Abstract
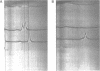
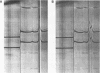
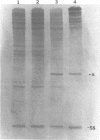
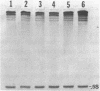
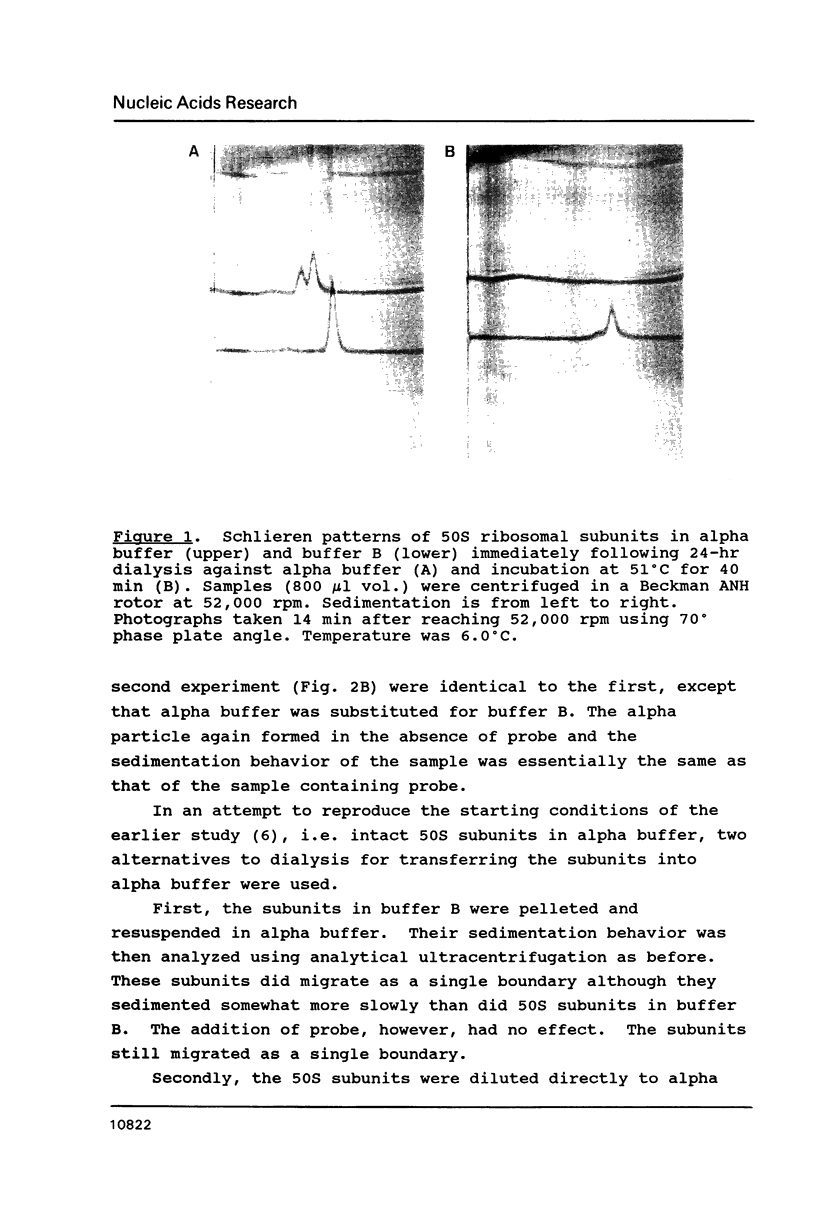
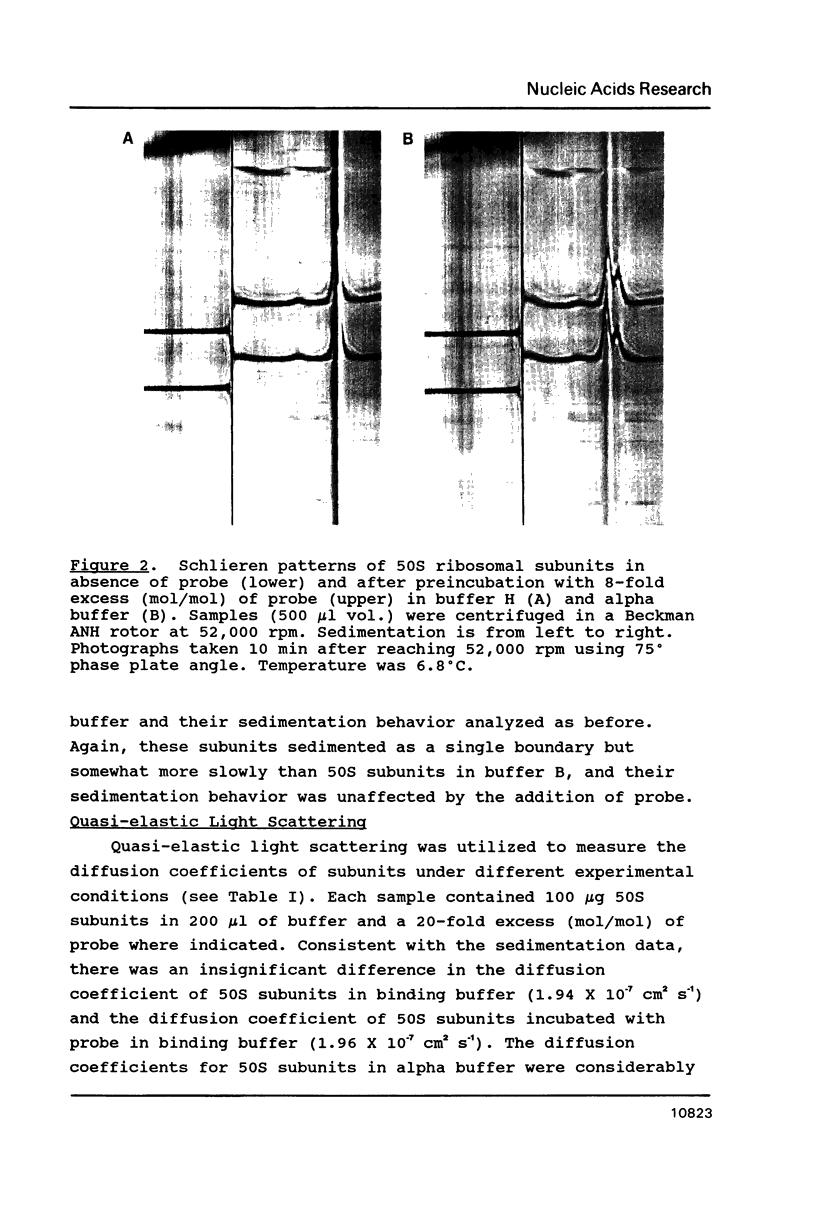
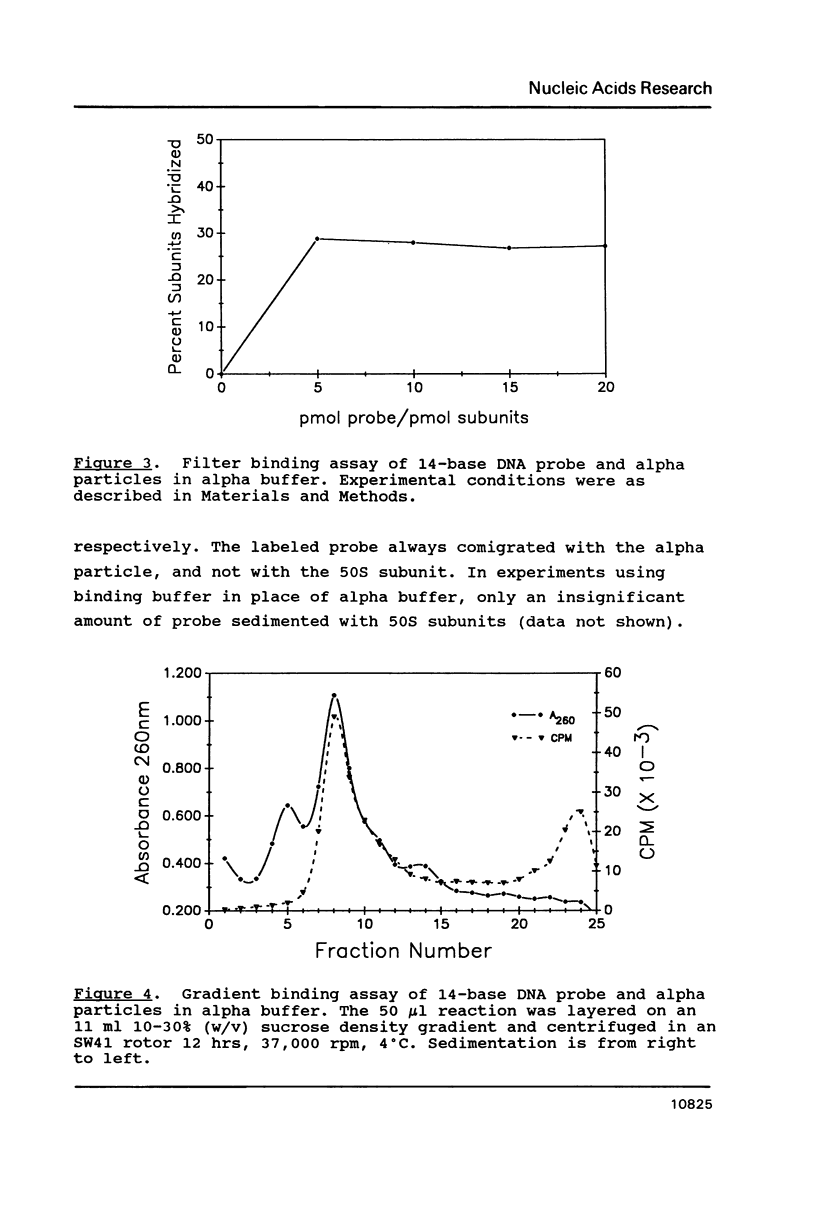
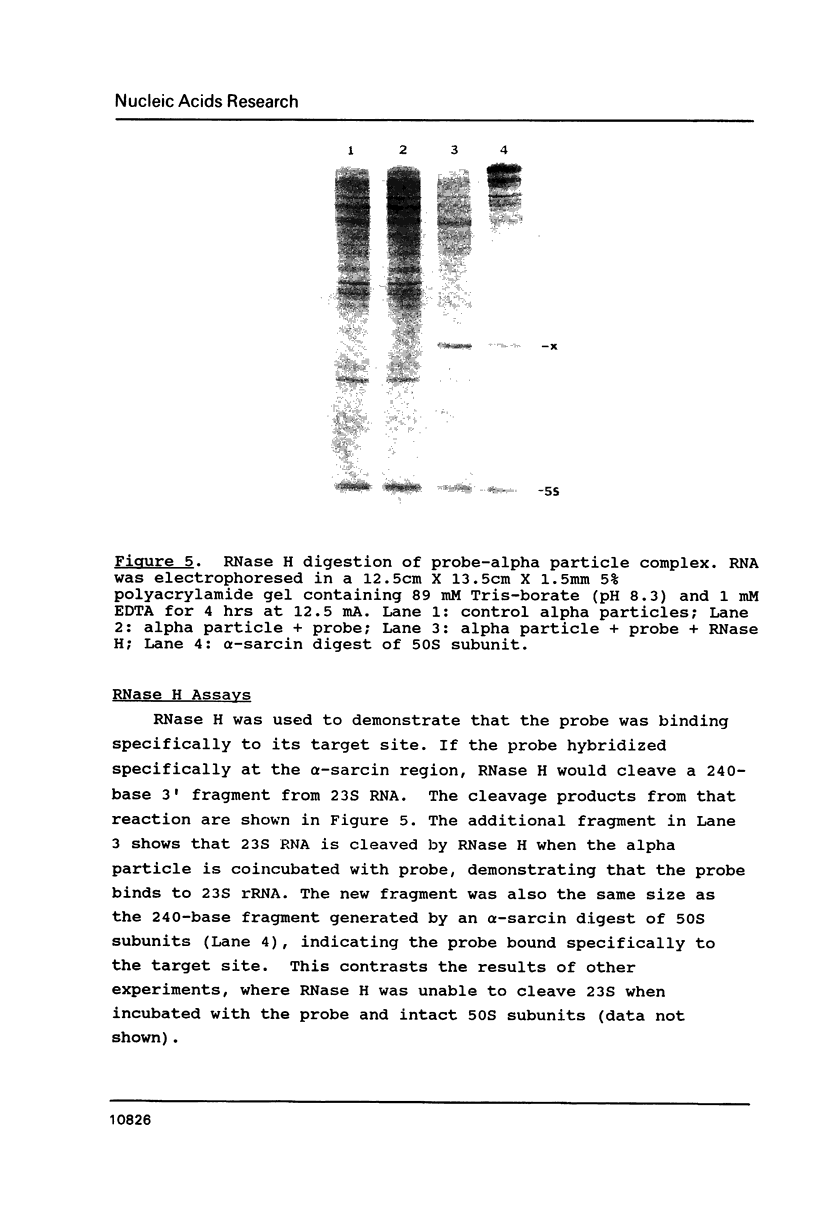
The cause of 50S ribosomal subunit collapse reportedly triggered by hybridization of a 14-base cDNA probe to the alpha-sarcin region of 23S rRNA was investigated by physical measurement of probe-subunit complexes in varying buffer conditions. The results reported here show that this probe was unable to hybridize to its target site in the intact 50S subunit and the physical characteristics of 50S subunits remained unchanged in its presence. Subunit collapse was induced in buffer containing 20mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 600 mM NH4Cl, 1 mM MgCl2, 1 mM DTT, and 0.1 mM EDTA in the absence of probe. The probe bound specifically to its target site in the collapsed particle, but did not promote further unfolding. The results demonstrate that a DNA probe bound to the alpha-sarcin region cannot cause the 50S subunit to unfold or cause 23S rRNA to degrade. We suggest that the previously reported collapse was most probably the result of the ionic conditions used.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Backendorf C., Ravensbergen C. J., Van der Plas J., van Boom J. H., Veeneman G., Van Duin J. Basepairing potential of the 3' terminus of 16S RNA: dependence on the functional state of the 30S subunit and the presence of protein S21. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Mar 25;9(6):1425–1444. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.6.1425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair D. P., Heilmann L., Hill W. E. Unfolded 30 S ribosomal subunits. Biophys Chem. 1981 Sep;14(1):81–89. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(81)87008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cammack K. A., Wade H. E. The sedimentation behaviour of ribonuclease-active and -inactive ribosomes from bacteria. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):671–680. doi: 10.1042/bj0960671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaconas G., van de Sande J. H. 5'-32P labeling of RNA and DNA restriction fragments. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65012-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H. Site specific enzymatic cleavage of RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Sep 11;7(1):179–192. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.1.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Huber P. W., Wool I. G. The ribonuclease activity of the cytotoxin alpha-sarcin. The characteristics of the enzymatic activity of alpha-sarcin with ribosomes and ribonucleic acids as substrates. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2662–2667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Wool I. G. The site of action of alpha-sarcin on eukaryotic ribosomes. The sequence at the alpha-sarcin cleavage site in 28 S ribosomal ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):9054–9060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Puentes C., Vazquez D. Effects of some proteins that inactivate the eukaryotic ribosome. FEBS Lett. 1977;78(1):143–146. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80292-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gesteland R. F. Unfolding of Escherichia coli ribosomes by removal of magnesium. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jul;18(2):356–371. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80253-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill W. E., Anderegg J. W., Van Holde K. E. Effects of solvent environment and mode of preparation on the physical properties of ribosomes fron Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):107–121. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90048-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill W. E., Rossetti G. P., Van Holde K. E. Physical studies of ribosomes from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 Sep 14;44(2):263–277. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90174-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobden A. N., Cundliffe E. The mode of action of alpha sarcin and a novel assay of the puromycin reaction. Biochem J. 1978 Jan 15;170(1):57–61. doi: 10.1042/bj1700057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mankin A. S., Skripkin E. A., Chichkova N. V., Kopylov A. M., Bogdanov A. A. An enzymatic approach for localization of oligodeoxyribonucleotide binding sites on RNA. Application to studying rRNA topography. FEBS Lett. 1981 Aug 31;131(2):253–256. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80378-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miall S. H., Walker I. O. Structural studies on ribosomes. II. Denaturation and sedimentation of ribosomal subunits unfolded in EDTA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Feb 18;174(2):551–560. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90284-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler D. G., Davies J. E. Specific cleavage of ribosomal RNA caused by alpha sarcin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Apr;4(4):1097–1110. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.4.1097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tam M. F., Hill W. E. Physical characteristics of the reconstitution intermediates (RI30 and RI30*) from the 30S ribosomal subunit of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1981 Oct 27;20(22):6480–6484. doi: 10.1021/bi00525a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapprich W. E., Hill W. E. Involvement of bases 787-795 of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA in ribosomal subunit association. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):556–560. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WELLER D. L., HOROWITZ J. A 30-S RIBONUCLEOPROTEIN PARTICLE DERIVED FROM 50-S RIBOSOMES OF ESCHERICHIA COLI. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Jun 22;87:361–364. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(64)90239-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller D. L., Schechter Y., Musgrave D., Rougvie M., Horowitz J. Conformational changes in Escherichia coli ribosomes at low magnesium ion concentrations. Biochemistry. 1968 Oct;7(10):3668–3675. doi: 10.1021/bi00850a046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]