Abstract
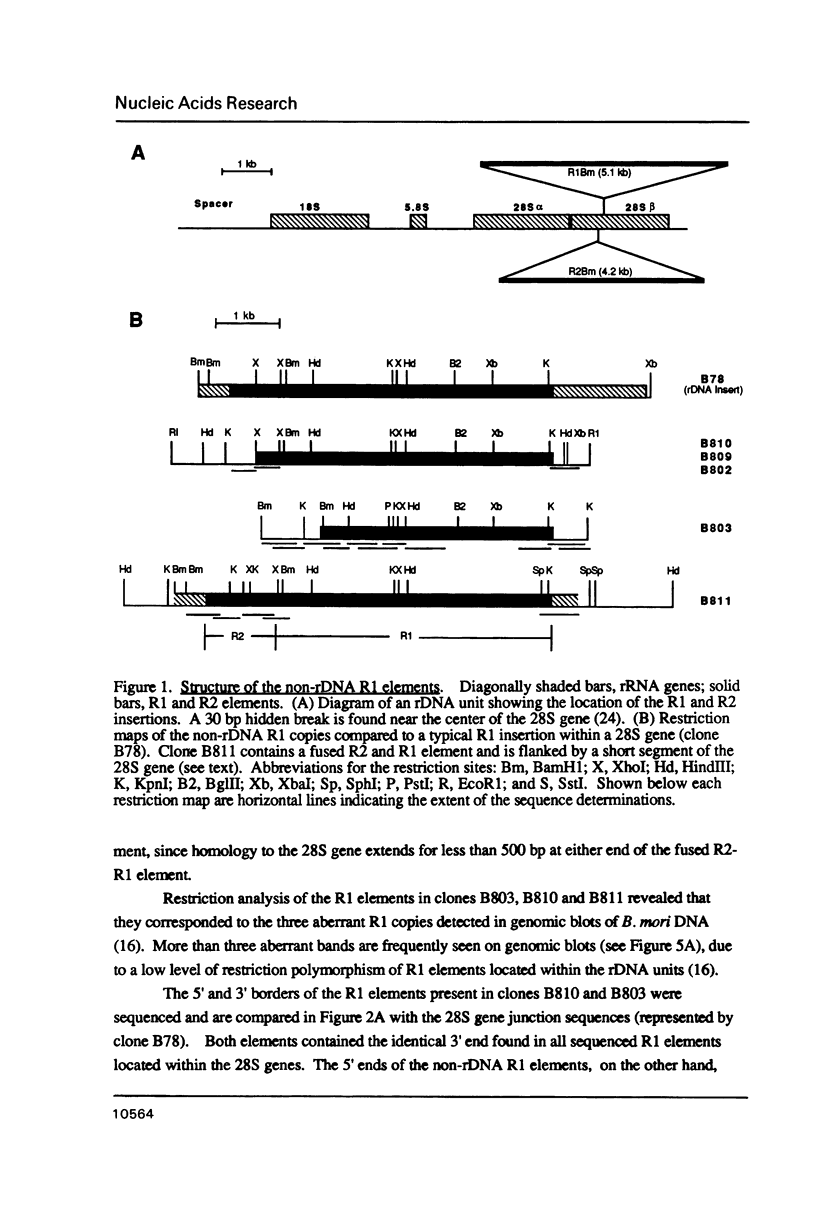
A fraction of the ribosomal 28S genes in some insects are interrupted at specific sites by insertion elements R1 and R2 (also called Type I and II). These elements contain long open-reading frames with homology to reverse transcriptase. We have identified in the silkmoth, Bombyx mori, copies of these elements which have inserted into sites outside the ribosomal DNA (rDNA) units. The 3' ends of all "non-rDNA" elements are identical to the elements within the 28S genes; however their 5' ends are often truncated. Each non-rDNA copy has inserted into sequences that exhibit similarity to their target sites in the 28S gene. We also demonstrate by genomic blot analysis of different strains of B. mori that insertions of R1 and R2 outside the rDNA units have been infrequent, while considerable turnover of elements has occurred within the rDNA locus. One race of B. mori has lost all copies of R1 from its rDNA units, while retaining normal levels of R2. The level of both R1 and R2 have significantly increased in a tissue culture line. These findings add considerable support to the model that R1 and R2 are retrotransposable elements that utilize sequence specific endonucleases in their integration into the genome.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. S., Eickbush T. H., Herrera R. J., Lizardi P. M. A highly reiterated family of transcribed oligo(A)-terminated, interspersed DNA elements in the genome of Bombyx mori. J Mol Biol. 1986 Feb 20;187(4):465–478. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90327-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Back E., Van Meir E., Müller F., Schaller D., Neuhaus H., Aeby P., Tobler H. Intervening sequences in the ribosomal RNA genes of Ascaris lumbricoides: DNA sequences at junctions and genomic organization. EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2523–2529. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02167.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browne M. J., Read C. A., Roiha H., Glover D. M. Site specific insertion of a type I rDNA element into a unique sequence in the Drosophila melanogaster genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 11;12(23):9111–9122. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.23.9111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke W. D., Calalang C. C., Eickbush T. H. The site-specific ribosomal insertion element type II of Bombyx mori (R2Bm) contains the coding sequence for a reverse transcriptase-like enzyme. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2221–2230. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawid I. B., Rebbert M. L. Nucleotide sequences at the boundaries between gene and insertion regions in the rDNA of Drosophilia melanogaster. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 10;9(19):5011–5020. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.19.5011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawid I. B., Wellauer P. K., Long E. O. Ribosomal DNA in Drosophila melanogaster. I. Isolation and characterization of cloned fragments. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 25;126(4):749–768. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90018-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Nocera P. P., Casari G. Related polypeptides are encoded by Drosophila F elements, I factors, and mammalian L1 sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5843–5847. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Nocera P. P. Close relationship between non-viral retroposons in Drosophila melanogaster. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 11;16(9):4041–4052. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.9.4041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Nocera P. P., Graziani F., Lavorgna G. Genomic and structural organization of Drosophila melanogaster G elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 24;14(2):675–691. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.2.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle W. F., Sapienza C. Selfish genes, the phenotype paradigm and genome evolution. Nature. 1980 Apr 17;284(5757):601–603. doi: 10.1038/284601a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dover G., Coen E. Springcleaning ribosomal DNA: a model for multigene evolution? Nature. 1981 Apr 30;290(5809):731–732. doi: 10.1038/290731a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eickbush T. H., Kafatos F. C. A walk in the chorion locus of Bombyx mori. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):633–643. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90179-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eickbush T. H., Robins B. Bombyx mori 28S ribosomal genes contain insertion elements similar to the Type I and II elements of Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2281–2285. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03927.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fawcett D. H., Lister C. K., Kellett E., Finnegan D. J. Transposable elements controlling I-R hybrid dysgenesis in D. melanogaster are similar to mammalian LINEs. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):1007–1015. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90815-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finnegan D. J., Fawcett D. H. Transposable elements in Drosophila melanogaster. Oxf Surv Eukaryot Genes. 1986;3:1–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freund R., Meselson M. Long terminal repeat nucleotide sequence and specific insertion of the gypsy transposon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4462–4464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara H., Ishikawa H. Molecular mechanism of introduction of the hidden break into the 28S rRNA of insects: implication based on structural studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 26;14(16):6393–6401. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.16.6393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara H., Ogura T., Takada N., Miyajima N., Ishikawa H., Maekawa H. Introns and their flanking sequences of Bombyx mori rDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 11;12(17):6861–6869. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.17.6861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith M. R., Clermont-Rattner E. Organization of the Chorion Genes of BOMBYX MORI, a Multigene Family. II. Partial Localization of Three Gene Clusters. Genetics. 1979 Aug;92(4):1173–1185. doi: 10.1093/genetics/92.4.1173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grace T. D. Establishment of a line of cells from the silkworm Bombyx mori. Nature. 1967 Nov 11;216(5115):613–613. doi: 10.1038/216613a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iatrou K., Tsitilou S. G., Goldsmith M. R., Kafatos F. C. Molecular analysis of the GrB mutation in Bombyx mori through the use of chorion cDNA library. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):659–669. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90312-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikenaga H., Saigo K. Insertion of a movable genetic element, 297, into the T-A-T-A box for the H3 histone gene in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4143–4147. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Yuki S., Saigo K. Sequence-specific insertion of the Drosophila transposable genetic element 17.6. 1984 Jul 26-Aug 1Nature. 310(5975):332–333. doi: 10.1038/310332a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamrich M., Miller O. L., Jr The rare transcripts of interrupted rRNA genes in Drosophila melanogaster are processed or degraded during synthesis. EMBO J. 1984 Jul;3(7):1541–1545. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02008.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd S. J., Glover D. M. A DNA segment from D. melanogaster which contains five tandemly repeating units homologous to the major rDNA insertion. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90392-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmel B. E., ole-MoiYoi O. K., Young J. R. Ingi, a 5.2-kb dispersed sequence element from Trypanosoma brucei that carries half of a smaller mobile element at either end and has homology with mammalian LINEs. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1465–1475. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruger K., Grabowski P. J., Zaug A. J., Sands J., Gottschling D. E., Cech T. R. Self-splicing RNA: autoexcision and autocyclization of the ribosomal RNA intervening sequence of Tetrahymena. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):147–157. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90414-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecanidou R., Eickbush T. H., Kafatos F. C. Ribosomal DNA genes of Bombyx mori: a minor fraction of the repeating units contain insertions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 11;12(11):4703–4713. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.11.4703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb D. D., Padgett R. W., Hardies S. C., Shehee W. R., Comer M. B., Edgell M. H., Hutchison C. A., 3rd The sequence of a large L1Md element reveals a tandemly repeated 5' end and several features found in retrotransposons. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):168–182. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long E. O., Dawid I. B. Expression of ribosomal DNA insertions in Drosophila melanogaster. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1185–1196. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90231-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F., Dujon B. Conservation of RNA secondary structures in two intron families including mitochondrial-, chloroplast- and nuclear-encoded members. EMBO J. 1983;2(1):33–38. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01376.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuhaus H., Müller F., Etter A., Tobler H. Type I-like intervening sequences are found in the rDNA of the nematode Ascaris lumbricoides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 12;15(19):7689–7707. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.19.7689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orgel L. E., Crick F. H. Selfish DNA: the ultimate parasite. Nature. 1980 Apr 17;284(5757):604–607. doi: 10.1038/284604a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock W. J., Appels R., Endow S., Glover D. Chromosomal distribution of the major insert in Drosophila melanogaster 28S rRNA genes. Genet Res. 1981 Apr;37(2):209–214. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300020176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rae P. M., Kohorn B. D., Wade R. P. The 10 kb Drosophila virilis 28S rDNA intervening sequence is flanked by a direct repeat of 14 base pairs of coding sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Aug 25;8(16):3491–3504. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.16.3491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roiha H., Glover D. M. Duplicated rDNA sequences of variable lengths flanking the short type I insertions in the rDNA of Drosophila melanogaster. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 11;9(21):5521–5532. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.21.5521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roiha H., Miller J. R., Woods L. C., Glover D. M. Arrangements and rearrangements of sequences flanking the two types of rDNA insertion in D. melanogaster. Nature. 1981 Apr 30;290(5809):749–753. doi: 10.1038/290749a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roiha H., Read C. A., Browne M. J., Glover D. M. Widely differing degrees of sequence conservation of the two types of rDNA insertion within the melanogaster species sub-group of Drosophila. EMBO J. 1983;2(5):721–726. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01491.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz-Sommer Z., Leclercq L., Göbel E., Saedler H. Cin4, an insert altering the structure of the A1 gene in Zea mays, exhibits properties of nonviral retrotransposons. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):3873–3880. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02727.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith V. L., Beckingham K. The intron boundaries and flanking rRNA coding sequences of Calliphora erythrocephala rDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Feb 10;12(3):1707–1724. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.3.1707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellauer P. K., Dawid I. B., Tartof K. D. X and Y chromosomal ribosomal DNA of Drosophila: comparison of spacers and insertions. Cell. 1978 Jun;14(2):269–278. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90113-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wild M. A., Sommer R. Sequence of a ribosomal RNA gene intron from Tetrahymena. Nature. 1980 Feb 14;283(5748):693–694. doi: 10.1038/283693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong Y., Eickbush T. H. The site-specific ribosomal DNA insertion element R1Bm belongs to a class of non-long-terminal-repeat retrotransposons. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):114–123. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]