Abstract
In this study, we report a novel mechanism of action for a cytotoxic derivative of betulinic acid (BA). B10 is a semi-synthetic glycosylated derivative of BA selected for its enhanced cytotoxic activity. Interestingly, although B10 induces apoptosis, caspase-3 downregulation incompletely prevents B10-induced cell death, Bcl-2 overexpression fails to protect cells and DNA fragmentation rates do not reflect cell death rates in contrast to cytoplasmic membrane permeabilization. These results implicate that apoptotic and non-apoptotic cell death coexist upon B10 treatment. Unexpectedly, we found that B10 induces autophagy and also abrogates the autophagic flux. B10 destabilizes lysosomes as shown by Lysotracker Red staining and by cathepsin Z and B release from lysosomes into the cytoplasm. Consistently, the cathepsin inhibitor Ca074Me significantly decreases B10-induced cell death, further supporting the fact that the release of lysosomal enzymes contributes to B10-triggered cell death. Downregulation of ATG7, ATG5 or BECN1 by RNAi significantly decreases caspase-3 activation, lysosomal permeabilization and cell death. Thus, by concomitant induction of autophagy and inhibition of the autophagic flux, B10 turns autophagy into a cell death mechanism. These findings have important implications for the therapeutic exploitation of BA derivatives, particularly in apoptosis-resistant cancers.
Keywords: betulinic acid, apoptosis, autophagy, lysosomes
Bioactive natural compounds or their semi-synthetic derivatives offer a considerable therapeutic potential against cancer.1 Among these, betulinic acid (BA), a triterpenoid initially derived from white birch tree, has received attention because of its multiple biological activities in mammalian cells. The pluripotency of BA is of great interest, as this compound is active against HIV, parasitic diseases and cancer.2, 3, 4, 5 Nevertheless, the therapeutic application of this drug is currently limited because of its poor solubility in aqueous solvents and an ill-defined mode of action. To overcome these limitations, a wide variety of semi-synthetic derivatives of BA has been generated to improve its pharmacological properties for in vivo studies. In addition, detailed studies are being performed to elucidate the mechanisms of action underlying their cytotoxic activity. To date, BA and its derivatives have been reported to induce cell death in cancer cells via the activation of the intrinsic pathway of apoptosis.6 Accordingly, BA triggers the release of pro-apoptotic factors, such as cytochrome-c, from the mitochondria supposedly by interacting with the permeability pore transition complex and by modifying the balance of pro- and anti-apoptotic proteins of the Bcl-2 protein family.6 In addition, BA and its derivatives appear to interfere with multiple signaling pathways involved in survival. PI3K, NF-κB and lipid metabolism are modulated by BA-related compounds, but whether and how these effects contribute to cell death is unknown.7, 8, 9, 10 A better understanding of the mechanism of action of these compounds is critical to promote their therapeutic usage. Therefore, we investigated in the present study the mode of action of B10, a new glycosylated derivative of BA presenting enhanced cytotoxic activity. We show that B10 triggers a mixed phenotype of cell death characterized by morphological and biochemical features of apoptotic and non-apoptotic cell death. This complex mode of cell death previously unreported for BA and its derivatives is related to induction of autophagy and to the disruption of the autophagic flux, which contributes to the intracytoplasmic release of lysosomal enzymes. Our findings refine the conception of the mechanism of action of BA-derived triterpenoids. These novel inputs might influence the therapeutic application of BA-related compounds.
Results
B10 triggers non-apoptotic forms of cell death
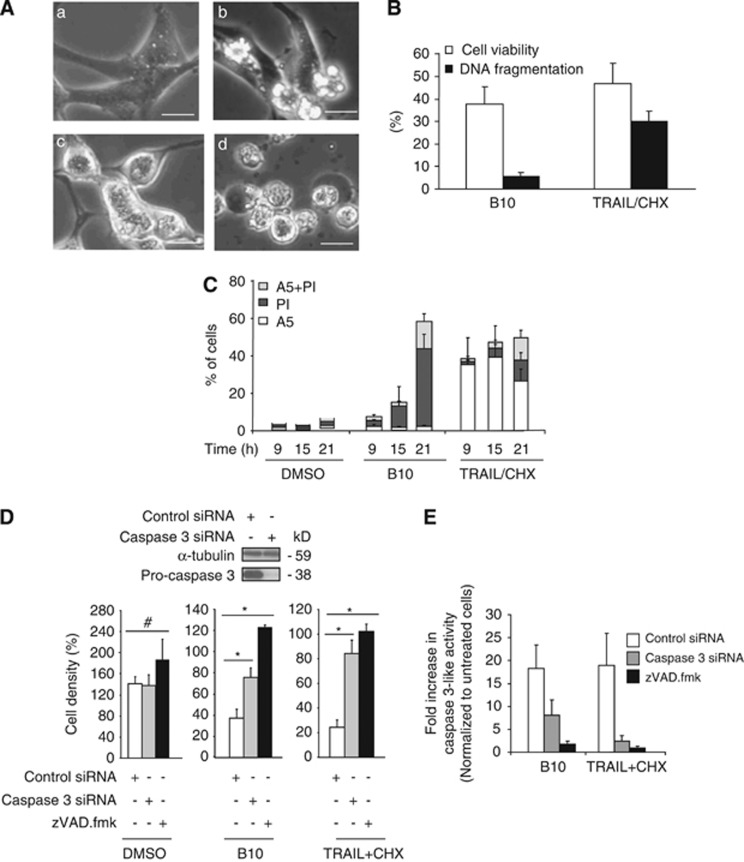
First, we evaluated the effect of B10 on a panel of glioblastoma cell lines. B10 induced a profound loss of viability in all cell lines (Supplementary Figure S1). Interestingly, the morphology of dying cells was rarely typically apoptotic, suggesting that the cytotoxic activity of B10 is also mediated by non-apoptotic modes of cell death. In order to investigate this assumption in detail, the well-characterized U87MG cell line was selected for further studies. Analysis of morphological alterations by microscopy revealed a mixed phenotype of dying cells among the cell population over time. Although a minor subpopulation of U87MG cells clearly displayed typical apoptotic blebbing, which is also observed in these cells upon treatment with TRAIL and cycloheximide (CHX) used as a positive control for apoptotic cell death,11 the majority of cells treated with B10 did not present intense membrane blebbing (Figure 1Ab). Instead, spherical and swollen cells were observed during an intermediate phase of cell death (Figure 1Ac). At a late phase, these cells ended up with a terminal bleb, characterized by a dense aggregate of the intracytoplasmic material segregated into a rounded cytoplasmic membrane before detaching from the substrate (Figure 1Ad). This morphology is usually not found during apoptosis and therefore suggests the occurrence of a non-apoptotic mode of cell death.
Figure 1.
B10-induced cell death is partially apoptotic. (A) Morphological alterations of B10-treated U87MG cells were analyzed using microscopy. Representative pictures of the cell death phenotype of untreated cells (a), cells treated with TRAIL (20 ng/ml) and CHX (1 μg/ml) (b) or cells exposed to B10 (18 μM) for 9 h (c) or 21 h (d) are shown (scale bar: 30 μm). The combination treatment with TRAIL and CHX was used as a positive control for apoptotic morphology. (B) U87MG cells treated with B10 (18 μM) or TRAIL/CHX were analyzed for loss of cell viability by determining cell density via crystal violet staining, and DNA fragmentation by analysis of sub-G1 DNA content (n=3, mean+S.D.). (C) The exposure of phosphatidylserine was analyzed by annexin V staining in parallel to membrane permeabilization assessed by PI in B10- or TRAIL/CHX-treated cells. Mean+S.D. of three independent experiments are shown. (D) The cytotoxic activity of B10 was evaluated using crystal violet staining in U87MG with downregulated pro-caspase-3 or in the presence of 40 μM zVAD.fmk. Mean+S.D. of three independent experiments are shown, *P<0.02, #P>0.05. TRAIL/CHX combination treatment was used as a positive control for apoptosis inhibition upon pro-caspase-3 downregulation. (E) Caspase-3-like activity was measured in cells transfected with control or caspase-3-specific siRNA incubated with B10 (21 h) or TRAIL/CHX (15 h) using the fluorogenic substrate zDEVD-R110 that measures caspase-3 and other DEVD-specific protease activities
In line with this notion, the amount of DNA fragmentation, a characteristic feature of apoptosis, did not correspond to the death rates determined by changes in cell density (Figure 1B). In contrast, TRAIL/CHX-induced loss of viability was accompanied by a concomitant increase in DNA fragmentation (Figure 1B). In addition, annexin V/propidium iodide (PI) staining revealed that treatment with B10 predominately caused an increase in PI-positive cells, whereas treatment with TRAIL/CHX resulted in an increase in Annexin V positive cells (Figure 1C). Further, overexpression of Bcl-2 did not prevent B10-induced cell death or caspase-3 activation, whereas Bcl-2 protected against cell death and caspase-3 activation upon treatment with TRAIL (Supplementary Figure S2). To determine whether caspase-3 activity is necessary for B10-induced cell death, caspase-3 expression was downregulated via RNA interference. Knockdown of caspase-3 resulted in a significant, yet incomplete decrease in B10-induced caspase-3-like activity and cytotoxicity (Figures 1D and E), pointing to a partial involvement of caspase-3 in B10-induced cell death. In comparison, caspase-3-silencing almost completely protected against TRAIL/CHX-induced caspase-3-like activity and cell death (Figures 1D and E). Noteworthy, the addition of zVAD.fmk provided a better protection against B10-induced caspase-3-like activity and cell death than caspase-3 downregulation (Figures 1D and E). Besides residual caspase-3 expression upon RNAi-mediated silencing, this difference may be attributed to the inhibition of additional proteases unrelated to caspases but sensitive to zVAD.fmk,12, 13 which might also contribute to caspase-3-like activity and cell death upon B10 treatment. In comparison, caspase-3-silencing was nearly as effective as zVAD.fmk in preventing TRAIL/CHX-induced caspase-3-like activity and cell death (Figures 1D and E). Together, these results indicate that B10 triggers a mixed type of cell death with apoptotic and non-apoptotic features compared with the prototypic apoptotic stimulus TRAIL. This prompted us to investigate the alternative mechanisms of action for B10.
B10 treatment destabilizes lysosomes
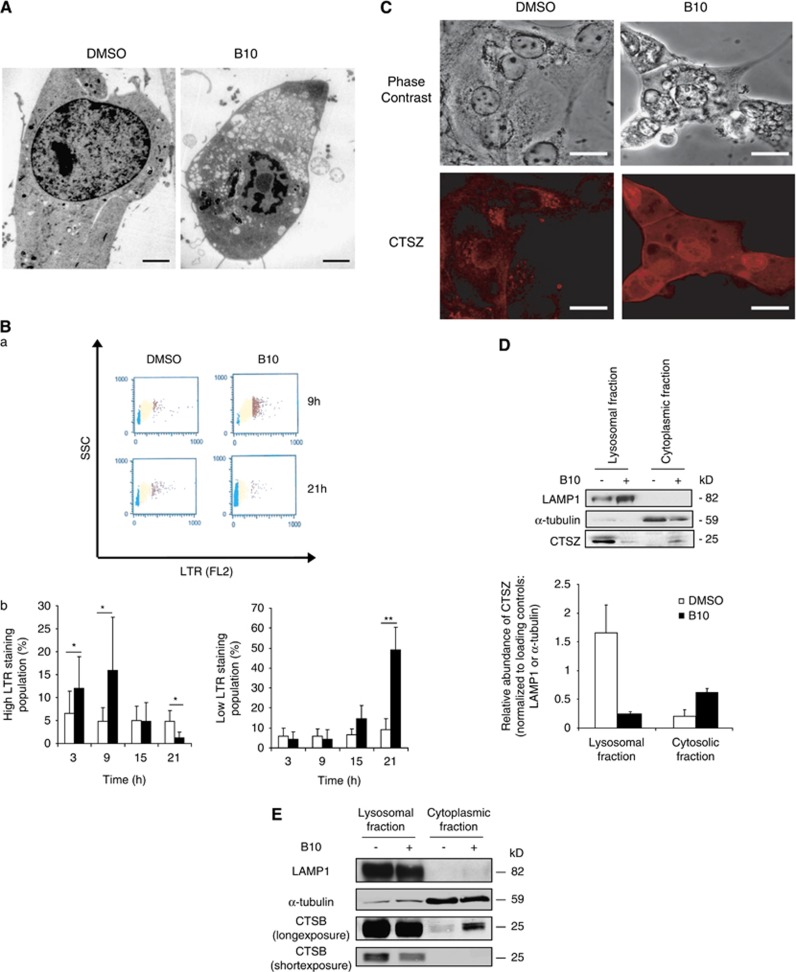
Analysis of B10-treated cells using electron microscopy revealed a marked cytoplasmic accumulation of vesicles (Figure 2A). Because this points to a possible alteration of lysosomal/endosomal trafficking, we investigated its implication in B10-induced cell death. Firstly, to evaluate the integrity of the lysosomal compartment, we used LysoTracker Red (LTR), a dye that accumulates in acidic compartments. Interestingly, the appearance of a subpopulation of cells presenting a high LTR fluorescence within 9 h of treatment pointed to an increased volume of the acidic compartment in B10-treated cells (Figure 2B). However, this increase was transient as it was not detectable at later time points (Figure 2B). Conversely, a population of low LTR fluorescence increased from 15 h onwards, indicating that the volume of the acidic compartment decreases over time in B10-treated cells (Figure 2B). To further determine whether the reduction of the volume of the acidic compartment upon B10 treatment was due to lysosomal permeabilization, the localization of cathepsin Z (CTSZ) and cathepsin B (CTSB), two lysosomal enzymes, was analyzed by immunofluorescence. Although CTSZ was found in the lysosomes of untreated cells, the enzyme was detected diffusely in the cytoplasm and in the nucleus upon B10 treatment (Figure 2C). In addition, separation into lysosomal and cytoplasmic fractions revealed that treatment with B10 caused a decrease of CTSZ and CTSB in the lysosomal fraction and their concomitant increase in the cytoplasmic fraction (Figures 2D and E). This altered distribution of CTSZ and CTSB therefore confirms the permeabilization of lysosomal membranes upon B10 treatment.
Figure 2.
B10 destabilizes the lysosomal compartment. (A) Electron microscopy was performed on U87MG cells treated with 18 μM B10 or DMSO for 24 h. Representative pictures are presented, scale bar: 3000 nm. (B) The volume of the acidic compartments B10- or DMSO-treated cells was analyzed by LTR staining and flow cytometry. (a) Representative dot plots are shown at 9 h and 21 h, coloring of the dots distinguishes populations of cells according to their fluorescence intensity. Red, yellow and green colors stand for populations of cells with high, normal and low LTR fluorescence intensity, respectively. (b) Quantitative analysis of cell populations with high and low LTR fluorescence intensity of cells treated with 18 μM B10 (black bars) or DMSO (white bars). Mean+S.D. of six independent experiments are shown, *P<0.04; **P<0.01. (C) CTSZ staining of cells treated with 18 μM B10 or DMSO for 24 h was performed and analyzed by confocal microscopy (scale bar: 20 μm). (D and E) Cell fractionation was performed to separate lysosomal and cytosolic fraction from DMSO- or B10-treated cells (21 h). CTSZ and CTSB were detected by western blotting in the different fractions. A representative blot is shown (D, upper panel and E). The relative amounts of CTSZ were quantified from two independent experiments by normalizing CTSZ expression to LAMP1 or α-Tubulin expression for the lysosomal and cytosolic fractions, respectively (D, lower panel). The color reproduction of this figure is available at the Cell Death and Differentiation journal online
Cathepsins are implicated in B10-induced cell death by apoptotic and non-apoptotic cell death
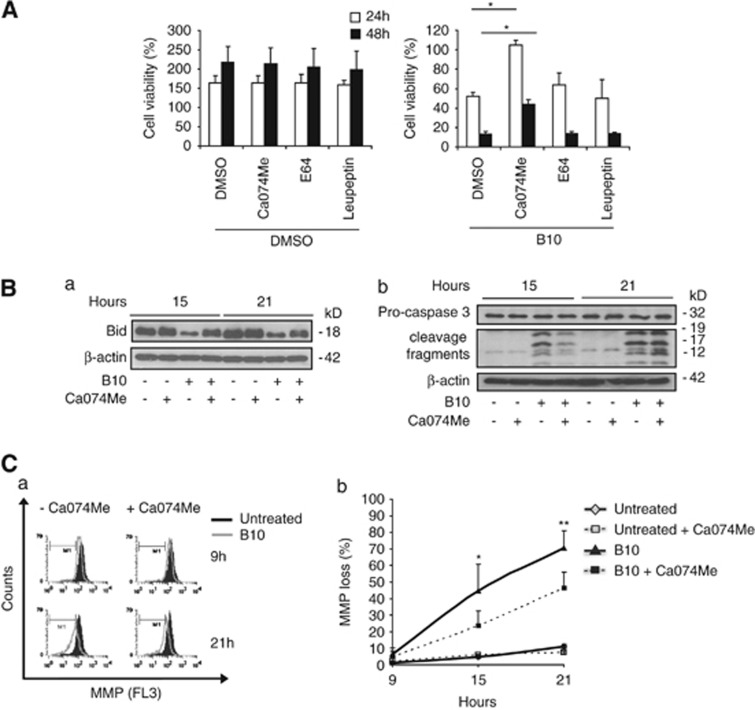
As B10 induces lysosomal permeabilization (Figure 2), the role of lysosomal enzymes in B10-induced cell death was investigated using chemical inhibitors of lysosomal enzymes. As shown in Figure 3A, Ca074Me, an inhibitor of CTSB, L, and S, significantly delayed cell death in U87MG, whereas neither E64 nor leupeptin prevented B10-induced cell death (Figure 3A). Cathepsins can cleave a number of substrates upon their release into the cytoplasm. To explore possible substrates of the lysosomal enzymes inhibited by CA074Me, we focussed on some components of the apoptotic machinery.14 We found that Ca074Me prevented the B10-induced decrease of Bid protein expression (Figure 3Ba), indicating that Bid may be degraded by cathepsins that are inhibited by CA074Me. However, knockdown of Bid did not protect against B10-induced cell death, whereas it significantly inhibited TRAIL/CHX-triggered cell death (data not shown). Ca074Me delayed MMP loss upon B10 exposure and transiently reduced caspase-3 activation at 15 h, whereas no difference in caspase-3 cleavage was observed at a later time point (Figures 3Bb and C). Noteworthy, this transient inhibitory effect of Ca074Me on caspase-3 activation did not reflect the 24-h delay of cell death upon treatment with this inhibitor (Figure 3A). This set of experiments suggests that lysosomal enzymes are involved both in apoptotic and non-apoptotic cell death in B10-treated cells.
Figure 3.
Ca074Me delays B10-induced cell death and transiently reduces Bid degradation, caspase-3 activation and mitochondrial membrane depolarization. (A) U87MG cells were incubated with 18 μM B10 or DMSO in combination with Ca074Me (10 μM), E64 (50 μM) or leupeptin (100 μM). Cell viability was quantified by crystal violet staining after 24 h (black bars) and 48 h (white bars). Results are expressed as the percentage of cell density value prior to stimulation. Mean+S.D. of three independent experiments are shown, *P<0.01. (B) Expression levels of Bid (a) and caspase-3 cleavage (b) were analyzed by immunoblot after 15 h and 21 h incubation with 18 μM B10 or DMSO in the presence or absence of 10 μM Ca074Me. (C) Mitochondrial membrane potential was measured by flow cytometry and TMRM staining of cells treated for indicated times with 18 μM B10 or DMSO in the presence or absence of Ca074Me. (a) Representative histograms are shown. (b) Quantification of the percentage of cells with reduced MMP is represented. Mean+S.D. of four independent experiments are shown; *P<0.02, **P<0.05 comparing cells treated with B10 and Ca074Me versus cells treated with B10 alone
B10 induces autophagy and disrupts the autophagic flux
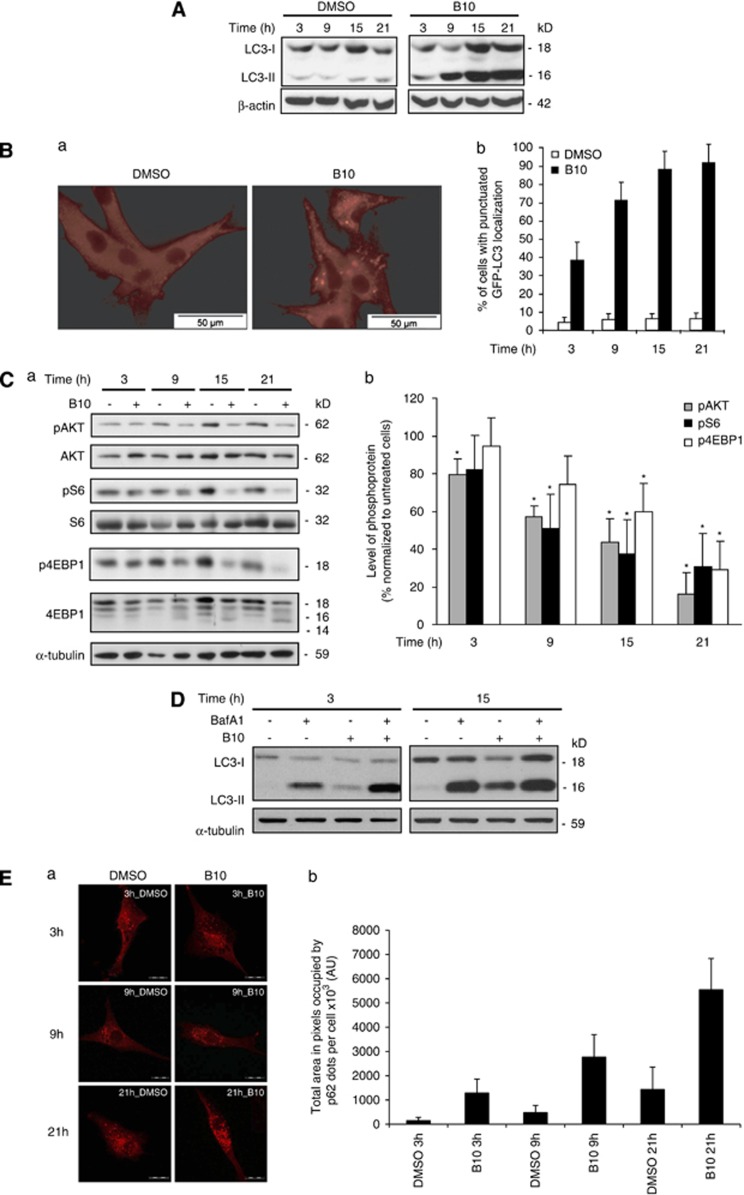
As B10 impairs the integrity of the lysosomal compartment and because autophagy relies on lysosomes for the degradation of autophagosomal cargos to promote cell fitness, we investigated the effects of B10 on autophagy using LC3 as a marker of autophagic activity. Remarkably, LC3 lipidation (LC3-II) increased upon B10 treatment in a time-dependent manner (Figure 4A) and this marker translocated to autophagosomes represented by vesicular structures containing LC3 (Figure 4B). These results indicate that B10 induces autophagy and/or blocks the autophagic flux. To investigate possible causes for autophagy induction by B10, we analyzed the activation status of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in B10-treated cells, as this pathway is a key regulator of autophagy. PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling was progressively inhibited upon treatment with B10 as indicated by decreased phosphorylation of Akt, a downstream target of PI3K, as well as decreased phosphorylation of S6 and 4EBP1, both downstream targets of mTOR (Figure 4C). Moreover, the kinetic of inactivation of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling occurred in parallel with the induction of autophagy as assessed by GFP-LC3 localization to autophagosomes (Figure 4Bb). To further determine the role of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling in B10-triggered autophagy, we used α-tocopherol to prevent the B10-mediated inhibition of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway, as α-tocopherol has previously been reported to stabilize lipid rafts, thereby stimulating PI3K activity and thus PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling.15 Addition of α-tocopherol partly preserved phosphorylation of Akt and S6, reduced LC3 lipidation upon B10 treatment and significantly reduced B10-induced lysosomal permeabilization and cell death (Supplementary Figure S3). Because α-tocopherol indirectly stimulates PI3K signaling and can exert additional functions, for example, antioxidant functions,16 we also knocked down TSC2 to activate mTOR. However, silencing of TSC2 had no effect on mTOR signaling in glioblastoma cells and did not rescue the B10-induced LC3 conversion or cytotoxicity (Supplementary Figure S4). Therefore, additional studies are required to define the role of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling in B10-triggered autophagy.
Figure 4.
Accumulation of lipidated LC3 correlates with the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway inactivation upon B10 treatment. (A) U87MG cells were treated for indicated times with 18 μM B10 or DMSO, and LC3 and its lipidated form were detected by immunoblot analysis. (B) The localization of endogenous LC3 was determined by immunofluorescence in cells treated with 18 μM B10 or DMSO for 21 h (a and b). The kinetic of GFP-LC3 translocation was determined by counting cells presenting with a punctuated GFP-LC3 localization after treatment with 18 μM B10 for indicated times. Mean+S.D. of three independent experiments are shown. (C) Phosphorylation status of Akt, ribosomal protein S6 and 4EBP1 was analyzed by western blot analysis upon with 18 μM B10 or DMSO for the indicated time points (a). Quantitation of phosphoproteins was normalized to total protein levels and and mean+S.D. of three independent experiments are shown; P values were calculated against DMSO, *P<0.05 (b). (D) U87MG cells were treated for indicated times with 18 μM B10 or DMSO in the absence or presence of BafA1. LC3 and its lipidated form were detected by immunoblot analysis. (E) p62 protein expression was assessed by immunofluorescence using confocal microscopy in U87MG cells treated with 18 μM B10 for indicated times; scale bar: 100 μm (a). The area occupied by p62 dots per cell was quantified using ImageJ digital imaging software (b). Mean+S.D. of five cells per sample are shown
Next, the integrity of the autophagic flux was evaluated, because autophagy relies on lysosomes for the degradation of autophagosomal cargos. To this purpose, LC3-II levels were assayed upon B10 treatment in the absence or presence of bafilomycin A1 (BafA1), a drug that blocks the fusion of autophagosomes with lysosomes. An increase of LC3-II was observed after 3 h in cells treated with B10 and BafA1 compared with B10 alone (Figure 4D). Moreover, LC3 lipidation at 3 h was increased in B10-treated cells in the presence of BafA1 compared with cells treated with BafA1 alone (Figure 4D). These findings indicate that B10 induces autophagy at an early time point, while LC3-II levels in B10-treated cells in the presence of BafA1 were similar to cells treated with BafA1 alone at later time points (Figure 4D), suggesting that the autophagic flux is progressively disrupted in B10-treated cells. In line with this notion, the levels of p62, a protein that is normally degraded upon fusion of autophagosomes with lysosomes,17 increased at later time points of B10 treatment (Figure 4E). Together, these observations indicate that B10 triggers both autophagy induction and progressively disrupts the autophagic flux leading to an accumulation of the undigested autophagosomes.
Destructive autophagy contributes to cell death upon B10 treatment
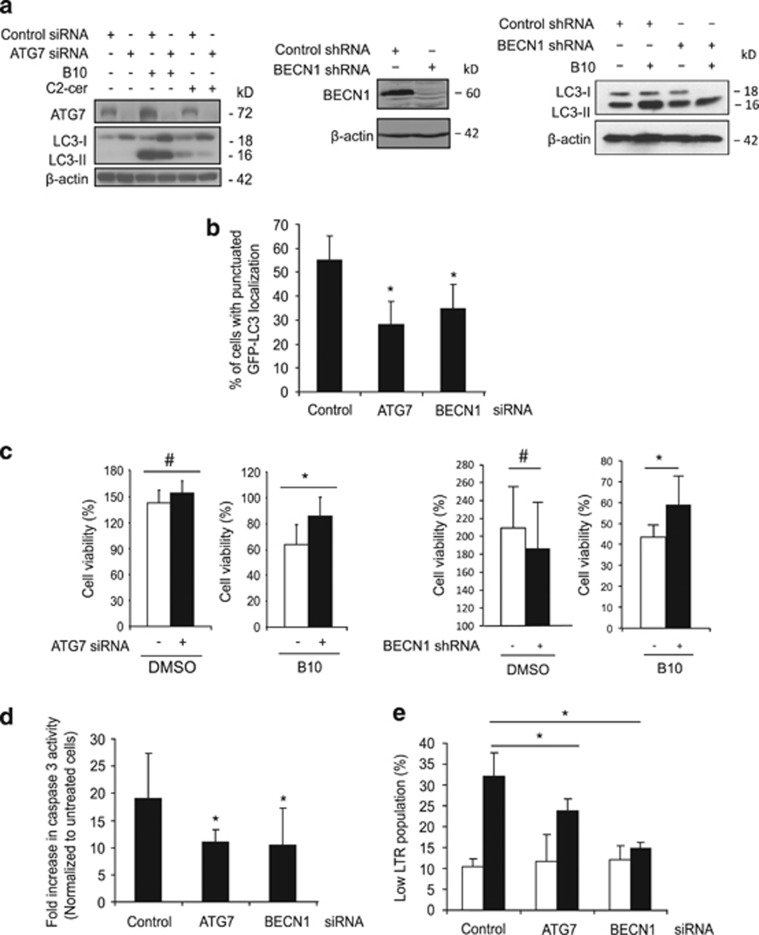
Autophagy can favor cell survival or on the contrary can promote cell death under stress conditions.18, 19 Importantly, PI3K/Akt/mTOR inhibition per se is not cytotoxic in U87MG cells as we and others previously reported,20, 21 but recent evidence indicates that late-stage disruption of the autophagic process can cause detrimental autophagy.21 Therefore, the role of autophagy in B10-induced cell death was addressed by RNAi-mediated knockdown of ATG7, ATG5 or BECN1, key regulators of autophagy. C2-Ceramide was used as a positive control to induce autophagy.22 Downregulation of ATG7, ATG5 or BECN1 reduced B10-induced LC3 lipidation (Figure 5a, Supplementary Figure S5). Also, B10-mediated GFP-LC3 translocation to autophagosomes was significantly decreased upon ATG7 or BECN1 silencing (Figure 5b). Importantly, downregulation of ATG7, ATG5 or BECN1 significantly inhibited the B10-induced loss of cell viability (Figure 5c, Supplementary Figure S5), which argues for a detrimental role of autophagy in B10-induced cell death. Also, knockdown of ATG7 or BECN1 significantly reduced the B10-triggered increase in caspase-3-like activity (Figure 5d), indicating that autophagy at least partially contributes to caspase-3 activation. In addition, the effect of autophagy on lysosomal stability was evaluated, because accumulation of undigested autophagosomes might contribute to lysosomal permeabilization.23 ATG7 or BECN1 knockdown significantly suppressed B10-triggered lysosomal permeabilization (Figure 5e). This set of experiments indicates that B10-induced autophagy contributes to caspase-3 activation, lysosomal permeabilization and cell death. We also investigated the effect of combined inhibition of autophagy and lysosomal enzymes. Ca074Me cooperated with ATG7 knockdown to rescue cells from B10-induced loss of viability (Supplementary Figure S6), indicating that lysosomal disruption and autophagy contribute to cell death.
Figure 5.
Autophagy promotes B10 cytotoxic activity. (a) U87MG cells transfected with ATG7 or control siRNA or with BECN1 or control shRNA vectors were treated with 18 μM B10, DMSO or (C2-ceramide, 75 μM). LC3 lipidation was analyzed by immunoblot. (b) The amount of cells presenting a punctuated localization of GFP-LC3 was quantified upon treatment with 18 μM B10. Mean+S.D. of three independent experiments are shown; *P<0.05. (c) Cell viability was determined by crystal violet staining in control cells (white bars) or ATG7 or BECN1 knockdown cells (black bars) after treatment for 24 h with 18 μM B10 or DMSO. Mean+S.D. of at least three independent experiments are presented; *P<0.05, #P>0.05. (d and e) The effect of ATG7 and BECN1 downregulation on caspase-3 activity using a caspase-3 fluorogenic substrate (d) or on lysosomal permeabilization using LTR staining (e) following treatment for 21 h with 18 μM B10 (black bars) or without B10 (white bars) was analyzed. Mean+S.D. of three independent experiments are shown, *P<0.05
Discussion
In the present study, we identify a novel mode of action for the cytotoxic activity of the BA derivative B10 (Figure 6). This mechanism unexpectedly involves an early activation of autophagy and the permeabilization of lysosomes upon B10-treatment. This later event concomitantly leads to the release of lysosomal enzymes into the cytoplasm and impairs the late stages of autophagy, thus turning autophagy into a destructive process. Ultimately, these alterations commit cells to death via the apoptotic and non-apoptotic pathways.
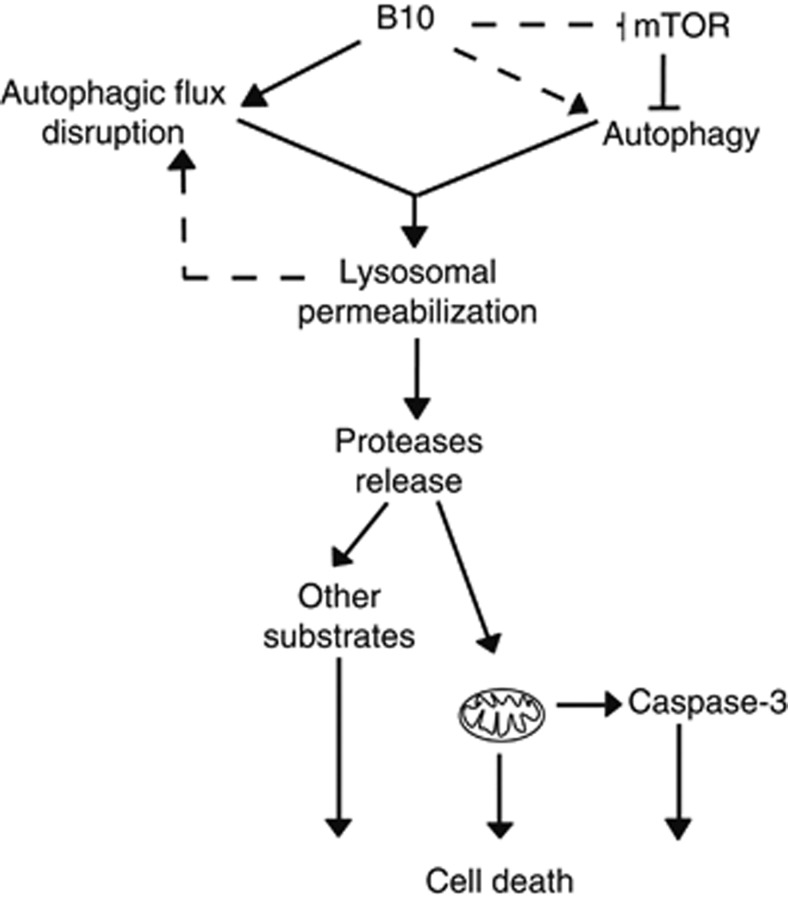
Figure 6.
Proposed mode of action for B10 cytotoxic activity. B10 triggers autophagy in an early phase, either by Akt/mTOR inhibition and/or by the mTOR-independent pathways. Progressively, B10 impairs the autophagic flux possibly by destabilizing lysosomes. In turn, the accumulation of enlarged and unstable autophagolysomes or the accumulation of undegraded material promotes the release of lysosomal enzymes into the cytoplasm. Subsequently, lysosomal proteases contribute directly or indirectly to apoptosis by caspase-3 activation and to non-apoptotic cell death by a non-selective degradation of cellular substrates
B10-induced mixed phenotype of cell death is supported by the fact that DNA fragmentation does not closely correlate with cell death rates, that Bcl-2 overexpression does not prevent nor delay B10-induced cell death and that downregulation of caspase-3 only partially rescues B10-induced cell death. In addition, we show that PI incorporation matches cell death kinetics, which points to necrotic features. Although the pan-caspase inhibitor zVAD.fmk significantly delays cell death, this finding does not necessarily argue for caspase involvement in B10-induced cell death, because zVAD.fmk can also block other enzymes at the concentration used in this study, such as cathepsins, which have previously been reported to be involved in caspase-dependent and -independent cell death.13, 24 Importantly, this might explain that apoptotic and non-apoptotic modes of cell death can coexist as a consequence of the intracytoplasmic release of lysosomal enzymes upon B10 treatment. Indeed, although cathepsin activity can lead to the activation of substrates specifically involved in apoptosis, such as Bid and caspase-3,12, 14 their ability to cleave a large number of substrates can also commit cells to die via the non-apoptotic pathways.23, 25 Accordingly, we observe that Ca074Me only transiently reduces MMP loss and caspase-3 activation. Firstly, this indicates that mitochondrial permeabilization also relies on lysosomal proteases that cannot be inhibited by CA074Me and/or on other parallel processes arising upon B10 treatment such as direct permeabilization of mitochondrial membrane by B10.6 Secondly, because Ca074Me delays cell death for significantly longer periods than caspase-3 activation, these results also implicate that lysosomal permeabilization has a role in cell death independently of induction of apoptosis via the mitochondrial pathway in B10-treated cells. This is possibly related to the degradation of substrates not directly implicated in apoptosis, but required for the maintenance of cell viability as discussed above. Together, these novel findings suggest that B10 might overcome resistance to apoptosis by exploiting alternative modes of cell death.
The role of autophagy in cell death is controversial, as there is evidence for pro- and anti-survival functions of this process depending on the context.18, 19 Importantly, autophagy contributes to B10-induced cell death as silencing of autophagy genes, such as ATG5, ATG7 or BECN1, reduces cell death following treatment with B10. Although induction of autophagy is required to promote cell death upon B10 treatment, this is per se insufficient for cell death execution. This assumption is supported by the fact that PI3K/Akt/mTOR inhibition is not cytotoxic in U87MG, although it enhances autophagy (data not shown and Opel et al20; Degtyarev et al21). Therefore, a second event might be necessary to drive autophagy into its detrimental branch. Along this line, recent studies show that disruption of the late stages of autophagy can turn autophagy into a destructive process,21, 26, 27 suggesting that the conversion of protective autophagy into destructive autophagy might rely on a balance between autophagosome production and appropriate degradation capacity by the lysosomes. Remarkably, we demonstrate for the first time that the same conversion of the autophagic function is achieved upon single treatment with B10 in a sequence of two steps. Firstly, B10 induces autophagy and secondly, B10 disrupts the autophagic flux subsequently to lysosomal permeabilization. Although the exact underlying causes of B10-stimulated lysosomal permeabilization have not yet been determined, this might involve ROS generation and lipid peroxidation, because BA has previously been reported to trigger ROS production,6 or alternatively alterations in the metabolism of sterols, which are critical for the stability of biomembranes, as recently shown for another BA derivative.10 Disruption of the autophagic flux can lead to the excessive accumulation of autophagosomes containing deleterious undegraded material.21 Alternatively, a blockade of the fission step upon autophagolysosome formation might lead to the accumulation of enlarged and unstable acidic vesicles. The observation of large vesicles in B10-treated cells supports this latter hypothesis. In that case, autophagy would contribute to lysosomal permeabilization by promoting cathepsin release from destabilized autophagolysosomes.28 The question whether these events are indeed key mediators in B10-induced cell death deserves further investigation.
In summary, we report that B10-induced cell death involves induction of autophagy and lysosomal permeabilization that turns autophagy into a cell death process and leads to the release of lysosomal enzymes into the cytoplasm. These novel properties of B10 are expected to have important implications for the therapeutic exploitation of BA derivatives, particularly in apoptosis-resistant cancers.
Materials and Methods
Cell culture and reagents
Cell lines were maintained at 37°C under 5% CO2 in DMEM medium Life Technologies Inc. (Eggenstein, Germany) supplemented with 10% FBS (Life Technologies Inc.), 1 mmol/l glutamine (Biochrom, Berlin, Germany), 1% penicillin/streptomycin (Biochrom) and 25 mmol/l HEPES (Biochrom). B10 was synthesized by BioService Halle (Halle, Germany). Ca074Me, E64, leupeptin and α-tocopherol were purchased from Sigma (Taufkirchen, Germany) and zVAD.fmk from Bachem (Weil am Rhein, Germany).
Determination of cell viability
Cell viability was evaluated by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5–diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) as described29 or by measuring cell density using crystal violet staining. Briefly, cells were fixed and stained for 10 min at room temperature (RT) by crystal violet solution (0.5% of crystal violet, 30% of ethanol and 3% of paraformaldehyde). Plates were then washed in water and crystal violet incorporated by the cells was resolubilised in a solution containing 1% SDS. Absorbance at 550 nm was measured using a microplate reader (EL800, Biotek, Bad Friedrichshall, Germany). All experiments are expressed as percentage of the value of cell density measured prior to stimulation. When indicated, zVAD.fmk, E64, Ca074Me, leupeptin or α-tocopherol were used at 40 μM, 50 μM, 10 μM, 100 μM and 500 μM, respectively.
Determination of apoptosis
Fluorescence-activated cell-sorting (FACScan, Becton Dickinson, Heidelberg, Germany) analysis of DNA fragmentation of PI-stained nuclei was performed as described.30 Annexin V/PI (BD Biosciences, Heidelberg, Germany) staining was performed according to the manufacturer's protocol. Caspase-3-like activity was measured by FACS (FL1) using the fluorogenic substrate N-benzyloxycarbonyl-Asp-Glu-Val-Asp-fluoromethylketone-R110 (zDEVD-R110, Molecular Probes, Eugene, OR, USA) conjugated to rhodamine R110 that measures the activities of caspase-3 and other DEVD-specific proteases such as caspase-7. U87MG cells stably overexpressing Bcl-2 were obtained by transducing cells with a virus containing empty pMSCV vector or pMSCV vector encoding murine Bcl-2. Cells were selected with 10 μg/ml of blasticidin.
Western blot analysis
Cells were lysed in a lysis buffer containing 30 mM Tris, 150 mM NaCl, 1% Triton X-100 and 10% glycerol for 15 min on ice. A solution of 200 μM phenylmethanesulfonyl fluoride (PMSF), 2 mM dithiothreitol, 1 μM sodiumorthovanadate, 1 mM β-Glycerophosphate and 5 mM NaF were added to the lysis buffer when samples were prepared for phosphoprotein detection. After centrifugation at 13 000 r.p.m. for 15 min at 4 °C, the supernatant was collected and protein levels were quantified. The samples were loaded onto an acrylamide gel and then transferred on a PVDF or nitrocellulose membrane. Immunodetection of proteins was performed using anti-caspase-3, anti-Bid, anti-phospho-Akt (Ser-473), anti-phospho-S6 ribosomal protein and anti-S6 ribosomal protein, all from Cell Signaling (Beverly, MA, USA), anti-Akt (BD Biosciences), anti-LC3 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Braunschweig, Germany), anti-Beclin1 (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA, USA), anti-ATG7 (Abcam, Cambridge, UK), anti-p62 (Sigma), anti-CD107a (Lamp1) (BD Pharmingen, Heidelberg, Germany), anti-ß-actin (Sigma) and anti-α-Tubulin (Calbiochem, Darmstadt, Germany) antibodies. ImageJ (Wayne Rasband, NIH, Bethesda, MD, USA) was used to quantify protein levels. Expression of phosphoproteins was normalized to α-Tubulin levels.
Determination of autophagy and autophagic flux integrity
GFP-LC3-overexpressing U87MG cells were generated by selecting cells transfected with pBabe-GFP-LC3.31 Using an inverted fluorescence microscope (CK40, Olympus, Hamburg, Germany), the amount of cells presenting a punctuated localization for GFP-LC3 was determined after counting a minimum of 100 cells over at least three different fields of observation. Cut-off level for positivity was set to 1 puncta/cell for untransfected U87MG and to 5 puncta/cell for U87MG cells transfected with control, ATG7 or BECN1 small interfering RNA (siRNA). The data presented are the result from three independent experiments made in duplicates. To evaluate the status of the autophagic flux, 20 nM of BafA1 was added to the culture medium 2 h before cell lysis in order to inhibit the degradation of autophagosomes by blocking their fusion with lysosomes.32 Lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting for LC3.
Immunofluorescence staining
Cells were fixed/permeabilized in a pre-cooled methanol: acetone (1 : 1) solution for 10 min at 4 °C. Next, the slides were incubated in a PBS solution containing 0.1% of triton for 5 min at RT and washed with PBS before incubation overnight at 4 °C with a rabbit anti-LC3 antibody (Thermo Fisher Scientific) or a rabbit anti-CTSZ antibody (Abcam) diluted in PBS solution containing 2% BSA. The slides were then washed in PBS and incubated with an anti-rabbit IgG (H+L) antibody coupled to Texas-Red (Vector Laboratories Inc., Burlingame, CA, USA) or a sheep anti-mouse IgG antibody coupled to FITC (Millipore, Schwalbach, Germany) for 2 h at RT. Slides were imaged by an epifluorescence microscope (AX70, Olympus) for LC3 staining and images were analyzed by analySIS software (Olympus Soft Imaging System GmbH). Fluoview FV10i confocal laser microscope (Olympus) was used to image CTSZ staining.
Cell fractionation
At 21 h after stimulation, 1.4 millions/sample were collected and washed twice in ice-cold extraction buffer (210 mM mannitol, 70 mM sucrose, 1 mM EDTA and 20 mM Hepes, pH 7.5) complemented with 100 mM PMSF and protease inhibitors (Roche Diagnostics). Cells were disrupted into the extraction buffer by passing the sample through a G27 needle until approximately 50% of the cells were positive for trypan blue. The total extracts were centrifuged at 1000 g for 5 min at 4 °C. The supernatants were collected and centrifuged at 20 800 g for 1 h at 4 °C. The supernatant (cytosolic fraction) was collected and the pellet (lysosomal fraction) was lysed in the lysis buffer described in the procedure for western blotting. Samples were analyzed by immunoblotting.
Determination of mitochondrial membrane potential
To measure mitochondrial membrane potential, cells were incubated for 10 min with 100 ng/ml of tetramethylrhodamine methyl ester perchlorate (TMRM) (Sigma) at 37 °C, trypsinized, washed and immediately analyzed using flow cytometry.
Staining of the acidic compartment
Staining of the acidic compartment of cells was performed using LTR, a lysosomotropic probe (Invitrogen, Darmsadt, Germany). The cells were incubated for 10 min at 37 °C with 50 nM of LysoTracker in complete medium. Fluorescence intensity was then measured using a FACScalibur on channel 2 (FL2). The results were analyzed using Cell Quest (Becton Dickinson) by defining three cell populations determined by low, medium or high LTR fluorescence. Dead cells were excluded from the analysis by FSC/SSC analysis.
Electron microscopy
Cells fixed with 2.5%. glutaraldehyde, 0.1 M phosphate cacodylate and 1% saccharose, pH 7.3. After dehydratation, thin layers were stained using osmium tetraoxyde. Imaging was performed using a Philips 400 Transmission electron microscope (Hamburg, Germany).
Downregulation of protein expression using RNA interference
Cells grown for 24 h were transfected with single-siRNA duplexes using transmessenger transfection reagent from Qiagen (Hilden, Germany). All siRNAs were purchased from Invitrogen (control siRNA: negative universal control 46–2001, caspase-3: HSS101372, Bid: BIDHSS141377 and ATG7: ATG7HSS116183). At 72 h post transfection, transfected cells were trypsinized and reseeded at equivalent cell density in each experiments. For gene silencing by lentiviral shRNA vectors, HEK293T cells were transfected with 7.5 μg pGIPZ-shRNAmir vector, 12.5 μg pCMV-dR8.91 and 1 μg pMD2.G (Addgene no. 12259) using calcium phosphate transfection. All pGIPZ-shRNAmir-vectors were purchased from Thermo Fisher Scientific (non-silencing control: RHS4346, shATG5: RHS4430-98715191, shBECN1: RHS4430-101032612, shTSC2 shRNA_1: RHS4430-99879929 and TSC2 shRNA_2: RHS4430-101130117). Virus containing supernatant was collected, filtered and used for spin transduction of U87MG cells at RT in the presence of 8 μg/ml polybrene. Transduced cells were selected with 1 μg/ml puromycin.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was calculated using Student's t-test (two-tailed distribution, two-sample, unequal variance).
Acknowledgments
We thank C Payer for expert technical assistance and C Hugenberg for excellent secretarial assistance. This work has been partially supported by Grants from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung, European Community (ApopTrain, APO-SYS) and IAP6/18 (to SF).
Glossary
- ATG
autophagy-related genes
- BA
betulinic acid
- CHX
cycloheximide
- CTSZ
cathepsin Z
- LTR
lysotracker red
- KD
knock-down
- MMP
mitochondrial membrane potential
- MTT
3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltretrazolium bromide
- PI
propidium iodide
- PI3K
phosphoinositide 3-kinase
- siRNA
small interfering RNA
- TMRM
tetramethylrhodamine methyl ester perchlorate
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Footnotes
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Cell Death and Differentiation website (http://www.nature.com/cdd)
Edited by P Mehlen
Supplementary Material
References
- Cragg GM, Newman DJ. Plants as a source of anti-cancer agents. J Ethnopharmacol. 2005;100:72–79. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2005.05.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alakurtti S, Makela T, Koskimies S, Yli-Kauhaluoma J. Pharmacological properties of the ubiquitous natural product betulin. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2006;29:1–13. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2006.04.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cichewicz RH, Kouzi SA. Chemistry, biological activity, and chemotherapeutic potential of betulinic acid for the prevention and treatment of cancer and HIV infection. Med Res Rev. 2004;24:90–114. doi: 10.1002/med.10053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulda S, Kroemer G. Targeting mitochondrial apoptosis by betulinic acid in human cancers. Drug Discov Today. 2009;14:885–890. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2009.05.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury AR, Mandal S, Goswami A, Ghosh M, Mandal L, Chakraborty D, et al. Dihydrobetulinic acid induces apoptosis in Leishmania donovani by targeting DNA topoisomerase I and II: implications in antileishmanial therapy. Mol Med. 2003;9:26–36. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulda S, Friesen C, Los M, Scaffidi C, Mier W, Benedict M, et al. Betulinic acid triggers CD95 (APO-1/Fas)- and p53-independent apoptosis via activation of caspases in neuroectodermal tumors. Cancer Res. 1997;57:4956–4964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasperczyk H, La Ferla-Bruhl K, Westhoff MA, Behrend L, Zwacka RM, Debatin KM, et al. Betulinic acid as new activator of NF-kappaB: molecular mechanisms and implications for cancer therapy. Oncogene. 2005;24:6945–6956. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1208842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qiu L, Wang Q, Di W, Jiang Q, Schefeller E, Derby S, et al. Transient activation of EGFR/AKT cell survival pathway and expression of survivin contribute to reduced sensitivity of human melanoma cells to betulinic acid. Int J Oncol. 2005;27:823–830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieber M, Rieber MS. Signalling responses linked to betulinic acid-induced apoptosis are antagonized by MEK inhibitor U0126 in adherent or 3D spheroid melanoma irrespective of p53 status. Int J Cancer. 2006;118:1135–1143. doi: 10.1002/ijc.21478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willmann M, Wacheck V, Buckley J, Nagy K, Thalhammer J, Paschke R, et al. Characterization of NVX-207, a novel betulinic acid-derived anti-cancer compound. Eur J Clin Invest. 2009;39:384–394. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.2009.02105.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulda S, Meyer E, Debatin KM. Metabolic inhibitors sensitize for CD95 (APO-1/Fas)-induced apoptosis by down-regulating Fas-associated death domain-like interleukin 1-converting enzyme inhibitory protein expression. Cancer Res. 2000;60:3947–3956. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Droga-Mazovec G, Bojic L, Petelin A, Ivanova S, Romih R, Repnik U, et al. Cysteine cathepsins trigger caspase-dependent cell death through cleavage of bid and antiapoptotic Bcl-2 homologues. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:19140–19150. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M802513200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schotte P, Declercq W, Van Huffel S, Vandenabeele P, Beyaert R. Non-specific effects of methyl ketone peptide inhibitors of caspases. FEBS Lett. 1999;442:117–121. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(98)01640-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoka V, Turk B, Schendel SL, Kim TH, Cirman T, Snipas SJ, et al. Lysosomal protease pathways to apoptosis. Cleavage of bid, not pro-caspases, is the most likely route. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:3149–3157. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M008944200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vejux A, Guyot S, Montange T, Riedinger JM, Kahn E, Lizard G. Phospholipidosis and down-regulation of the PI3-K/PDK-1/Akt signalling pathway are vitamin E inhibitable events associated with 7-ketocholesterol-induced apoptosis. J Nutr Biochem. 2009;20:45–61. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2007.12.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banks R, Speakman JR, Selman C. Vitamin E supplementation and mammalian lifespan. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2010;54:719–725. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.200900382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorkoy G, Lamark T, Pankiv S, Overvatn A, Brech A, Johansen T. Monitoring autophagic degradation of p62/SQSTM1. Methods Enzymol. 2009;452:181–197. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(08)03612-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White E, DiPaola RS. The double-edged sword of autophagy modulation in cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15:5308–5316. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-5023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenific CM, Thorburn A, Debnath J. Autophagy and metastasis: another double-edged sword. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2010;22:241–245. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2009.10.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opel D, Westhoff MA, Bender A, Braun V, Debatin KM, Fulda S. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibition broadly sensitizes glioblastoma cells to death receptor- and drug-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res. 2008;68:6271–6280. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-6769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degtyarev M, De Maziere A, Orr C, Lin J, Lee BB, Tien JY, et al. Akt inhibition promotes autophagy and sensitizes PTEN-null tumors to lysosomotropic agents. J Cell Biol. 2008;183:101–116. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200801099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarlatti F, Bauvy C, Ventruti A, Sala G, Cluzeaud F, Vandewalle A, et al. Ceramide-mediated macroautophagy involves inhibition of protein kinase B and up-regulation of beclin 1. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:18384–18391. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M313561200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagedal K, Zhao M, Svensson I, Brunk UT. Sphingosine-induced apoptosis is dependent on lysosomal proteases. Biochem J. 2001;359:335–343. doi: 10.1042/0264-6021:3590335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozman-Pungercar J, Kopitar-Jerala N, Bogyo M, Turk D, Vasiljeva O, Stefe I, et al. Inhibition of papain-like cysteine proteases and legumain by caspase-specific inhibitors: when reaction mechanism is more important than specificity. Cell Death Differ. 2003;10:881–888. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4401247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boya P, Kroemer G. Lysosomal membrane permeabilization in cell death. Oncogene. 2008;27:6434–6451. doi: 10.1038/onc.2008.310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boya P, Gonzalez-Polo RA, Casares N, Perfettini JL, Dessen P, Larochette N, et al. Inhibition of macroautophagy triggers apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol. 2005;25:1025–1040. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.3.1025-1040.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanzawa T, Germano IM, Komata T, Ito H, Kondo Y, Kondo S. Role of autophagy in temozolomide-induced cytotoxicity for malignant glioma cells. Cell Death Differ. 2004;11:448–457. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4401359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mora R, Abschuetz A, Kees T, Dokic I, Joschko N, Kleber S, et al. TNF-alpha- and TRAIL-resistant glioma cells undergo autophagy-dependent cell death induced by activated microglia. Glia. 2009;57:561–581. doi: 10.1002/glia.20785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denizot F, Lang R. Rapid colorimetric assay for cell growth and survival. Modifications to the tetrazolium dye procedure giving improved sensitivity and reliability. J Immunol Methods. 1986;89:271–277. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90368-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogler M, Durr K, Jovanovic M, Debatin KM, Fulda S. Regulation of TRAIL-induced apoptosis by XIAP in pancreatic carcinoma cells. Oncogene. 2007;26:248–257. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabeya Y, Mizushima N, Ueno T, Yamamoto A, Kirisako T, Noda T, et al. LC3, a mammalian homologue of yeast Apg8p, is localized in autophagosome membranes after processing. EMBO J. 2000;19:5720–5728. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.21.5720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto A, Tagawa Y, Yoshimori T, Moriyama Y, Masaki R, Tashiro Y. Bafilomycin A1 prevents maturation of autophagic vacuoles by inhibiting fusion between autophagosomes and lysosomes in rat hepatoma cell line, H-4-II-E cells. Cell Struct Funct. 1998;23:33–42. doi: 10.1247/csf.23.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.