Abstract
Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) are persistent organic pollutants and have been associated with abnormal liver enzymes and suspected non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), obesity, and the metabolic syndrome in epidemiological studies. In epidemiological surveys of human PCB exposure, PCB 153 has the highest serum levels among PCB congeners. To determine the hepatic effects of PCB 153 in mice, C57BL/6J mice were fed either a control diet (CD) or a high fat diet (HFD) for 12 weeks, with or without PCB 153 co-exposure. The metabolite extracts from mouse livers were analyzed using linear trap quadruple - Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometer (LTQ-FTICR MS) via direct infusion nano-electrospray ionization (DI-nESI) mass spectrometry. The metabolomics analysis indicated no difference in the metabolic profile between mice fed the control diet with PCB 153 exposure (CD+PCB 153) and mice fed the control diet (CD) without PCB 153 exposure. However, compared with CD group, levels of 10 metabolites were increased and 15 metabolites were reduced in mice fed HFD. Moreover, compared to CD+PCB 153 group, the abundances of 6 metabolites were increased and 18 metabolites were decreased in the mice fed high fat diet with PCB 153 exposure (HFD+PCB 153). Compared with HFD group, the abundances of 2 metabolites were increased and of 12 metabolites were reduced in HFD+PCB 153 group. These observations agree with the histological results and indicate that the metabolic effects of PCB 153 were highly dependent on macronutrient interactions with HFD. Antioxidant depletion is likely to be an important consequence of this interaction, as this metabolic disturbance has previously been implicated in obesity and NAFLD.
Keywords: FTICR-MS, metabolomics, liver, PCB 153, persistent organic pollutants
1 Introduction
The burden of liver disease has increased in the United States in parallel with the obesity epidemic. The most common liver problems, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) or its more advanced form, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), are thought to be due to overweight/obesity. Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) are persistent environmental pollutants. Exposures to PCBs have been associated with NAFLD in epidemiologic studies.1 Among PCB congeners, PCB 153 is present at the highest levels.1 Our previous work demonstrated that chronic PCB 153 exposure worsened obesity/NAFLD in mice fed a high fat diet (HFD), but had no pathologic effect in mice fed control diet (CD).2 To better understand the biochemical mechanisms underlying these observations, a comprehensive investigation using high throughput analysis such as metabolomics is necessary.
Metabolomics is the study of low molecular weight molecules (i.e., metabolites) found within cells and biological systems. Several types of instruments have been utilized to analyze metabolites including nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR)3,4 and mass spectrometry (MS).5–7 Each type of instrumental analysis affords limited coverage of the metabolites, and therefore only provides a partial metabolite profile of each sample. With the advantages of high sensitivity and accuracy, wide dynamic range, and the ability to identify metabolites from complex samples,8,9 high-resolution mass spectrometry, such as Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometer (FTICR-MS), is an attractive option in metabolomics research.10,11
The objective of this study was to determine if PCB 153 induces NAFLD in mice fed a control diet and/or alters the metabolite profile, and/or exacerbates NAFLD in mice fed a high fat diet. C57BL/6J mice were fed either a control diet (normal chow, CD) or 43% milk fat diet (high fat diet, HFD) for 12 weeks with or without PCB 153 co-exposure. At the end of feeding period, mice were anesthetized and liver samples were collected. The metabolite extracts from mouse livers were analyzed using linear trap quadruple – Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometer (LTQ-FTICR MS) via direct infusion chip-based nano-electrospray ionization (DI-nESI) – mass spectrometry.
2 Experimental Methods
2.1 Animals and Diets
The animal protocol was approved by the University of Louisville Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee. Male C57BL/6J mice (8 weeks old, n = 40; The Jackson Laboratory, Bar Harbor, Maine) were divided into 4 study groups (n = 10 per group) based on diet and PCB 153 exposure in this 12-week study utilizing a 2×2 design. The control diet (CD) was the Autoclavable Rodent Diet 5010 from LabDiet, Lebanon, IN; and it consisted of 12.7% kcal from fat, 58.5% carbohydrate, and 28.7% protein from both animal and vegetable sources. The high fat diet (HFD) was TD.88137 from Harlan Laboratories, Madison, WI; and it consisted of 42.7% kcal from fat (milk fat), 42.0% carbohydrate (sucrose and corn starch), and 15.2% protein (casein). PCB 153 (Ultra Scientific, North Kingstown, RI) was administered in corn oil (vehicle) by i.p. injection (vs. corn oil alone) at a dose of 50 mg/kg on weeks 4, 6, 8, and 10. Mice were housed in a temperature- and light-controlled room (12 h light; 12 h dark) with food and water ad libitum. The animals were euthanized (sodium pentobarbital, 40 mg/kg body weight, i.p.) at the end of week 12. Thus, four different treatment groups were evaluated in this fashion: CD, CD+PCB 153, HFD, HFD+PCB 153.
2.2 Liver Histological Studies
Liver sections were frozen using optimal cutting temperature (OCT), a liquid embedding medium or fixed in 10% buffered formalin for 24 h and embedded in paraffin for histological examinations. Tissue sections were stained with either Oil Red O (frozen OCT), hematoxylin–eosin (H&E; formalin-fixed) or Sirius red stain (formalin-fixed) and examined under light microscopy at 200× magnification. Photomicrographs were captured using a Nikon Eclipse E600 Microscope.
2.3 Metabolite Sample Preparation
Metabolites were extracted based on Bligh & Dyer’s method to cover both the polar and non-polar metabolites.12 Each sample of liver tissue was weighed and homogenized for 2 min after adding water at a concentration of 100 mg liver tissue/mL water. The homogenized sample was then stored at −80 °C until use. To extract metabolites from the homogenized liver tissue, 100 µL of homogenized liver tissue, 300 µL of water, and 1.5 mL of chloroform–methanol (v/v = 1:2) were mixed in a glass tube and vortexed for 1 min, followed by adding 0.5 mL chloroform, vortexing 1 min, adding 0.5 mL water and vortexing for 1 min. The mixture was then separated by centrifuging at room temperature for 8 min at 1100 rpm. 400 µL of the organic phase (bottom) were aspirated into another glass tube and dried under nitrogen. Each of the dried samples was dissolved in 100 µL of chloroform–methanol (v/v = 1:1) and further diluted 25 times before analysis. The aqueous phase was dried in a SpeedVac at 4 °C to remove methanol, followed by freeze drying to vaporize water. Each of the dried water phase samples was re-dissolved in 100 µL methanol and then further diluted 5 times before analysis.
2.4 Spike-In Samples
About 180 mg of liver tissue from three mice was mixed with deionized water at a concentration of 100 mg/mL. The mixture was then homogenized for 2 min and stored at −80 °C until use. To extract metabolites from liver, a 200 µL of homogenized liver sample was mixed with 1.6 mL of methanol and vortexed for 1 min, followed by centrifugation at 4 °C for 10 min at 15,000 rpm. 1.4 mL of the top solution was aspirated into a plastic tube and dried by N2 flow. After dissolving the dried sample with 200 µL of methanol, a stock solution was prepared by diluting the sample 10 times. Thirty aliquots of the stock solution were then prepared with a volume of 50 µL per aliquot.
A mixture of 15 acid standards was prepared at a concentration of 10 µg/mL per acid. The acids included L-proline, L-cystine, L-histidine, L-phenylalanine, L-tyrosine, L-lysine, L-glutamic acid, L-aspartic acid, L-leucine, nonadecanoic acid, hepadecanoic acid, heptanoic acid, nonanoic acid, pentadecanoic acid, and undecanoic acid. Twenty µL of the acid mixture was added to each of the first 10 aliquots of the stock solution, while 24 and 100 µL of the acid mixture were added to each of the second 10 aliquots and the third 10 aliquots, respectively. Methanol was then added to each of the 30 aliquots to make the total volume of each aliquot to 200 µL. This resulted in three sample groups with spiked-in acid standards. The acid concentration in each of the spike-in sample groups is 1.0 µg/mL, 1.2 µg/mL, and 5.0 µg/mL, respectively.
2.5 FTICR-MS and LTQ-MS/MS Analysis
The direct infusion experiments were performed on a hybrid mass spectrometer, the so-called linear trap quadruple – Fourier transform ion cyclotron mass spectrometer (LTQ-FTICR MS or LTQ-FT MS) (Thermo Electron Corporation, Bremen, Germany) equipped with a chip-based nano-electrospray ionization (nESI) ion source (Triversa NanoMate) (Advion Biosciences, Ithaca, NY, USA). The mass spectrometer was operated in positive ion mode. Each metabolite extract was analyzed for 5 minutes with an m/z range of 50–1,600. Mass spectra were recorded using FTICR in the profile mode and the resolving power (RP) was set at 200,000 @ m/z = 400. The maximum ion accumulation time was set at 1,000 ms. The ion optics was tuned for the sodium adduct of tricaprylin ([C27H50O6+Na+]) at m/z = 493.25 using the linear ion trap (LIT). The two most important nESI parameters were as follows: the spray voltage = +1.8 kV and the nitrogen gas pressure = 0.5 psi. The MS/MS spectrum of each metabolite ion was acquired with the LTQ-MS. The parameters were set as follows: parent ion m/z isolation window = ±0.5, spectrum accumulation time = 1 min. The collision-induced dissociation (CID) voltage is a molecule dependent parameter and ranged from 16 to 40 mV.
2.6 Data Analysis
The FTICR-MS data were processed using the software package MetSign.13 For metabolite peak quantification, the raw instrument data were first reduced into a peak list using second-order polynomial fitting (SPF) and Gaussian mixture model (GMM). After peak alignment, a contrast based method was employed for normalization.14,15 Pairwise two-tail t-test was used to study the abundance change of each metabolite between two testing sample groups.
For metabolite identification, each peak detected in the FTICR-MS data was first assigned to metabolite(s) recorded in the public databases (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG), LIPID MAPS, and the Human Metabolome Database (HMDB)), by matching the experimentally measured metabolite ion m/z value and the profile of the isotopic peaks with the theoretical data of database metabolites. The thresholds for m/z variation and isotopic peak profile similarity measured by Pearson’s correlation coefficient were set as ≤ 5 ppm and > 0.75, respectively. To narrow down the metabolite candidates of the initial assignment, the MS/MS spectra were acquired for metabolites detected with significant abundance changes between two testing sample groups. Each experimental MS/MS spectrum was compared to the in silico MS/MS spectra of all candidate metabolites generated by Mass Frontier 7.0 (Thermo Scientific, FL, US). The spectral similarity between the experimental MS/MS spectrum and the in silico MS/MS spectrum of metabolite of interest was evaluated using Pearson’s correlation coefficient. The metabolite candidate(s) with the best MS/MS spectral similarity was (were) considered as the metabolite giving rise to the experimental spectrum, while the other candidates were discarded. The authentic standards of the metabolites of interest were then analyzed on LTQ-MS/MS to further confirm the metabolite identification.
To evaluate the accuracy of both the analytical platform and the data analysis method, the true-positive rate (TPR), the positive predictive value (PPV), and their harmonic mean F1 score were calculated as follows:
| (1) |
| (2) |
| (3) |
where TP (true-positive) is the number of spiked-in acids that were detected as molecules with significant peak area changes between groups of spike-in samples by the statistical analysis, FP (false-positive) is the number of molecules that were not spiked-in acids but detected as molecules with significant peak area changes, and FN (false-negative) is the number of spiked-in acids that were not detected as molecules with significant peak area changes. TPR is called recall, and PPV is called precision and their harmonic mean F1 score can be used as an accuracy of the statistical significant test.
3 Results and Discussion
3.1 PCB 153 Worsened Steatosis in Mice Fed a High Fat Diet (HFD)
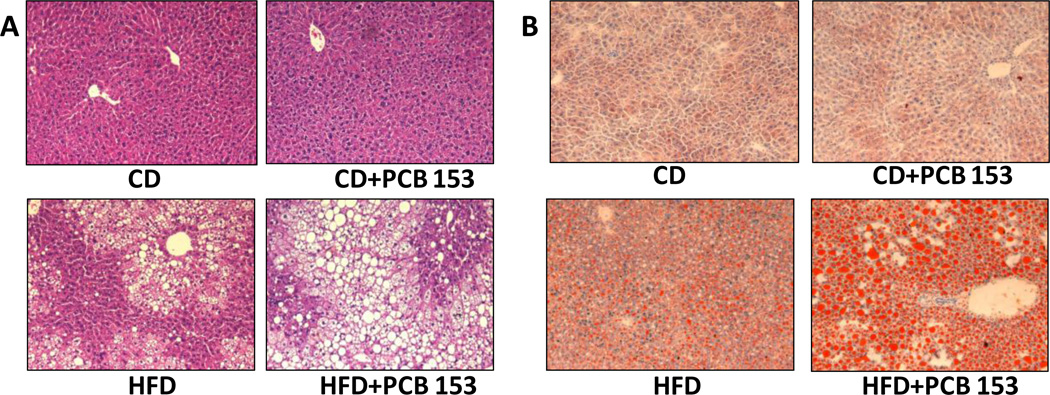
Histological examination showed that mice fed a control diet did not develop significant steatosis with or without PCB 153 administration (Oil Red O and H&E stains-Figure 1 A&B). Mice fed HFD showed minimal steatosis, but PCB 153 co-exposure drastically augmented this effect. Thus, co-administration of PCB 153 to HFD–fed mice clearly worsened hepatic steatosis while PCB 153 had no effect in the control diet fed-mice.
Figure 1.
PCB 153 worsened hepatic steatosis in mice fed a high fat diet. (A) The same group of mice also showed macro-vesicular steatosis by H&E staining. (B) Oil Red O staining of hepatic sections established the occurrence of micro-vesicular steatosis in the HFD+PCB 153 mice.
3.2 Evaluation of Metabolomics Analysis Platform
The FTICR-MS data of the spike-in samples were processed using MetSign.13 Of the 15 spiked-in acids, the metabolite peaks of 10 acids (L-proline, L-cystine, L-histidine, L-phenylalanine, L-tyrosine, L-lysine, L-glutamic acid, L-aspartic acid, L-leucine, and nonadecanoic acid) were recognized based on the match of m/z values and isotopic peak profile. Of the 10 detected acids, L-histidine, L-lysine, and nonadecanoic acid were already present in the liver metabolite extract before the addition of the acid standards. On the basis of the design of the spike-in experiment, all of the 10 detected spiked-in acids are the true-positive metabolites that have different concentrations between the two sample groups, while all other metabolites are false-positives if they are detected as the metabolites with significant concentration change between two sample groups.
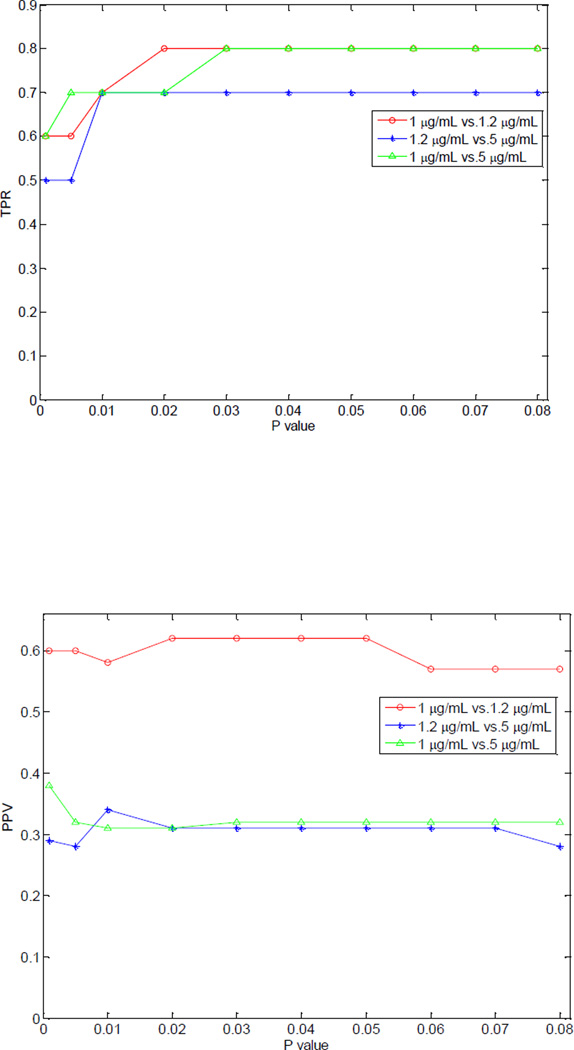
A pairwise two-tail t-test was performed to recognize the metabolite peaks with significant peak area changes between the two testing groups constructed from the three sample groups of the spike-in experiment. Figure 2 displays the relation between the p-value threshold of the t-test and the recall, the precision and F1, respectively. With the increase in the p-value threshold, the TPR increases and it reaches the highest value of 0.80 at a p-value of 0.03. There is a relatively large deviation between the PPV values of these three pairs of testing groups. The best PPV value reaches a value of 0.63 when comparing testing groups 1.0 µg/mL vs. 1.2 µg/mL, while it is only 0.30 for 1.0 µg/mL vs. 5.0 µg/mL and 1.2 µg/mL vs. 5.0 µg/mL at a p-value of 0.05. The F1 value ranges from 0.43 to 0.70 at a p-value of 0.05. The high value of TPR and moderate value of F1 indicate that the analytical platform and the data analysis method employed in this study are able to detect the metabolites with abundance changes from the biological samples. However, the analytical platform variations also introduce a certain level of false-positive discovery, resulting moderate values of PPV and F1.
Figure 2.
Relationship between the cutoff value of the p-value of t-test and the values of TPR, PPV, and F1 during the analysis of the spiked-in experiments.
3.2 Metabolite Identification
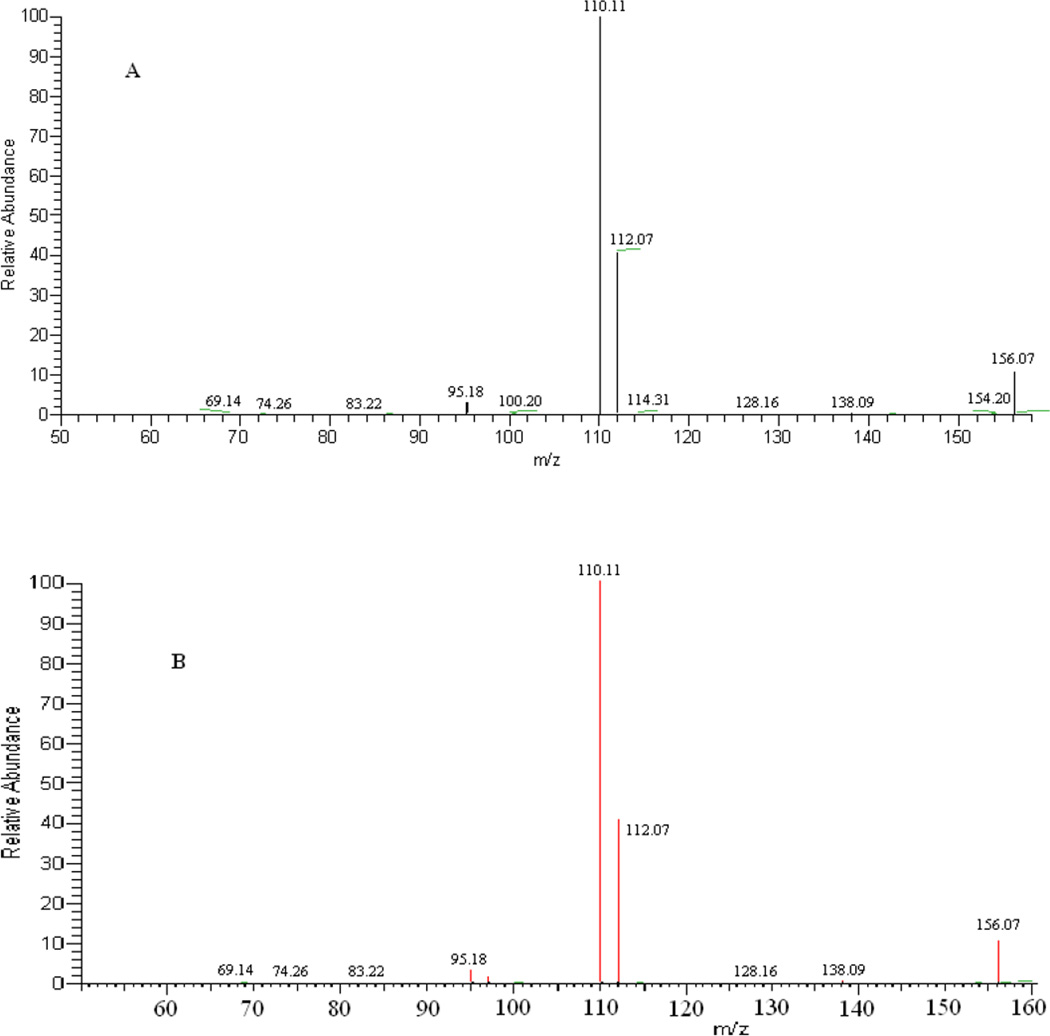
The metabolite putative assignment was accomplished by MetSign13 software using the FTICR-MS data. About 800 metabolite peaks were putatively assigned to at least one database metabolite with an m/z variation window of ≤ 5 ppm and a minimum value of 0.75 as Pearson’s correlation coefficient between the theoretical isotopic peak profile and the experimental one. To the metabolite peaks detected with significant abundance changes between two testing sample groups, an experimental MS/MS spectrum was acquired for each of these peaks on LTQ-MS/MS. An in silico MS/MS spectrum was generated for each of the putative metabolite candidates assigned to the metabolite peaks with significant abundance changes. The in silico MS/MS spectra were then matched to the experimental MS/MS spectrum of the metabolite ion. The metabolite candidate with the best MS/MS spectral match was considered as the metabolite present in the sample. Figure 3 depicts an example of MS/MS identification. The molecular ion m/z value of the peak measured by FTICR-MS is 156.07731, which was tentatively assigned to the metabolite L-histidine (a metabolite recorded in human metabolite database with database identification number HMDB00177) with an m/z value deviation of 0.06 ppm and the isotopic peak profile similarity of 0.9974. The in silico MS/MS spectrum of this putatively assigned metabolite was obtained using Mass Frontier, and the in silico MS/MS spectrum (Figure 3A) is highly similar to the experimental spectrum (Figure 3B) with a Pearson’s correlation coefficient of 1.00. Figure 3C shows the MS/MS spectrum of authentic L-histidine standard. The Pearson’s correlation coefficient between the MS/MS spectrum of the authentic L-histidine and the experimental MS/MS spectrum acquired from the biological sample is 0.85. Such a high spectral similarity significantly increases the identification confidence of L-histidine from the biological samples.
Figure 3.
An example of identifying metabolites using MS/MS information. The metabolite ion m/z value was measured using FTICR-MS as 156.0773. (A) is the experiment MS/MS spectrum of the metabolite ion. (B) is the matching result of the metabolite between the experiment MS/MS spectrum and the in silico MS/MS spectrum of the same metabolite ion generated by Mass Frontier 7.0. The matched fragment ions are highlighted in red and the unmatched fragment ions in black. (C) is the MS/MS spectrum of the L-histidine standard.
3.3 Metabolite Quantification
Four sample groups were generated in this study, including CD group (animals fed a control diet), CD+PCB 153 group (animals fed a control diet with exposure to PCB 153), HFD group (animals fed a high fat diet), and HFD+PCB 153 group (animals fed a high fat diet with exposure to PCB 153). To investigate the metabolite abundance change between two sample groups, pairwise two-tail t-test was employed with a p-value threshold of 0.05. Four pairs of sample groups were compared in this study after normalization. Specifically, we compared the metabolite profile difference between CD group and CD+PCB 153 group, CD group and HFD group, CD+PCB 153 group and HFD+PCB 153 group, and HFD group and HFD+PCB 153 group.
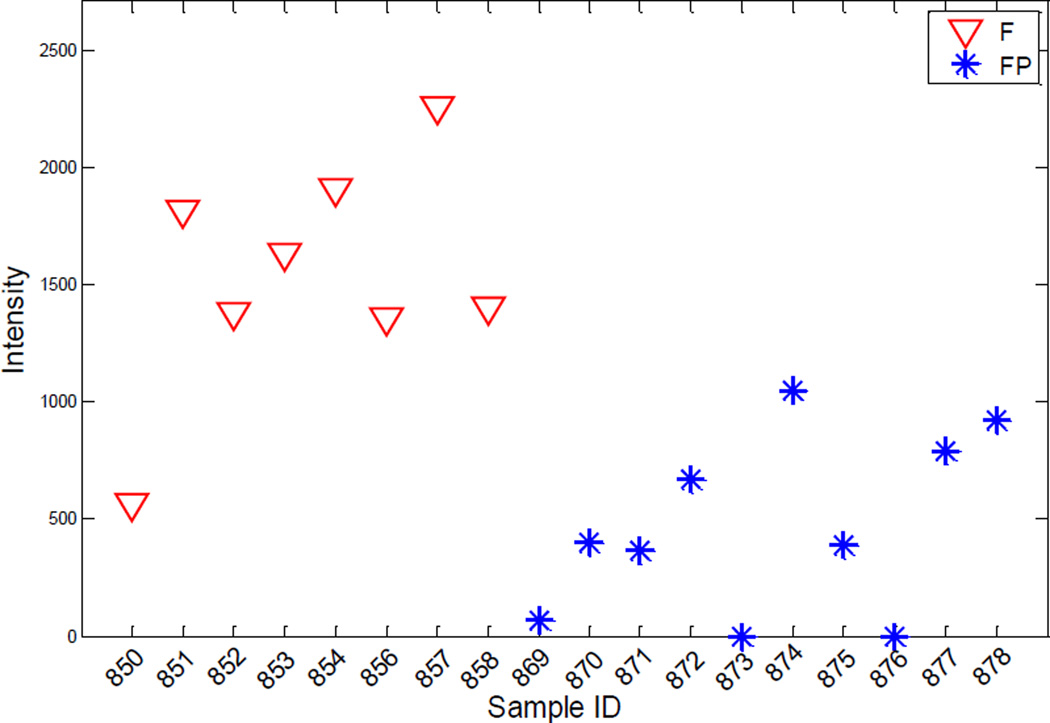
In order to have high metabolite coverage, two samples were collected from each mouse liver: water phase metabolite extract and organic phase metabolite extract. The statistical test was applied to the water phase samples and the organic phase samples, respectively. The test results were then merged for summary. A few metabolites were detected in both the organic phase samples and the water phase samples, but none of them was recognized as a molecule with significant abundance changes between two sample groups. For each of the comparisons, the peak distribution of each metabolite in the samples of the two testing sample groups was generated. Figure 4 depicts a sample peak intensity distribution of metabolites recognized with significant abundance changes between the HFD group and the HFD+PCB 153 group. It can be seen that the abundance of this metabolite (fucose 1-phosphate) is significantly decreased in the HFD+PCB 153 group with a fold-change of 2.65 and a p-value of 4.84×10−4.
Figure 4.
The peak area distribution of metabolite fucose 1-phosphate in the HFD samples (red triangles) and in the HFD+PCB 153 samples (blue stars). The abundance test (pairwise two-tail t-test) shows that the regulation of this metabolite in the HFD+PCB 153 group is decreased with a fold change of 2.65 and a p-value of 4.84×10−4.
To measure the metabolite abundance changes between two sample groups, the term fold-change was defined as the ratio of the large abundance value (peak area) of a metabolite in one group divided by the small abundance value of the same metabolite in the other group. The positive sign and negative sign indicate the abundance increase and decrease in the testing group, respectively. No metabolite was detected with significant abundance changes between the CD group and the CD+PCB 153 group. This indicates that PCB 153 alone has no significant effect on liver at the metabolite level. However, a total of 14 metabolites were detected with significant abundance changes between the HFD and HFD+PCB 153 groups, as listed in Table 1.
Table 1.
Metabolites detected with significant abundance changes between the HFD group and the HFD+PCB 153 group.
| Adduct | Metabolite database | fold | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | p_value | ||||
| m/z | ion | IDs | change | ||
| 156.07731 | L-Histidine | H+ | C00135,HMDB00177 | −1.80 | 4.64E-02 |
| 170.03332 | Creatine | K+ | HMDB00064,C00300 | −1.83 | 4.72E-02 |
| 175.00113 | Erythronic acid | K+ | HMDB00613 | 28.77 | 8.35E-05 |
| 260.05434 | D-Glucosamine6-phosphate | H+ | C00352 | −2.19 | 4.14E-03 |
| 262.07009 | Fucose 1-phosphate | NH4+ | HMDB01265 | −2.65 | 4.84E-04 |
| 376.05929 | S-(Hydroxymethyl)glutathione | K + | HMDB04662 | −2.97 | 1.14E-02 |
| 346.0469 | Glutathione | K+ | HMDB00125,C00051 | −5.91 | 2.04E-03 |
| 459.25103 | Stearoylglyceronephosphate | Na+ | C03805 | −1.67 | 3.14E-02 |
| 266.153 | Isobutylphendienamide | Na+ | C10944 | −2.57 | 1.71E-02 |
| 309.16728 | Fructoselysine | H+ | C16488 | −2.94 | 5.96E-03 |
| 347.1235 | Fructoselysine | K+ | C16488 | −2.08 | 1.70E-02 |
| 283.03409 | Uridine | K+ | HMDB00296,C00299 | −1.80 | 4.99E-02 |
| 559.30352 | Cucurbitacin P | K+ | LMST01010114 | −2.02 | 1.25E-02 |
| 15alpha,25-dihydroxy-16beta,23R:16alpha,24S-diepox | |||||
| 685.39477 | y-9beta,19-cyclolanostan-3beta-yl | Na+ | LMST01100006 | 2.05 | 3.68E-03 |
| 2-O-acetylalpha-L-arabinopyranoside |
Among the metabolites with significant changes between the HFD and HFD+PCB 153 groups, erythronic acid had the largest abundance changes with a 28.8-fold increase in the HFD+PCB 153 group (p = 8.35×10−5). Erythronic acid is formed either by oxidation of D-N-acetyl glucosamine, an alternating unit of hyaluronic acid,16 or by degradation of ascorbic acid (vitamin C) and glycated proteins.17
Compared with the changes observed between the CD group and CD+PCB 153 group, the metabolite abundance changes between the HFD and HFD+PCB 153 groups demonstrated the presence of a diet-toxin interaction between PCB 153 and HFD. This interaction may affect some metabolic pathways, and therefore induce the abundance changes of these measured compounds. Thus, PCB 153 alone does not induce NAFLD but it worsens NAFLD caused by a HFD, which agrees with our histological examination (Figure 1).
For the CD+PCB 153 vs. HFD+PCB 153 groups, 50 FTICR-MS peaks were detected with significant abundance changes in water phase samples and 14 peaks in organic phase samples. Combining the water phase and the organic phase results, 24 metabolites were identified by in silico MS/MS spectral matching, although three of them (m/z = 369.1178, 203.0535 and 365.1075) do not have unique identification (Table 2). The identified metabolites include glycerolipids, sterol lipids, phospholipids, sphingolipids and other small molecules. It should be noted that the FTICR-MS peaks with m/z = 309.1673 and 347.1235 were both identified as fructoselysine with different adduct ions H+ and K+, respectively. The same fold change (−2.43) between the two testing sample groups confirms the accuracy of our FTIRC-MS and data analysis platforms. Another case is the identification of FTICR-MS peaks with m/z = 156.0773 and 194.0335. The in silico MS/MS spectral matching identified these two peaks as being generated by the metabolite L-histidine, with adduct ions H+ and K+, respectively. The fold changes of these two FTICR-MS peaks between the two testing groups are −1.90 and −1.94, respectively.
Table 2.
Metabolites detected with significant abundance changes between the CD+PCB 153 group and the HFD+PCB 153 group.
|
m/z |
Metabolite Name |
Adduct ion |
Metabolite database IDs |
Fold change |
p_value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 156.0773 | L-histidine | H+ | C00135,HMDB00177 | −1.90 | 1.18E-02 |
| 194.0335 | L-histidine | K+ | C00135,HMDB00177 | −1.95 | 2.77E-02 |
| 227.0439 | N-acetylglutamine | K+ | HMDB06029 | −2.17 | 2.23E-02 |
| 175.0011 | Erythronic acid | K+ | HMDB00613 | 16.73 | 2.90E-04 |
| 219.0274 | 2S,4S,5R,6-tetrahydroxy-hexanoic acid | K+ | LMFA01050392 | −2.81 | 1.64E-03 |
| 249.0383 | Chorismate | Na+ | HMDB12199 | −2.38 | 3.39E-03 |
| 260.0543 | D-glucosamine6-phosphate | H+ | C00352 | −1.84 | 4.85E-02 |
| 268.1054 | Adenosine | H+ | HMDB00050 | −1.64 | 2.76E-02 |
| 286.2757 | heptadecasphing-4-enine | H+ | LMSP01040002 | 3.29 | 5.64E-03 |
| 347.1235 | Fructoselysine | K+ | C16488 | −2.43 | 3.62E-02 |
| 309.1673 | Fructoselysine | H+ | C16488 | −2.43 | 4.25E-02 |
| 346.0469 | Glutathione | K+ | C00051,HMDB00125 | −19.86 | 9.13E-03 |
| 376.0593 | S-(hydroxymethyl)glutathione | K+ | HMDB04662 | −3.67 | 5.56E-04 |
| 381.0813 | Melibiose | K+ | HMDB00048 | −3.79 | 8.55E-04 |
| 402.0964 | S-lactoylglutathione | Na+ | C03451,HMDB01066 | −3.51 | 9.51E-04 |
| 559.3035 | Cucurbitacin P | K+ | LMST01010114,C08804 | −1.87 | 1.87E-02 |
| 867.6961 | PC(o-22:1(13Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) | NH4+ | HMDB13451 | 2.45 | 1.20E-03 |
| 615.4948 | 1,2-di-(9Z-heptadecenoyl)-sn-glycerol 15alpha,25-dihydroxy-16beta,23R:16alpha,24S-diepoxy-9 |
Na+ | LMGL02010021 | −2.37 | 6.24E-04 |
| 685.3948 | beta,19-cyclolanostan-3beta-yl 2-O-acetyl-alpha-L-arabinopyranoside |
Na+ | LMST01100006 | 2.25 | 5.01E-04 |
| 903.7553 | 1-docosanoyl-2-(15Z-tetracosenoyl)-sn-glycero-3-phosph oethanolamine |
NH4+ | LMGP02010292 | 8.09 | 1.13E-03 |
| 899.7505 | 1-heptadecanoyl-2-(9Z-heptadecenoyl)-3-octadecanoyl-sn -glycerol |
K+ | LMGL03010071 | 5.86 | 1.44E-05 |
| 369.1178 | O-feruloylquinate | Na+ | C02572 | −3.29 | 2.01E-02 |
| Aucubin | Na+ | C09771,LMPR0102070006 | |||
| 203.0535 | D-glucose | Na+ | C00031 | −2.22 | 5.73E-03 |
| 2S,4S,5R,6-tetrahydroxy-hexanoic acid | Na+ | LMFA01050392 | |||
| 365.1075 | Melibiose | Na+ | C05402,HMDB00048 | −5.86 | 5.38E-05 |
| Sucrose | Na+ | C00089 |
For the CD vs. HFD groups, 57 FTICR-MS peaks were detected having significant abundance different between the CD group and the HFD group in the water phase samples and 17 peaks in the organic phase samples. Combining the results of the water phase and the organic phase samples, 25 metabolites were further confirmed by MS/MS spectral matching. Of the 25 compounds, two do not have a unique identification (Table 3). It should be noted that metabolite PC (o-22:1(13Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) has a 4.44-fold increase in the HFD group, which agrees with a previous study.18
Table 3.
Metabolites detected with significant abundance changes between the CD group and the HFD group.
|
m/z |
Metabolite Name |
Adduct ion |
Metabolite database IDs |
Fold Change |
p_value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 175.0011 | Erythronic acid | K+ | HMDB00613 | −26.70 | 4.16E-02 |
| 219.0274 | 2S,4S,5R,6-tetrahydroxy-hexanoic acid | K+ | LMFA01050392 | −1.72 | 1.21E-02 |
| 251.054 | 2-Hydroxy-3-carboxy-6-oxo-7-methylocta-2,4-dienoate | Na+ | C06581 | −2.25 | 4.58E-03 |
| 262.0701 | Fucose 1-phosphate | NH4+ | HMDB01265 | 1.93 | 5.55E-03 |
| 286.2757 | heptadecasphing-4-enine | H+ | LMSP01040002 | 3.92 | 1.74E-03 |
| 355.0671 | 2-Caffeoylisocitrate | H+ | C02927 | −1.92 | 4.54E-02 |
| 364.1238 | Lactosamine | Na+ | HMDB06591 | 1.77 | 9.17E-03 |
| 365.0966 | Streptidine6-phosphate | Na+ | C01121 | −1.80 | 6.33E-03 |
| 365.102 | Hinokitiolglucoside | K+ | C15451 | −3.93 | 3.16E-04 |
| 380.0977 | Lactosamine | K+ | HMDB06591 | 1.36 | 4.94E-02 |
| 381.069 | Streptidine6-phosphate | K+ | C01121 | −2.36 | 1.41E-03 |
| 384.1218 | Acutumidine | H+ | C10565 | −1.87 | 1.26E-02 |
| 390.3365 | N-(5-hydroxy-pentyl)-5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z-eicosatetraenoyl amine | H+ | LMFA08020020 | −4.94 | 3.06E-02 |
| 399.0858 | Elephantopin | K+ | LMPR0103090004,C09403 | −2.55 | 5.92E-03 |
| 459.251 | Stearoylglyceronephosphate | Na+ | C03805 | 2.10 | 1.33E-03 |
| 497.3475 | 25-Hydroxy-24-epi-brassinolide | H+ | C11050 | 2.05 | 4.42E-02 |
| 519.3296 | 25-Hydroxy-24-epi-brassinolide | Na+ | C11050 | 1.96 | 7.21E-03 |
| 527.1377 | 3-Fucosyllactose | K+ | HMDB02094 | −2.53 | 1.15E-02 |
| 535.3036 | 25-Hydroxy-24-epi-brassinolide | K+ | C11050 | 1.64 | 2.11E-02 |
| 615.4948 | 1,2-di-(9Z-heptadecenoyl)-sn-glycerol | Na+ | LMGL02010021 | −3.66 | 3.02E-02 |
| 663.0984 | Isoorientin 3'-O-glucuronide | K+ | LMPK12110311 | −5.87 | 6.50E-04 |
| 867.6961 | PC(o-22:1(13Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) | NH4+ | HMDB13451 | 4.44 | 5.25E-05 |
| 879.6859 | 1-heptadecanoyl-2,3-di-(9Z,12Z-heptadecadienoyl)-sn-gly cerol | K+ | LMGL03010067 | 28.39 | 1.34E-05 |
| 203.0535 | 2S,4S,5R,6-tetrahydroxy-hexanoic acid | Na+ | LMFA01050392 | −1.47 | 2.23E-02 |
| D-Glucose | Na+ | C00031 | |||
| 365.1075 | Melibiose | Na+ | C05402,HMDB00048 | −3.18 | 1.49E-04 |
| Sucrose | Na+ | C00089 |
Several important limitations in the study design could impact the generalizability of these results. First, differences existed between CD and HFD, not only in macronutrient content and source, but also in micronutrient composition. However, similar, but not identical, vitamin and mineral mixes were given with each diet. These potential confounders could impact metabolite differences observed between diet groups regardless of PCB administration. The primary objective of this study was to determine the effects of PCB administration within a given diet (e.g. HFD vs. HFD+PCB 153, and CD vs. CD+PCB 153), and these analyses would be unaffected. Thus, the most important conclusion from our work is that macronutrient-toxicant interactions are critical determinants of PCB 153’s effects on hepatic metabolites. Additional consideration must also be given to the PCB dosing protocol. PCBs were manufactured as mixtures, and multiple highly chlorinated PCB congeners have simultaneously bio-accumulated in humans primarily by ingestion.1 This study investigated only a single congener (PCB 153), which is the single most abundant PCB in humans.1 Because a metabolomics dose response curve has never been performed for any PCB, for this initial study a relatively high cumulative dose (200 mg/kg, administered to mice i.p., over 12 weeks) was selected based on a previously published National Toxicology Program Protocol (NTP TR 530, 210 mg/kg cumulative dose, administered to rats by gavage over 14-weeks.19 The NTP protocol produced lipid-adjusted serum PCB levels approximately 10-fold higher than the most highly exposed subject from the Anniston, Alabama human cohort of highly-exposed residents living near a former PCB production facility.20 Limitations regarding our PCB dosing protocol must be acknowledged and future studies investigating PCB mixtures at lower doses and more physiologic routes of administration (e.g. gavage) have been planned. However, the most important finding of this study is that even at a relatively high dose of PCB 153, no effects on hepatic metabolites were observed in the absence of high fat feeding. Therefore, the data suggest that the PCB-HFD interaction could be more important than the cumulative PCB dose.
3.4 Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA)
As demonstrated by the spike-in experimental data, the analytical platform and the data analysis method employed in this study can introduce a certain level of technical variations. Such variations can cause both false-positive and false-negative discoveries. On the other hand, the quantitative analysis was performed on the abundance of each individual metabolite. The inter-relationships between the various metabolites were not considered however, and thus, IPA was employed. IPA correlates specifically targeted metabolites with potential metabolic pathways for data analysis that helps researchers to model, analyze, and understand complex biological and chemical systems at the core of life science research.21,22 Therefore, it is necessary to incorporate the analytical discovery with the metabolite pathway analysis to further filter and/or enrich the analytical discovery.
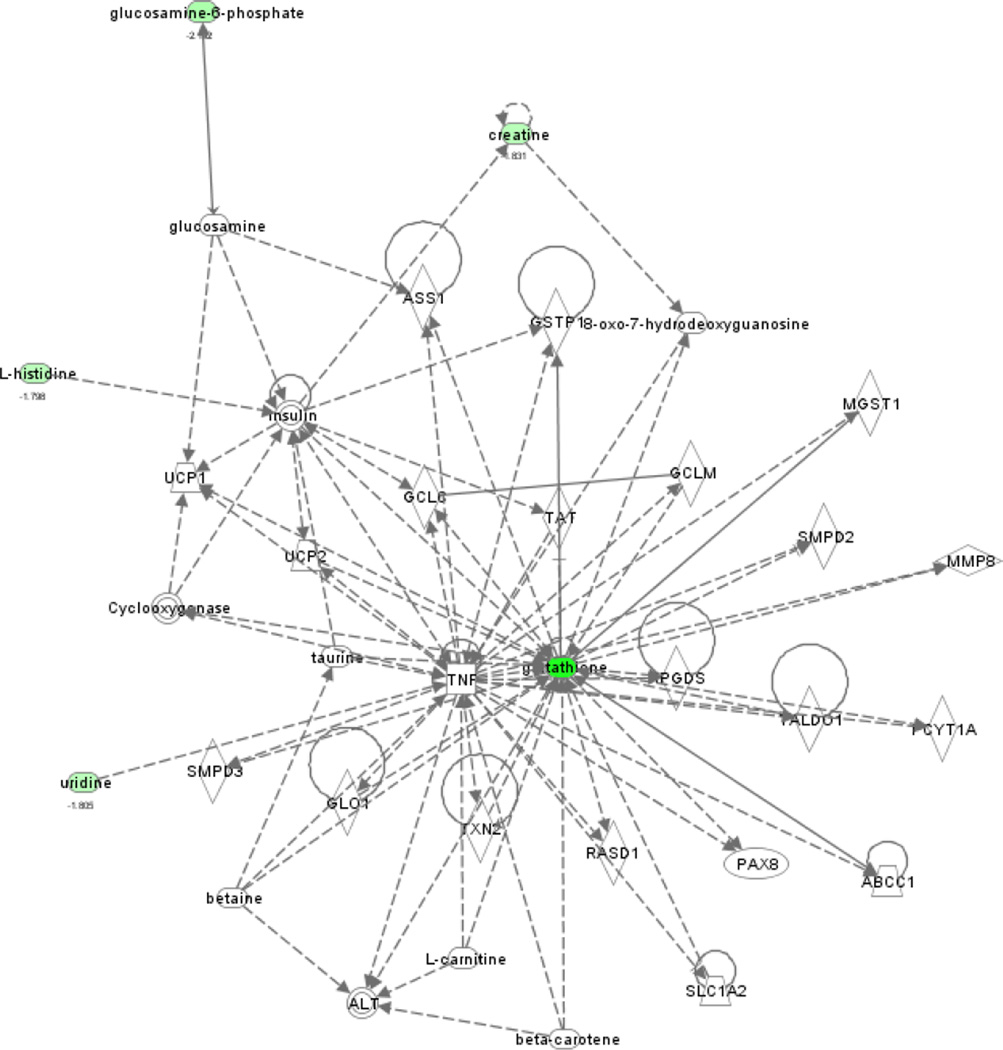
All 14 metabolites recognized with significant abundance changes between the HFD group and the HFD+PCB 153 group were subjected to IPA for network analysis. Six metabolites were mapped into the IPA database. The most probable metabolite network reported by IPA contained 5 metabolites including creatine, glucosamine-6-phosphate, glutathione, L-histidine and uridine with a score of 14 (Figure 5). The IPA analysis resulted in that the top hepatotoxicity function is glutathione (GSH) depletion in liver and the top canonical pathway is glutamate metabolism. GSH, a tripeptide composed of glutamine, cysteine and glycine, is the major intracellular anti-oxidant in the liver, and its physiological function is to prevent damage to cellular components that may be caused by xenobiotic metabolites, reactive oxygen species (ROS) and free radicals.23 In the liver, glutamate is the terminus for release of ammonia from amino acids, and the intrahepatic concentration of glutamate modulates the rate of ammonia detoxification into urea.24
Figure 5.
IPA proof-of-knowledge characterization of the metabolic networks in mouse liver affected by PCB 153. The dashed line indicates indirect interactions between metabolites while the solid line means a direct metabolite interaction. Filled circles represent metabolites discovered in this work and the color of each filled circle represents the direction and magnitude of fold-changes. Green color means down-regulated, red color means up-regulated.
GSH (entry 7 of Table 1) had a 5.91-fold decrease in the HFD+PCB 153 group (p-value of 2.03×10−3) and its conjugate, S-(hydroxymethyl)glutathione (entry 6) had a 2.97-fold decrease (p-value of 1.14×10−2). Hepatic mitochondrial GSH depletion has been associated with the progression of alcoholic liver disease25 and blood GSH depletion with obesity and diabetes.26 Lower hepatic GSH content has also been reported in non-alcoholic steatosis.27 Furthermore, Swenberg et al. reported the formation of oxidative DNA lesions in PCB 126-exposed rats which was likely due to ROS generation.28 Therefore, the GSH depletion noted in the steatotic livers of mice treated with HFD+PCB 153 implies increased oxidative stress leading to extensive utilization of GSH which eventually decreased liver GSH stores. Further evidence for oxidative stress can also be accounted for by the increased levels of erythronic acid, the degradation product of vitamin C, another crucial anti-oxidant.
The mechanism by which PCB 153 induces oxidative stress needs further investigation. PCB 153 is very poorly metabolized29 and therefore conjugation of its metabolites is very unlikely to deplete glutathione. Unlike PCB 126, which is a potent Ah-receptor agonist strongly inducing CYP1A activity, PCB 153 is reported to have weak “Phenobarbital” activity30 suggesting it will be a relatively poor inducer of CYP2B and thus is expected to have relatively poor ability to induce monooxygenase activity which could increase the levels of reactive compounds that reduce glutathione levels. However, it is possible that the depletion could be due to glutathione consumption by increased lipid peroxides which should have been generated within the steatotic livers of the HFD+PCB 153 group. It must also be noted that our results are consistent with the findings of Twaroski et al., as we observed no effects of PCB 153 on glutathione in the presence of a normal rodent chow diet.31 PCB 153-mediated glutathione depletion occurring only in the presence of HFD is not only innovative, but also probably the most important finding in this study.
Regardless of its mechanism, the reduction in glutathione (entry 7 of Table 1) would diminish its availability for transformation into S-(hydroxymethyl)glutathione (entry 6), and should trigger the up-regulation of glutathione biosynthesis from glutamate, glycine, and cysteine, its component amino acids. Glutamate is made from the TCA cycle intermediate 2-oxoglutarate and ammonia, which could account for the decrease in measured D-glucosamine 6-phosphate (entry 4), either from its use as an ammonia source or from lowered production due to ammonia depletion. Histidine (entry 1) can also be rationalized as an ammonia source by decarboxylation and oxidation or as a source of both ammonia and glutamate via the pathway initiated by the action of histidine ammonia-lyase. The synthesis of uridine (entry 12) likely falls as ammonia is shunted into glutamate production. The degradation of creatine (entry 2) gives rise to glycine through the action of creatinase and sarcosine dehydrogenase. Interestingly, reduced serum creatine levels in humans and mouse models has recently been reported in a metabolomic profiling studies of steatosis32,33 and NAFLD progression.34 Such a simple accounting of glutathione consumption upon exposure of the liver to PCB 153, therefore, provides good rationalization of the observed reduction in metabolite levels (Table 1), centered on the glutamate metabolism.
IPA mapped 7 of the 24 metabolites recognized with significant abundance changes between the CD+PCB 153 group and HFD+PCB 153 group. The most probable metabolite network reported by IPA contained 6 metabolites including adenosine, L-histidine, glutathione, D-glucose, melibiose and S-lactoylglutathione with a score of 16. The top hepatotoxicity function is glutathione depletion in liver and the top canonical pathway is also glutamate metabolism. D-glucose was detected with a 2.22-fold decrease in the HFD+PCB 153 group, indicating a significant decrease of D-glucose in the liver due to the exposure to PCB 153. D-glucose has been used as a biomarker for diagnosis of liver cancer.35 GSH was detected with a 19.9-fold decrease in the HFD+PCB 153 group, and this provides further evidence in the importance of HFD in PCB 153-mediated GSH depletion.
Seven of the 25 metabolites with significant abundance changes between the CD group and HFD group were mapped to the IPA database. The most probable metabolite network lipid metabolism, molecular transport, small molecule biochemistry reported by IPA has a score of 11 and contains 5 metabolites including stearoylglyceronephosphate, L-fucose 1-phosphate, melibiose, streptidine 6-phosphate, and 2-Hydroxy-3-carboxy-6-oxo-7-methylocta-2,4-dienoate.
4 Conclusions
Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) are persistent environmental pollutants. The hepatic effects of PCB 153 in mice were investigated via a direct infusion nano-electrospray ionization linear trap quadrupole – Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry (DI-nESI-LTQ-FTICR MS). No difference was observed in the metabolite profile of mice a fed control diet with or without PCB 153 exposure. However, when mice fed a high fat diet were compared with mice fed a control diet, 15 metabolites were reduced and 10 metabolites were increased. Compared to the CD+PCB 153 group, 18 metabolites were reduced while 6 metabolites were increased in the HFD+PCB 153 group. Compared with the HFD group, 12 metabolites were reduced including glutathione and creatine and 2 metabolites were increased, most notably erythronic acid, in the HFD+PCB 153 group. These data indicate that PCB 153 had no observable effects on metabolites when administered to mice fed CD, which is consistent with the absence of histopathology. In contrast, when administered with HFD, PCB 153 produced significant metabolic changes (vs. HFD, or CD+PCB 153), which are consistent with worsened obesity/NAFLD pathology. Thus, the metabolic effects of PCB 153 were heavily dependent on macronutrient interactions with HFD. Antioxidant depletion is likely to be an important consequence of this interaction, as this mechanism has previously been implicated in obesity/NAFLD.
Acknowledgment
The authors thank Mrs. Marion McClain for review of this manuscript. The authors also thank to the mass spectrometry facility of the Center for Regulatory and Environmental Analytical Metabolomics (CREAM) at the University of Louisville. This work was supported by NIH grants 1R01ES021375-01, 1RC2AA019385, 1RO1GM087735, P01AA017103, P30AA019360, R01AA015970, R37AA010762, R01AA018016, R01AA018869, R01DK7071765, R01AA018844, 5P20RR024489-02 and K23AA18399-01A, and the VA.
References
- 1.Cave M, Appana S, Patel M, Falkner KC, McClain CJ, Brock G. Polychlorinated Biphenyls, Lead, and Mercury Are Associated with Liver Disease in American Adults: NHANES 2003–2004. Environ Health Persp. 2010;118(12):1735–1742. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1002720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Wahlang B, Falkner K, Conklin D, McClain C, Cave M. Polychlorinated biphenyl 153 worsens non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in C57BL/6 mice. The Toxicologist CD Supplement to Toxicological Sciences — An Official Journal of the Society of Toxicology. 2012;126(1):84. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Zhang S, Nagana Gowda GA, Ye T, Raftery D. Advances in NMR-based biofluid analysis and metabolite profiling. Analyst. 2010;135(7):1490–1498. doi: 10.1039/c000091d. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Schripsema J. Application of NMR in plant metabolomics: techniques, problems and prospects. Phytochem Anal. 2010;21(1):14–21. doi: 10.1002/pca.1185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Mohamed R, Varesio E, Ivosev G, Burton L, Bonner R, Hopfgartner G. Comprehensive analytical strategy for biomarker identification based on liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry and new candidate confirmation tools. Anal Chem. 2009;81(18):7677–7694. doi: 10.1021/ac901087t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Zhong W, Zhao YT, Tang YN, Wei XL, Shi X, Sun WL, Sun XH, Yin XM, Sun XG, Kim S, McClain CJ, Zhang X, Zhou ZX. Chronic Alcohol Exposure Causes Adipose Fat Overflux to the Liver in Mice: A Mechanistic Link between Lipodystrophy and Steatosis. Hepatology. 2011;54:978a–978a. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Thysell E, Surowiec I, Hornberg E, Crnalic S, Widmark A, Johansson AI, Stattin P, Bergh A, Moritz T, Antti H, Wikstrom P. Metabolomic characterization of human prostate cancer bone metastases reveals increased levels of cholesterol. PLoS One. 2010;5(12):e14175. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0014175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Weber RJM, Southam AD, Sommer U, Viant MR. Characterization of Isotopic Abundance Measurements in High Resolution FT-ICR and Orbitrap Mass Spectra for Improved Confidence of Metabolite Identification. Anal Chem. 2011;83(10):3737–3743. doi: 10.1021/ac2001803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Tan AM, Benetton S, Henion JD. Chip-based solid-phase extraction pretreatment for direct electrospray mass spectrometry analysis using an array of monolithic columns in a polymeric substrate. Anal Chem. 2003;75(20):5504–5511. doi: 10.1021/ac030196w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Higgs RE, Zahn JA, Gygi JD, Hilton MD. Rapid method to estimate the presence of secondary metabolites in microbial extracts. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2001;67(1):371–376. doi: 10.1128/AEM.67.1.371-376.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Bradford BU, O'Connell TM, Han J, Kosyk O, Shymonyak S, Ross PK, Winnike J, Kono H, Rusyn I. Metabolomic profiling of a modified alcohol liquid diet model for liver injury in the mouse uncovers new markers of disease. Toxicol Appl Pharm. 2008;232(2):236–243. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2008.06.022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bligh EG, Dyer WJ. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Wei XSW, Shi X, Koo I, Wang B, Zhang J, Yin X, Tang Y, Bogdanov B, Kim S, Zhou Z, McClain C, Zhang X. MetSign: A Computational Plaform for High-resolution Mass Spectrometry-based Metabolomics. Anal. Chem. 2011;83(20):7668–7675. doi: 10.1021/ac2017025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Bolstad BM, Irizarry RA, Astrand M, Speed TP. A comparison of normalization methods for high density oligonucleotide array data based on variance and bias. Bioinformatics. 2003;19(2):185–193. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/19.2.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Astrand M. Contrast normalization of oligonucleotide arrays. Journal of Computational Biology. 2003;10(1):95–102. doi: 10.1089/106652703763255697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Jahn M, Baynes JW, Spiteller G. The reaction of hyaluronic acid and its monomers, glucuronic acid and N-acetylglucosamine, with reactive oxygen species. Carbohydr Res. 1999;321(3–4):228–234. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(99)00186-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Harding JJ, Hassett PC, Rixon KC, Bron AJ, Harvey DJ. Sugars including erythronic and threonic acids in human aqueous humour. Curr Eye Res. 1999;19(2):131–136. doi: 10.1076/ceyr.19.2.131.5334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kim HJ, Kim JH, Noh S, Hur HJ, Sung MJ, Hwang JT, Park JH, Yang HJ, Kim MS, Kwon DY, Yoon SH. Metabolomic Analysis of Livers and Serum from High-Fat Diet Induced Obese Mice. J Proteome Res. 2011;10(2):722–731. doi: 10.1021/pr100892r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.NTP Toxicology and Carcinogenesis Studies of a Binary Mixture of 3,3',4,4',5-Pentachlorobiphenyl (PCB 126) (CAS No. 57465-28-8) and 2,2',4,4',5,5'-Hexachlorobiphenyl (PCB 153) (CAS No. 35065-27-1) in Female Harlan Sprague-Dawley Rats (Gavage Studies) Natl Toxicol Program Tech Rep Ser. 2006;(530):1–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Goncharov A, Pavuk M, Foushee HR, Carpenter DO. Blood pressure in relation to concentrations of PCB congeners and chlorinated pesticides. Environ Health Perspect. 2011;119(3):319–325. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1002830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Nehme A, Lobenhofer EK, Stamer WD, Edelman JL. Glucocorticoids with different chemical structures but similar glucocorticoid receptor potency regulate subsets of common and unique genes in human trabecular meshwork cells. Bmc Med Genomics. 2009;2:58. doi: 10.1186/1755-8794-2-58. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Lv HT, Liu L, Palacios G, Chen X. Metabolomic analysis characterizes tissue specific indomethacin-induced metabolic perturbations of rats. Analyst. 2011;136(11):2260–2269. doi: 10.1039/c1an15126f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Pompella A, Visvikis A, Paolicchi A, De Tata V, Casini AF. The changing faces of glutathione, a cellular protagonist. Biochem Pharmacol. 2003;66(8):1499–1503. doi: 10.1016/s0006-2952(03)00504-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kellly A, Stanley CA. Disorders of glutamate metabolism. Ment. Retard. Dev. D. R. 2001;7:287–295. doi: 10.1002/mrdd.1040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Hirano T, Kaplowitz N, Tsukamoto H, Kamimura S, Fernandez-Checa JC. Hepatic mitochondrial glutathione depletion and progression of experimental alcoholic liver disease in rats. Hepatology. 1992;16(6):1423–1427. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840160619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Pastore A, Ciampalini P, Tozzi G, Pecorelli L, Passarelli C, Bertini E, Piemonte F. All glutathione forms are depleted in blood of obese and type 1 diabetic children. Pediatr Diabetes. 2011:1399–5448. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-5448.2011.00806.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Altomare E, Vendemiale G, Albano O. Hepatic glutathione content in patients with alcoholic and non alcoholic liver diseases. Life Sci. 1988;43(12):991–998. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(88)90544-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Jeong YC, Walker NJ, Burgin DE, Kissling G, Gupta M, Kupper L, Birnbaum LS, Swenberg JA. Accumulation of M1dG DNA adducts after chronic exposure to PCBs, but not from acute exposure to polychlorinated aromatic hydrocarbons. Free Radic Biol Med. 2008;45(5):585–591. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2008.04.043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Lutz RJ, Dedrick RL, Tuey D, Sipes IG, Anderson MW, Matthews HB. Comparison of the pharmacokinetics of several polychlorinated biphenyls in mouse, rat, dog, and monkey by means of a physiological pharmacokinetic model. Drug Metab Dispos. 1984;12(5):527–535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Safe S, Bandiera S, Sawyer T, Robertson L, Safe L, Parkinson A, Thomas PE, Ryan DE, Reik LM, Levin W, et al. PCBs: structure-function relationships and mechanism of action. Environ Health Perspect. 1985;60:47–56. doi: 10.1289/ehp.856047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Twaroski TP, O'Brien ML, Robertson LW. Effects of selected polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB) congeners on hepatic glutathione, glutathione-related enzymes, and selenium status: implications for oxidative stress. Biochem Pharmacol. 2001;62(3):273–281. doi: 10.1016/s0006-2952(01)00668-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Kalhan SC, Guo L, Edmison J, Dasarathy S, McCullough AJ, Hanson RW, Milburn M. Plasma metabolomic profile in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Metabolism. 2011;60(3):404–413. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2010.03.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Mallin K, McCann K, D'Aloisio A, Freels S, Piorkowski J, Dimos J, Persky V. Cohort mortality study of capacitor manufacturing workers, 1944–2000. J Occup Environ Med. 2004;46(6):565–576. doi: 10.1097/01.jom.0000128156.24767.12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Barr J, Vazquez-Chantada M, Alonso C, Perez-Cormenzana M, Mayo R, Galan A, Caballeria J, Martin-Duce A, Tran A, Wagner C, Luka Z, Lu SC, Castro A, Le Marchand-Brustel Y, Martinez-Chantar ML, Veyrie N, Clement K, Tordjman J, Gual P, Mato JM. Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry-based parallel metabolic profiling of human and mouse model serum reveals putative biomarkers associated with the progression of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Proteome Res. 2010;9(9):4501–4512. doi: 10.1021/pr1002593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Jisuk Bae Y-CH, Y K-Y. Factors of metabolic syndrome and risk of cancer: The Korean Multi-Center Cancer Cohort (KMCC) and the Incheon Health Examinees Cohort (IHEC) Amer Assoc Cancer Res. 2006;47 [Google Scholar]