Abstract
We describe here a novel but simple nuclear transcription system in which nuclei make RNA in an isotonic buffer for a long time and respond to a cloned external factor by accurately initiating new transcription.
Full text
PDF

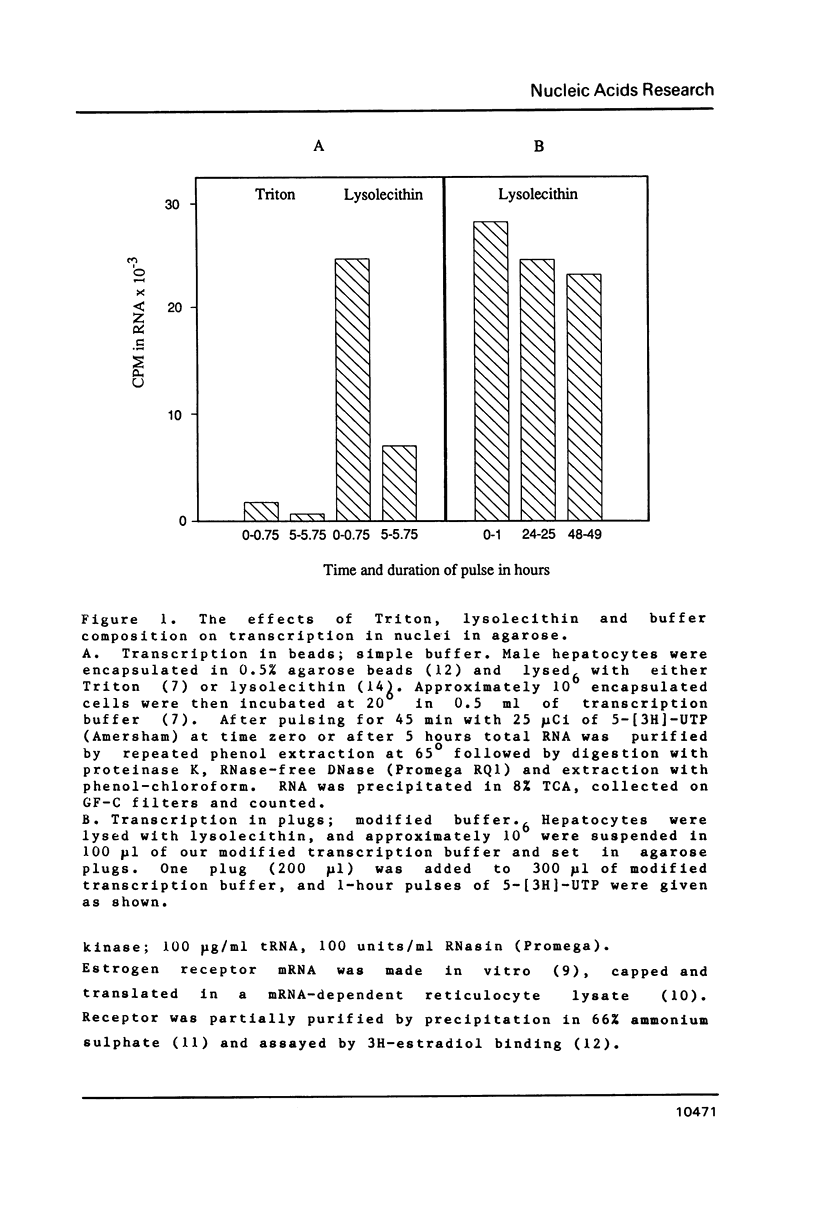


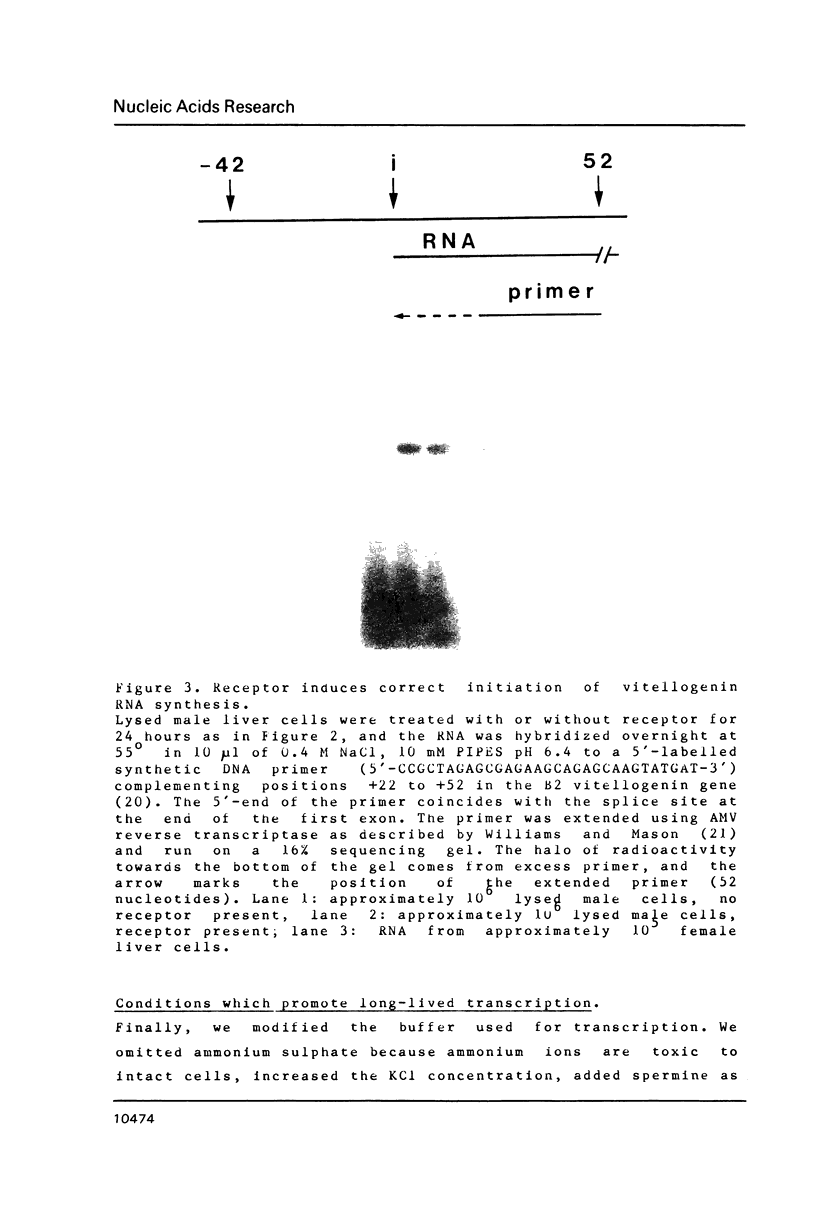


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cook P. R. A general method for preparing intact nuclear DNA. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1837–1842. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02056.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Robertis E. M., Gurdon J. B. Gene activation in somatic nuclei after injection into amphibian oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2470–2474. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germond J. E., Walker P., ten Heggeler B., Brown-Luedi M., de Bony E., Wahli W. Evolution of vitellogenin genes: comparative analysis of the nucleotide sequences downstream of the transcription initiation site of four Xenopus laevis and one chicken gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 26;12(22):8595–8609. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.22.8595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurdon J. B. Injected nuclei in frog oocytes: fate, enlargement, and chromatin dispersal. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1976 Dec;36(3):523–540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson D. A., Cook P. R. A general method for preparing chromatin containing intact DNA. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):913–918. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03718.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jost J. P., Moncharmont B., Jiricny J., Saluz H., Hertner T. In vitro secondary activation (memory effect) of avian vitellogenin II gene in isolated liver nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(1):43–47. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein-Hitpass L., Schorpp M., Wagner U., Ryffel G. U. An estrogen-responsive element derived from the 5' flanking region of the Xenopus vitellogenin A2 gene functions in transfected human cells. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1053–1061. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90705-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowland J., Theulaz I., Wright C. V., Wahli W. Injection of partially purified estrogen receptor protein from Xenopus liver nuclei into oocytes activates the silent vitellogenin locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5777–5781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar V., Green S., Staub A., Chambon P. Localisation of the oestradiol-binding and putative DNA-binding domains of the human oestrogen receptor. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2231–2236. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04489.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May F. E., Weber R., Westley B. R. Isolation and characterisation of the Xenopus laevis albumin genes: loss of 74K albumin gene sequences by library amplification. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2791–2807. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson K., Scheirer W., Merten O. W., Ostberg L., Liehl E., Katinger H. W., Mosbach K. Entrapment of animal cells for production of monoclonal antibodies and other biomolecules. Nature. 1983 Apr 14;302(5909):629–630. doi: 10.1038/302629a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipp B. W., Morgan E. A., Shapiro D. J. Quantitation of estrogen effect on Xenopus laevis albumin mRNA levels by hybridization to cloned albumin cDNA. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8496–8501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryffel G. U., Muellener D. B., Gerber-Huber S., Wyler T., Wahli W. Scattering of repetitive DNA sequences in the albumin and vitellogenin gene loci of Xenopus laevis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 25;11(22):7701–7716. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.22.7701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searle P. F., Tata J. R. Vitellogenin gene expression in male Xenopus hepatocytes during primary and secondary stimulation with estrogen in cell cultures. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):741–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90437-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiler-Tuyns A., Walker P., Martinez E., Mérillat A. M., Givel F., Wahli W. Identification of estrogen-responsive DNA sequences by transient expression experiments in a human breast cancer cell line. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 25;14(22):8755–8770. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.22.8755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tata J. R., Baker B. S. Specific switching on of silent egg protein genes in vitro by an S-100 fraction in isolated nuclei from male Xenopus. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3253–3258. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04074.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker P., Germond J. E., Brown-Luedi M., Givel F., Wahli W. Sequence homologies in the region preceding the transcription initiation site of the liver estrogen-responsive vitellogenin and apo-VLDLII genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 26;12(22):8611–8626. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.22.8611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westley B., Knowland J. An estrogen receptor from Xenopus laevis liver possibly connected with vitellogenin synthesis. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):367–374. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90005-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright C. V., Wright S. C., Knowland J. Partial purification of estradiol receptor from Xenopus laevis liver and levels of receptor in relation to estradiol concentration. EMBO J. 1983;2(6):973–977. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01530.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]