Abstract
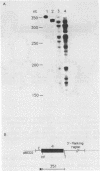
The mature apo Very Low Density Lipoprotein II (apo VLDLII) mRNA appears in chicken liver within a few hours after estrogen administration. Apart from this mRNA species, shorter RNA molecules hybridizing to apo VLDLII sequences have been detected in rooster liver upon estrogen stimulation. These molecules are present in the non-polyadenylated fraction of the total cellular- and polysomal RNA. Northern blotting and electron microscopy of R-loops were employed to show that these shorter RNA molecules are truncated at their 3'-end. The 3'-termini were further characterized by nuclease S1 analyses, and are located predominantly in the 3' untranslated region of the mRNA. Using a secondary structure model (Shelness and Williams, J. Biol. Chem. 260, 8637-8646, 1985), we show that the 3' termini map mainly in unpaired regions of the structure.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ab G., Roskam W. G., Dijkstra J., Mulder J., Willems M., Van der Ende A., Gruber M. Estradiol-induced synthesis of vitellogenin. III. The isolation and characterization of vitellogenin messenger RNA from avian liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Nov 12;454(1):67–78. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(76)90355-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albrecht G., Krowczynska A., Brawerman G. Configuration of beta-globin messenger RNA in rabbit reticulocytes. Identification of sites exposed to endogenous and exogenous nucleases. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 5;178(4):881–896. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90317-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnberg A. C., Meijlink F. C., Mulder J., van Bruggen E. F., Gruber M., Geert A. B. Isolation and characterization of genomic clones covering the chicken vitellogenin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 24;9(14):3271–3286. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.14.3271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Spliced early mRNAs of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1274–1278. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawerman G. Determinants of messenger RNA stability. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):5–6. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90346-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer G., Ross J. Poly(A) shortening and degradation of the 3' A+U-rich sequences of human c-myc mRNA in a cell-free system. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1697–1708. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock M. L., Shapiro D. J. Estrogen stabilizes vitellogenin mRNA against cytoplasmic degradation. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):207–214. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90151-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey J. L., Hentze M. W., Koeller D. M., Caughman S. W., Rouault T. A., Klausner R. D., Harford J. B. Iron-responsive elements: regulatory RNA sequences that control mRNA levels and translation. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):924–928. doi: 10.1126/science.2452485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutscher M. P. The metabolic role of RNases. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Apr;13(4):136–139. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90070-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon D. A., Shelness G. S., Nicosia M., Williams D. L. Estrogen-induced destabilization of yolk precursor protein mRNAs in avian liver. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):2625–2631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Flavell R. A. A physical map of the DNA regions flanking the rabbit beta-globin gene. Cell. 1977 Oct;12(2):429–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90119-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jäck H. M., Wabl M. Immunoglobulin mRNA stability varies during B lymphocyte differentiation. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):1041–1046. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02911.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback D. B., Angerer L. M., Davidson N. Improved methods for the formation and stabilization of R-loops. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jun 11;6(7):2499–2317. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.7.2499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noteborn M. H., Bakker O., de Jonge M. A., Gruber M., Ab G. Differential estrogen responsiveness of the vitellogenin and apo very low density lipoprotein II genes in the rooster liver. J Steroid Biochem. 1986 Jan;24(1):281–285. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(86)90065-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paek I., Axel R. Glucocorticoids enhance stability of human growth hormone mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1496–1507. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao T. R., Slobin L. I. The stability of mRNA for eucaryotic elongation factor Tu in Friend erythroleukemia cells varies with growth rate. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1085–1092. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roskam W. G., Tichelaar W., Schirm J., Gruber M., Ab G. Estradiol-induced synthesis of vitellogenin. I. The isolation of large polysomes from estrogenized rooster liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jun 2;435(1):82–90. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(76)90194-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross J., Kobs G. H4 histone messenger RNA decay in cell-free extracts initiates at or near the 3' terminus and proceeds 3' to 5'. J Mol Biol. 1986 Apr 20;188(4):579–593. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(86)80008-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelness G. S., Williams D. L. Secondary structure analysis of apolipoprotein II mRNA using enzymatic probes and reverse transcriptase. Evaluation of primer extension for high resolution structure mapping of mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 15;260(14):8637–8646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalker D. M., Kolter R., Helinski D. R. Nucleotide sequence of the region of an origin of replication of the antibiotic resistance plasmid R6K. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1150–1154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., Gage L. P., Brown D. D. The genes for silk fibroin in Bombyx mori. J Mol Biol. 1972 Oct 14;70(3):637–649. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90563-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Transient accumulation of c-fos RNA following serum stimulation requires a conserved 5' element and c-fos 3' sequences. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):889–902. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90285-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver R. F., Weissmann C. Mapping of RNA by a modification of the Berk-Sharp procedure: the 5' termini of 15 S beta-globin mRNA precursor and mature 10 s beta-globin mRNA have identical map coordinates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1175–1193. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieringa B., Ab G., Gruber M. The nucleotide sequence of the very low density lipoprotein II mRNA from chicken. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Feb 11;9(3):489–501. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.3.489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiskocil R., Bensky P., Dower W., Goldberger R. F., Gordon J. I., Deeley R. G. Coordinate regulation of two estrogen-dependent genes in avian liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4474–4478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolford J. L., Jr, Rosbash M. The use of R-looping for structural gene identification and mRNA purification. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jun 11;6(7):2483–2497. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.7.2483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. R. Steroid receptor regulated transcription of specific genes and gene networks. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:209–252. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.001233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van het Schip A. D., Meijlink F. C., Strijker R., Gruber M., van Vliet A. J., van de Klundert J. A., Ab G. The nucleotide sequence of the chicken apo very low density lipoprotein II gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 May 11;11(9):2529–2540. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.9.2529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van het Schip F. D., Samallo J., Broos J., Ophuis J., Mojet M., Gruber M., AB G. Nucleotide sequence of a chicken vitellogenin gene and derived amino acid sequence of the encoded yolk precursor protein. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jul 20;196(2):245–260. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90688-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]