Abstract
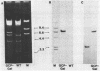
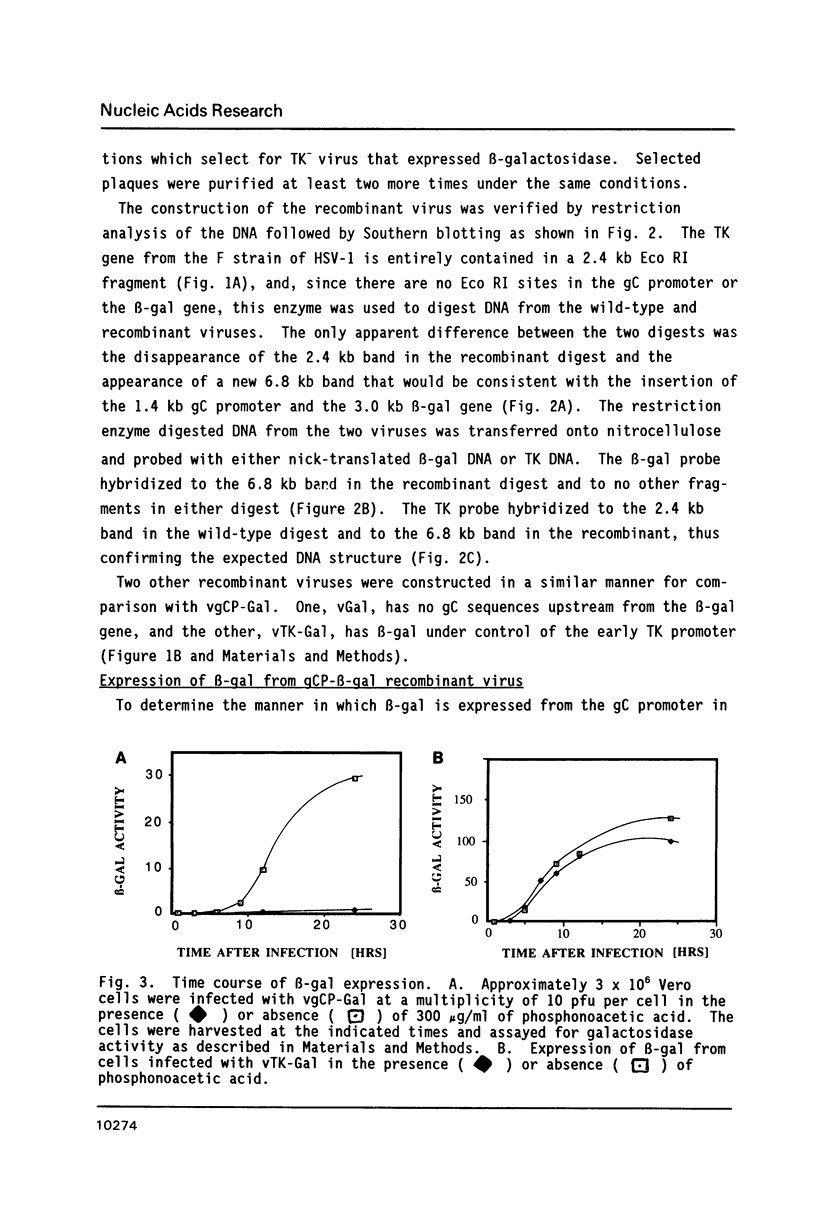
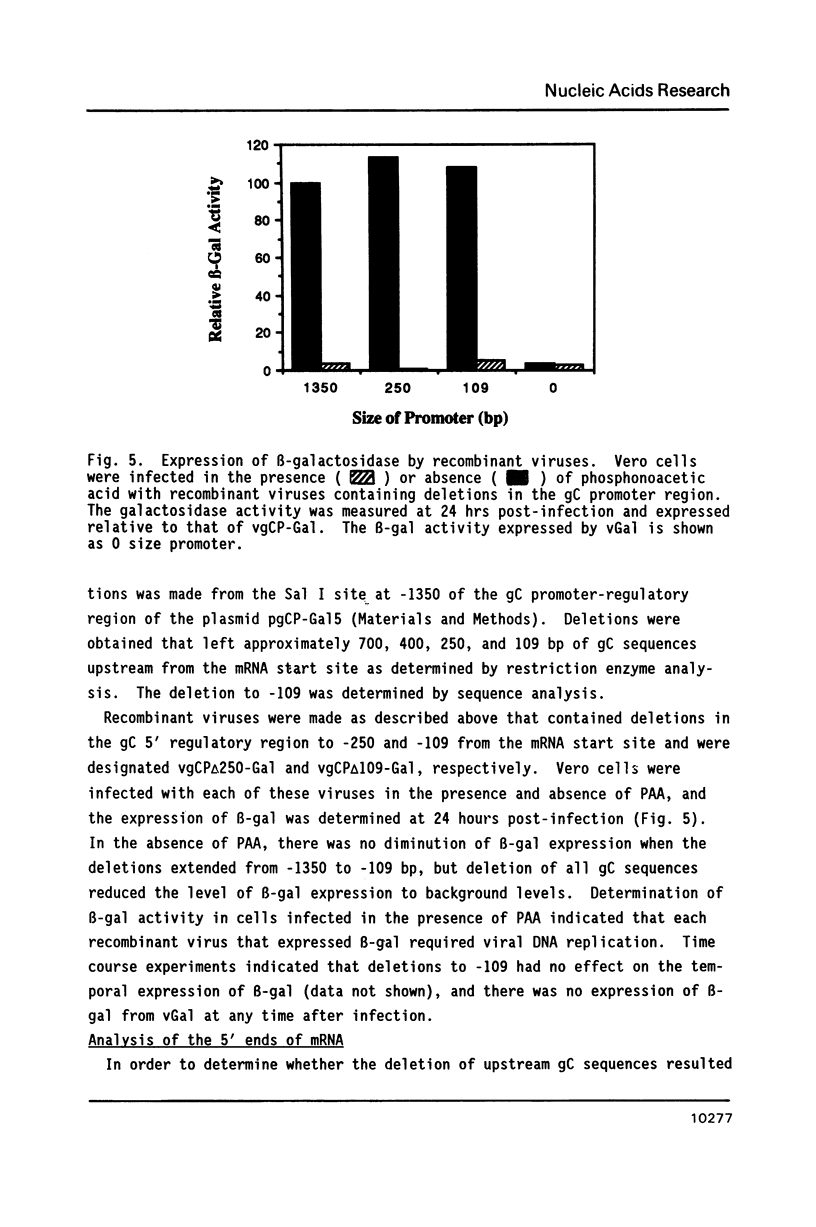
The expression of Herpes Simplex Virus 1 (HSV-1) glycoprotein C (gC), a well defined herpesvirus late gene, was studied by linking the promoter-regulatory region of this gene to the coding sequences for the bacterial enzyme, beta-galactosidase (beta-gal). A chimeric gene, containing the beta-gal gene under the control of gC sequences from -1350 to +30 relative to the mRNA start site, was inserted by homologous recombination into the thymidine kinase (TK) locus of the HSV-1 genome. Selection of the TK- recombinant virus by plaque assay was facilitated by addition of a beta-gal indicator to the agarose overlay. Recombinant virus containing the gC promoter-beta-gal chimeric gene faithfully expressed beta-gal as a viral late gene, as shown by the absence of beta-gal expression when viral DNA replication was inhibited with phosphonoacetic acid. In contrast, the inhibition of viral DNA replication had no effect on the expression of beta-gal when the beta-gal gene was under the control of the early HSV-1 TK promoter in a separate recombinant virus. Analysis of recombinant viruses containing 5' to 3' deletions in the gC regulatory region revealed no apparent difference in beta-gal expression as deletions extended from -1350 to -109 base-pairs (bp) before the RNA start site, demonstrating that sequences between -109 and +30 are sufficient for regulated gC expression in the viral genome. Analysis of the mRNA made by these recombinant viruses confirmed the results of the beta-gal assays, and demonstrated that the transcriptional start sites of the gC promoter-beta-gal chimeric genes were the same as the start site of the gC gene.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Batterson W., Roizman B. Characterization of the herpes simplex virion-associated factor responsible for the induction of alpha genes. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):371–377. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.371-377.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair E. D., Wagner E. K. A single regulatory region modulates both cis activation and trans activation of the herpes simplex virus VP5 promoter in transient-expression assays in vivo. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):460–469. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.460-469.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell M. E., Palfreyman J. W., Preston C. M. Identification of herpes simplex virus DNA sequences which encode a trans-acting polypeptide responsible for stimulation of immediate early transcription. J Mol Biol. 1984 Nov 25;180(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90427-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti S., Brechling K., Moss B. Vaccinia virus expression vector: coexpression of beta-galactosidase provides visual screening of recombinant virus plaques. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3403–3409. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coen D. M., Weinheimer S. P., McKnight S. L. A genetic approach to promoter recognition during trans induction of viral gene expression. Science. 1986 Oct 3;234(4772):53–59. doi: 10.1126/science.3018926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa R. H., Cohen G., Eisenberg R., Long D., Wagner E. Direct demonstration that the abundant 6-kilobase herpes simplex virus type 1 mRNA mapping between 0.23 and 0.27 map units encodes the major capsid protein VP5. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):287–292. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.287-292.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa R. H., Draper K. G., Devi-Rao G., Thompson R. L., Wagner E. K. Virus-induced modification of the host cell is required for expression of the bacterial chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene controlled by a late herpes simplex virus promoter (VP5). J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):19–30. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.19-30.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis D., Smiley J. R. Transactivation of a late herpes simplex virus promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;4(3):544–551. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.3.544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denniston K. J., Madden M. J., Enquist L. W., Vande Woude G. Characterization of coliphage lambda hybrids carrying DNA fragments from Herpes simplex virus type 1 defective interfering particles. Gene. 1981 Dec;15(4):365–378. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90180-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ElKareh A., Murphy A. J., Fichter T., Efstratiadis A., Silverstein S. "Transactivation" control signals in the promoter of the herpesvirus thymidine kinase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1002–1006. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D. DNA sequence elements required for regulated expression of the HSV-1 glycoprotein D gene lie within 83 bp of the RNA capsites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Oct 11;11(19):6647–6666. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.19.6647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frink R. J., Eisenberg R., Cohen G., Wagner E. K. Detailed analysis of the portion of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome encoding glycoprotein C. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):634–647. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.634-647.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godowski P. J., Knipe D. M. Identification of a herpes simplex virus function that represses late gene expression from parental viral genomes. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):357–365. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.357-365.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein D. J., Weller S. K. Herpes simplex virus type 1-induced ribonucleotide reductase activity is dispensable for virus growth and DNA synthesis: isolation and characterization of an ICP6 lacZ insertion mutant. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):196–205. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.196-205.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homa F. L., Glorioso J. C., Levine M. A specific 15-bp TATA box promoter element is required for expression of a herpes simplex virus type 1 late gene. Genes Dev. 1988 Jan;2(1):40–53. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.1.40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homa F. L., Otal T. M., Glorioso J. C., Levine M. Transcriptional control signals of a herpes simplex virus type 1 late (gamma 2) gene lie within bases -34 to +124 relative to the 5' terminus of the mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3652–3666. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. I. Cascade regulation of the synthesis of three groups of viral proteins. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):8–19. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.8-19.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jean J. H., Ben-Porat T., Kaplan A. S. Early functions of the genome of herpesvirus. 3. Inhibition of the transcription of the viral genome in cells treated with cycloheximide early during the infective process. Virology. 1974 Jun;59(2):516–523. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90461-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis: nuclear retention of nontranslated viral RNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4322–4326. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristie T. M., Roizman B. Separation of sequences defining basal expression from those conferring alpha gene recognition within the regulatory domains of herpes simplex virus 1 alpha genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4065–4069. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang J. C., Spandidos D. A., Wilkie N. M. Transcriptional regulation of a herpes simplex virus immediate early gene is mediated through an enhancer-type sequence. EMBO J. 1984 Feb;3(2):389–395. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01817.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackem S., Roizman B. Structural features of the herpes simplex virus alpha gene 4, 0, and 27 promoter-regulatory sequences which confer alpha regulation on chimeric thymidine kinase genes. J Virol. 1982 Dec;44(3):939–949. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.3.939-949.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mavromara-Nazos P., Silver S., Hubenthal-Voss J., McKnight J. L., Roizman B. Regulation of herpes simplex virus 1 genes: alpha gene sequence requirements for transient induction of indicator genes regulated by beta or late (gamma 2) promoters. Virology. 1986 Mar;149(2):152–164. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90117-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Gavis E. R. Expression of the herpes thymidine kinase gene in Xenopus laevis oocytes: an assay for the study of deletion mutants constructed in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 20;8(24):5931–5948. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.24.5931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Kingsbury R. Transcriptional control signals of a eukaryotic protein-coding gene. Science. 1982 Jul 23;217(4557):316–324. doi: 10.1126/science.6283634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker B. A., Stark G. R. Regulation of simian virus 40 transcription: sensitive analysis of the RNA species present early in infections by virus or viral DNA. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):360–369. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.360-369.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post L. E., Conley A. J., Mocarski E. S., Roizman B. Cloning of reiterated and nonreiterated herpes simplex virus 1 sequences as BamHI fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4201–4205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M., Cordingley M. G., Stow N. D. Analysis of DNA sequences which regulate the transcription of a herpes simplex virus immediate early gene. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):708–716. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.708-716.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks W. R., Greene C. C., Aschman D. P., Schaffer P. A. Herpes simplex virus type 1 ICP27 is an essential regulatory protein. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):796–805. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.796-805.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapira M., Homa F. L., Glorioso J. C., Levine M. Regulation of the herpes simplex virus type 1 late (gamma 2) glycoprotein C gene: sequences between base pairs -34 to +29 control transient expression and responsiveness to transactivation by the products of the immediate early (alpha) 4 and 0 genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 10;15(7):3097–3111. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.7.3097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih M. F., Arsenakis M., Tiollais P., Roizman B. Expression of hepatitis B virus S gene by herpes simplex virus type 1 vectors carrying alpha- and beta-regulated gene chimeras. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5867–5870. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver S., Roizman B. gamma 2-Thymidine kinase chimeras are identically transcribed but regulated a gamma 2 genes in herpes simplex virus genomes and as beta genes in cell genomes. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;5(3):518–528. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.3.518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaete R. R., Mocarski E. S. Regulation of cytomegalovirus gene expression: alpha and beta promoters are trans activated by viral functions in permissive human fibroblasts. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):135–143. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.135-143.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner M. J., Sharp J. A., Summers W. C. Nucleotide sequence of the thymidine kinase gene of herpes simplex virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1441–1445. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Clements J. B. A herpes simplex virus type 1 function continuously required for early and late virus RNA synthesis. Nature. 1980 May 29;285(5763):329–330. doi: 10.1038/285329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir J. P., Moss B. Regulation of expression and nucleotide sequence of a late vaccinia virus gene. J Virol. 1984 Sep;51(3):662–669. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.3.662-669.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]