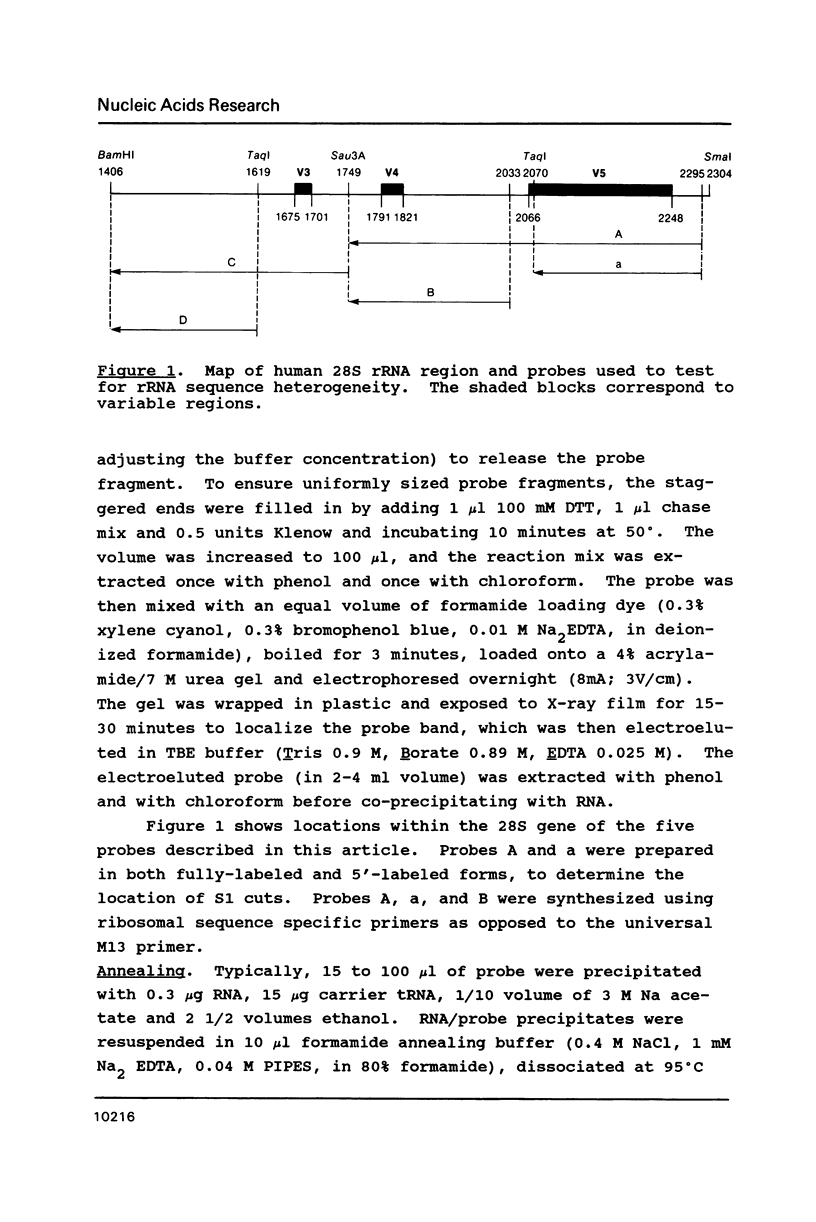
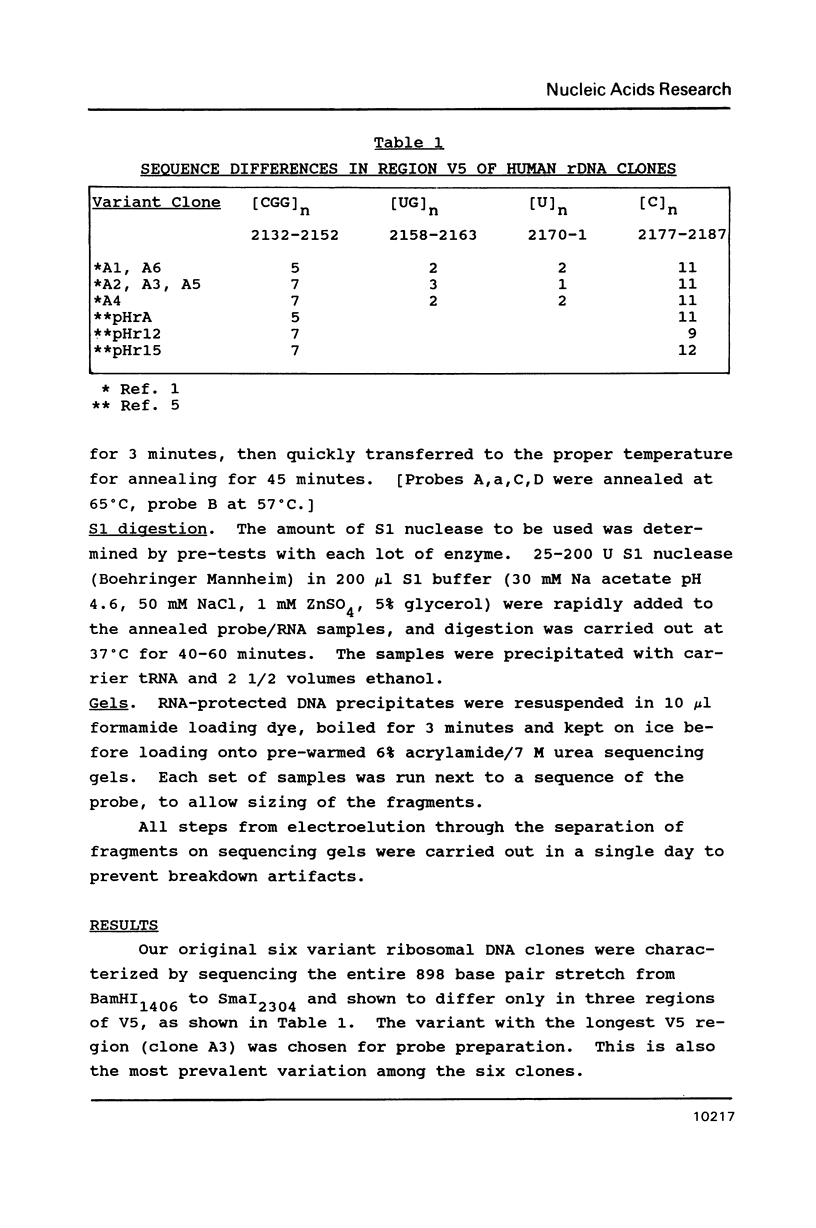
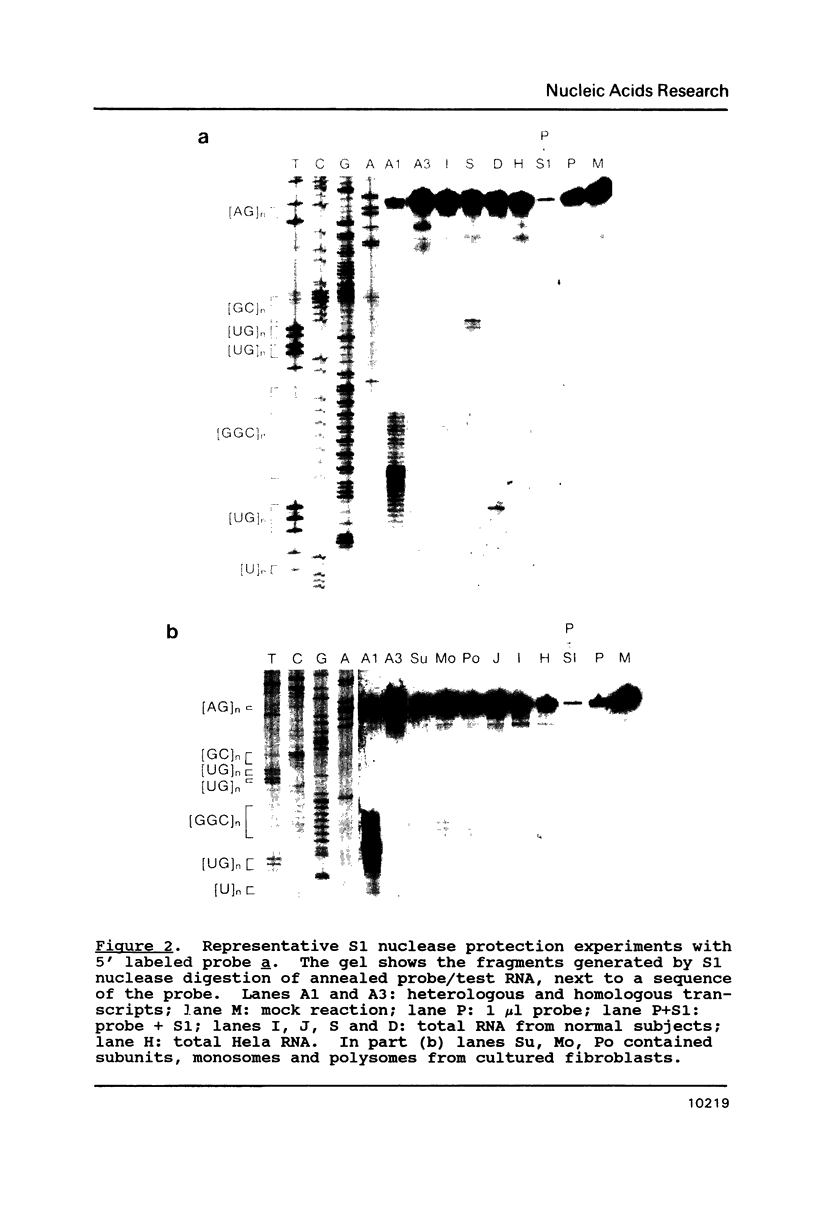
Abstract
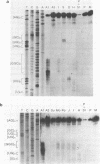
DNA sequencing of several cloned human 28S ribosomal RNA gene fragments has revealed sequence heterogeneity (1) but it was not clear whether these are inactive pseudogenes or are active genes that are transcribed and represented in ribosomes. S1 nuclease analysis allowed us to examine the population of ribosomal RNA molecules of a cell, and we found that 28S rRNA is a heterogeneous assortment of molecules in both mono- and polysomal preparations. Sequence variation, although largely concentrated in variable regions of the molecule, apparently also occurs in the conserved regions.
Full text
PDF




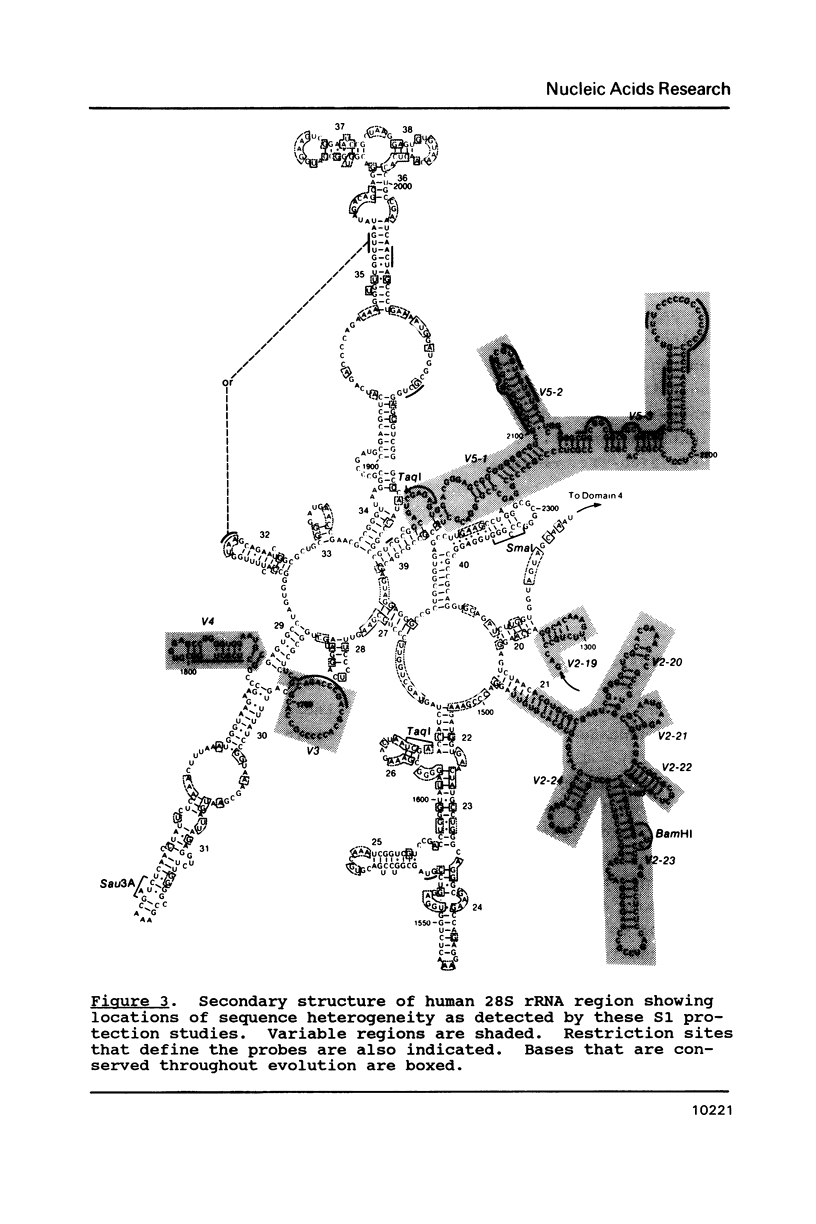



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnheim N., Krystal M., Schmickel R., Wilson G., Ryder O., Zimmer E. Molecular evidence for genetic exchanges among ribosomal genes on nonhomologous chromosomes in man and apes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7323–7327. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark C. G. On the evolution of ribosomal RNA. J Mol Evol. 1987;25(4):343–350. doi: 10.1007/BF02603119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coen E. S., Thoday J. M., Dover G. Rate of turnover of structural variants in the rDNA gene family of Drosophila melanogaster. Nature. 1982 Feb 18;295(5850):564–568. doi: 10.1038/295564a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez I. L., Gorski J. L., Campen T. J., Dorney D. J., Erickson J. M., Sylvester J. E., Schmickel R. D. Variation among human 28S ribosomal RNA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7666–7670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski J. L., Gonzalez I. L., Schmickel R. D. The secondary structure of human 28S rRNA: the structure and evolution of a mosaic rRNA gene. J Mol Evol. 1987;24(3):236–251. doi: 10.1007/BF02111237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassouna N., Michot B., Bachellerie J. P. The complete nucleotide sequence of mouse 28S rRNA gene. Implications for the process of size increase of the large subunit rRNA in higher eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 25;12(8):3563–3583. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.8.3563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain S. K., Crampton J., Gonzalez I. L., Schmickel R. D., Drysdale J. W. Complementarity between ferritin H mRNA and 28 S ribosomal RNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Sep 16;131(2):863–867. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91319-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson G., Gutman G. A. Slipped-strand mispairing: a major mechanism for DNA sequence evolution. Mol Biol Evol. 1987 May;4(3):203–221. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebhaber S. A., Goossens M., Kan Y. W. Homology and concerted evolution at the alpha 1 and alpha 2 loci of human alpha-globin. Nature. 1981 Mar 5;290(5801):26–29. doi: 10.1038/290026a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maden B. E., Dent C. L., Farrell T. E., Garde J., McCallum F. S., Wakeman J. A. Clones of human ribosomal DNA containing the complete 18 S-rRNA and 28 S-rRNA genes. Characterization, a detailed map of the human ribosomal transcription unit and diversity among clones. Biochem J. 1987 Sep 1;246(2):519–527. doi: 10.1042/bj2460519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsnes S. Closing in on ricin action. Nature. 1987 Aug 6;328(6130):474–475. doi: 10.1038/328474b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks C. L., Jones T. R., Gonzalez I. L., Schmickel R. D., Hyman R. W., Spector D. J. A simple repetitive sequence common to herpes simplex virus type 1 and human ribosomal DNAs. Virology. 1986 Oct 30;154(2):381–388. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90463-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peattie D. A., Douthwaite S., Garrett R. A., Noller H. F. A "bulged" double helix in a RNA-protein contact site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7331–7335. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen S. H., Slightom J. L., Smithies O. A history of the human fetal globin gene duplication. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(2 Pt 2):191–203. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90302-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. P. Unequal crossover and the evolution of multigene families. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:507–513. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartof K. D. Unequal mitotic sister chromatid exchange and disproportionate replication as mechanisms regulating ribosomal RNA gene redundancy. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:491–500. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tautz D., Trick M., Dover G. A. Cryptic simplicity in DNA is a major source of genetic variation. Nature. 1986 Aug 14;322(6080):652–656. doi: 10.1038/322652a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler W. C., Honeycutt R. L. Paired sequence difference in ribosomal RNAs: evolutionary and phylogenetic implications. Mol Biol Evol. 1988 Jan;5(1):90–96. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]