=HF_READ_03392351 | Thaps, Phatr, Ampca | −9 to −14 |
| BATS | BATS_READ_00574637/accession=BATS_READ_00574637 | Ampca, Thaps | −19 to −26 |
| BATS | BATS_READ_00574637/accession=BATS_READ_00574637 | Ampca, Thaps | −19 to −26 |
| BATS | BATS_READ_02761309/accession=BATS_READ_02761309 | Thaps, Ampca | −4 to −8 |
| BATS | BATS_READ_00987768/accession=BATS_READ_00987768 | Ampca | −6 |
| BATS | BATS_READ_00987768/accession=BATS_READ_00987768 | Ampca | −6 |
*Ampca: Amphidinium carterae (dinoflagellate); Phatr: Phaeodactylum tricornutum (diatom); Thalassiosira pseudonana (diatom).
Computationally predicted different subcellular localizations of alkaline phosphatases in dinoflagellates and other eukaryotic phytoplankton
The test runs using protein sequences from various organisms showed that most of the proteins were predicted correctly when the prediction was supported by two or more of the four models used. APs in humans were predicted to be extracellular by YLoc+, WoLF PSORT, and CELLO and cell membrane by Euk-mPLoc, consistent to observed extracellular space distribution of this protein (Cutler et al., 1974). Like phoX in bacteria, the phoX-like APs in chlorophyte C. reinhardtii and V. carteri have been shown to be extracellular (Hallmann, 1999; Moseley et al., 2006); both of them were predicted to be extracellular by two of the models (Table S1 in Supplementary Material). Among dinoflagellate proteins, actin was uniformly predicted to be cytoskeleton by Euk-mPLoc, and to be cytoplasmic by YLoc+ and CELLO, the two models that do not have the cytoskeleton category. PCP was correctly and uniformly predicted to be chloroplastic by all four models. Rhodopsin, a known transmembrane protein, was predicted as a plasma membrane protein in all the 19 cases by Euk-mPLoc and CELLO and 11 of these are supported by three or more of the models. All 16 Rubisco sequences, from various species of dinoflagellates, were predicted as chloroplast proteins by three or more models. All 16 PCNA genes examined were predicted to be nuclear proteins, and 5 of these were supported by three or more models. All these results confirmed that the joint-multiple prediction models could be applied to dinoflagellates and other phytoplankton proteins by the majority rule (≥2 models). Predicting results based on this “rule” are shown in Table 3. Putative AP in “A. catenella” would be localized in the extracellular space (2 models) and chloroplast (2 models), with equal probability. Putative AP in A. carterae would most likely be in the extracellular space (plus endoplasmic reticulum, which can be considered as transporting and secreting out of the cell; 3 models) but cytoplasm (1 model) and chloroplast (1 model) are possible as well. In K. brevis, putative AP was predicted to be most likely extracellular (also plus Endoplasmic Reticulum; 4 models) or cell surface (cell wall plus membrane; 2 models) with a small probability to be found in other intracellular compartments (1 model each).
Table 3.
Predicted subcellular localization for alkaline phosphatase in eukaryotic phytoplankton using Yloc, Euk-mPLoc2.0, WoLF PSORT, and CELLO computational models.
| Extracellular space | Cell wall | Plasma membrane | Cytoplasm | Nucleus | Mitochondrion | Chloroplast | Golgi apparatus | Endoplasmic reticulum | Peroxisome | Vacuole | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PhoA-like | |||||||||||
| “Alexandrium catenella” JQ806383 | 2 | 2 | |||||||||
| Amphidinium carterae ADT91623 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| Karenia brevis JQ670749 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Phaeodactylum tricornutum XP_002182197.1 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| Thalassiosira pseudonana jgi|Thaps3|1179|jgi|Thaps3|1179|fgenesh1_pg.C_chr_1000313:22-645 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| Aureococcus anophagefferens jgi|Auran1||scaffold_13:864419-866137_putative | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| Emiliania huxleyi jgi|Emihu1|444279|estExtDG_fgenesh_newKGs_kg.C_3060016:21-652 | 3 | 2 | |||||||||
| Chlamydomonas reinhardtii Chlre_XP_001702318.1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| Volvox carteri f. nagariensis Volca_XP_002958226.1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| PhoX like | |||||||||||
| Chlamydomonas reinhardtii XP_001703098* | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| Volvox carteri CAA10030* | 2 | 2 | |||||||||
| Other types | |||||||||||
| Emiliania huxleyi ABI51308* | 2 | 2 | 1 |
Shade darkness denotes the number of models that support the prediction, from highest (darkest = 3) to lowest (lightest = 1).
*APs that have been previously characterized. The rest of the sequences (except Dino-APs) are tblastn hits using Dino-APs as query.
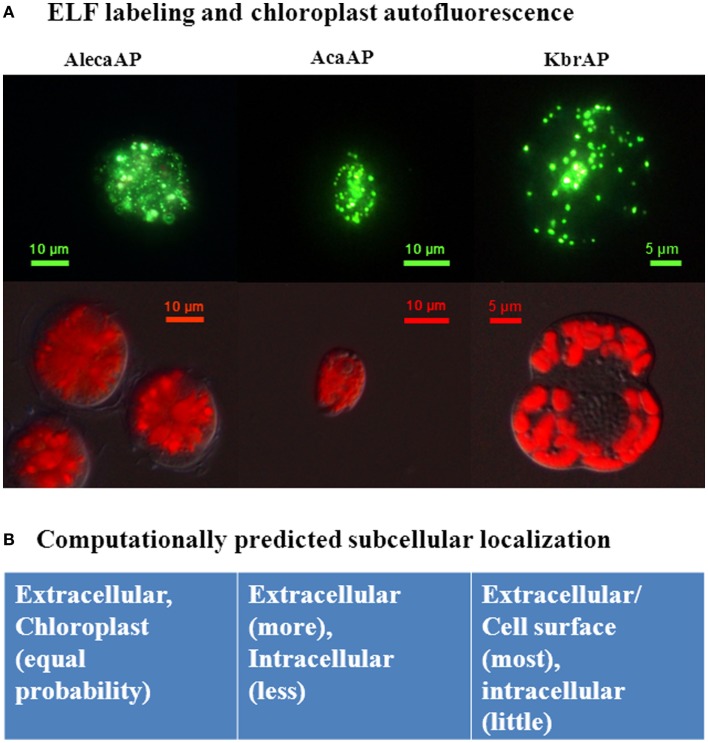
These computational predictions of putative Dino-AP localization were verified by enzyme labeled fluorescence (ELF) labeling. In the three dinoflagellate species we have analyzed so far, AP activity as indicated by ELF showed different localization patterns (Figure 3). In “A. catenella,” AP appeared to be located both intracellularly and on the cell surface. In A. carterae, AP activity was more on the cell surface than intracellular but both locations had substantial activities. In K. brevis, AP activity was mostly distributed on the cell surface. The ELF labeling patterns were consistent with model predictions.
Figure 3.
Subcellular localizations of Dino-APs observed in ELF-labeled cells (A) and computationally predicted (B) for three different dinoflagellate species. Aleca, Alexandrium catenella AP; AcaAP, Amphidinium carterae AP; KbrAP, Karenia brevis AP, reproduced from Lin et al. (2012) with the permission of Elsevier. (A) Green fluorescence (top row) representing the hydrolyzed precipitate attributed to alkaline phosphatase activity, and the red autofluorescent images (bottom row) indicating autofluorescence of chloroplasts in corresponding species. (B) Computational prediction of subcellular localization of putative Dino-APs is combined results rom different models.
Among other groups of eukaryotic phytoplankton putative AP was predicted to be in the extracellular space and plasma membrane of P. tricornutum and most likely in the cytoplasm of T. pseudonana and A. anophagefferens. In E. huxleyi, the phoA-like AP (jgi|Emihu1|444279|estExtDG_fgenesh_newKGs_kg.C_3060016:21-652) was more likely extracellular but could be cytoplasmic as well whereas EHAP1 (ABI51308) was predicted to be extracellular and cell surface (plasma membrane; Table 3). EHAP1 has been experimentally shown to be extracellular (Xu et al., 2006).
Discussion
Alkaline phosphatase seems to be common in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic phytoplankton. AP genes have been studied extensively in bacteria and scarcely in eukaryotes, while AP activity has been detected in a wide range of eukaryotic phytoplankton (Table S2 in Supplementary Material). The combination of the new molecular data retrieved in this study with literature information on AP activities indicates that AP is an ancient and common feature in marine microbes, attesting to the notion that phosphorus is a common limiting factor of phytoplankton production. The association of AP activity in eukaryotic phytoplankton with DIP limitation in the environment has been widely established. Recently, AP gene expression in dinoflagellates was also found to be regulated by DIP availability (Lin et al., 2011, 2012). To date, AP activity has not been detected in raphidophytes, and the AP gene has not been identified in the genomes of rhodophytes, such as Cyanidioschyzon merolae (Table S2 in Supplementary Material). If verified, the lack of AP in these organisms would suggest loss of the function during evolution and raise questions about how these algae cope with DIP limitation. Molecular data on AP in eukaryotic phytoplankton is still too limited to draw definitive conclusions about the general evolutionary trend and their ecological significance. However, some interesting insights can be derived from the results of our exploratory analyses conducted in this study.
Variable types of alkaline phosphatase in marine phytoplankton
With different forms and unique characteristics found in this study and documented in literature, AP is clearly a highly variable gene in marine microorganisms. Three AP families, phoA, phoX, and phoD have been found in marine bacteria, and their gene sequences, subcellular localizations, metal cofactor requirements, and substrates have been analyzed experimentally and computationally (Luo et al., 2009, 2011; Sebastian and Ammerman, 2009). Similar cases (but more complicated) were also observed in cyanobacteria, which are one of the most common phytoplankton lineages. So far, the only well-characterized AP genes in marine cyanobacterium were phoA (145 kDa) and phoV (61.3 kDa) from Synechococcus strain PCC7942 (Ray et al., 1991; Wagner et al., 1995). The previously identified atypical phoA, with an unusually large molecular weight, showed no sequence homology with other AP genes and was believed to exhibit extracellular phosphatase activity without a cleavable signal sequence (Ray et al., 1991). The phoD type of AP was characterized in halotolerant cyanobacterium Aphanothece halophytica (Kageyama et al., 2011). The heterogeneous sequences of AP made it very difficult to identify the AP gene homology in different strains of Synechococcus and Prochlorococcus (Moore et al., 2005). In addition, a fourth type, PhoV, was identified as a membrane-associated protein localized in the periplasmic space requiring Zn2+ for activity (as required by phoA in bacteria); the sequence of this gene was 34% identical to phoA in the α-proteobacterium Zymomonas mobilis (Wagner et al., 1995). A recent study on the genome sequence of Trichodesmium spp. confirmed that there are two putative APs, one sharing a conserved domain with the characterized phoX from marine γ-proteobacteria, and the other sharing 52% identity to 50% of the translated phoA gene from Synechococcus PCC7942 (Orchard et al., 2009).
Among eukaryotic microalgae, only APs from chlorophyte C. reinhardtii and V. carteri have been categorized with respect the types recognized in bacteria; phoX like sequences occur in both species (Hallmann, 1999; Moseley et al., 2006). The transcriptomic and proteomic study indicated that there are several putative APs in T. pseudonana (Dyhrman et al., 2012). Before the analysis of the AP genes from dinoflagellates reported here, the only characterized AP coding gene in marine eukaryotic phytoplankton is ehap1, identified in E. huxleyi (Xu et al., 2006). The gene product EHAP1, with its signal peptide identified at the N-terminus and without a GPI anchor at the C-terminus, can be released from the cell surface into the medium. But it does not show any similarity to the known types of APs. Because of the very limited knowledge of eukaryotic phytoplankton AP genes, it is difficult to categorize the putative APs from dinoflagellates and other eukaryotic phytoplankton into those recognized types of marine APs. However, our sequence comparison results showed that Dino-APs and other putative AP sequences in other eukaryotic phytoplankton genomes retrieved from the public databases share highest (despite still very low) identifiable sequence similarity with the phoA AP from bacteria and cyanobacteria among all the recognized types of AP. These AP amino acid sequences clustered together in the phylogenetic tree (Figure 2). Regardless if these are indeed phoA type APs, all our analyses suggest that they are undoubtedly a subset of putative APs.
It is interesting to observe that while cyanobacteria, chlorophytes C. reinhardtii and V. carteri, and the haptophyte E. huxleyi have multiple types of AP, essentially only one form of putative AP sequence has been identified in dinoflagellates. There is little sequence variation in the coding region, most of which involves synonymous nt substitutions (Lin et al., 2011, 2012). In the 2,181-bp long AP cDNA coding region in “A. catenella,” only two sites show changes. This is striking because most of the genes in dinoflagellates that have been studied exist in numerous variations. For instance, pcna, which usually occurs in one copy in other eukaryotes, exists in tens of copies in the dinoflagellate Pfiesteria piscicida, which contain many synonymous and substantial numbers of non-synonymous nucleotide substitutions (Zhang et al., 2006). Similarly, Rubisco genes in P. minimum occurs in over 100 copies, which differ from each other by as much as 5%, with both synonymous and non-synonymous changes as well as insertions/deletions (Zhang and Lin, 2003). If the duplication of genes in dinoflagellates has resulted from whole genome duplication, as recently postulated (Hou and Lin, 2009), the negligible level of variation in AP relative to that of other genes may suggest that Dino-APs probably face strong evolutionary purifying selection (Kim et al., 2011). However, if dinoflagellate genes duplicated independently, then the low variability of the gene can simply indicate that the gene copies have only arisen from recent duplication events (Thornton, 2007 and the refs there in).
High alkaline phosphatase sequence variability across lineages
The sequence variability of putative AP between lineages is strikingly high. Although it has been shown that 25–30% of the aa residues, especially the active sites, in APs are well conserved among mammals, yeast, and E. coli (Murphy et al., 1995), this does not seem to be the case for dinoflagellates and other eukaryotic phytoplankton. Putative Dino-APs did not share obvious similarity with APs from other eukaryotes. There were also no obvious conserved domains observed between putative Dino-APs and phoV from S. elongatus PCC 7942. When comparing putative Dino-APs with phoA from Trichodesmium spp. (Orchard et al., 2009) and Synechococcus PCC7942 (Ray et al., 1991), more than 10 conserved domains were identified between putative Dino-APs and phoA; however, no conserved region was found between putative Dino-APs and phoX. The lack of long conserved sequence regions and the overall high variability rendered the alignment of nt sequences of counterparts from different lineages (e.g., dinoflagellates and diatoms) impossible; however, our careful alignment of aa sequences did reveal several conserved domains (Figure 1). The putative Dino-APs shared no similarity with EHAP1 from E. huxelyi (Xu et al., 2006, 2010), but hit several unidentified E. huxelyi genome contigs with significant E-values (e.g., jgi 444279, 3e−157 to 0.0). A recently identified protein with AP activity in A. lagunensis also shared similarity with the AP from proteobacteria Idiomarina baltica OS145 (Sun et al., 2012). In the phylogenetic tree, putative Dino-APs formed a monophyletic group with other eukaryotes whose chloroplasts belong to the red-type (i.e., chromalveolate), which as a whole is sister to APs from some bacteria. This is likely due to the existence of a number of chemically similar aa residues among the chromalveolate APs, which increased the similarities between the sequences. Whether the somewhat closer phylogenetic relationship between the red-type algae and bacteria has resulted from a horizontal gene transfer cannot be determined with the limited data currently available, but is worth exploring in the future.
Possible different subcellular localizations and different P strategies associated with the variable alkaline phosphatase sequences
The computational study of subcellular localization of marine bacterial APs implies different strategies of DOP utilization by different forms of AP (Luo et al., 2009, 2011). The high abundance of cytoplasmic APs (phoA and phoD) suggests that intracellular hydrolysis of transported small DOP molecules is also an important P acquisition mechanism (Luo et al., 2009). Presence of phoX (extracellular) and its relatively wide distribution is thought to provide a growth advantage to the bacteria (may be cyanobacteria too) because it has broad substrate specificity as well as using Ca2+ as co-factor instead of Zn2+, which is often limited in the oligotrophic ocean (Orchard etal.,2009; Sebastian and Ammerman, 2009). According to previous studies, APs are located on the cell surface in most of the species examined (e.g., Chaetoceros affinis, Skeletonema costatum, P. tricornutum, Chlorella sp., Isochrysis galbana, P. Donghaiense, and Peridiniumcinctum) whereas are intracellular in some other species (e.g., P. mican, “A. fundyense,” and “A. catenella”; Ou et al., 2010). Our ELF labeling patterns were suggestive of AP being localized both intracellularly and on the cell surface of “A. catenella,” which is consistent with the computational prediction of chloroplast and cell surface localization. Chloroplast in “A. catenella” was highly branched and abundant in the cytoplasm (Hansen and Moestrip, 1998), rendering chloroplast AP ELF labeling as scattered in the cytoplasm (Figure 3). Comparative studies have shown that the diatom S. costatum quickly released the AP into the medium while “A. catenella” and P. donghaiense harbor most of the AP inside the cells and on the cell surface, respectively, so that these algae could use DOP in the ambient water and survive longer under P-limited condition (Ou et al., 2008, 2010).
The computational prediction of some putative eukaryotic phytoplankton APs also showed that AP localization (i.e., cell surface or intracellular) varied with species. AP localized in the extracellular space may enable that species to utilize DOP from the external environment as cleaved phosphate. This would obviate the need to import bulky DOP into the cell. In contrast, APs located inside the cell would only be able to utilize DOP found inside the cell, either transported from the external environment or produced inside the cell (e.g., degraded or denatured proteins and other organic matter). As suggested in marine bacteria, cytoplasmic APs probably function in internal organophosphate hydrolysis (Luo et al., 2009). The differentiation of subcellular localization thus would confer adaptive strategies in utilizing different sources of DOP. This differentiation may be the reason that different phytoplankton species respond to DIP limitation in the environment in different manner. For instance, A. carterae responded to DIP limitation by expressing AP activities detectable on live cells (i.e., likely extracellular or cell surface) very quickly and is able to maintain growth rates comparable to that under DIP-replete conditions (Lin et al., 2011). In contrast, K. brevis growth rate declined shortly after DIP was depleted and detectable AP activity increased long after (Lin et al., 2012). Perhaps the more cytoplasmic presence of AP enables A. carterae to access DOP generated inside the cell quickly compared to K. brevis, in which the dominant extracellular/cell surface distribution of AP may force the cells to rely on external DOP generated from cell death and on the import process for the cleaved DIP to enter the cell. Yet, such linkage between AP sequence, subcellular localization, and P nutritional strategy requires much more dedicated studies to verify.
Conclusion
Alkaline phosphatase appears to be common in eukaryotic phytoplankton, thus likely an ancient feature, but how many lineages have lost this feature and consequently how they cope with potential phosphate limitation warrant further studies. The high diversity of AP genes in phytoplankton may be related to diversification of subcellular localization and strategies of accessing and utilizing DOP. Currently sequence data are still too limited to infer a definitive evolutionary trend of the gene and functional diversification of the encoded enzyme. Much work is needed to: (1) determine the origin of the AP gene in eukaryotic phytoplankton; (2) elucidate what drives the rapid evolution of this gene in comparison to other genes in the same organism; (3) examine the linkage of the highly variable AP sequences with subcellular localizations and access of the host algae to diverse sources of DOP inside and outside the cells. In addition, on the practical side, the high diversity probably will make the AP gene a promising phylogenetic marker for resolving closely related lineages that cannot be distinguished based on morphology or conserved genes such as those coding for rRNA. Yet convincing evidence ratifying such utility of the AP gene also awaits further studies with broader taxon sampling and more in-depth phylogenetic analyses.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at http://www.frontiersin.org/Aquatic_Microbiology/10.3389/fmicb.2012.00235/abstract
Test runs of the four subcellular localization predicting models with AP from dinoflagellates and various other organisms and a variety of other porteins in dinoflagellates.
Eukaryotic phytoplankton in which Alkaline phosphatase activity or coding gene that has been detected.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Yong Zhang for growing the Alexandrium culture, Yongqiang Tian for acquiring microscopic images of the ELF-labeled cells, and Michael Finiguerra for correcting English grammar. This work was supported by China NSF grant 41176091.
Footnotes
References
- Anderson D. M., Glibert P. M., Burkholder J. M. (2002). Harmful algal blooms and eutrophication: nutrient sources, composition, and consequences. Estuaries Coast 25, 704–726 10.1007/BF02804901 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Armbrust E. V., Berges J. A., Bowler C., Green B. R., Martinez D., Putnam N. H., Zhou S., Allen A. E., Apt K. E., Bechner M., Brzezinski M. A., Chaal B. K., Chiovitti A., Davis A. K., Demarest M. S., Detter J. C., Glavina T., Goodstein D., Hadi M. Z., Hellsten U., Hildebrand M., Jenkins B. D., Jurka J., Kapitonov V. V., KrÖger N., Lau W. W., Lane T. W., Larimer F. W., Lippmeier J. C., Lucas S., Medina M., Montsant A., Obornik M., Parker M. S., Palenik B., Pazour G. J., Richardson P. M., Rynearson T. A., Saito M. A., Schwartz D. C., Thamatrakoln K., Valentin K., Vardi A., Wilkerson F. P., Rokhsar D. S. (2004). The genome of the diatom Thalassiosira pseudonana: ecology, evolution, and metabolism. Science 306, 79–86 10.1126/science.1101156 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benitez-Nelson C. R. (2000). The biogeochemical cycling of phosphorus in marine systems. Earth-Sci. Rev. 51, 109–135 10.1016/S0012-8252(00)00018-0 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Bowler C., Allen A. E., Badger J. H., Grimwood J., Jabbari K., Kuo A., Maheswari U., Martens C., Maumus F., Otillar R. P., Rayko E., Salamov A., Vandepoele K., Beszteri B., Gruber A., Heijde M., Katinka M., Mock T., Valentin K., Verret F., Berges J. A., Brownlee C., Cadoret J.-P., Chiovitti A., Choi C. J., Coesel S., De Martino A., Detter J. C., Durkin C., Falciatore A., Fournet J., Haruta M., Huysman M. J. J., Jenkins B. D., Jiroutova K., Jorgensen R. E., Joubert Y., Kaplan A., Kröger N., Kroth P. G., Roche J. L., Lindquist E., Lommer M., Martin-Jézéquel V., Lopez P. J., Lucas S., Mangogna M., McGinnis K., Medlin L. K., Montsant A., Secq M.-P. O. L., Napoli C., Obornik M., Parker M. S., Petit J.-L., Porcel B. M., Poulsen N., Robison M., Rychlewski L., Rynearson T. A., Schmutz J., Shapiro H., Siaut M., Stanley M., Sussman M. R., Taylor A. R., Vardi A., Peter V. D., Vyverman W., Willis A., Wyrwicz L. S., Rokhsar D. S., Weissenbach J., Armbrust E. V., Green B. R., Yves V. d. P., Grigoriev I. V. (2008). The Phaeodactylum genome reveals the evolutionary history of diatom genomes. Nature 456, 239–244 10.1038/nature07410 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briesemeister S., Rahnenfuhrer J., Kohlbacher O. (2010). YLoc – an interpretable web server for predicting subcellular localization. Nucleic Acids Res. 38, W497–W502 10.1093/nar/gkq477 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou K.-C., Shen H.-B. (2010). A new method for predicting the subcellular localization of eukaryotic proteins with both single and multiple sites: Euk-mPLoc 2.0. PLoS ONE 5, e9931 10.1371/journal.pone.0009931 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark L. L., Ingall E. D., Benner R. (1998). Marine phosphorus is selectively remineralized. Nature 393, 426. 10.1038/30881 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Cloern J. E. (2001). Our evolving conceptual model of the coastal eutrophication problem. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 210, 223–253 10.3354/meps210223 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Cutler L. S., Chaudhry A. P., Montes M. (1974). An ultrastructural study of alkaline phosphatase activity in normal and neoplastic human salivary glands. Arch. Oral Biol. 19, 499–504 10.1016/0003-9969(74)90064-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duhamel S., Björkman K. M., Wambeke F. V., Moutin T., Karl D. M. (2011). Characterization of alkaline phosphatase activity in the North and South Pacific Subtropical Gyres: implications for phosphorus cycling. Limnol. Oceanogr. 56, 1244–1254 10.4319/lo.2011.56.4.1244 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Duhamel S., Dyhrman S. T., Karl D. M. (2010). Alkaline phosphatase activity and regulation in the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre. Limnol. Oceanogr. 55, 1414–1425 10.4319/lo.2010.55.3.1414 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Dyhrman S. T., Ammerman J. W., Van Mooy B. A. S. (2007). Microbes and the marine phosphorus cycle. Oceanography 20, 110–116 10.5670/oceanog.2007.54 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Dyhrman S. T., Benitez-Nelson C. R., Orchard E. D., Haley S. T., Pellechia P. J. (2009). A microbial source of phosphonates in oligotrophic marine systems. Nat. Geosci. 2, 696–699 10.1038/ngeo639 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Dyhrman S. T., Chappell P. D., Haley S. T., Moffett J. W., Orchard E. D., Waterbury J. B., Webb E. A. (2006). Phosphonate utilization by the globally important marine diazotroph Trichodesmium. Nature 439, 68–71 10.1038/nature04203 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyhrman S. T., Jenkins B. D., Rynearson T. A., Saito M. A., Mercier M. L., Alexander H., Whitney L. P., Drzewianowski A., Bulygin V. V., Bertrand E. M., Wu Z., Benitez-Nelson C., Heithoff A. (2012). The transcriptome and proteome of the diatom Thalassiosira pseudonana reveal a diverse phosphorus stress response. PLoS ONE 7, e33768 10.1371/journal.pone.0033768 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyhrman S. T., Palenik B. P. (1997). The identification and purification of a cell-surface alkaline phosphatase from the dinoflagellate 4Prorocentrum minimum (Dinophyceae). J. Phycol. 33, 602–612 10.1111/j.0022-3646.1997.00602.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Emanuelsson O., Nielsen H., Brunak S., Von Heijne G. (2000). Predicting subcellular localization of proteins based on their N-terminal amino acid sequence. J. Mol. Biol. 300, 1005–1016 10.1006/jmbi.2000.3903 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkner R., Wagner F., Aiba H., Falkner G. (1998). Phosphate-uptake behaviour of a mutant of Synechococcus sp. PCC7942 lacking one protein of the high-affinity phosphate-uptake system. Planta 206, 461–465 10.1007/s004250050422 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Fankhauser N., Mäser P. (2005). Identification of GPI anchor attachment signals by a Kohonen self-organizing map. Bioinformatics 21, 1846–1852 10.1093/bioinformatics/bti299 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu F-X., Place A. R., Garcia N. S., Hutchins D. A. (2010). CO2 and phosphate availability control the toxicity of the harmful bloom dinoflagellate Karlodinium veneficum. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 59, 55–65 10.3354/ame01398 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Ghamsari L., Balaji S., Shen Y., Yang X., Balcha D., Fan C., Hao T., Yu H., Papin J. A., Salehi-Ashtiani K. (2011). Genome-wide functional annotation and structural verification of metabolic ORFeome of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. BMC Genomics 12, S4 10.1186/1471-2164-12-S4-S4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González-Gil S., Keafer B. A., Jovine R. V. M., Aguilera A., Lu S., Anderson D. M. (1998). Detection and quantification of alkaline phosphatase in single cells of phosphorus-starved marine phytoplankton. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 164, 21–35 10.3354/meps164021 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Hallmann A. (1999). Enzymes in the extracellular matrix of Volvox: an inducible calcium-dependent phophatase with a modular composition. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 1691–1697 10.1074/jbc.274.3.1691 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen G., Moestrip Ø. (1998). Fine-structural characterization of Alexandrium catenella (Dinophyceae) with special emphasis on the flagellar apparatus. Eur. J. Phycol. 33, 281–291 10.1080/09670269810001736783 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Horton P., Park K. J., Obayashi T., Fujita N., Harada H., Adams-Collier C. J., Nakai K. (2007). WoLF PSORT: protein localization predictor. Nucleic Acids Res. 35, W585–W587 10.1093/nar/gkm259 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hou Y., Lin S. (2009). Distinct gene number-genome size relationships for eukaryotes and non-eukaryotes: gene content estimation for dinoflagellate genomes. PLoS ONE 4, e6978. 10.1371/journal.pone.0006978 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang B., Ou L., Wang X., Huo W., Li R., Hong H., Zhu M., Qi Y. (2007). Alkaline phosphatase activity of phytoplankton in East China Sea coastal waters with frequent harmful algal bloom occurrences. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 49, 195–206 10.3354/ame01135 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Huang X. P., Huang L. M., Yue W. Z. (2003). The characteristics of nutrients and eutrophication in the Pearl River estuary, South China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 47, 30–36 10.1016/S0025-326X(03)00070-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hueslenbeck J. P., Ronquist F. (2001). MRBAYES: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 17, 754–755 10.1093/bioinformatics/17.8.754 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilikchyan I. N., McKay R. M. L., Zehr J. P., Dyhrman S. T., Bullerjahn G. S. (2009). Detection and expression of the phosphonate transporter gene phnD in marine and freshwater picocyanobacteria. Environ. Microbiol. 11, 1314–1324 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2009.01869.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John E. H., Flynn K. J. (2002). Modelling changes in paralytic shellfish toxin content of dinoflagellates in response to nitrogen and phosphorus supply. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 225, 147–160 10.3354/meps225147 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- John U., Fensome R. A., Medlin L. K. (2003). The application of a molecular clock based on molecular sequences and the fossil record to explain biogeographic distributions within the Alexandrium tamarense species complex (Dinophyceae). Mol. Biol. Evol. 20, 1015–1027 10.1093/molbev/msg105 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kageyama H., Tripathi K., Rai A. K., Cha-um S., Waditee-Sirisattha R., Takabe T. (2011). An alkaline phosphatase/phosphodiesterase, PhoD, induced by salt stress and secreted out of the cells of Aphanothece halophytica, a halotolerant cyanobacterium. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 77, 5178–5183 10.1128/AEM.00667-11 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karl D. M. (2000). Phosphorus, the staff of life. Nature 406, 31–32 10.1038/35017686 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller M. D., Guillard R. R. L. (1985). “Factors significant to marine diatom culture.” in Toxic Dinoflagellates, eds Anderson D. M., White A. W., Baden D. G. (New York: Elsevier; ), 113–116 [Google Scholar]
- Keller M. D., Selvin R. C., Claus W., Guillard R. R. L. (1987). Media for the culture of oceanic ultraphytoplankton. J. Phycol. 23, 633–638 10.1111/j.1529-8817.1987.tb04217.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S., Bachvaroff T. R., Handy S. M., Delwiche C. F. (2011). Dynamics of actin evolution in dinoflagellates. Mol. Biol. Evol. 28, 1469–1480 10.1093/molbev/msq332 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolowith L. C., Ingall E. D., Benner R. (2001). Composition and cycling of marine organic phosphorus. Limnol. Oceanogr. 46, 309–321 10.4319/lo.2001.46.2.0309 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Labry C., Delmas D., Herbland A. (2005). Phytoplankton and bacterial alkaline phosphatase activities in relation to phosphate and DOP availability within the Gironde plume waters (Bay of Biscay). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 318, 213–225 10.1016/j.jembe.2004.12.017 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Landry D. M., Gaasterland T., Palenik B. P. (2006). Molecular characterization of a phosphate-regulated cell-surface protein from the Coccolithophorid, Emiliania huxleyi (Prymnesiophyceae). J. Phycol. 42, 814–821 10.1111/j.1529-8817.2006.00247.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin X., Zhang H., Huang B., Lin S. (2011). Alkaline phosphatase gene sequence and transcriptional regulation by phosphate limitation in Amphidinium carterae (Dinophyceae). J. Phycol. 47, 1110–1120 10.1111/j.1529-8817.2011.01038.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin X., Zhang H., Huang B., Lin S. (2012). Alkaline phosphatase gene sequence characteristics and transcriptional regulation by phosphate limitation in Karenia brevis (Dinophyceae). Harmful Algae 17, 14–24 10.1016/j.hal.2012.02.005 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Luo H., Benner R., Long R. A., Hu J. (2009). Subcellular localization of marine bacterial alkaline phosphatases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 106, 21219–21223 10.1073/pnas.0810731105 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo H., Zhang H., Long R. A., Benner R. (2011). Depth distributions of alkaline phosphatase and phosphonate utilization genes in the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 62, 61–69 10.3354/ame01458 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Mather R. L., Reynolds S. E., Wolff G. A., Williams R. G., Torres-Valdes S., Woodward E. M. S., Landolfi A., Pan X., Sanders R., Achterberg E. P. (2008). Phosphorus cycling in the North and South Atlantic Ocean subtropical gyres. Nat. Geosci. 1, 439–443 10.1038/ngeo232 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Meseck S. L., Alix J. H., Wikfors G. H., Ward J. E. (2009). Differences in the soluble, residual phosphate concentrations at which coastal phytoplankton species up-regulate alkaline-phosphatase expression, as measured by flow-cytometric detection of ELF-97® fluorescence. Estuaries Coast 32, 1195–1204 10.1007/s12237-009-9211-7 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Mills M. M., Ridame C., Davey M., La Roche J., Geider R. J. (2004). Iron and phosphorus co-limit nitrogen fixation in the eastern tropical North Atlantic. Nature 429, 292–294 10.1038/nature02550 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miranda L. N., Zhang H., Zhuang Y., Lin S. (2012). Phylogenetic analysis guided by intragenomic SSU rDNA polymorphism refines classification of “Alexandrium tamarense” species complex. Harmful Algae 16, 35–48 10.1016/j.hal.2012.01.002 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Mooney B. D., Hallegraeff G. M., Place A. R. (2010). Ichthyotoxicity of four species of gymnodinioid dinoflagellates (Kareniaceae, Dinophyta) and purified karlotoxins to larval sheepshead minnow. Harmful Algae 9, 557–562 10.1016/j.hal.2010.04.005 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Moore L. R., Ostrowski M., Scanlan D. J., Feren K., Sweetsir T. (2005). Ecotypic variation in phosphorus-acquisition mechanisms within marine picocyanobacteria. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 39, 257–269 10.3354/ame039257 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Morey J. S., Monroe1 E. A., Kinney A. L., Beal M., Johnson J. G., Hitchcock G. L., Van Dolah F. M. (2011). Transcriptomic response of the red tide dinoflagellate, Karenia brevis, to nitrogen and phosphorus depletion and addition. BMC Genomics 12 10.1186/1471-2164-12-346 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley J. L., Chang C-W., Grossman A. R. (2006). Genome-based approaches to understanding phosphorus deprivation responses and PSR1 control in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Eukaryotic Cell 5, 26–44 10.1128/EC.5.1.26-44.2006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. E., Tibbitts T. T., Kantrowitz E. R. (1995). Mutations at positions 153 and 328 in Escherichia coli alkaline phosphatase provide insight towards the structure and function of mammalian and yeast alkaline phosphatase. J. Mol. Biol. 253, 604–617 10.1006/jmbi.1995.0576 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson D., Dyhrman S., Chavez F., Paytan A. (2006). Alkaline phosphatase activity in the phytoplankton communities of Monterey Bay and San Francisco Bay. Limnol. Oceanogr. 51, 874–883 10.4319/lo.2006.51.2.0874 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Orchard E. D., Webb E. A., Dyhrman S. T. (2009). Molecular analysis of the phosphorus starvation response in Trichodemium spp. Environ. Microbiol. 11, 2400–2411 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2009.01968.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ou L., Huang B., Hong H., Qi Y., Lu S. (2010). Comparative alkaline phosphatase characteristics of the algal bloom dinoflagellates Prorocentrum donghaiense and Alexandrium catenella, and the diatom Skeletonema costatum. J. Phycol. 46, 260–265 10.1111/j.1529-8817.2009.00800.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Ou L., Wang D., Huang B., Hong H., Qi Y., Lu S. (2008). Comparative study of phosphorus strategies of three typical harmful algae in Chinese coastal waters. J. Plankton Res. 30, 1007–1017 10.1093/plankt/fbn058 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Paytan A., McLaughlin K. (2007). The oceanic phosphorus cycle. Chem. Rev. 107, 563–576 10.1021/cr0503613 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen T. N., Brunak S., Von Heijne G., Nielsen H. (2011). SignalP 4.0: discriminating signal peptides from transmembrane regions. Nat. Methods 8, 785–786 10.1038/nmeth.1701 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierlenoi A., Martelli P. L., Casadio R. (2008). PredGPI: a GPI-anchor predictor. BMC Bioinformatics 9, 392 10.1186/1471-2105-9-392 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quisel J. D., Wykoff D. D., Grossman A. R. (1996). Biochemical characterization of the extracellular phosphatases produced by phosphorus-deprived Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Physiol. 111, 839–848 10.1104/pp.111.3.839 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rai A., Suprasanna P., D’Souza S., Kumar V. (2012). Membrane topology and predicted RNA-binding function of the “early response to dehydration (ERD4)” palnt protein. PLoS ONE 7, e32658 10.1371/journal.pone.0032658 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray J. M., Bhaya D., Block M. A., Grossman A. R. (1991). Isolation, transcription, and inactivation of the gene for an atypical alkaline phosphatase of Synechococcus sp. Strain PCC 7942. J. Bacteriol. 173, 4297–4309 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rensing S. A., Lang D., Schumann E., Reski R., Hohe A. (2005). EST Sequencing from embryogenic cyclamen persicum cell cultures identifies a high proportion of transcripts homologous to plant genes involved in somatic embryogenesis. J. Plant Growth Regul. 24, 102–115 10.1007/s00344-005-0033-y [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Saitou N., Nei M. (1987). The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 4, 406–425 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sañudo-Wilhelmy S. A., Kustka A. B., Gobler C. J., Hutchins D. A., Yang M., Lwiza K., Burns J., Capone D. G., Raven J. A., Carpenter E. J. (2001). Phosphorus limitation of nitrogen fixation by Trichodesmium in the central Atlantic Ocean. Nature 411, 66–69 10.1038/35075041 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scanlan D. J., Wilson W. H. (1999). Application of molecular techniques to addressing the role of P as a key effector in marine ecosystems. Hydrobiologia 401, 149–175 10.1023/A:1003742528262 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Scavia D., Bricker S. B. (2006). Coastal eutrophication assessment in the United States. Biogeochemistry 79, 187–208 10.1007/s10533-006-9011-0 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Sebastian M., Ammerman J. W. (2009). The Alkaline Phosphatase PhoX is more widely distributed in marine bacteria than the classical PhoA. ISME J. 3, 563–572 10.1038/ismej.2009.10 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soanes D. M., Richards T. A., Talbot N. J. (2007). Insights from sequencing fungal and oomycete genomes: what can we learn about plant disease and the evolution of pathogenicity? Plant Cell 19, 3318–3326 10.1105/tpc.107.056663 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun M-M., Sun J., Qiu J-W., Jing H., Liu H. (2012). Characterization of the proteomic profiles of the brown tide alga Aureoumbra lagunensis under phosphate- and nitrogen-limiting conditions and of its phosphate limitation-specific protein with alkaline phosphatase activity. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 78, 2025–2033 10.1128/AEM.06770-11 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thingstad T. F., Krom M. D., Mantoura R. F. C., Flaten G. A. F., Groom S., Herut B., Kress N., Law C. S., Pasternak A., Pitta P., Psarra S., Rassoulzadegan F. T., Tanaka A. T., Wassmann P., Woodward E. M. S., Riser C. W., Zodiatis G., Zohary T. (2005). Nature of phosphorus limitation in the ultraoligotrophic Eastern Mediterranean. Science 309, 1068–1071 10.1126/science.1112632 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. D., Gibson T. J., Plewniak F., Jeanmougin F., Higgins D. G. (1997). The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 25, 4876–4882 10.1093/nar/25.24.4876 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornton K. R. (2007). The neutral coalescent process for recent gene duplications and copy-number variants. Genetics 177, 987–1000 10.1534/genetics.107.074948 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueno S., Provost G. L., Léger V., Klopp C., Noirot C., Frigerio J.-M., Salin F., Salse J., Abrouk M., Murat F., Brendel O., Derory J., Abadie P., Léger P., Cabane C., Barré A., de Daruvar A., Couloux A., Wincker P., Reviron M.-P., Kremer A., Plomion C. (2010). Bioinformatic analysis of ESTs collected by Sanger and pyrosequencing methods for a keystone forest tree species: oak. BMC Genomics 11, 650 10.1186/1471-2164-11-650 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Mooy B. A. S., Fredricks H. F., Pedler B. E., Dyhrman S. T., Karl D. M., Koblí~ek M., Lomas M. W., Mincer T. J., Moore L. R., Moutin T., Rappé M. S., Webb E. A. (2009). Phytoplankton in the ocean use non-phosphorus lipids in response to phosphorus scarcity. Nature 458, 69–72 10.1038/nature07659 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Mooy B. A. S., Rocap G., Fredricks H. F., Evans C. T., Devol A. H. (2006). Sulfolipids dramatically decrease phosphorus demand by picocyanobacteria in oligotrophic marine environments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103, 8607–8612 10.1073/pnas.0600540103 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner K-U., Masepohl B., Pistorius E. K. (1995). The cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. strain PCC7942 contains a second alkaline phosphatase encoded by phoV. Microbiology 141, 3049–3058 10.1099/13500872-141-12-3049 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White A. E. (2009). New insights into bacterial acquisition of phosphorus in the surface ocean. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 106, 21013–21014 10.1073/pnas.0912475107 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J., Sunda W., Boyle E. A., Karl D. M. (2000). Phosphate depletion in the western North Atlantic Ocean. Science 289, 759–762 10.1126/science.289.5480.759 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu Y., Boucher J. M., Morel F. M. M. (2010). Expression and diversity of alkaline phosphatase EHAP1 in Emiliania huxleyi (Prymnesiophyceae). J. Phycol. 46, 85–92 10.1111/j.1529-8817.2009.00788.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Xu Y., Wahlund T. M., Feng L., Shaked Y., Morel F. M. M. (2006). A novel alkaline phosphatase in the Coccolithophore Emiliania huxleyi (Prymnesiophyceae) and its regulation by phosphorus. J. Phycol. 42, 835–844 10.1111/j.1529-8817.2006.00243.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Yu C. S., Chen Y. C., Lu C. H., Hwang J. K. (2006). Prediction of protein subcellular localization. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinformatics 64, 643–651 10.1002/prot.21018 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang H., Bhattacharya D., Lin S. (2007a). A three-gene dinoflagellate phylogeny suggests reconciliation of exuviaella with Prorocentrum and a basal position for Amphidinium and Heterocapsa. J. Mol. Evol. 65, 463–474 10.1007/s00239-007-9000-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang H., Hou Y., Miranda L., Campbell D. A., Sturm N. R., Gaasterland T., Lin S. (2007b). Spiced leader RNA trans-splicing in dinoflagellates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 104, 4618–4623 10.1073/pnas.0708101104 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J., Liu S. M., Ren J. L., Wu Y., Zhang G. L. (2007c). Nutrient gradients from the eutrophic Changjiang (Yangtze River) Estuary to the oligotrophic Kuroshio waters and re-evaluation of budgets for the East China Sea Shelf. Prog. Oceanogr. 74, 449–478 10.1016/j.pocean.2007.04.019 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang H., Hou Y., Lin S. (2006). Isolation and characrization of proliferating cell nuclear antigen from the dinoflagellate Pfiesteria piscicida. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 53, 1–9 10.1111/j.1550-7408.2006.00113.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang H., Lin S. (2003). Complex gene structure of the form II Rubisco in the dinoflagellate Prorocentrum minimum (dinophyceae). J. Phycol. 39, 1160–1171 10.1111/j.0022-3646.2003.03-055.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Test runs of the four subcellular localization predicting models with AP from dinoflagellates and various other organisms and a variety of other porteins in dinoflagellates.
Eukaryotic phytoplankton in which Alkaline phosphatase activity or coding gene that has been detected.