Abstract
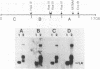
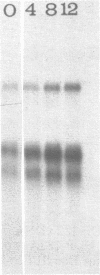
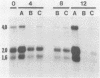
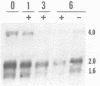
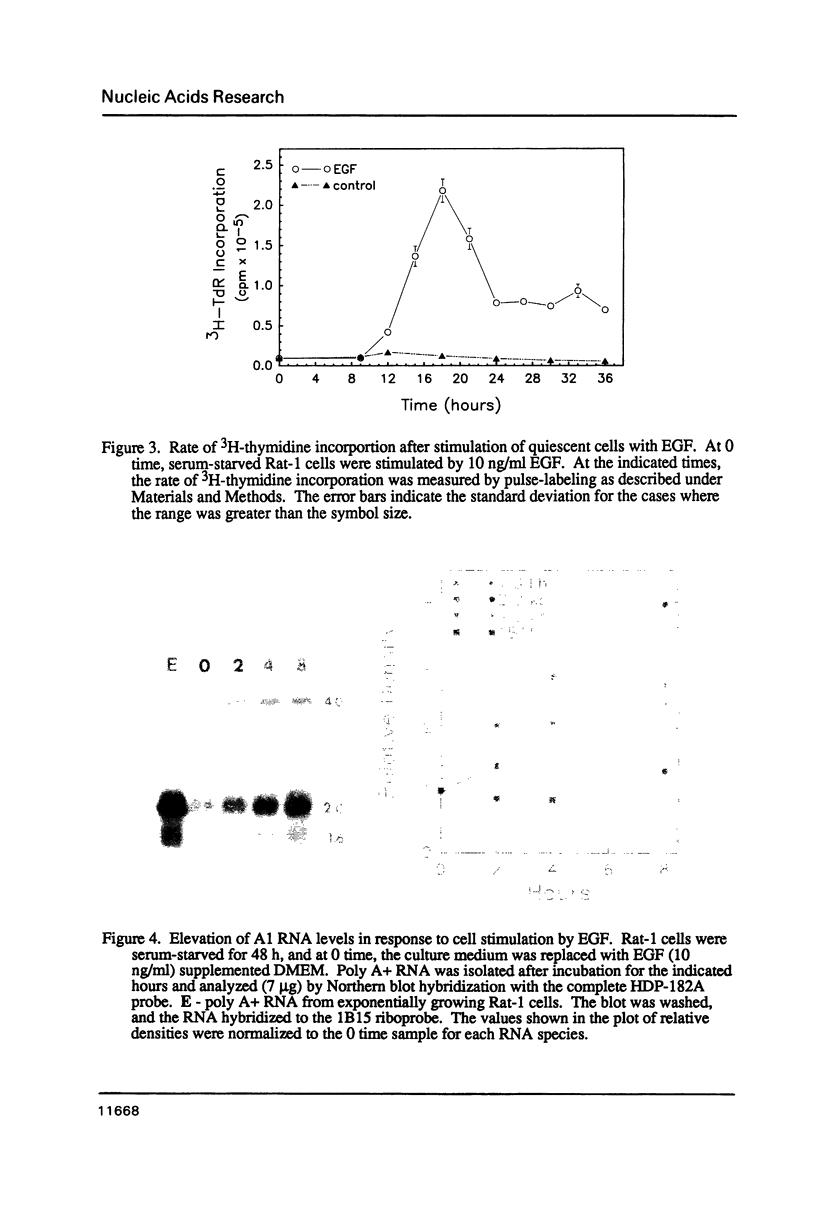
The levels of mRNA encoding hnRNP core protein A1 have been compared in quiescent and proliferating Rat-1 embryonic fibroblasts. Northern blot hybridization analyses using probes made from an A1 cDNA clone, lambda HDP-182, isolated by Cobianchi et al. (J. Biol. Chem. 261:3536-2543 (1986] indicated that three sizes of poly A + RNAs, 1.6, 2.0, & 4.0 kb, have extensive sequence homology. The levels of all three A1 RNA species are responsive to the proliferation state of the cells. Stimulation of quiescent Rat-1 cells with serum or epidermal growth factor resulted in a 2- to 5-fold increase in the levels of each of these three RNAs that was evident after 2 hours and reached a peak after about 8 hours. Addition of the protein synthesis inhibitor, cycloheximide, along with epidermal growth factor completely blocked the upsurge in A1 RNA levels. Thus, the A1 RNA species are not primary transcriptional targets of epidermal growth factor but do show an induction pattern similar to mRNAs encoding some glycolytic enzymes.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beyer A. L., Bouton A. H., Miller O. L., Jr Correlation of hnRNP structure and nascent transcript cleavage. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(2 Pt 2):155–165. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90299-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyer A. L., Christensen M. E., Walker B. W., LeStourgeon W. M. Identification and characterization of the packaging proteins of core 40S hnRNP particles. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):127–138. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90323-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bravo R., Celis J. E. Human proteins sensitive to neoplastic transformation in cultured epithelial and fibroblast cells. Clin Chem. 1982 Apr;28(4 Pt 2):949–954. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buvoli M., Biamonti G., Tsoulfas P., Bassi M. T., Ghetti A., Riva S., Morandi C. cDNA cloning of human hnRNP protein A1 reveals the existence of multiple mRNA isoforms. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 11;16(9):3751–3770. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.9.3751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celis J. E., Bravo R., Arenstorf H. P., LeStourgeon W. M. Identification of proliferation-sensitive human proteins amongst components of the 40 S hnRNP particles. Identity of hnRNP core proteins in the HeLa protein catalogue. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jan 1;194(1):101–109. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80059-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobianchi F., SenGupta D. N., Zmudzka B. Z., Wilson S. H. Structure of rodent helix-destabilizing protein revealed by cDNA cloning. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 15;261(8):3536–3543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway G., Wooley J., Bibring T., LeStourgeon W. M. Ribonucleoproteins package 700 nucleotides of pre-mRNA into a repeating array of regular particles. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;8(7):2884–2895. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.7.2884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielson P. E., Forss-Petter S., Brow M. A., Calavetta L., Douglass J., Milner R. J., Sutcliffe J. G. p1B15: a cDNA clone of the rat mRNA encoding cyclophilin. DNA. 1988 May;7(4):261–267. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder P. K., Schmidt L. J., Ono T., Getz M. J. Specific stimulation of actin gene transcription by epidermal growth factor and cycloheximide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7476–7480. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Hermanowski A. L., Ziff E. B. Effect of protein synthesis inhibitors on growth factor activation of c-fos, c-myc, and actin gene transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1050–1057. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar A., Williams K. R., Szer W. Purification and domain structure of core hnRNP proteins A1 and A2 and their relationship to single-stranded DNA-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11266–11273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau L. F., Nathans D. Expression of a set of growth-related immediate early genes in BALB/c 3T3 cells: coordinate regulation with c-fos or c-myc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1182–1186. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeStourgeon W. M., Beyer A. L., Christensen M. E., Walker B. W., Poupore S. M., Daniels L. P. The packaging proteins of core hnRNP particles and the maintenance of proliferative cell states. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 2):885–898. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb J. E., Ritz E., Creuzet C., Jami J. Comparison of chromosomal proteins of mouse primitive teratocarcinoma, liver and L cells. Exp Cell Res. 1976 Dec;103(2):450–453. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90287-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lothstein L., Arenstorf H. P., Chung S. Y., Walker B. W., Wooley J. C., LeStourgeon W. M. General organization of protein in HeLa 40S nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles. J Cell Biol. 1985 May;100(5):1570–1581. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.5.1570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matrisian L. M., Bowden G. T., Magun B. E. Mechanism of synergistic induction of DNA synthesis by epidermal growth factor and tumor promoters. J Cell Physiol. 1981 Sep;108(3):417–425. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041080316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matrisian L. M., Larsen B. R., Finch J. S., Magun B. E. Further purification of epidermal growth factor by high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1982 Sep 15;125(2):339–351. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90015-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matrisian L. M., Leroy P., Ruhlmann C., Gesnel M. C., Breathnach R. Isolation of the oncogene and epidermal growth factor-induced transin gene: complex control in rat fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1679–1686. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matrisian L. M., Rautmann G., Magun B. E., Breathnach R. Epidermal growth factor or serum stimulation of rat fibroblasts induces an elevation in mRNA levels for lactate dehydrogenase and other glycolytic enzymes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 11;13(3):711–726. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.3.711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad I., Zouzias D., Basilico C. State of the viral DNA in rat cells transformed by polyoma virus. I. Virus rescue and the presence of nonintergrated viral DNA molecules. J Virol. 1976 May;18(2):436–444. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.2.436-444.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider J. A., Diamond I., Rozengurt E. Glycolysis of quiescent cultures of 3T3 cells. Addition of serum, epidermal growth factor, and insulin increases the activity of phosphofructokinase in a protein synthesis-independent manner. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 10;253(3):872–877. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab M., Alitalo K., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M., George D. A cellular oncogene (c-Ki-ras) is amplified, overexpressed, and located within karyotypic abnormalities in mouse adrenocortical tumour cells. Nature. 1983 Jun 9;303(5917):497–501. doi: 10.1038/303497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spritz R. A., Strunk K., Surowy C. S., Hoch S. O., Barton D. E., Francke U. The human U1-70K snRNP protein: cDNA cloning, chromosomal localization, expression, alternative splicing and RNA-binding. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 23;15(24):10373–10391. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.24.10373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson M. S., Nakagawa T. Y., LeVan K., Dreyfuss G. Primary structure of human nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle C proteins: conservation of sequence and domain structures in heterogeneous nuclear RNA, mRNA, and pre-rRNA-binding proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1731–1739. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilk H. E., Werr H., Friedrich D., Kiltz H. H., Schäfer K. P. The core proteins of 35S hnRNP complexes. Characterization of nine different species. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jan 2;146(1):71–81. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08621.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wooley J., Chung S. Y., Wall J., Lestourgeon W. Architecture of pre-messenger, nuclear ribonucleoprotein monoparticles. Biophys J. 1986 Jan;49(1):17–19. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83575-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]