Abstract
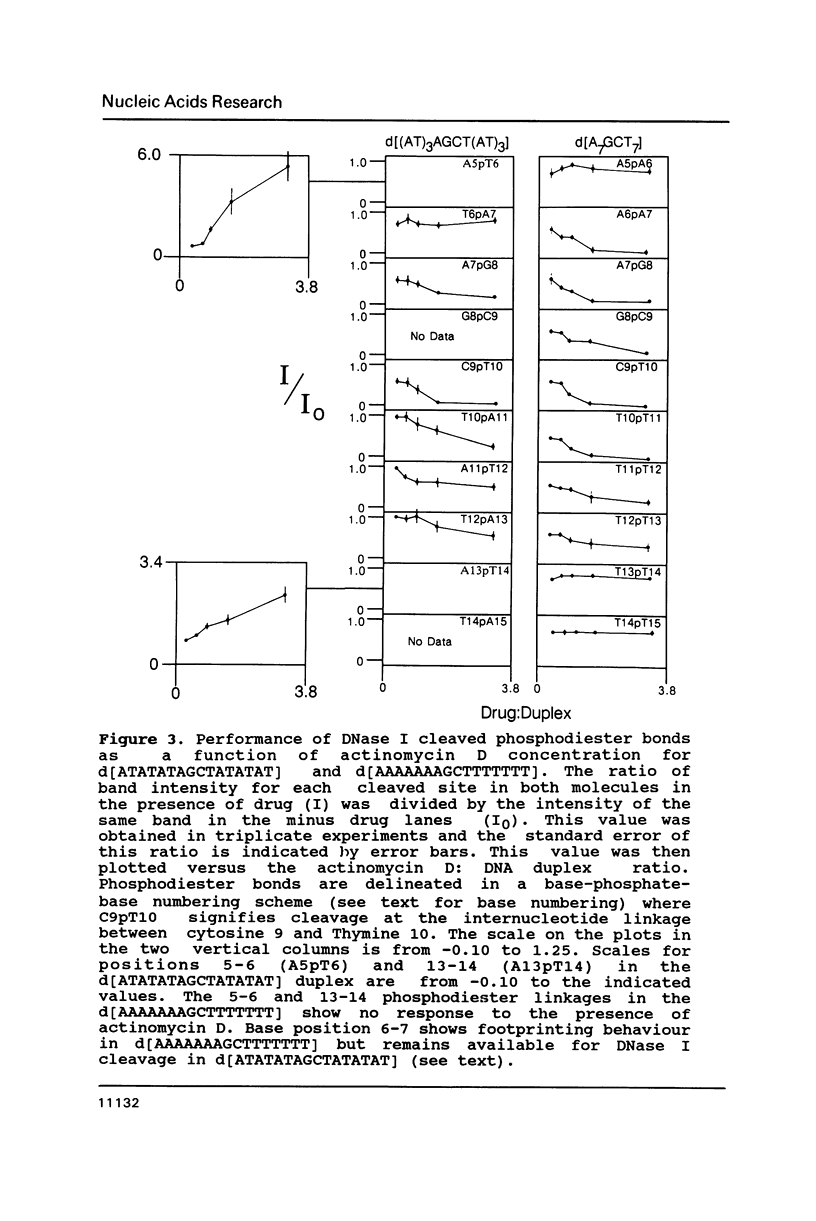
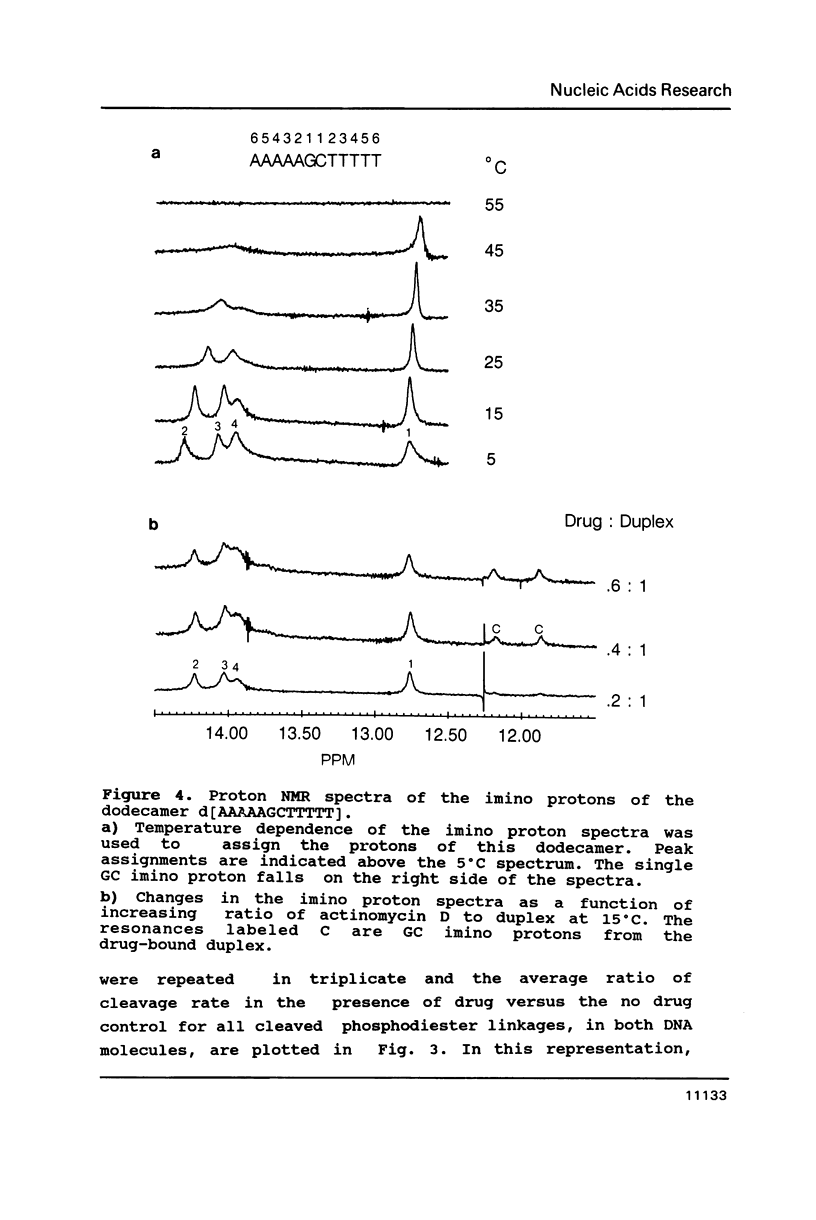
Two DNA hexadecamers containing one central 5'-GC-3' base step have been examined by footprinting methodology in the presence and absence of actinomycin D. The results of these studies, coupled with imino proton NMR measurements indicate that the antitumor drug causes a change in DNA conformation at a distance from the actinomycin intercalation site in a molecule of sequence d[ATATATAGCTATATAT] that does not occur in d[AAAAAAAGCTTTTTTT]. The experiments demonstrate that DNase I rate enhancements associated with actinomycin D binding are caused by ligand alteration of equilibrium DNA structure.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. E., Ptashne M., Harrison S. C. Structure of the repressor-operator complex of bacteriophage 434. 1987 Apr 30-May 6Nature. 326(6116):846–852. doi: 10.1038/326846a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bittman R., Blau L. Stopped-flow kinetic studies of actinomycin binding to DNAs. Biochemistry. 1975 May 20;14(10):2138–2145. doi: 10.1021/bi00681a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. C., Shafer R. H. Kinetic studies of actinomycin D binding to mono-, oligo-, and polynucleotides. Biochemistry. 1987 Jan 13;26(1):277–282. doi: 10.1021/bi00375a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burd J. F., Larson J. E., Wells R. D. Further studies on telestability in DNA. The synthesis and characterization of the duplex block polymers d(C20A10) - d(T10G20) and d(C20A15) - d(T15G20). J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):6002–6007. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burd J. F., Wartell R. M., Dodgson J. B., Wells R. D. Transmission of stability (telestability) in deoxyribonucleic acid. Physical and enzymatic studies on the duplex block polymer d(C15A15) - d(T15G15). J Biol Chem. 1975 Jul 10;250(13):5109–5113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaires J. B. Long-range allosteric effects on the B to Z equilibrium by daunomycin. Biochemistry. 1985 Dec 3;24(25):7479–7486. doi: 10.1021/bi00346a067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dattagupta N., Hogan M., Crothers D. M. Interaction of netropsin and distamycin with deoxyribonucleic acid: electric dichroism study. Biochemistry. 1980 Dec 23;19(26):5998–6005. doi: 10.1021/bi00567a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E. Base sequence and helix structure variation in B and A DNA. J Mol Biol. 1983 May 25;166(3):419–441. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E., Drew H. R. Structure of a B-DNA dodecamer. II. Influence of base sequence on helix structure. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 15;149(4):761–786. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90357-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H. R. Structural specificities of five commonly used DNA nucleases. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jul 15;176(4):535–557. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90176-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H. R., Travers A. A. DNA structural variations in the E. coli tyrT promoter. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):491–502. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90379-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H. R., Wing R. M., Takano T., Broka C., Tanaka S., Itakura K., Dickerson R. E. Structure of a B-DNA dodecamer: conformation and dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2179–2183. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox K. R., Waring M. J. Kinetic evidence for redistribution of actinomycin molecules between potential DNA-binding sites. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Dec 17;145(3):579–586. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08596.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogan M. E., Austin R. H. Importance of DNA stiffness in protein-DNA binding specificity. Nature. 1987 Sep 17;329(6136):263–266. doi: 10.1038/329263a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogan M., Dattagupta N., Crothers D. M. Transmission of allosteric effects in DNA. Nature. 1979 Apr 5;278(5704):521–524. doi: 10.1038/278521a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain S. C., Sobell H. M. Stereochemistry of actinomycin binding to DNA. I. Refinement and further structural details of the actinomycin-deoxyguanosine crystalline complex. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jul 14;68(1):1–20. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90258-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koudelka G. B., Harrison S. C., Ptashne M. Effect of non-contacted bases on the affinity of 434 operator for 434 repressor and Cro. 1987 Apr 30-May 6Nature. 326(6116):886–888. doi: 10.1038/326886a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamos M. L., Walker G. T., Krugh T. R., Turner D. H. Fluorescence-detected circular dichroism of ethidium bound to poly(dG-dC) and poly(dG-m5dC) under B- and Z-form conditions. Biochemistry. 1986 Feb 11;25(3):687–691. doi: 10.1021/bi00351a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane M. J., Dabrowiak J. C., Vournakis J. N. Sequence specificity of actinomycin D and Netropsin binding to pBR322 DNA analyzed by protection from DNase I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3260–3264. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane M. J., Laplante S., Rehfuss R. P., Borer P. N., Cantor C. R. Actinomycin D facilitates transition of AT domains in molecules of sequence (AT)nAGCT(AT)n to a DNAse I detectable alternating structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 26;15(2):839–852. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.2.839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomonossoff G. P., Butler P. J., Klug A. Sequence-dependent variation in the conformation of DNA. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 15;149(4):745–760. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90356-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low C. M., Drew H. R., Waring M. J. Sequence-specific binding of echinomycin to DNA: evidence for conformational changes affecting flanking sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 25;12(12):4865–4879. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.12.4865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low C. M., Fox K. R., Olsen R. K., Waring M. J. DNA sequence recognition by under-methylated analogues of triostin A. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 11;14(5):2015–2033. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.5.2015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClarin J. A., Frederick C. A., Wang B. C., Greene P., Boyer H. W., Grable J., Rosenberg J. M. Structure of the DNA-Eco RI endonuclease recognition complex at 3 A resolution. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1526–1541. doi: 10.1126/science.3024321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClellan J. A., Palecek E., Lilley D. M. (A-T)n tracts embedded in random sequence DNA--formation of a structure which is chemically reactive and torsionally deformable. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Dec 9;14(23):9291–9309. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.23.9291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W., Crothers D. M. Studies of the binding of actinomycin and related compounds to DNA. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jul 28;35(2):251–290. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(68)80024-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidle S., Abraham Z. Structural and sequence-dependent aspects of drug intercalation into nucleic acids. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1984;17(1):73–121. doi: 10.3109/10409238409110270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohl F. M., Jovin T. M., Baehr W., Holbrook J. J. Ethidium bromide as a cooperative effector of a DNA structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3805–3809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigley G. J., Ughetto G., van der Marel G. A., van Boom J. H., Wang A. H., Rich A. Non-Watson-Crick G.C and A.T base pairs in a DNA-antibiotic complex. Science. 1986 Jun 6;232(4755):1255–1258. doi: 10.1126/science.3704650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes D., Klug A. Sequence-dependent helical periodicity of DNA. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):378–380. doi: 10.1038/292378a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafer R. H., Burnette R. R., Mirau P. A. Spectroscopic analysis of the equilibrium and kinetic DNA binding properties of several actinomycin analogs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Mar 11;8(5):1121–1132. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.5.1121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobell H. M. The stereochemistry of actinomycin binding to DNA and its implications in molecular biology. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1973;13:153–190. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60103-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobell H. M. The stereochemistry of actinomycin binding to DNA. Cancer Chemother Rep. 1974 Jan-Feb;58(1):101–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss F., Gaillard C., Prunell A. Helical periodicity of DNA, Poly(dA) . poly(dT) and poly(dA-dT). poly(dA-dT) in solution. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Aug;118(2):215–222. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06389.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suck D., Lahm A., Oefner C. Structure refined to 2A of a nicked DNA octanucleotide complex with DNase I. Nature. 1988 Mar 31;332(6163):464–468. doi: 10.1038/332464a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suck D., Oefner C. Structure of DNase I at 2.0 A resolution suggests a mechanism for binding to and cutting DNA. Nature. 1986 Jun 5;321(6070):620–625. doi: 10.1038/321620a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takusagawa F., Dabrow M., Neidle S., Berman H. M. The structure of a pseudo intercalated complex between actinomycin and the DNA binding sequence d(GpC). Nature. 1982 Apr 1;296(5856):466–469. doi: 10.1038/296466a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward B., Rehfuss R., Goodisman J., Dabrowiak J. C. Rate enhancements in the DNase I footprinting experiment. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 25;16(4):1359–1369. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.4.1359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wartell R. M. Evidence for long-range interactions in DNA. Analysis of melting curves of block polymers d(C15A15)-d(T15G15),d(C20A15)-d(T15G20), and d(T15G20). Biopolymers. 1976 Aug;15(8):1461–1479. doi: 10.1002/bip.1976.360150803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkle S. A., Krugh T. R. Equilibrium binding of carcinogens and antitumor antibiotics to DNA: site selectivity, cooperativity, allosterism. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3175–3186. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





