Abstract
12(S)-Hydroxyheptadeca-5Z,8E,10E-trienoic acid (12-HHT) is an enzymatic product of prostaglandin H2 (PGH2) derived from cyclooxygenase (COX)-mediated arachidonic acid metabolism. Despite the high level of 12-HHT present in tissues and bodily fluids, its precise function remains largely unknown. In this study, we found that 12-HHT treatment in HaCaT cells remarkably down-regulated the ultraviolet B (UVB) irradiation-induced synthesis of interleukin-6 (IL-6), a pro-inflammatory cytokine associated with cutaneous inflammation. In an approach to identify the down-stream signaling mechanism by which 12-HHT down-regulates UVB-induced IL-6 synthesis in keratinocytes, we observed that 12-HHT inhibits the UVB-stimulated activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB). In addition, we found that 12-HHT markedly up-regulates MAPK phosphatase-1 (MKP-1), a critical negative regulator of p38 MAPK. When MKP-1 was suppressed by siRNA knock-down, the 12-HHT-mediated inhibitory effects on the UVB-stimulated activation of p38 MAPK and NF-κB, as well as the production of IL-6, were attenuated in HaCaT cells. Taken together, our results suggest that 12-HHT exerts anti-inflammatory effect via up-regulation of MKP-1, which negatively regulates p38 MAPK and NF-κB, thus attenuating IL-6 production in UVB-irradiated HaCaT cells. Considering the critical role of IL-6 in cutaneous inflammation, our findings provide the basis for the application of 12-HHT as a potential anti-inflammatory therapeutic agent in UV-induced skin diseases.
Keywords: dermatitis; dual specificity phosphatase 1; 12-hydroxy-5,8,10-heptadecatrienoic acid; interleukin-6; ultraviolet rays
Introduction
The UV spectrum is divided by wavelength into UVA (320-400 nm), UVB (290-320 nm) and UVC (200-290 nm) (Matsumura and Ananthaswamy, 2004). Among them, the acute and chronic exposure of skin to UVB irradiation can cause various inflammatory responses, including sunburn cell formation (erythema), alterations of vascular responses, the production of inflammatory mediators and the infiltration of inflammatory cells, leading to skin disorders (Clydesdale et al., 2001). Upon UVB irradiation in skin epidermis, keratinocytes are a major cell type that contributes to the synthesis of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α, IL-1α, IL-6 and IL-8 (Kock et al., 1990; Chung et al., 1996; Gebhardt et al., 2007).
IL-6 is up-regulated in skin inflammatory diseases (e.g., psoriasis and atopic dermatitis) and is involved in the pathogenesis of skin squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) (Grossman et al., 1989; Shinoda et al., 1998; Nishimoto and Kishimoto, 2004; Lederle et al., 2011). In psoriasis, IL-6 potentially induces lymphocyte infiltration and stimulates keratinocyte proliferation (Grossman et al., 1989). In addition, up-regulated IL-6 exacerbates the symptoms of atopic dermatitis (Shinoda et al., 1998). Also upon UV irradiation, IL-6 is markedly increased and contributes to cutaneous inflammatory responses (Chung et al., 1996; Grone, 2002). IL-6-deficient mice show a defective cutaneous immune response following UVB exposure, indicating that IL-6 is a crucial mediator in the inflammatory response of skin (Shinoda et al., 1998; Nishimura et al., 1999). Thus, the regulation of IL-6 expression is expected to be important in understanding inflammatory skin diseases.
12(S)-Hydroxyheptadeca-5Z,8E,10E-trienoic acid (12-HHT) is a cyclooxygenase (COX)-derived arachidonic acid metabolite that is mainly produced by activated human platelets (Hamberg et al., 1974; Okuno et al., 2008). 12-HHT is an abundant metabolite of the arachidonic acid cascade in tissues and cell types, e.g., vascular tissue, intestinal tissue, alveolar macrophages and bodily fluids (Caprino et al., 1982; Punnonen et al., 1984; John et al., 1998), but little is known about its physiological roles and pathological relevance.
In this study, we found that 12-HHT inhibits the UVB-induced activation of the p38 MAPK/NF-κB pathway by up-regulating MAPK phosphatase-1 (MKP-1), which leads to the down-regulation of IL-6 synthesis in keratinocytes. These findings provide a novel insight into the function of 12-HHT in UVB-induced skin inflammation and suggest a potential application agent for the treatment of skin inflammatory diseases.
Results
12-HTT down-regulates UVB-induced IL-6 synthesis in HaCaT cells
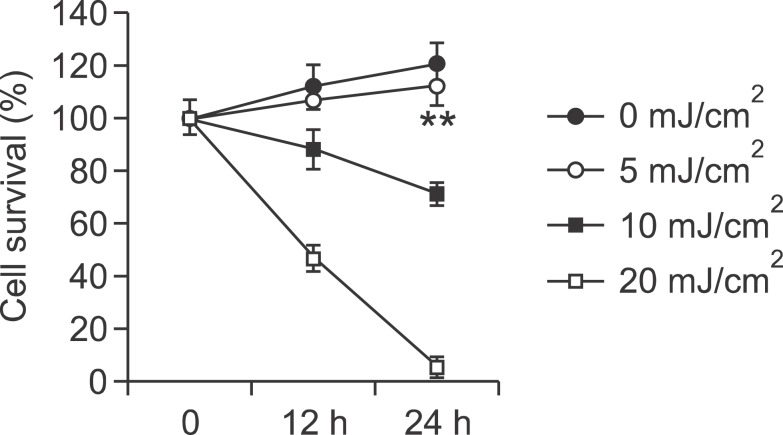
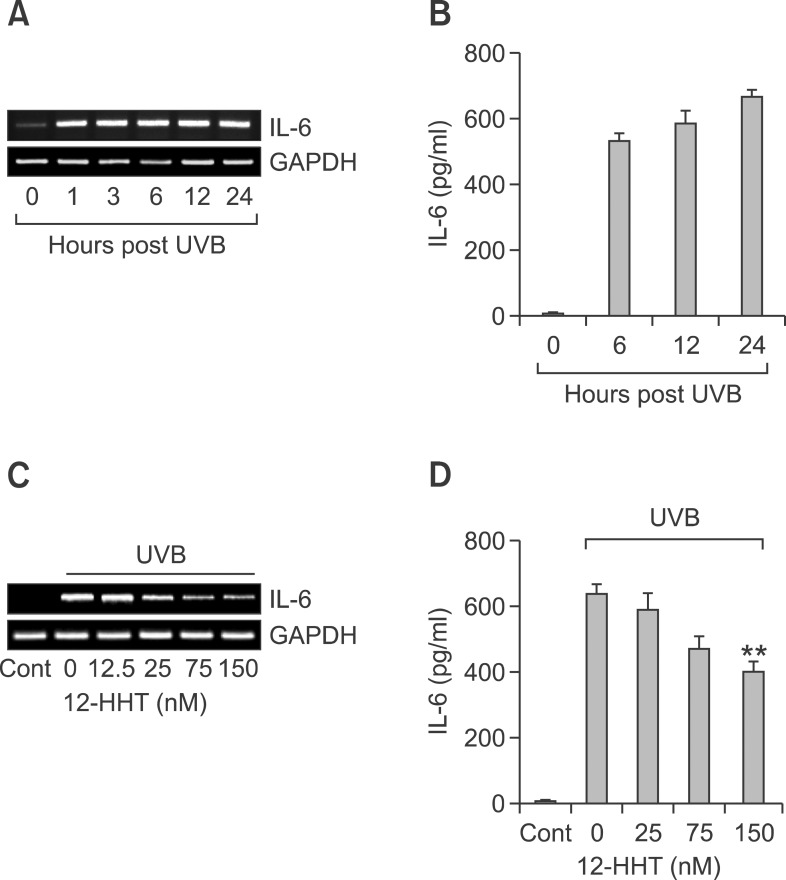
To investigate the role of 12-HHT in the inflammatory responses of keratinocytes, we initially examined the effect of various UV doses on cell viability. HaCaT cells were irradiated with UVB at 5, 10 and 20 mJ/cm2, and the number of viable cells was estimated by a trypan-blue exclusion assay. At 5 mJ/cm2, UVB had no effect on cell viability (Figure 1), and thus, a dose of 5 mJ/cm2 was chosen for further experiments. To assess the role of 12-HHT in UVB-induced inflammation, we analyzed the effect of 12-HHT on the UVB-induced inflammatory cytokine, IL-6. UVB (5 mJ/cm2) irradiation markedly up-regulated IL-6 synthesis and release (Figures 2A and 2B), which was suppressed by the treatment with 12-HHT in a concentration-dependent manner (Figures 2C and 2D). Taken together, these results suggest that 12-HHT has anti-inflammatory activity by attenuating the UVB-induced IL-6 synthesis in HaCaT cells.
Figure 1.
Determination of the optimal UVB irradiation dose that would not damage HaCaT cells. HaCaT cells were starved with serum-free DMEM for 12 h and then irradiated with the indicated doses of UVB. The irradiated cells were further incubated for 12 or 24 h. The cell viability was determined by the trypan blue exclusion assay. Data indicate the means ± S.D. of three independent experiments (**P < 0.01).
Figure 2.
12-HTT down-regulates UVB-induced IL-6 synthesis in HaCaT cells. (A) HaCaT cells were starved with serum-free DMEM for 12 h and irradiated with UVB (5 mJ/cm2). Total RNA was extracted from the cells at the indicated times (0, 1, 3, 6, 12 and 24 h). (B) HaCaT cells were starved with serum-free DMEM for 12 h and irradiated with UVB (5 mJ/cm2). The culture media were harvested at the indicated times (0, 6, 12 and 24 h) for IL-6 ELISA. (C) HaCaT cells were treated with 12-HHT (0, 12.5, 25, 75 or 150 nM) and further incubated for 3 h. Total RNA was extracted from the cells, and the level of IL-6 mRNA was analyzed by semi-quantitative RT-PCR. (D) 12-HHT was added to the culture media (0, 25, 75 or 150 nM). After 24 h, the culture media were harvested, and IL-6 was measured by ELISA. Data indicate the means ± S.D. of three independent experiments (**P < 0.01).
12-HHT reduces UVB-induced IL-6 synthesis via inhibition of the p38 MAPK/NF-κB pathway
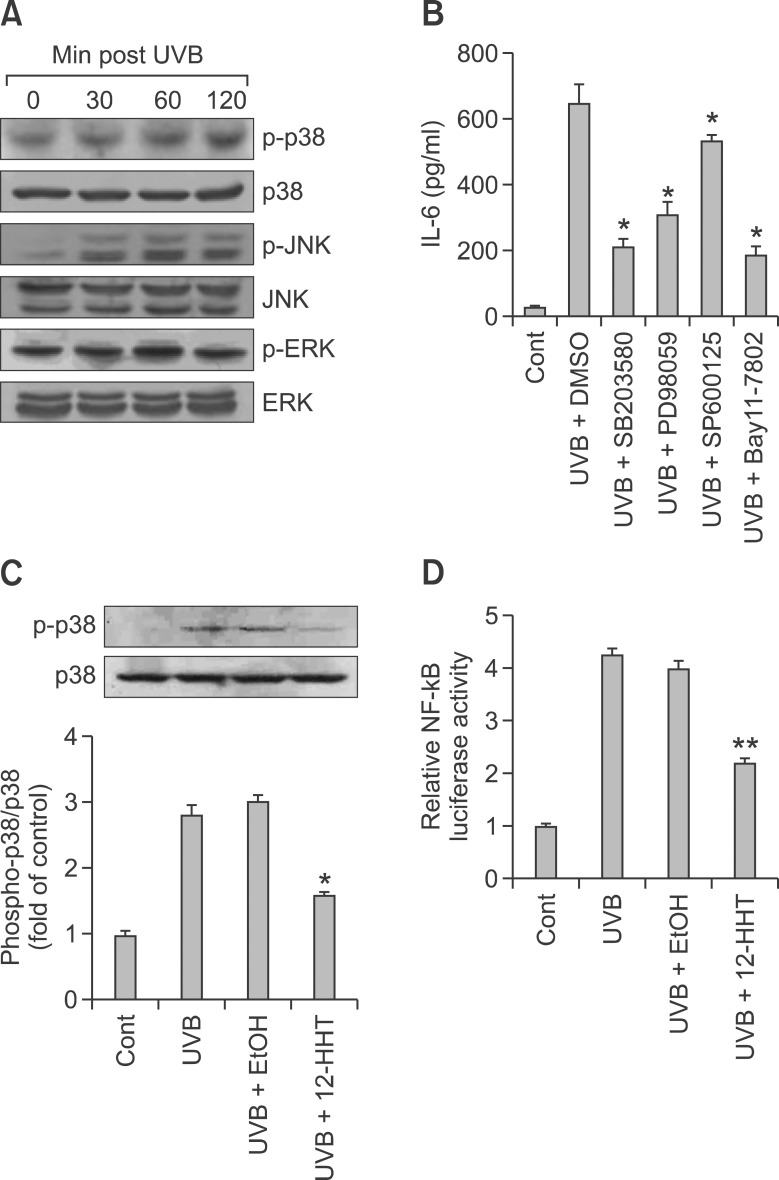
We next investigated the signaling mechanism by which 12-HHT down-regulates IL-6 synthesis upon UVB irradiation. MAPK has been implicated in the synthesis of the inflammatory cytokines induced by UV irradiation (Peus et al., 1999; Pfundt et al., 2001; Bode and Dong, 2003). Thus, we hypothesized that the ability of 12-HHT to modulate IL-6 synthesis would be mediated by MAPK and, subsequently, the pro-inflammatory activities of transcription factors, such as NF-κB. In accordance with previous reports, the activation of MAPK reached a maximum at 60 min post-irradiation (Figure 3A). Furthermore, IL-6 synthesis upon UVB irradiation was attenuated when the HaCaT cells were treated with MAPK inhibitors [e.g., p38 kinase inhibitor SB203580, ERK inhibitor PD98059 or JNK inhibitor SP600125], and, among these, SB203580 showed the most marked attenuation effect (Figure 3B). These results suggest that p38 MAPK is a major regulator of IL-6 synthesis. Next, the measurement of MAPK phosphorylation using western blotting revealed that the UVB-induced phosphorylation of p38 MAPK was significantly suppressed by 12-HHT treatment (Figure 3C); in contrast, no notably changes were detected in the phosphorylation of ERK or JNK (Supplemental Data Figure S1), indicating that 12-HHT down-regulates UVB-induced IL-6 synthesis in a largely p38 MAPK-dependent manner. It is well known that NF-κB acts down-stream of p38 MAPK in UV-induced signal transduction, thus regulating the expression of a variety of inflammatory cytokines. Therefore, we investigated the effect of 12-HHT on UVB-induced NF-κB activation, using a luciferase reporter gene assay. We detected an inhibitory effect of 12-HHT on the UVB-induced activation of NF-κB, showing that pretreatment with Bay11-7082, a specific inhibitor of NF-κB, markedly prevented UVB-induced IL-6 synthesis (Figure 3B) and that treatment with 12-HHT substantially reduced the transcriptional activity of NF-κB in HaCaT cells after UVB irradiation (Figure 3D). Taken together, these results suggest that 12-HHT inhibits the p38 MAPK/NF-κB pathway which is activated by UVB irradiation, thus leading to the reduction of IL-6 synthesis.
Figure 3.
12-HHT reduces UVB-induced IL-6 synthesis via inhibition of the p38 MAPK/NF-κB pathway. (A) HaCaT cells were starved for 12 h and irradiated with UVB (5 mJ/cm2) for various times (0, 30, 60 and 120 min). The cell lysates were examined by western blotting to analyze p-p38, p38, p-JNK, JNK, p-ERK and ERK. (B) Starved HaCaT cells were pretreated with SB203580 (20 µM), PD98059 (20 µM), SP600125 (20 µM) or Bay11-7082 (20 µM) for 60 min and then irradiated with UVB (5 mJ/cm2) for 24 h. The level of IL-6 synthesis was measured by ELISA. (C) Upon UVB irradiation (5 mJ/cm2), the HaCaT cells were immediately incubated with ethanol (control) or 12-HHT (150 nM) for 60 min. The cell lysates were prepared and examined by western blotting using antibodies specifically recognizing p38 MAPK and p-p38 MAPK. The p-p38 MAPK signals are presented as the fold induction relative to the control samples and are shown with densitometry values expressed as the means ± S.D. of three independent experiments. (D) HaCaT cells were co-transfected with both NF-κB-dependent luciferase construct and pSV40-β-galactosidase construct for 24 h and serum-starved for an additional 6 h. These transfected cells were either sham-irradiated or stimulated with UVB (5 mJ/cm2) and treated with ethanol (control) or 12-HHT (150 nM) for 1 h. The relative fold increase of luciferase activity was calculated, as described in the Methods. Data indicate the means ± S.D. of three independent experiments (*P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01).
12-HHT inhibits UVB-induced IL-6 synthesis through the induction of MKP-1
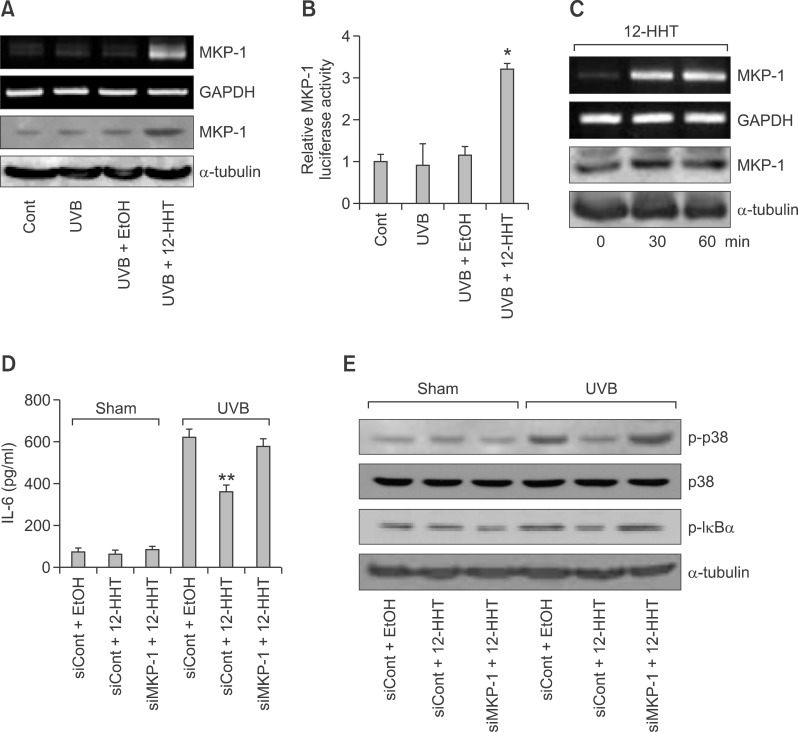
MKP-1 is a dual-specificity phosphatase that directly dephosphorylates p38 MAPK and, thus, attenuates UV-induced inflammation (Keyse, 1995; Li et al., 2011). To examine whether 12-HHT regulates MKP-1, we performed semi-quantitative RT-PCR and western blotting. As shown in Figure 4A, the levels of MKP-1 mRNA and protein were markedly enhanced by 12-HHT treatment upon UVB irradiation. This result was further confirmed by a MKP-1-dependent luciferase assay, which demonstrated that 12-HHT increased the activity of the MKP-1 promoter (Figure 4B). Additionally, treatment with 12-HHT alone rapidly augmented the MKP-1 level under normal conditions without UVB irradiation (Figure 4C). Subsequently, to determine whether the inhibitory effect of exogenous 12-HHT on IL-6 synthesis is mediated by the up-regulation of MKP-1 upon UVB irradiation, we performed knock-down experiments, using MKP-1-specific siRNA in 12-HHT-treated HaCaT cells. As shown in Figure 4D, the MKP-1 knock-down with siRNA significantly rescued the 12-HHT-suppressed IL-6 synthesis upon UVB irradiation. These results suggest that MKP-1 plays a critical role in mediating the anti-inflammatory action of 12-HHT. Moreover, the up-regulation of MKP-1 by exogenous 12-HHT was correlated with a suppression of the phosphorylation of both p38 MAPK and IκBα, showing that the blockage of MKP-1 markedly recovers the phosphorylation of both p38 MAPK and IκBα which was attenuated by 12-HHT (Figure 4E). Collectively, these results strongly suggest that 12-HHT induces MKP-1 expression, which is necessary for the down-regulation of p38 MAPK/NF-κB signaling, resulting in the reduction of IL-6 synthesis in UVB-irradiated HaCaT cells.
Figure 4.
12-HHT inhibits UVB-induced IL-6 synthesis through the induction of MKP-1. (A) Serum-starved HaCaT cells were irradiated with UVB (5 mJ/cm2) and immediately incubated with ethanol (control) or 12-HHT (150 nM) for 1 h. Total RNA and proteins were extracted from the cells, and the MKP-1 mRNA and protein levels were analyzed by semi-quantitative RT-PCR (upper panel) and western blotting (lower panel), respectively. (B) HaCaT cells were transiently co-transfected with both human MKP-1 luciferase reporter construct and pSV40-β-galactosidase construct for 24 h and starved for another 12 h. These cells were either sham-irradiated or stimulated with UVB (5 mJ/cm2) and immediately treated with ethanol (control) or 12-HHT (150 nM) for 1 h. The relative luciferase activity was calculated as described in the Methods. (C) Starved HaCaT cells were stimulated with 12-HHT (150 nM for 0, 30 or 60 min). Total RNA and proteins were extracted from the cells, and the MKP-1 mRNA and protein levels were analyzed by semi-quantitative RT-PCR (upper panel) and western blotting (lower panel), respectively. (D) HaCaT cells were transfected with control or MKP-1 siRNA (20 nM) for 24 h. Then, these cells were starved for 6 h, sham-irradiated or exposed to UVB (5 mJ/cm2) and treated with either ethanol (control) or 12-HHT (150 nM). After 24 h, the level of secreted IL-6 in the culture medium was quantified by ELISA. (E) HaCaT cells were transfected with control or MKP-1 siRNA (20 nM) for 24 h. Then, these cells were starved for 6 h, sham-irradiated or exposed to UVB (5 mJ/cm2) and treated with either ethanol (control) or 12-HHT (150 nM). The extracted proteins were analyzed by western blotting with antibodies against p-p38 MAPK, p38 MAPK and p-IκBα for 1 h. α-Tubulin was used as the loading control. Data indicate the means ± S.D. of three independent experiments (*P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01).
Discussion
In the present study, we demonstrated that 12-HHT plays a role in reducing UVB-induced IL-6 synthesis, thereby potentially mediating the anti-inflammatory actions of keratinocytes. Additionally, we extensively analyzed the key molecules contributing to the reduction of IL-6 in the 12-HHT-induced pathway and found that the up-regulation of MKP-1 by exogenous 12-HHT inhibits UVB-stimulated p38 MAPK and NF-κB signaling. Our findings provide valuable insight into potential therapies for skin inflammation.
The chronic exposure to UVB irradiation causes several skin disorders, such as sunburn, skin cancer and photo-aging, via inflammatory responses (Clydesdale et al., 2001; Kim et al., 2010; Ryu et al., 2010). These inflammatory responses are mediated by various cytokines, including IL-1, IL-6 and TNF-α upon UVB irradiation (Kock et al., 1990; Chung et al., 1996; Grone, 2002; Gebhardt et al., 2007). Among these cytokines, we focused on the regulation of IL-6, a critical pro-inflammatory cytokine that induces a local skin inflammatory response following UV irradiation (Wlaschek et al., 1994). IL-6 expression depends on the UVB-induced activation of MAPK, which leads to such down-stream events as NF-κB activation (Simon et al., 1994; Chen and Bowden, 1999; Wan et al., 2001; Kim et al., 2005a; Katiyar and Meeran, 2007). In this study, we examined whether the down-regulation of IL-6 by 12-HHT treatment is mediated by the inhibition of MAPK phosphorylation upon UVB irradiation. We observed that, upon UVB irradiation, the 12-HHT treatment significantly inhibited p38 MAPK activation (Figure 3C), but did not affect ERK or JNK activation (Supplemental Data Figure S1). Furthermore, the inhibition of p38 MAPK resulted in more significant reduction of UVB-induced IL-6 synthesis than did the inhibition of ERK or JNK (Figure 3B). Thus, our results suggest the importance of p38 MAPK as a major component in the 12-HHT-induced signaling pathway. Since it has been reported that p38 MAPK could up-regulate NF-κB activity (Guha and Mackman, 2001; Shin et al., 2011), next, we examined the role of p38 MAPK in NF-κB activation for the synthesis of IL-6 in UV-irradiated HaCaT cells. As expected, p38 MAPK inhibition by SB203580 significantly diminished phosphorylation of IκBα, which suggests that p38 MAPK leads to NF-κB activation by inducing phosphorylation of IκBα (Supplemental Data Figure S2). In addition, we showed that the induction of NF-κB transcriptional activity by UVB irradiation is clearly suppressed by treatment with 12-HHT (Figure 3D). Taken together, our results demonstrate that 12-HHT inhibits UVB-induced IL-6 synthesis via the negative regulation of p38 MAPK and the subsequent suppression of NF-κB activity.
As a novel anti-inflammatory molecule, MKP-1, a dual-specificity (Ser/Thr or Thr/Thr) protein phosphatase, plays a crucial role in the regulation of inflammatory responses (Abraham and Clark, 2006; Lang et al., 2006; Quante et al., 2008). In particular, MKP-1 negatively regulates immune responses by directly deactivating p38 MAPK, which leads to the attenuation of pro-inflammatory cytokine synthesis (Wang and Richmond, 2001). Furthermore, anti-inflammatory agents, such as glucocorticoids, IL-10 and glutamine, inhibit the p38 MAPK and JNK cascade by up-regulating MKP-1 (Wang and Liu, 2007). In addition, recently, it was reported that 15-deoxy-Δ12,14-PGJ2, a COX-derived lipid molecule, suppresses monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) expression in IFN-γ-stimulated astrocytes through the induction of MKP-1 (Kim et al., 2005b; Lee et al., 2008). Thus, we hypothesized that MKP-1 is a critical mediator of the reduction of p38 MAPK-mediated IL-6 synthesis in 12-HHT-treated HaCaT cells. Indeed, we observed that 12-HHT upregulated MKP-1 expression in both non-irradiated and irradiated HaCaT cells (Figures 4A-4C). Like many other immediate-early genes, MKP-1 expression is regulated mainly at the transcriptional level and several transcription factors including activator protein-1 (AP-1), AP-2, trans-acting transcription factor-1 (SP-1), cAMP-responsive element sites (CRE) and neurofibromin 1 (CTF/NF-1) influence the MKP-1 gene transcription (Kwak et al., 1994; Casals-Casas et al., 2009). Thus, we speculate that 12-HHT somehow stimulates those transcription factors to up-regulate transcription of MKP-1. However, the detail signaling mechanism by which 12-HHT leads to MKP-1 transcriptional up-regulation needs to be further determined. Additionally, the silencing of MKP-1 by specific siRNA prevented the effects of 12-HHT, leading to the recovery of p38 MAPK/NF-κB signaling and subsequently, IL-6 synthesis in UVB-irradiated cells (Figures 4D and 4E and (Supplemental Data Figure S3). Based on our results, 12-HHT inhibits the p38 MAPK signaling pathway that leads to IL-6 synthesis by up-regulating MKP-1 expression.
12-HHT, a COX-derived arachidonic acid metabolite, is abundant in tissues and bodily fluids (Caprino et al., 1982; Punnonen et al., 1984; Peus et al., 1999), but little is known about its physiological functions. Recently, Iizuka et al. suggested that 12-HHT may mediate an anti-inflammatory response via its possible receptor, BLT2, in dextran sodium sulfate (DSS)-induced inflammatory colitis (Iizuka et al., 2010). In the present study, we discovered a potential anti-inflammatory role of 12-HHT, showing that IL-6 synthesis is reduced by 12-HHT-induced MKP-1 expression in UV-irradiated keratinocytes. To evaluate the mechanism of 12-HHT action further, we also examined the effect of BLT2 inhibition on MKP-1 expression in UVB-irradiated HaCaT cells. As shown in Supplemental Data Figures S4A and S4B, BLT2 inhibition by the specific antagonist, LY255283, or specific siRNA abolished the 12-HHT-induced expression of MKP-1 upon UVB irradiation, indicating that 12-HHT may act in a BLT2-dependent manner. BLT2 has a broad substrate specificity for several eicosanoids, including LTB4, 12(S)-HETE, 12(S)-HPETE, 15(S)-HETE and 12-HHT (Tager and Luster, 2003; Okuno et al., 2008; Cho et al., 2011). Furthermore, as LTB4 and 12(S)-HETE are increased by UVB irradiation (Ryu et al., 2010), LTB4 and 12(S)-HETE may have potential roles in skin inflammation. Thus, further studies will be needed to determine whether BLT2 ligands other than 12-HHT are involved in the skin inflammatory responses to UVB irradiation.
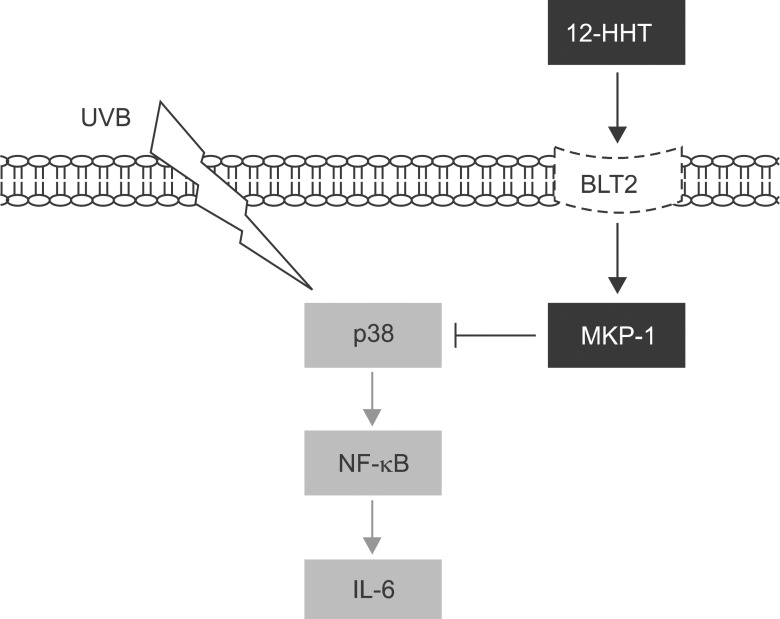
In conclusion, we showed that 12-HHT inhibits the UVB-stimulated p38 MAPK/NF-κB pathway by up-regulating MKP-1, which leads to the suppression of IL-6 synthesis (Figure 5). Considering the critical role of IL-6 in skin inflammatory responses, our results suggest that 12-HHT exerts anti-inflammatory effects as an inhibitor of IL-6 function. Furthermore, we believe that these findings will contribute to the development of effective therapies for skin inflammatory diseases.
Figure 5.
A model by which a 12-HHT-linked cascade inhibits IL-6 synthesis upon UVB irradiation. 12-HHT inhibits the p38 MAPK/NF-κB pathway by up-regulating MKP-1, leading to the reduction of IL-6 synthesis in UVB-irradiated HaCaT cells.
Methods
Cell culture and chemicals
The human skin immortalized keratinocyte cell line HaCaT was maintained in DMEM (GIBCO, Grand Island, NY) supplemented with 10% FBS (HyClone, Logan, UT) and antibiotic-antimycotic solution (GIBCO) at 37℃ in a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2. LY255283 and 12-HHT were purchased from the Cayman Chemical Company (Ann Arbor, MI). The polyclonal antibodies against JNK, ERK and p38 MAPK were obtained from Cell Signaling Technology (Danvers, MA), and the polyclonal antibodies against MKP-1 and α-tubulin were purchased from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Santa Cruz, CA). SB203580, PD98059, SP600125 and Bay11-7082 were all obtained from Calbiochem (San Diego, CA). All of the other chemicals were from standard sources and were of molecular biology grade or higher.
UVB irradiation
Cells were starved with serum-free DMEM for 12 h. Prior to the UVB irradiation, the medium was removed from the dishes, and the cells were washed with PBS, followed by the addition of 200 µl PBS into the dish to keep the cells wet. The cells were irradiated using a UV cross-linker (Upland, CA), with five 8 W tubes that emitted most of their energy within the UVB range, with an emission peak at 302 nm. The dose of UVB was exactly calculated using a UVB meter. Conditioned medium was added to the dish after the removal of the PBS.
Trypan blue exclusion assay
Cell viability was assessed by the trypan blue exclusion assay after UVB irradiation. The cells were trypsinized at each time point and counted using a hemocytometer under light microscopy after adding 0.14% (w/v) trypan blue solution. The cell viability is expressed as a percentage of the total cell population.
Semi-quantitative RT-PCR
Total cellular RNA was extracted using Easy Blue™ (Intron Company, Seongnam, Korea), and 2 µg of the extracted RNA was reverse-transcribed using M-MLV reverse transcriptase (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA). IL-6, MKP-1 and GAPDH transcripts were amplified using an RT-PCR PreMix Kit (Intron Company). For the semi-quantitative analysis of the transcripts, we first determined the optimal PCR conditions for the linear amplification of GAPDH. The primers used were as follows: 5'-CCAGTACCCCCAGGAG AAGA-3' (forward) and 5'-GCATCCATCTTTTTCAGCCA-3' (reverse) for human IL-6; 5'-CCTCAAAGGAGGATACGAA GC-3' (forward) and 5'-GCTCTTGTACTGGTAGTGACC-3' (reverse) for human MKP-1; and 5'-CTGCACCACCAACT GCTTAGC-3' (forward) and 5'-CTTCACCACCTTCTTGAT GTC-3' (reverse) for GAPDH. The PCR products were electrophoresed on an agarose gel and visualized using ethidium bromide staining.
Western blotting
Protein samples were heated at 95℃ for 3 min and then subjected to SDS-PAGE on acrylamide gels, followed by transfer to PVDF membranes using a wet transfer unit (NOVEX; 1 h at 100 V). The membranes were then blocked for 1 h with TBS containing 0.05% (v/v) Tween 20 plus 5% (w/v) nonfat dry milk and incubated for 2 h with the appropriate primary antibodies in TBS containing 0.05% (v/v) Tween 20 plus 3% (w/v) BSA, followed by incubation for 1 h with HRP-conjugated secondary antibodies. The bands were developed using an ECL kit (Amersham Biosciences, Piscataway, NJ).
Quantification of IL-6 using ELISA
HaCaT cells were seeded on 60 mm dishes and grown to 90% confluence. The cells were starved with serum-free DMEM for 12 h and then irradiated with UVB (5 mJ/cm2). At the indicated times, 1 ml of the medium was centrifuged for 15 min at 4℃. The supernatants containing IL-6 were freeze-dried, and the level of IL-6 was quantified using an IL-6 ELISA kit (Koma Biotech, Seoul, Korea) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
RNA interference for MKP-1 and BLT2
The MKP-1-specific siRNA (5'-CCAAUUGUCCCAACCAU UU-3') was purchased from Dharmacon Research (Lafayette, CO), and the BLT2-specific siRNA (5'-CCACG CAGTCAACCTTCTG-3') and control (scrambled) siRNA were purchased from Bioneer (Daejeon, Korea) (Hennig et al., 2008). For the RNA interference experiments, cells were plated at a density of 4 × 105 cells per 60 mm dish. After 24 h, the cells were transfected with the above oligonucleotides using the oligofectamine reagent (Invitrogen) in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions. After 24 h, the level of each mRNA was analyzed by RT-PCR to evaluate the degree of knock-down.
Luciferase reporter gene assay
HaCaT cells were transfected with 2.5 µg of luciferase reporter construct using the Lipofectamine transfection reagent (Invitrogen) in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions. The MKP-1-luciferase reporter plasmid was kindly provided by Dr. Yusen Liu (Ohio State University, OH). To monitor the variations in the cell number and transfection efficiency, HaCaT cells were also transfected with 1 µg of pSV40-β-galactosidase, a eukaryotic expression vector containing the Escherichia coli β-galactosidase (lacZ) structural gene under the control of the SV40 promoter. At 24 h after transfection, the cells were starved with serum-free DMEM prior to UVB irradiation. The luciferase activity was measured using a Junior luminometer (Berthold, Germany) at the indicated times after UVB irradiation (5 mJ/cm2). The relative fold increase in the luciferase activity was calculated as previously described (Woo et al., 2005).
Data analysis and statistics
The results are presented as the means ± SD. The analyses were performed using the Student's t test. Values of P < 0.05 were considered to be significant.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the generosity of Dr. Yusen Liu (The Ohio State University College of Medicine) for providing us with the pGL3-MKP-1-luc reporter plasmid. This research was supported by a General Researcher Support Project (2011-0004241) and the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program of the National Research (NRF) funded by the Korean government (MEST) (2011-0027753). In addition, this research was supported by a grant from the Korea Healthcare Technology R&D Project, Ministry of Health & Welfare, South Korea (A101032).
Abbreviations
- BLT
leukotriene B4 receptor
- HEPTE
hydroperoxyeicosatetraenoic acid
- HETE
hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid
- HHT
hydroxyheptadeca-5Z,8E,10E-trienoic acid
- LTB4
leukotriene B4
- MKP-1
MAPK phosphatase-1
Supplemental data
Supplemental data include four figures and can be found with this article online at http://e-emm.or.kr/article/article_files/SP-44-6-03.pdf.
References
- 1.Abraham SM, Clark AR. Dual-specificity phosphatase 1: a critical regulator of innate immune responses. Biochem Soc Trans. 2006;34:1018–1023. doi: 10.1042/BST0341018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bode AM, Dong Z. Mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in UV-induced signal transduction. Sci STKE. 2003;2003:RE2. doi: 10.1126/stke.2003.167.re2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Caprino L, Dolci N, Togna G, Villa P, Bucci R, Carunchio V. Effects of cadmium on platelet thromboxane and vascular prostacyclin production. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1982;65:185–188. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(82)90378-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Casals-Casas C, Alvarez E, Serra M, de la Torre C, Farrera C, Sánchez-Tilló E, Caelles C, Lloberas J, Celada A. CREB and AP-1 activation regulates MKP-1 induction by LPS or M-CSF and their kinetics correlate with macrophage activation versus proliferation. Eur J Immunol. 2009;39:1902–1913. doi: 10.1002/eji.200839037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Chen W, Bowden GT. Activation of p38 MAP kinase and ERK are required for ultraviolet-B induced c-fos gene expression in human keratinocytes. Oncogene. 1999;18:7469–7476. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Cho KJ, Seo JM, Kim JH. Bioactive lipoxygenase metabolites stimulation of NADPH oxidases and reactive oxygen species. Mol Cells. 2011;32:1–5. doi: 10.1007/s10059-011-1021-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Chung JH, Youn SH, Koh WS, Eun HC, Cho KH, Park KC, Youn JI. Ultraviolet B irradiation-enhanced interleukin (IL)-6 production and mRNA expression are mediated by IL-1 alpha in cultured human keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 1996;106:715–720. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12345608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Clydesdale GJ, Dandie GW, Muller HK. Ultraviolet light induced injury: immunological and inflammatory effects. Immunol Cell Biol. 2001;79:547–568. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1711.2001.01047.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Gebhardt C, Averbeck M, Viertel A, Kauer F, Saalbach A, Anderegg U, Simon JC. Ultraviolet-B irradiation enhances melanoma cell motility via induction of autocrine interleukin 8 secretion. Exp Dermatol. 2007;16:636–643. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0625.2007.00572.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Grone A. Keratinocytes and cytokines. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2002;88:1–12. doi: 10.1016/s0165-2427(02)00136-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Grossman RM, Krueger J, Yourish D, Granelli-Piperno A, Murphy DP, May LT, Kupper TS, Sehgal PB, Gottlieb AB. Interleukin 6 is expressed in high levels in psoriatic skin and stimulates proliferation of cultured human keratinocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1989;86:6367–6371. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Guha M, Mackman N. LPS induction of gene expression in human monocytes. Cell Signal. 2001;13:85–94. doi: 10.1016/s0898-6568(00)00149-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hamberg M, Svensson J, Samuelsson B. Prostaglandin endoperoxides. A new concept concerning the mode of action and release of prostaglandins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1974;71:3824–3828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.3824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hennig R, Osman T, Esposito I, Giese N, Rao SM, Ding XZ, Tong WG, Buchler MW, Yokomizo T, Friess H, Adrian TE. BLT2 is expressed in PanINs, IPMNs, pancreatic cancer and stimulates tumour cell proliferation. Br J Cancer. 2008;99:1064–1073. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6604655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Iizuka Y, Okuno T, Saeki K, Uozaki H, Okada S, Misaka T, Sato T, Toh H, Fukayama M, Takeda N, Kita Y, Shimizu T, Nakamura M, Yokomizo T. Protective role of the leukotriene B4 receptor BLT2 in murine inflammatory colitis. FASEB J. 2010;24:4678–4690. doi: 10.1096/fj.10-165050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.John H, Cammann K, Schlegel W. Development and review of radioimmunoassay of 12-S-hydroxyheptadecatrienoic acid. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 1998;56:53–76. doi: 10.1016/s0090-6980(98)00043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Katiyar SK, Meeran SM. Obesity increases the risk of UV radiation-induced oxidative stress and activation of MAPK and NF-kappaB signaling. Free Radic Biol Med. 2007;42:299–310. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2006.10.049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Keyse SM. An emerging family of dual specificity MAP kinase phosphatases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1995;1265:152–160. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(94)00211-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kim AL, Labasi JM, Zhu Y, Tang X, McClure K, Gabel CA, Athar M, Bickers DR. Role of p38 MAPK in UVB-induced inflammatory responses in the skin of SKH-1 hairless mice. J Invest Dermatol. 2005a;124:1318–1325. doi: 10.1111/j.0022-202X.2005.23747.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kim C, Ryu HC, Kim JH. Low-dose UVB irradiation stimulates matrix metalloproteinase-1 expression via a BLT2-linked pathway in HaCaT cells. Exp Mol Med. 2010;42:833–841. doi: 10.3858/emm.2010.42.12.086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kim HJ, Rho YH, Choi SJ, Lee YH, Cheon H, Um JW, Sohn J, Song GG, Ji JD. 15-Deoxy-delta12,14-PGJ2 inhibits IL-6-induced Stat3 phosphorylation in lymphocytes. Exp Mol Med. 2005b;37:179–185. doi: 10.1038/emm.2005.24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kock A, Schwarz T, Kirnbauer R, Urbanski A, Perry P, Ansel JC, Luger TA. Human keratinocytes are a source for tumor necrosis factor alpha: evidence for synthesis and release upon stimulation with endotoxin or ultraviolet light. J Exp Med. 1990;172:1609–1614. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.6.1609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kwak SP, Hakes DJ, Martell KJ, Dixon JE. Isolation and characterization of a human dual specificity protein-tyrosine phosphatase gene. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:3596–3604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Lang R, Hammer M, Mages J. DUSP meet immunology: dual specificity MAPK phosphatases in control of the inflammatory response. J Immunol. 2006;177:7497–7504. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.177.11.7497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Lederle W, Depner S, Schnur S, Obermueller E, Catone N, Just A, Fusenig NE, Mueller MM. IL-6 promotes malignant growth of skin SCCs by regulating a network of autocrine and paracrine cytokines. Int J Cancer. 2011;128:2803–2814. doi: 10.1002/ijc.25621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Lee JH, Woo JH, Woo SU, Kim KS, Park SM, Joe EH, Jou I. The 15-deoxy-delta12,14-prostaglandin J2 suppresses monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 expression in IFN-gamma-stimulated astrocytes through induction of MAPK phosphatase-1. J Immunol. 2008;181:8642–8649. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.12.8642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Li S, Zhu F, Zykova T, Kim MO, Cho YY, Bode AM, Peng C, Ma W, Carper A, Langfald A, Dong Z. T-LAK cell-originated protein kinase (TOPK) phosphorylation of MKP1 protein prevents solar ultraviolet light-induced inflammation through inhibition of the p38 protein signaling pathway. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:29601–29609. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.225813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Matsumura Y, Ananthaswamy HN. Toxic effects of ultraviolet radiation on the skin. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2004;195:298–308. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2003.08.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Nishimoto N, Kishimoto T. Inhibition of IL-6 for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2004;4:386–391. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2004.03.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Nishimura N, Tohyama C, Satoh M, Nishimura H, Reeve VE. Defective immune response and severe skin damage following UVB irradiation in interleukin-6-deficient mice. Immunology. 1999;97:77–83. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.1999.00733.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Okuno T, Iizuka Y, Okazaki H, Yokomizo T, Taguchi R, Shimizu T. 12(S)-Hydroxyheptadeca-5Z,8E,10E-trienoic acid is a natural ligand for leukotriene B4 receptor 2. J Exp Med. 2008;205:759–766. doi: 10.1084/jem.20072329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Peus D, Vasa RA, Beyerle A, Meves A, Krautmacher C, Pittelkow MR. UVB activates ERK1/2 and p38 signaling pathways via reactive oxygen species in cultured keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 1999;112:751–756. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1747.1999.00584.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Pfundt R, van Vlijmen-Willems I, Bergers M, Wingens M, Cloin W, Schalkwijk J. In situ demonstration of phosphorylated c-jun and p38 MAP kinase in epidermal keratinocytes following ultraviolet B irradiation of human skin. J Pathol. 2001;193:248–255. doi: 10.1002/1096-9896(2000)9999:9999<::AID-PATH780>3.0.CO;2-Y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Punnonen K, Uotila P, Mantyla E. The effects of aspirin and OKY-1581 on the metabolism of exogenous arachidonic acid in rat alveolar macrophages. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1984;44:367–374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Quante T, Ng YC, Ramsay EE, Henness S, Allen JC, Parmentier J, Ge Q, Ammit AJ. Corticosteroids reduce IL-6 in ASM cells via up-regulation of MKP-1. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2008;39:208–217. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2007-0014OC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Ryu HC, Kim C, Kim JY, Chung JH, Kim JH. UVB radiation induces apoptosis in keratinocytes by activating a pathway linked to "BLT2-reactive oxygen species". J Invest Dermatol. 2010;130:1095–1106. doi: 10.1038/jid.2009.436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Shin JS, Noh YS, Lee YS, Cho YW, Baek NI, Choi MS, Jeong TS, Kang E, Chung HG, Lee KT. Arvelexin from Brassica rapa suppresses NF-κB-regulated pro-inflammatory gene expression by inhibiting activation of IκB kinase. Br J Pharmacol. 2011;164:145–158. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01351.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Shinoda S, Kameyoshi Y, Hide M, Morita E, Yamamoto S. Histamine enhances UVB-induced IL-6 production by human keratinocytes. Arch Dermatol Res. 1998;290:429–434. doi: 10.1007/s004030050331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Simon MM, Aragane Y, Schwarz A, Luger TA, Schwarz T. UVB light induces nuclear factor kappa B (NF kappa B) activity independently from chromosomal DNA damage in cell-free cytosolic extracts. J Invest Dermatol. 1994;102:422–427. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12372194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Tager AM, Luster AD. BLT1 and BLT2: the leukotriene B(4) receptors. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2003;69:123–134. doi: 10.1016/s0952-3278(03)00073-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Wan YS, Wang ZQ, Voorhees J, Fisher G. EGF receptor crosstalks with cytokine receptors leading to the activation of c-Jun kinase in response to UV irradiation in human keratinocytes. Cell Signal. 2001;13:139–144. doi: 10.1016/s0898-6568(00)00146-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Wang D, Richmond A. Nuclear factor-kappa B activation by the CXC chemokine melanoma growth-stimulatory activity/growth-regulated protein involves the MEKK1/p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:3650–3659. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M006115200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Wang X, Liu Y. Regulation of innate immune response by MAP kinase phosphatase-1. Cell Signal. 2007;19:1372–1382. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2007.03.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Wlaschek M, Heinen G, Poswig A, Schwarz A, Krieg T, Scharffetter-Kochanek K. UVA-induced autocrine stimulation of fibroblast-derived collagenase/MMP-1 by interrelated loops of interleukin-1 and interleukin-6. Photochem Photobiol. 1994;59:550–556. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1994.tb02982.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Woo CH, Lim JH, Kim JH. VCAM-1 upregulation via PKCdelta-p38 kinase-linked cascade mediates the TNFalpha-induced leukocyte adhesion and emigration in the lung airway epithelium. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2005;288:L307–L316. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00105.2004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplemental data include four figures and can be found with this article online at http://e-emm.or.kr/article/article_files/SP-44-6-03.pdf.