Abstract
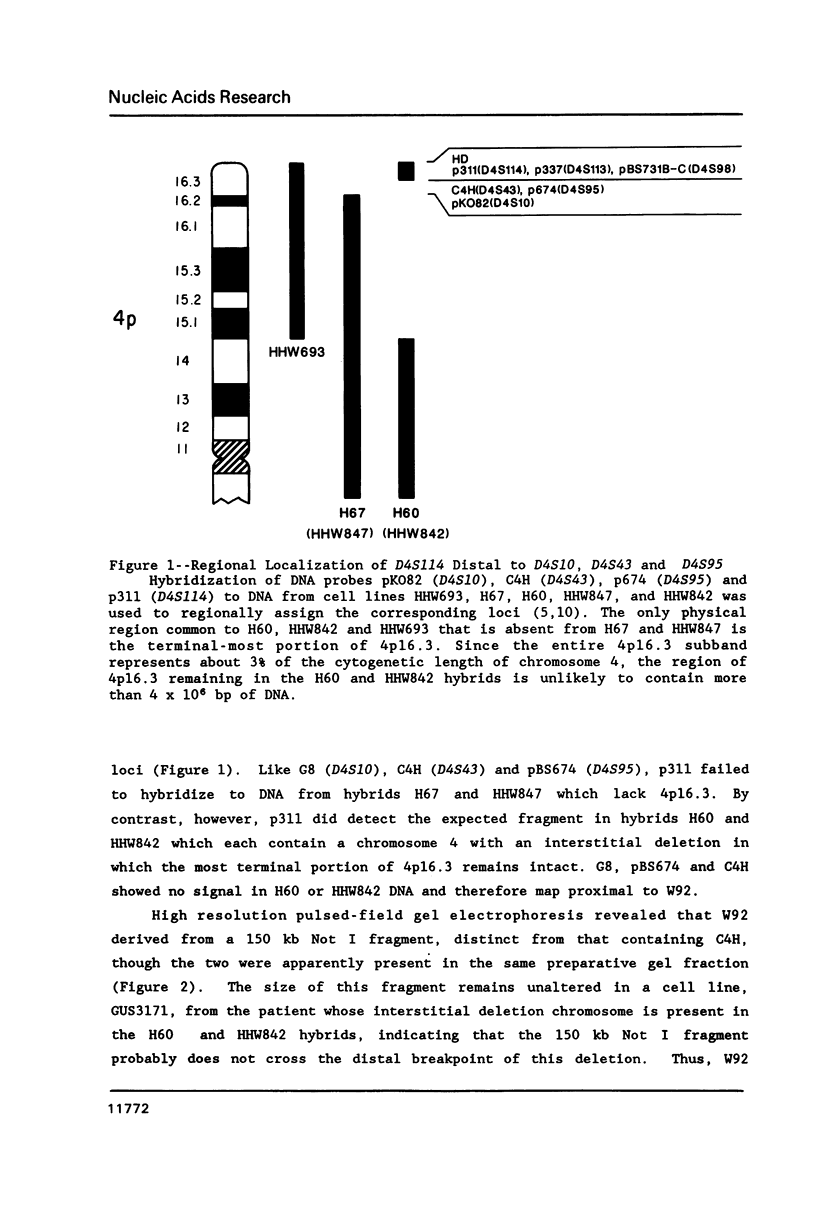
The dominant gene defect in Huntington's disease (HD) is linked to the DNA marker D4S10, near the telomere of the chromosome 4 short arm. Two other markers, D4S43 and D4S95, are closer, but still proximal to the HD gene in 4p16.3. We have characterized a new locus, D4S114, identified by cloning the end of a NotI fragment resolved by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. D4S114 was localized distal to D4S43 and D4S95 by both physical and genetic mapping techniques. The "end"-clone overlaps a previously isolated NotI "linking" clone, and is within 150 kb of a second "linking" clone defining D4S113. Restriction fragment length polymorphisms for D4S113 and D4S114, one of which is identical to a SacI polymorphism detected by the anonymous probe pBS731B-C (D4S98), were typed for key crossovers in HD and reference pedigrees. The data support the locus order D4S10-(D4S43, D4S95)-D4S98/S114/S113-HD-telomere. The D4S98/S114/S113 cluster therefore represents the nearest cloned sequences to HD, and provides a valuable new point for launching directional cloning strategies to isolate and characterize this disease gene.
Full text
PDF


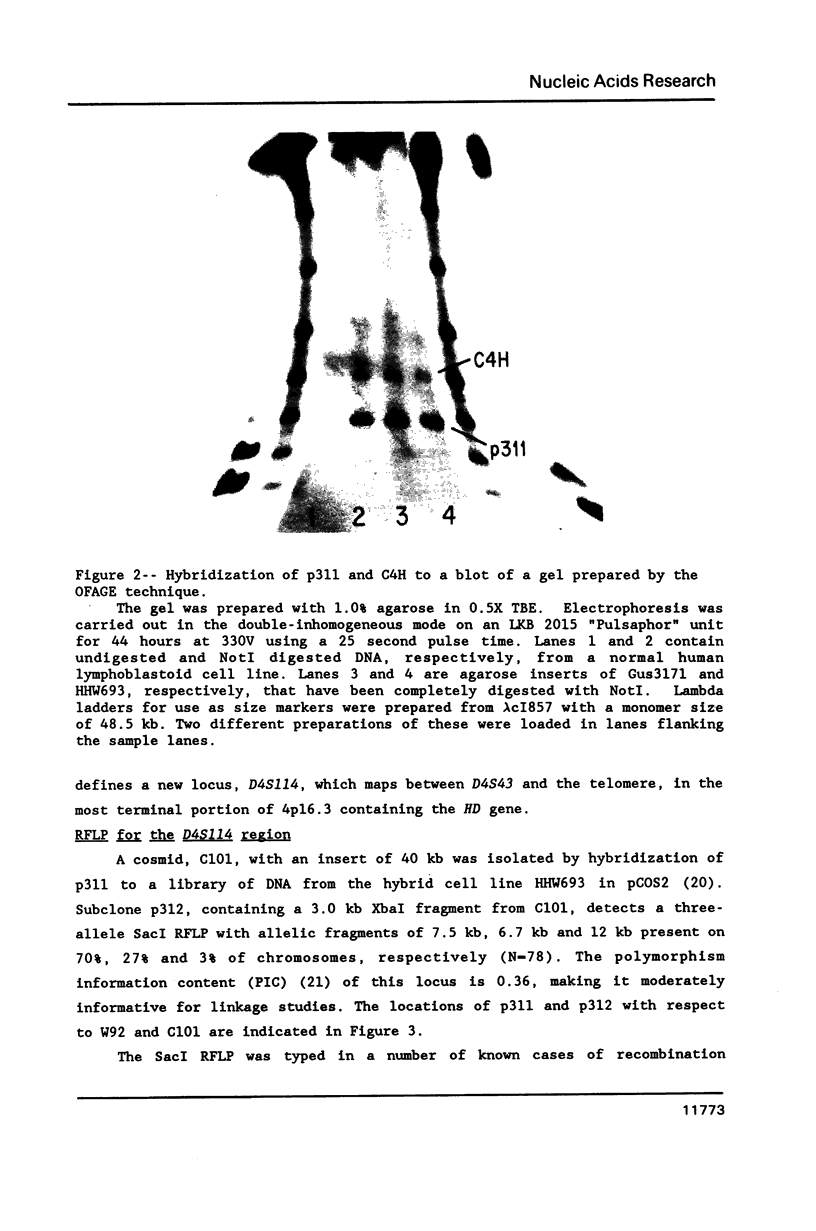





Images in this article
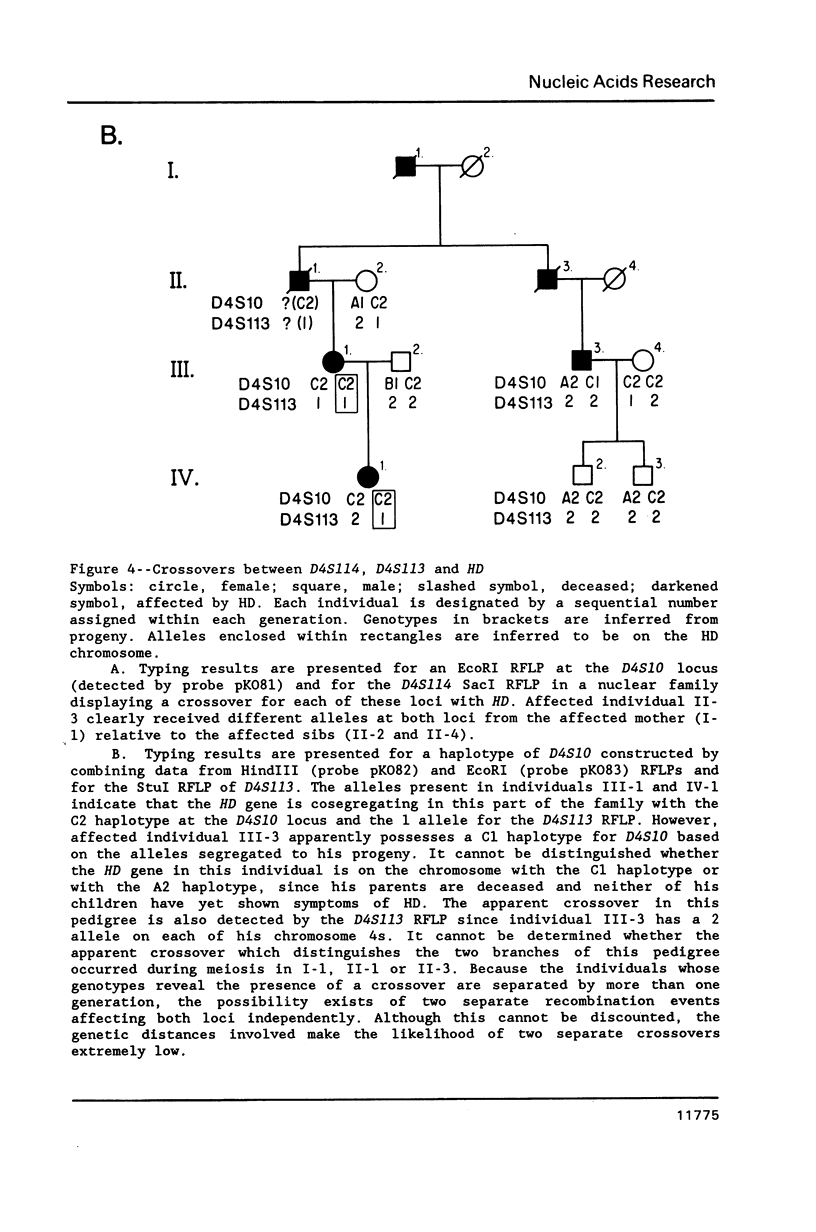
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carle G. F., Frank M., Olson M. V. Electrophoretic separations of large DNA molecules by periodic inversion of the electric field. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):65–68. doi: 10.1126/science.3952500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. S., Drumm M. L., Cole J. L., Lockwood W. K., Vande Woude G. F., Iannuzzi M. C. Construction of a general human chromosome jumping library, with application to cystic fibrosis. Science. 1987 Feb 27;235(4792):1046–1049. doi: 10.1126/science.2950591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilliam T. C., Bucan M., MacDonald M. E., Zimmer M., Haines J. L., Cheng S. V., Pohl T. M., Meyers R. H., Whaley W. L., Allitto B. A. A DNA segment encoding two genes very tightly linked to Huntington's disease. Science. 1987 Nov 13;238(4829):950–952. doi: 10.1126/science.2890209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilliam T. C., Healey S. T., MacDonald M. E., Stewart G. D., Wasmuth J. J., Tanzi R. E., Roy J. C., Gusella J. F. Isolation of polymorphic DNA fragments from human chromosome 4. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 25;15(4):1445–1458. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.4.1445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilliam T. C., Tanzi R. E., Haines J. L., Bonner T. I., Faryniarz A. G., Hobbs W. J., MacDonald M. E., Cheng S. V., Folstein S. E., Conneally P. M. Localization of the Huntington's disease gene to a small segment of chromosome 4 flanked by D4S10 and the telomere. Cell. 1987 Aug 14;50(4):565–571. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90029-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gusella J. F., Keys C., VarsanyiBreiner A., Kao F. T., Jones C., Puck T. T., Housman D. Isolation and localization of DNA segments from specific human chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2829–2833. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gusella J. F., Tanzi R. E., Anderson M. A., Hobbs W., Gibbons K., Raschtchian R., Gilliam T. C., Wallace M. R., Wexler N. S., Conneally P. M. DNA markers for nervous system diseases. Science. 1984 Sep 21;225(4668):1320–1326. doi: 10.1126/science.6089346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gusella J. F., Wexler N. S., Conneally P. M., Naylor S. L., Anderson M. A., Tanzi R. E., Watkins P. C., Ottina K., Wallace M. R., Sakaguchi A. Y. A polymorphic DNA marker genetically linked to Huntington's disease. Nature. 1983 Nov 17;306(5940):234–238. doi: 10.1038/306234a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Strategies for multilocus linkage analysis in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3443–3446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald M. E., Anderson M. A., Gilliam T. C., Tranejaerg L., Carpenter N. J., Magenis E., Hayden M. R., Healey S. T., Bonner T. I., Gusella J. F. A somatic cell hybrid panel for localizing DNA segments near the Huntington's disease gene. Genomics. 1987 Sep;1(1):29–34. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(87)90101-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. B., Gusella J. F. Huntington's disease. Pathogenesis and management. N Engl J Med. 1986 Nov 13;315(20):1267–1276. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198611133152006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissen G. J., Myers R. H., Mastromauro C. A., Koroshetz W. J., Klinger K. W., Farrer L. A., Watkins P. A., Gusella J. F., Bird E. D., Martin J. B. Predictive testing for Huntington's disease with use of a linked DNA marker. N Engl J Med. 1988 Mar 3;318(9):535–542. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198803033180903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michiels F., Burmeister M., Lehrach H. Derivation of clones close to met by preparative field inversion gel electrophoresis. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1305–1308. doi: 10.1126/science.3035716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poustka A., Pohl T. M., Barlow D. P., Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H. Construction and use of human chromosome jumping libraries from NotI-digested DNA. Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):353–355. doi: 10.1038/325353a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poustka A., Rackwitz H. R., Frischauf A. M., Hohn B., Lehrach H. Selective isolation of cosmid clones by homologous recombination in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4129–4133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sealey P. G., Whittaker P. A., Southern E. M. Removal of repeated sequences from hybridisation probes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 25;13(6):1905–1922. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.6.1905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B., Skarecky D., Bengtsson U., Magenis R. E., Carpenter N., Wasmuth J. J. Isolation of DNA markers in the direction of the Huntington disease gene from the G8 locus. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Feb;42(2):335–344. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasmuth J. J., Carlock L. R., Smith B., Immken L. L. A cell hybrid and recombinant DNA library that facilitate identification of polymorphic loci in the vicinity of the Huntington disease gene. Am J Hum Genet. 1986 Sep;39(3):397–403. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasmuth J. J., Hewitt J., Smith B., Allard D., Haines J. L., Skarecky D., Partlow E., Hayden M. R. A highly polymorphic locus very tightly linked to the Huntington's disease gene. Nature. 1988 Apr 21;332(6166):734–736. doi: 10.1038/332734a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]