Abstract
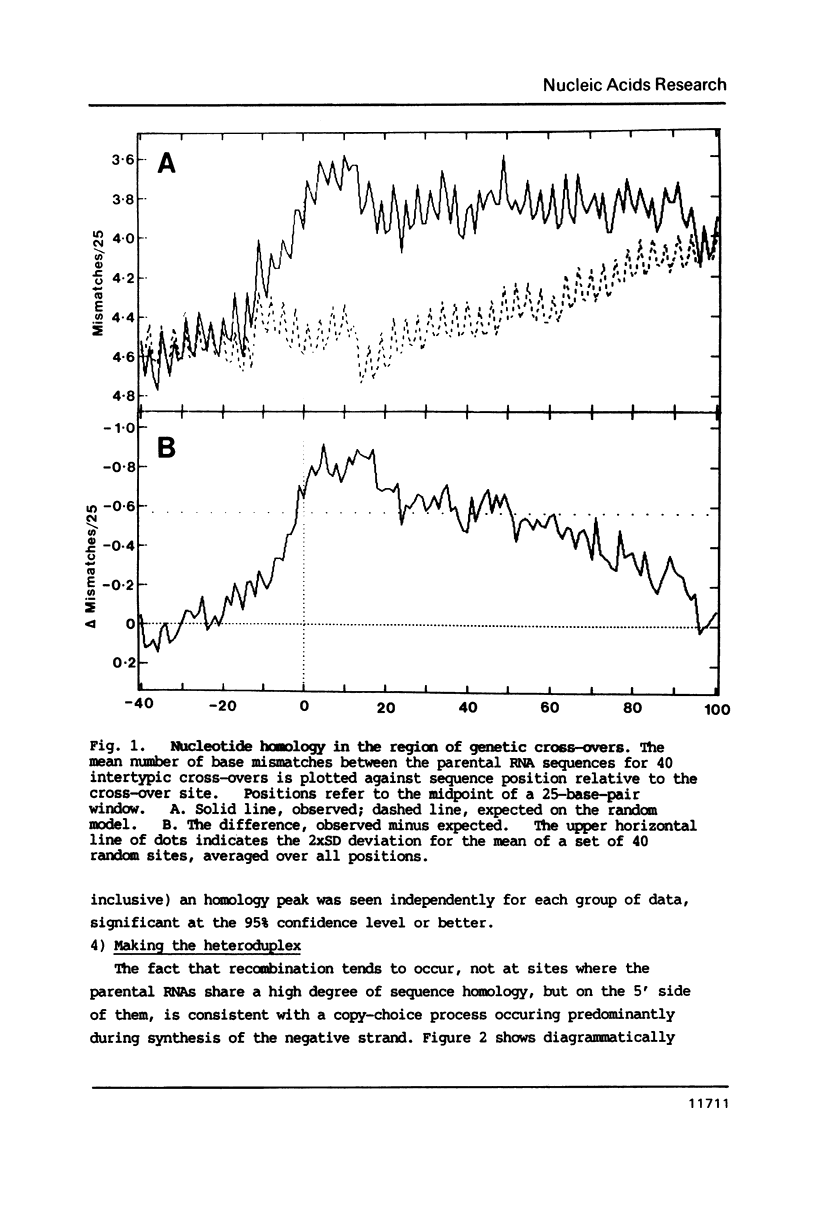
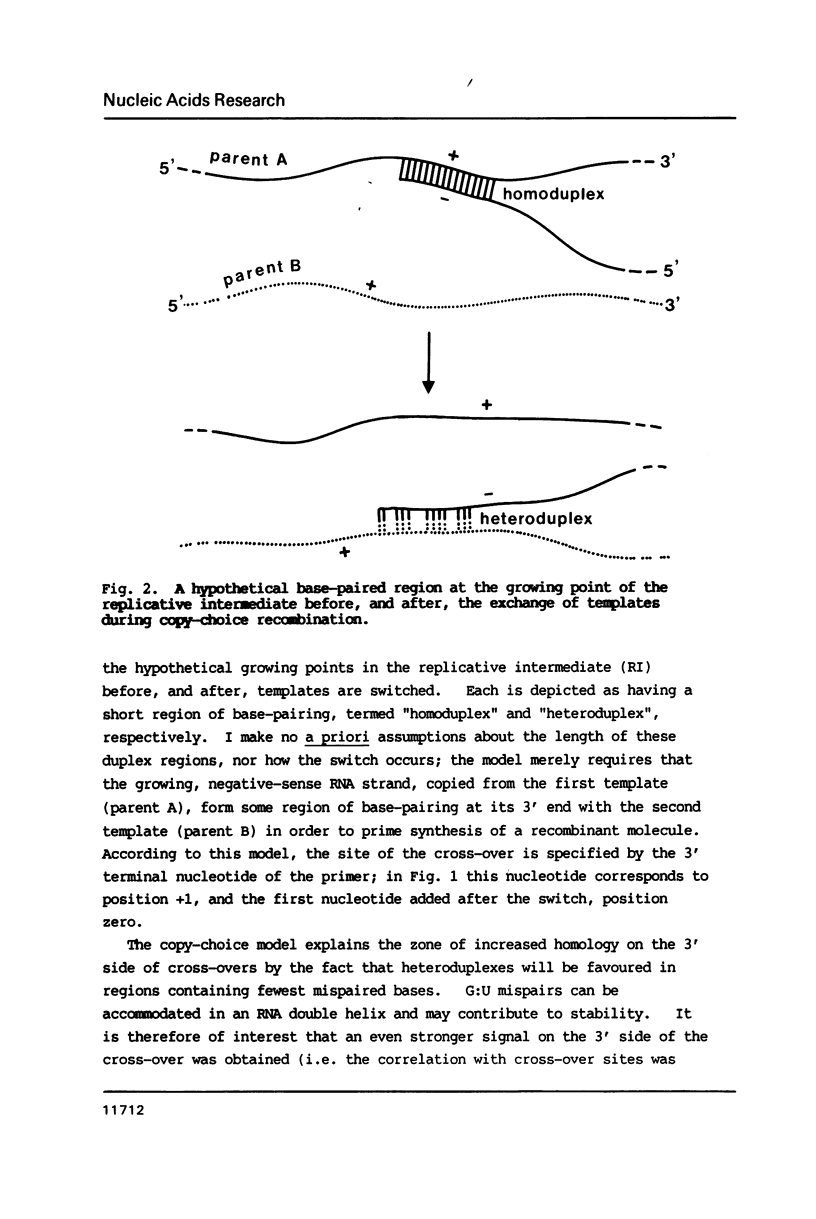
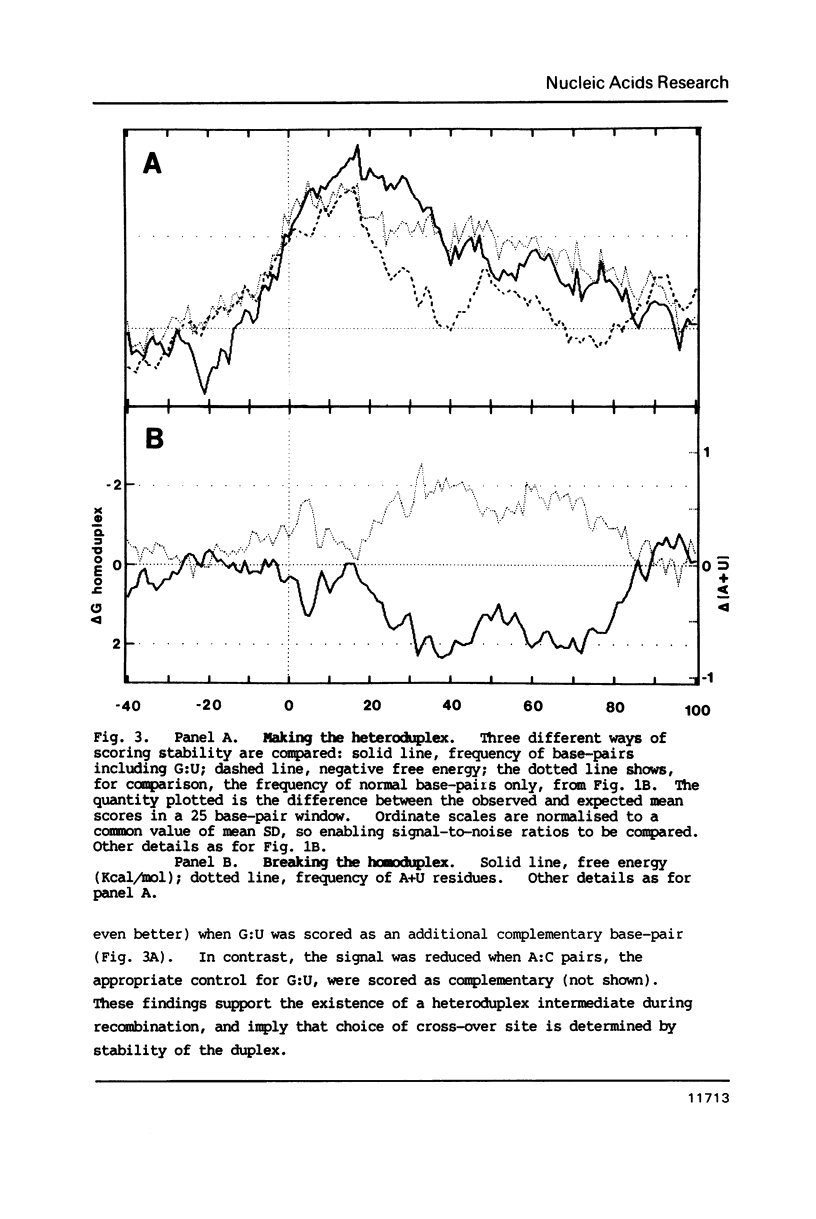
The genome of poliovirus consists of a single strand of RNA approximately 7.5 kb long. Analysis of the sequences around 40 unique recombination sites reveals several features that differ significantly from those expected of randomly located sites. These features, which include a broad zone of elevated homology on the 3' side of the cross-over, support the theory that RNA recombination occurs by a template-switching mechanism during synthesis of the complementary strand, and that sites are chosen to minimise the adverse free energy change involved in switching to a heterotypic template. There is also a strong sequence bias, almost two-thirds of cross-overs, according to a computer simulation, occurring immediately after synthesis of UU. These features shed new light on the extent of base-pairing in replicative intermediate RNA, and on the mechanism of chain initiation.
Full text
PDF





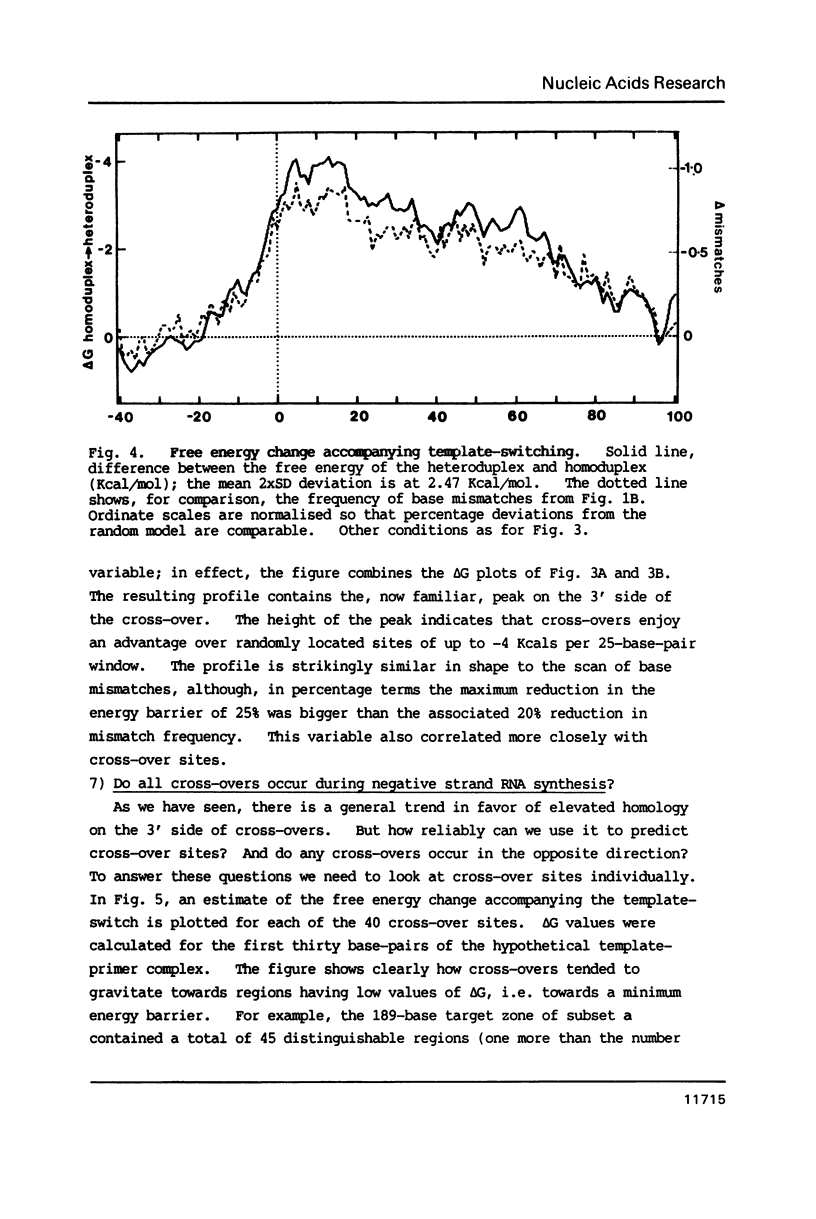
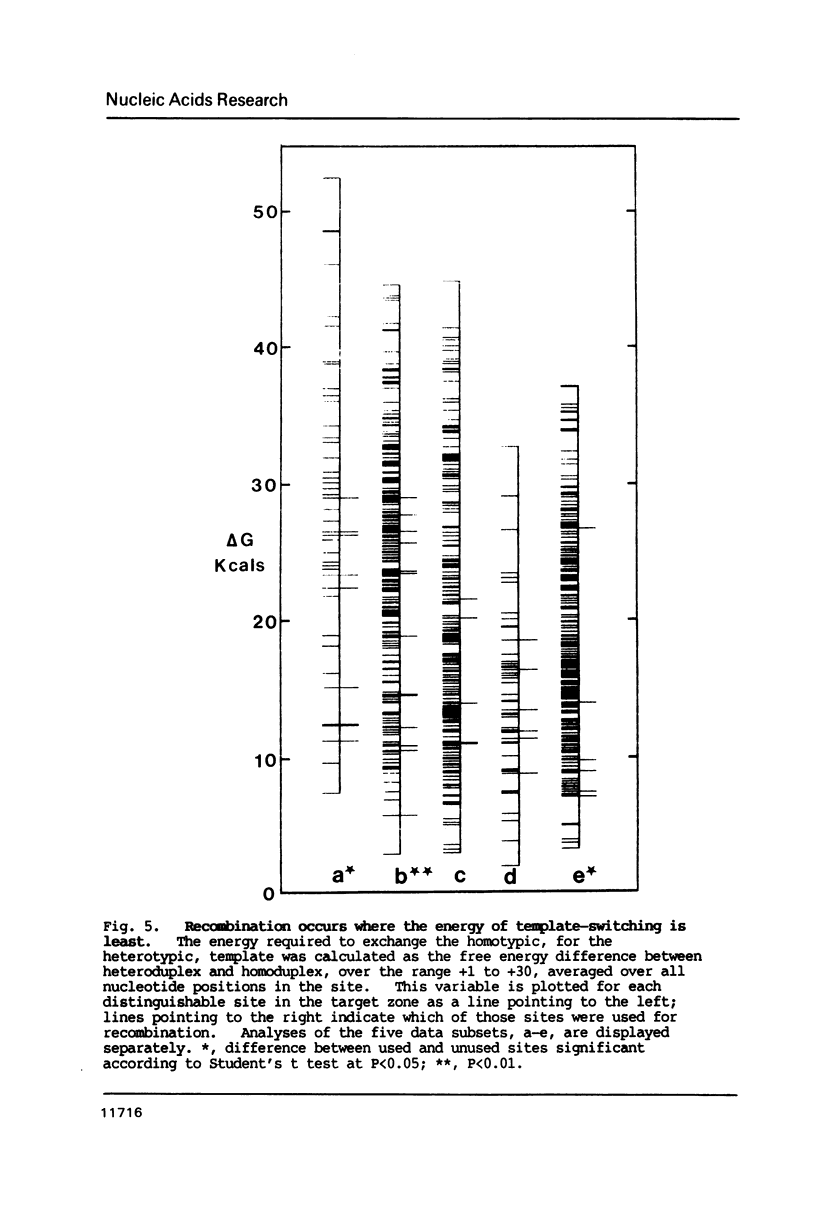

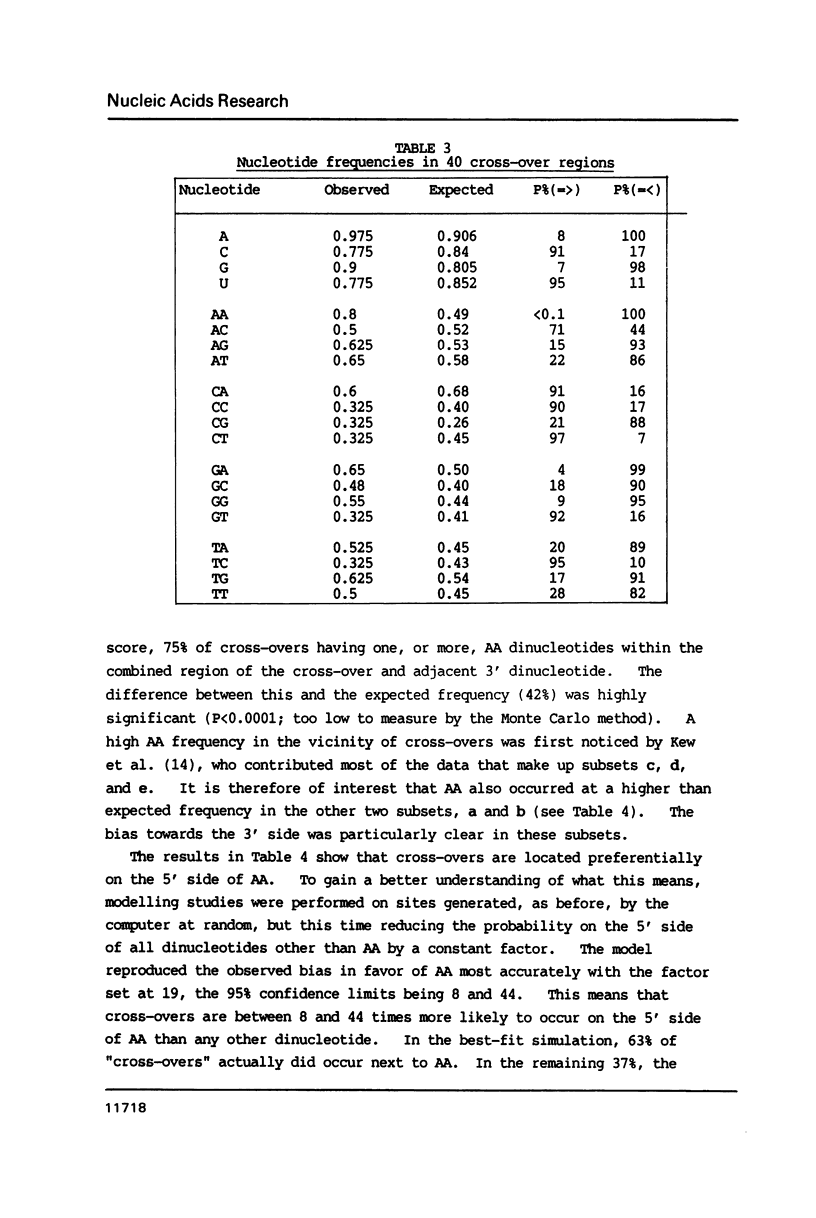





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews N. C., Levin D., Baltimore D. Poliovirus replicase stimulation by terminal uridylyl transferase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7628–7635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bujarski J. J., Kaesberg P. Genetic recombination between RNA components of a multipartite plant virus. 1986 May 29-Jun 4Nature. 321(6069):528–531. doi: 10.1038/321528a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper P. D. A genetic map of poliovirus temperature-sensitive mutants. Virology. 1968 Aug;35(4):584–596. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90287-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRST G. K. Genetic recombination with Newcastle disease virus, polioviruses, and influenza. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1962;27:303–309. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1962.027.001.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandolf R., Hofschneider P. H. Molecular cloning of the genome of a cardiotropic Coxsackie B3 virus: full-length reverse-transcribed recombinant cDNA generates infectious virus in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4818–4822. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King A. M., McCahon D., Saunders K., Newman J. W., Slade W. R. Multiple sites of recombination within the RNA genome of foot-and-mouth disease virus. Virus Res. 1985 Nov;3(4):373–384. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(85)90437-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkegaard K., Baltimore D. The mechanism of RNA recombination in poliovirus. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):433–443. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90600-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura N., Semler B. L., Rothberg P. G., Larsen G. R., Adler C. J., Dorner A. J., Emini E. A., Hanecak R., Lee J. J., van der Werf S. Primary structure, gene organization and polypeptide expression of poliovirus RNA. Nature. 1981 Jun 18;291(5816):547–553. doi: 10.1038/291547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuge S., Saito I., Nomoto A. Primary structure of poliovirus defective-interfering particle genomes and possible generation mechanisms of the particles. J Mol Biol. 1986 Dec 5;192(3):473–487. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90270-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEDINKO N. Genetic recombination with poliovirus type 1. Studies of crosses between a normal horse serum-resistant mutant and several guanidine-resistant mutants of the same strain. Virology. 1963 May;20:107–119. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90145-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Monica N., Meriam C., Racaniello V. R. Mapping of sequences required for mouse neurovirulence of poliovirus type 2 Lansing. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):515–525. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.515-525.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. M., Baric R. S., Makino S., Keck J. G., Egbert J., Leibowitz J. L., Stohlman S. A. Recombination between nonsegmented RNA genomes of murine coronaviruses. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):449–456. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.449-456.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino S., Keck J. G., Stohlman S. A., Lai M. M. High-frequency RNA recombination of murine coronaviruses. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):729–737. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.729-737.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCahon D., Slade W. R., Priston R. A., Lake J. R. An extended genetic recombination map for foot-and-mouth diseases virus. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jun;35(3):555–565. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-35-3-555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minor P. D., John A., Ferguson M., Icenogle J. P. Antigenic and molecular evolution of the vaccine strain of type 3 poliovirus during the period of excretion by a primary vaccinee. J Gen Virol. 1986 Apr;67(Pt 4):693–706. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-4-693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomoto A., Omata T., Toyoda H., Kuge S., Horie H., Kataoka Y., Genba Y., Nakano Y., Imura N. Complete nucleotide sequence of the attenuated poliovirus Sabin 1 strain genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5793–5797. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRINGLE C. R. EVIDENCE OF GENETIC RECOMBINATION IN FOOT-AND-MOUTH DISEASE VIRUS. Virology. 1965 Jan;25:48–54. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90250-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards O. C., Martin S. C., Jense H. G., Ehrenfeld E. Structure of poliovirus replicative intermediate RNA. Electron microscope analysis of RNA cross-linked in vivo with psoralen derivative. J Mol Biol. 1984 Mar 5;173(3):325–340. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90124-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romanova L. I., Blinov V. M., Tolskaya E. A., Viktorova E. G., Kolesnikova M. S., Guseva E. A., Agol V. I. The primary structure of crossover regions of intertypic poliovirus recombinants: a model of recombination between RNA genomes. Virology. 1986 Nov;155(1):202–213. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90180-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salser W. Globin mRNA sequences: analysis of base pairing and evolutionary implications. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 2):985–1002. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi Y. B., Gamper H., Van Houten B., Hearst J. E. Interaction of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase with DNA in an elongation complex arrested at a specific psoralen crosslink site. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jan 20;199(2):277–293. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90314-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanway G., Cann A. J., Hauptmann R., Hughes P., Clarke L. D., Mountford R. C., Minor P. D., Schild G. C., Almond J. W. The nucleotide sequence of poliovirus type 3 leon 12 a1b: comparison with poliovirus type 1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 25;11(16):5629–5643. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.16.5629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanway G., Hughes P. J., Mountford R. C., Reeve P., Minor P. D., Schild G. C., Almond J. W. Comparison of the complete nucleotide sequences of the genomes of the neurovirulent poliovirus P3/Leon/37 and its attenuated Sabin vaccine derivative P3/Leon 12a1b. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1539–1543. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda N., Kuhn R. J., Yang C. F., Takegami T., Wimmer E. Initiation of poliovirus plus-strand RNA synthesis in a membrane complex of infected HeLa cells. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):43–53. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.43-53.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolskaya E. A., Romanova L. I., Blinov V. M., Viktorova E. G., Sinyakov A. N., Kolesnikova M. S., Agol V. I. Studies on the recombination between RNA genomes of poliovirus: the primary structure and nonrandom distribution of crossover regions in the genomes of intertypic poliovirus recombinants. Virology. 1987 Nov;161(1):54–61. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90170-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoda H., Kohara M., Kataoka Y., Suganuma T., Omata T., Imura N., Nomoto A. Complete nucleotide sequences of all three poliovirus serotype genomes. Implication for genetic relationship, gene function and antigenic determinants. J Mol Biol. 1984 Apr 25;174(4):561–585. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90084-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



