Abstract
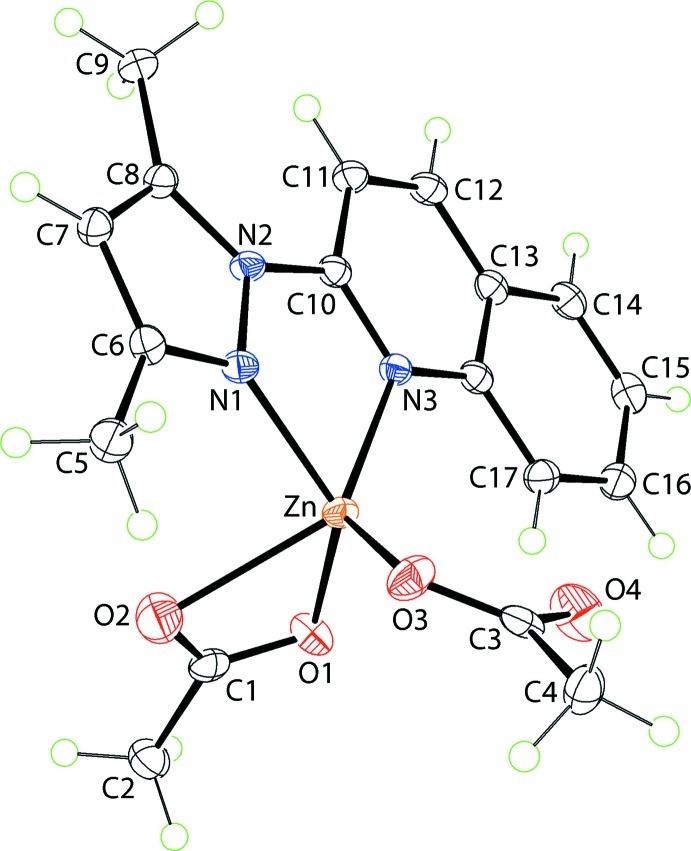
The ZnII atom in the title compound, [Zn(C2H3O2)2(C14H13N3)], is coordinated by an N2O3 donor set defined by the quinolinyl- and pyrazolyl-N atoms of the chelating heterocyclic ligand, and three carboxylate-O atoms derived from the monodentate and bidentate carboxylate ligands. Distortions from the ideal square-pyramidal coordination geometry relate to the restricted bite angle of the chelating ligands, i.e. O—Zn—O = 59.65 (5) and N—Zn—N = 76.50 (6)°, and the close approach of the non-coordinating carbonyl atom [Zn⋯O = 2.858 (2) Å]. In the crystal, molecules are consolidated into a three-dimensional architecture by C—H⋯O interactions
Related literature
For background to luminescent coordination complexes, see: Bai et al. (2011 ▶, 2012 ▶); Chou et al. (2011 ▶); Wang (2001 ▶). For the synthesis, see: Savel’eva et al. (2009 ▶); Scott et al. (1952 ▶). For the structure of the dichlorido analogue, see: Najib et al. (2012 ▶). For additional geometric analysis, see: Addison et al. (1984 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
[Zn(C2H3O2)2(C14H13N3)]
M r = 406.73
Triclinic,
a = 7.6586 (4) Å
b = 10.7334 (6) Å
c = 11.5772 (4) Å
α = 69.437 (4)°
β = 81.546 (3)°
γ = 72.736 (4)°
V = 849.93 (7) Å3
Z = 2
Cu Kα radiation
μ = 2.27 mm−1
T = 100 K
0.25 × 0.15 × 0.05 mm
Data collection
Agilent SuperNova Dual diffractometer with Atlas detector
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2012 ▶) T min = 0.617, T max = 1.000
6205 measured reflections
3498 independent reflections
3322 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.021
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.030
wR(F 2) = 0.081
S = 1.03
3498 reflections
239 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.67 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.45 e Å−3
Data collection: CrysAlis PRO (Agilent, 2012 ▶); cell refinement: CrysAlis PRO; data reduction: CrysAlis PRO; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 (Farrugia, 1997 ▶) and DIAMOND (Brandenburg, 2006 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: publCIF (Westrip, 2010 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812025664/hb6839sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812025664/hb6839Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Selected bond lengths (Å).
| Zn—O1 | 2.0388 (14) |
| Zn—O2 | 2.3240 (15) |
| Zn—O3 | 1.9397 (13) |
| Zn—N1 | 2.0570 (15) |
| Zn—N3 | 2.1460 (14) |
Table 2. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C4—H4B⋯O3i | 0.98 | 2.57 | 3.544 (2) | 176 |
| C5—H5A⋯O2ii | 0.98 | 2.60 | 3.417 (3) | 141 |
| C7—H7⋯O2ii | 0.95 | 2.56 | 3.235 (2) | 128 |
| C9—H9C⋯O4iii | 0.98 | 2.36 | 3.274 (2) | 156 |
| C12—H12⋯O1iv | 0.95 | 2.51 | 3.310 (2) | 142 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 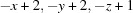 ; (ii)
; (ii) 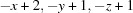 ; (iii)
; (iii) 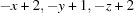 ; (iv)
; (iv) 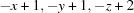 .
.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge funding from the Brunei Research Council, and thank the Ministry of Higher Education (Malaysia) for funding structural studies through the High-Impact Research scheme (UM.C/HIR/MOHE/SC/3).
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Many ZnII complexes of nitrogen-containing ligands exhibit intense emission at room temperature (Wang, 2001; Chou et al., 2011; Bai et al., 2011; Bai et al., 2012). The title compound was prepared as part of a series of potentially luminescent coordination complexes for use in organic light emitting diode (OLED) materials. We have previously reported the solid-state structure of dichlorido[2-(3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-1-yl-2)quinoline]zinc(II) (Najib et al., 2012), i.e. the dichlorido analogue of the title compound, (I).
The ZnII atom in (I), Fig. 1, is chelated by quinolinyl- and pyrazolyl-N atoms of the heterocyclic ligand, and three carboxylate-O atoms derived from the monodentate and bidentate carboxylates, Table 1. The resulting N2O3 donor set defines an approximate square pyramid with the Zn atom lying 0.8591 (8) Å out of the plane defined by the O1, O2, N1 and N3 atoms [r.m.s. deviation = 0.1122 Å] in the direction of the O3 atom. The assignment of coordination geometry is quantified by the value of τ = 0.06 which compares to the τ values of 0.0 and 1.0 for ideal square pyramidal and trigonal bipyramidal geometries, respectively (Addison et al., 1984). Significant distortions in the coordination geometry are apparent owing the restricted bite angles of the chelating ligands, i.e. O1—Zn—O2 = 59.65 (5)° and N1—Zn—N3 = 76.50 (6)°. Further distortions are related to the relatively close approach of the O4 atom to Zn, the Zn···O4 separation is 2.858 (2) Å. The five-membered chelate ring is approximately planar with a r.m.s. deviation = 0.088 Å and with maximum deviations of 0.074 (2) and -0.057 (1) Å for the N1 and Zn atoms, respectively. The bidentate ligand is planar with the dihedral angle between the quinolinyl and pyrazolyl rings being 2.14 (6)°.
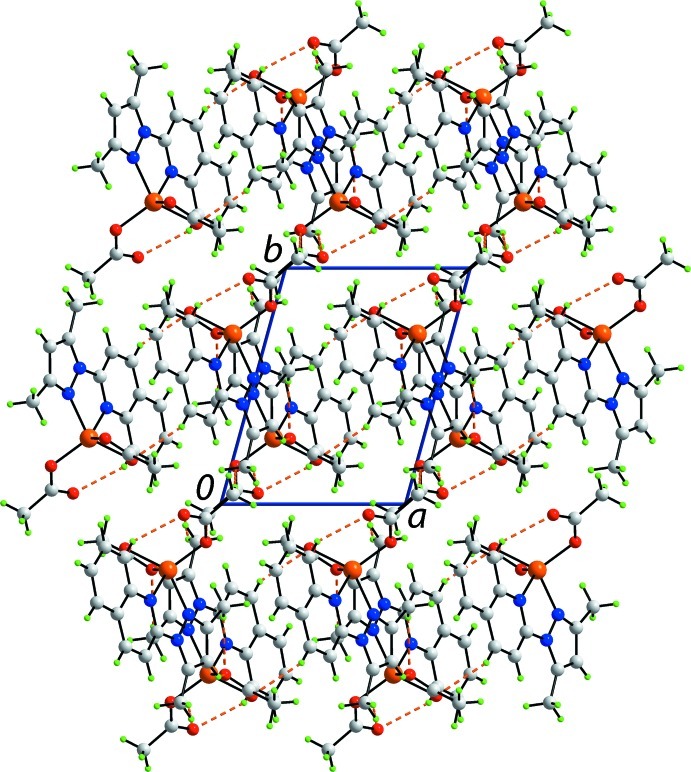
Molecules are consolidated into a three-dimensional architecture by C—H···O interactions, Fig. 2 and Table 2.
Experimental
The title compound was prepared by modification of a literature procedure (Savel'eva et al., 2009) and as previously described for the corresponding dichloride (Najib et al., 2012). 3,5-Dimethyl-1-(2'-quinolyl)pyrazole (0.0908 g), prepared as in the literature (Scott et al., 1952), in a mixture of EtOH (4 ml) and CH2Cl2 (2 ml) was added to a suspension of Zn(OAc)2 (0.0764 g) in EtOH (8 ml). The solution was heated to dissolve the Zn(OAc)2. Light-brown prisms formed over a period of 16 h and were collected by filtration, washed with EtOH and recrystallized from CH2Cl2/hexane. Yield 0.0733 g (44%). M.pt: 474 K. IR v/cm-1: 2925, 2864, 2365, 2323, 1604, 1507, 1424, 1388.
Refinement
Carbon-bound H-atoms were placed in calculated positions [C—H = 0.95–0.98 Å, Uiso(H) = 1.2–1.5Ueq(C)] and were included in the refinement in the riding model approximation.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of (I) showing displacement ellipsoids at the 50% probability level.
Fig. 2.
A view of the unit-cell contents of (I) in projection down the c axis. The C—H···O interactions are shown as orange dashed lines.
Crystal data
| [Zn(C2H3O2)2(C14H13N3)] | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 406.73 | F(000) = 420 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.589 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54184 Å |
| a = 7.6586 (4) Å | Cell parameters from 3775 reflections |
| b = 10.7334 (6) Å | θ = 4.6–76.3° |
| c = 11.5772 (4) Å | µ = 2.27 mm−1 |
| α = 69.437 (4)° | T = 100 K |
| β = 81.546 (3)° | Prism, light-brown |
| γ = 72.736 (4)° | 0.25 × 0.15 × 0.05 mm |
| V = 849.93 (7) Å3 |
Data collection
| Agilent SuperNova Dual diffractometer with Atlas detector | 3498 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: SuperNova (Cu) X-ray Source | 3322 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Mirror monochromator | Rint = 0.021 |
| Detector resolution: 10.4041 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 76.5°, θmin = 4.6° |
| ω scan | h = −9→9 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2012) | k = −12→13 |
| Tmin = 0.617, Tmax = 1.000 | l = −11→14 |
| 6205 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.030 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.081 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.03 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0448P)2 + 0.5376P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3498 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 239 parameters | Δρmax = 0.67 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.45 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Zn | 0.81157 (3) | 0.72065 (2) | 0.729830 (19) | 0.01539 (9) | |
| O1 | 0.54802 (18) | 0.81205 (15) | 0.67857 (12) | 0.0237 (3) | |
| O2 | 0.7235 (2) | 0.72283 (17) | 0.54526 (14) | 0.0333 (3) | |
| O3 | 0.97606 (19) | 0.83912 (14) | 0.66803 (13) | 0.0251 (3) | |
| O4 | 0.8163 (2) | 0.95459 (18) | 0.79237 (13) | 0.0346 (4) | |
| N1 | 0.9903 (2) | 0.53183 (15) | 0.73964 (13) | 0.0157 (3) | |
| N2 | 0.9663 (2) | 0.42401 (15) | 0.84284 (13) | 0.0148 (3) | |
| N3 | 0.76154 (19) | 0.59226 (15) | 0.91411 (13) | 0.0147 (3) | |
| C1 | 0.5715 (3) | 0.78835 (18) | 0.57607 (17) | 0.0191 (3) | |
| C2 | 0.4136 (3) | 0.8434 (2) | 0.49227 (18) | 0.0247 (4) | |
| H2A | 0.4333 | 0.7891 | 0.4366 | 0.037* | |
| H2B | 0.4053 | 0.9401 | 0.4436 | 0.037* | |
| H2C | 0.2996 | 0.8367 | 0.5421 | 0.037* | |
| C3 | 0.9376 (3) | 0.93922 (19) | 0.71118 (16) | 0.0203 (4) | |
| C4 | 1.0519 (3) | 1.0407 (2) | 0.65732 (18) | 0.0238 (4) | |
| H4A | 1.0008 | 1.1202 | 0.6865 | 0.036* | |
| H4B | 1.0515 | 1.0719 | 0.5670 | 0.036* | |
| H4C | 1.1778 | 0.9961 | 0.6834 | 0.036* | |
| C5 | 1.1702 (3) | 0.56456 (19) | 0.54237 (16) | 0.0216 (4) | |
| H5A | 1.1823 | 0.5196 | 0.4800 | 0.032* | |
| H5B | 1.2888 | 0.5773 | 0.5503 | 0.032* | |
| H5C | 1.0801 | 0.6546 | 0.5171 | 0.032* | |
| C6 | 1.1083 (2) | 0.47655 (18) | 0.66347 (16) | 0.0169 (3) | |
| C7 | 1.1602 (2) | 0.33201 (18) | 0.71639 (16) | 0.0172 (3) | |
| H7 | 1.2427 | 0.2686 | 0.6804 | 0.021* | |
| C8 | 1.0696 (2) | 0.29988 (18) | 0.82920 (16) | 0.0162 (3) | |
| C9 | 1.0774 (3) | 0.15864 (18) | 0.91825 (16) | 0.0197 (3) | |
| H9A | 1.1598 | 0.0897 | 0.8838 | 0.029* | |
| H9B | 0.9545 | 0.1441 | 0.9330 | 0.029* | |
| H9C | 1.1231 | 0.1494 | 0.9964 | 0.029* | |
| C10 | 0.8445 (2) | 0.45914 (18) | 0.93770 (15) | 0.0146 (3) | |
| C11 | 0.8173 (2) | 0.35645 (18) | 1.04951 (16) | 0.0175 (3) | |
| H11 | 0.8819 | 0.2624 | 1.0634 | 0.021* | |
| C12 | 0.6956 (2) | 0.39558 (19) | 1.13728 (16) | 0.0186 (3) | |
| H12 | 0.6735 | 0.3279 | 1.2127 | 0.022* | |
| C13 | 0.6026 (2) | 0.53597 (18) | 1.11662 (16) | 0.0165 (3) | |
| C14 | 0.4758 (2) | 0.5825 (2) | 1.20508 (16) | 0.0197 (4) | |
| H14 | 0.4464 | 0.5176 | 1.2803 | 0.024* | |
| C15 | 0.3960 (2) | 0.7202 (2) | 1.18233 (17) | 0.0212 (4) | |
| H15 | 0.3129 | 0.7509 | 1.2423 | 0.025* | |
| C16 | 0.4366 (2) | 0.81699 (19) | 1.06979 (17) | 0.0204 (4) | |
| H16 | 0.3813 | 0.9126 | 1.0554 | 0.025* | |
| C17 | 0.5549 (2) | 0.77526 (18) | 0.98073 (16) | 0.0183 (3) | |
| H17 | 0.5788 | 0.8414 | 0.9047 | 0.022* | |
| C18 | 0.6406 (2) | 0.63361 (18) | 1.00311 (15) | 0.0157 (3) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Zn | 0.01744 (13) | 0.01236 (13) | 0.01501 (13) | −0.00462 (9) | −0.00080 (9) | −0.00227 (9) |
| O1 | 0.0225 (7) | 0.0315 (7) | 0.0164 (6) | −0.0077 (6) | −0.0021 (5) | −0.0058 (5) |
| O2 | 0.0279 (8) | 0.0360 (8) | 0.0346 (8) | 0.0037 (6) | −0.0070 (6) | −0.0178 (7) |
| O3 | 0.0254 (7) | 0.0173 (6) | 0.0335 (7) | −0.0087 (5) | −0.0018 (6) | −0.0067 (5) |
| O4 | 0.0350 (8) | 0.0474 (9) | 0.0219 (7) | −0.0177 (7) | 0.0070 (6) | −0.0096 (6) |
| N1 | 0.0193 (7) | 0.0134 (7) | 0.0132 (6) | −0.0059 (6) | −0.0005 (5) | −0.0015 (5) |
| N2 | 0.0172 (7) | 0.0121 (6) | 0.0133 (6) | −0.0044 (5) | −0.0012 (5) | −0.0012 (5) |
| N3 | 0.0159 (7) | 0.0141 (7) | 0.0139 (6) | −0.0045 (5) | −0.0019 (5) | −0.0034 (5) |
| C1 | 0.0218 (9) | 0.0131 (8) | 0.0210 (8) | −0.0073 (7) | −0.0013 (7) | −0.0013 (6) |
| C2 | 0.0265 (10) | 0.0261 (10) | 0.0220 (9) | −0.0074 (8) | −0.0060 (7) | −0.0062 (7) |
| C3 | 0.0231 (9) | 0.0210 (9) | 0.0125 (7) | −0.0048 (7) | −0.0062 (6) | 0.0009 (6) |
| C4 | 0.0294 (10) | 0.0212 (9) | 0.0253 (9) | −0.0116 (8) | 0.0022 (7) | −0.0103 (7) |
| C5 | 0.0258 (9) | 0.0205 (9) | 0.0179 (8) | −0.0085 (7) | 0.0030 (7) | −0.0053 (7) |
| C6 | 0.0178 (8) | 0.0186 (8) | 0.0159 (8) | −0.0062 (7) | −0.0010 (6) | −0.0063 (7) |
| C7 | 0.0180 (8) | 0.0163 (8) | 0.0188 (8) | −0.0048 (6) | −0.0019 (6) | −0.0070 (7) |
| C8 | 0.0173 (8) | 0.0139 (8) | 0.0184 (8) | −0.0037 (6) | −0.0040 (6) | −0.0055 (6) |
| C9 | 0.0232 (9) | 0.0134 (8) | 0.0201 (8) | −0.0032 (7) | −0.0030 (7) | −0.0034 (7) |
| C10 | 0.0153 (8) | 0.0150 (8) | 0.0139 (7) | −0.0056 (6) | −0.0022 (6) | −0.0031 (6) |
| C11 | 0.0204 (8) | 0.0145 (8) | 0.0167 (8) | −0.0056 (6) | −0.0020 (6) | −0.0026 (6) |
| C12 | 0.0205 (8) | 0.0183 (8) | 0.0148 (8) | −0.0075 (7) | −0.0015 (6) | −0.0007 (6) |
| C13 | 0.0151 (8) | 0.0196 (8) | 0.0161 (8) | −0.0071 (7) | −0.0018 (6) | −0.0049 (7) |
| C14 | 0.0187 (8) | 0.0255 (9) | 0.0152 (8) | −0.0078 (7) | 0.0001 (6) | −0.0058 (7) |
| C15 | 0.0166 (8) | 0.0288 (10) | 0.0206 (8) | −0.0053 (7) | 0.0002 (6) | −0.0118 (7) |
| C16 | 0.0171 (8) | 0.0205 (9) | 0.0246 (9) | −0.0034 (7) | −0.0029 (7) | −0.0089 (7) |
| C17 | 0.0177 (8) | 0.0168 (8) | 0.0203 (8) | −0.0049 (7) | −0.0027 (6) | −0.0049 (7) |
| C18 | 0.0151 (8) | 0.0178 (8) | 0.0150 (8) | −0.0059 (6) | −0.0024 (6) | −0.0041 (6) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Zn—O1 | 2.0388 (14) | C5—H5B | 0.9800 |
| Zn—O2 | 2.3240 (15) | C5—H5C | 0.9800 |
| Zn—O3 | 1.9397 (13) | C6—C7 | 1.406 (2) |
| Zn—N1 | 2.0570 (15) | C7—C8 | 1.366 (2) |
| Zn—N3 | 2.1460 (14) | C7—H7 | 0.9500 |
| O1—C1 | 1.276 (2) | C8—C9 | 1.494 (2) |
| O2—C1 | 1.243 (2) | C9—H9A | 0.9800 |
| O3—C3 | 1.279 (2) | C9—H9B | 0.9800 |
| O4—C3 | 1.239 (2) | C9—H9C | 0.9800 |
| N1—C6 | 1.327 (2) | C10—C11 | 1.410 (2) |
| N1—N2 | 1.3752 (19) | C11—C12 | 1.366 (3) |
| N2—C8 | 1.383 (2) | C11—H11 | 0.9500 |
| N2—C10 | 1.414 (2) | C12—C13 | 1.412 (3) |
| N3—C10 | 1.326 (2) | C12—H12 | 0.9500 |
| N3—C18 | 1.383 (2) | C13—C18 | 1.418 (2) |
| C1—C2 | 1.507 (3) | C13—C14 | 1.422 (2) |
| C2—H2A | 0.9800 | C14—C15 | 1.365 (3) |
| C2—H2B | 0.9800 | C14—H14 | 0.9500 |
| C2—H2C | 0.9800 | C15—C16 | 1.413 (3) |
| C3—C4 | 1.507 (3) | C15—H15 | 0.9500 |
| C4—H4A | 0.9800 | C16—C17 | 1.376 (3) |
| C4—H4B | 0.9800 | C16—H16 | 0.9500 |
| C4—H4C | 0.9800 | C17—C18 | 1.411 (2) |
| C5—C6 | 1.491 (2) | C17—H17 | 0.9500 |
| C5—H5A | 0.9800 | ||
| O3—Zn—O1 | 115.05 (6) | H5A—C5—H5C | 109.5 |
| O3—Zn—N1 | 100.66 (6) | H5B—C5—H5C | 109.5 |
| O1—Zn—N1 | 133.70 (6) | N1—C6—C7 | 109.92 (15) |
| O3—Zn—N3 | 130.20 (6) | N1—C6—C5 | 121.23 (16) |
| O1—Zn—N3 | 99.32 (5) | C7—C6—C5 | 128.84 (16) |
| N1—Zn—N3 | 76.50 (6) | C8—C7—C6 | 107.15 (16) |
| O3—Zn—O2 | 100.51 (6) | C8—C7—H7 | 126.4 |
| O1—Zn—O2 | 59.65 (5) | C6—C7—H7 | 126.4 |
| N1—Zn—O2 | 86.61 (6) | C7—C8—N2 | 106.19 (15) |
| N3—Zn—O2 | 128.42 (6) | C7—C8—C9 | 126.73 (16) |
| C1—O1—Zn | 96.11 (11) | N2—C8—C9 | 127.07 (15) |
| C1—O2—Zn | 83.96 (12) | C8—C9—H9A | 109.5 |
| C3—O3—Zn | 113.89 (12) | C8—C9—H9B | 109.5 |
| C6—N1—N2 | 106.53 (14) | H9A—C9—H9B | 109.5 |
| C6—N1—Zn | 137.00 (12) | C8—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| N2—N1—Zn | 115.34 (10) | H9A—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| N1—N2—C8 | 110.21 (13) | H9B—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| N1—N2—C10 | 116.43 (14) | N3—C10—N2 | 115.77 (14) |
| C8—N2—C10 | 133.36 (14) | N3—C10—C11 | 123.55 (16) |
| C10—N3—C18 | 118.69 (14) | N2—C10—C11 | 120.68 (15) |
| C10—N3—Zn | 114.76 (11) | C12—C11—C10 | 118.35 (16) |
| C18—N3—Zn | 126.25 (11) | C12—C11—H11 | 120.8 |
| O2—C1—O1 | 120.25 (17) | C10—C11—H11 | 120.8 |
| O2—C1—C2 | 120.74 (17) | C11—C12—C13 | 120.42 (16) |
| O1—C1—C2 | 119.00 (17) | C11—C12—H12 | 119.8 |
| C1—C2—H2A | 109.5 | C13—C12—H12 | 119.8 |
| C1—C2—H2B | 109.5 | C12—C13—C18 | 117.95 (16) |
| H2A—C2—H2B | 109.5 | C12—C13—C14 | 122.76 (16) |
| C1—C2—H2C | 109.5 | C18—C13—C14 | 119.28 (16) |
| H2A—C2—H2C | 109.5 | C15—C14—C13 | 120.20 (16) |
| H2B—C2—H2C | 109.5 | C15—C14—H14 | 119.9 |
| O4—C3—O3 | 123.91 (18) | C13—C14—H14 | 119.9 |
| O4—C3—C4 | 120.51 (18) | C14—C15—C16 | 120.16 (17) |
| O3—C3—C4 | 115.58 (16) | C14—C15—H15 | 119.9 |
| C3—C4—H4A | 109.5 | C16—C15—H15 | 119.9 |
| C3—C4—H4B | 109.5 | C17—C16—C15 | 121.15 (17) |
| H4A—C4—H4B | 109.5 | C17—C16—H16 | 119.4 |
| C3—C4—H4C | 109.5 | C15—C16—H16 | 119.4 |
| H4A—C4—H4C | 109.5 | C16—C17—C18 | 119.54 (16) |
| H4B—C4—H4C | 109.5 | C16—C17—H17 | 120.2 |
| C6—C5—H5A | 109.5 | C18—C17—H17 | 120.2 |
| C6—C5—H5B | 109.5 | N3—C18—C17 | 119.36 (15) |
| H5A—C5—H5B | 109.5 | N3—C18—C13 | 121.01 (16) |
| C6—C5—H5C | 109.5 | C17—C18—C13 | 119.63 (16) |
| O3—Zn—O1—C1 | 86.61 (12) | Zn—N1—C6—C7 | −165.93 (13) |
| N1—Zn—O1—C1 | −50.21 (13) | N2—N1—C6—C5 | −178.46 (15) |
| N3—Zn—O1—C1 | −130.39 (11) | Zn—N1—C6—C5 | 15.0 (3) |
| O2—Zn—O1—C1 | −1.07 (10) | N1—C6—C7—C8 | −0.2 (2) |
| O3—Zn—O2—C1 | −111.88 (12) | C5—C6—C7—C8 | 178.77 (18) |
| O1—Zn—O2—C1 | 1.10 (10) | C6—C7—C8—N2 | −0.27 (19) |
| N1—Zn—O2—C1 | 147.89 (12) | C6—C7—C8—C9 | 178.33 (17) |
| N3—Zn—O2—C1 | 78.10 (13) | N1—N2—C8—C7 | 0.66 (19) |
| O1—Zn—O3—C3 | 65.51 (14) | C10—N2—C8—C7 | 179.74 (17) |
| N1—Zn—O3—C3 | −144.72 (13) | N1—N2—C8—C9 | −177.92 (16) |
| N3—Zn—O3—C3 | −63.46 (15) | C10—N2—C8—C9 | 1.2 (3) |
| O2—Zn—O3—C3 | 126.78 (13) | C18—N3—C10—N2 | 179.97 (14) |
| O3—Zn—N1—C6 | −55.42 (18) | Zn—N3—C10—N2 | 5.87 (19) |
| O1—Zn—N1—C6 | 85.47 (19) | C18—N3—C10—C11 | −0.4 (3) |
| N3—Zn—N1—C6 | 175.51 (19) | Zn—N3—C10—C11 | −174.50 (13) |
| O2—Zn—N1—C6 | 44.64 (18) | N1—N2—C10—N3 | 2.6 (2) |
| O3—Zn—N1—N2 | 138.85 (11) | C8—N2—C10—N3 | −176.44 (17) |
| O1—Zn—N1—N2 | −80.26 (13) | N1—N2—C10—C11 | −177.04 (15) |
| N3—Zn—N1—N2 | 9.79 (11) | C8—N2—C10—C11 | 3.9 (3) |
| O2—Zn—N1—N2 | −121.08 (12) | N3—C10—C11—C12 | 1.6 (3) |
| C6—N1—N2—C8 | −0.80 (18) | N2—C10—C11—C12 | −178.81 (16) |
| Zn—N1—N2—C8 | 169.09 (11) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | −1.1 (3) |
| C6—N1—N2—C10 | 179.95 (14) | C11—C12—C13—C18 | −0.4 (3) |
| Zn—N1—N2—C10 | −10.16 (18) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | −179.51 (17) |
| O3—Zn—N3—C10 | −101.18 (13) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | 177.08 (17) |
| O1—Zn—N3—C10 | 124.36 (12) | C18—C13—C14—C15 | −2.0 (3) |
| N1—Zn—N3—C10 | −8.53 (12) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | 1.1 (3) |
| O2—Zn—N3—C10 | 65.92 (14) | C14—C15—C16—C17 | 0.7 (3) |
| O3—Zn—N3—C18 | 85.24 (15) | C15—C16—C17—C18 | −1.5 (3) |
| O1—Zn—N3—C18 | −49.22 (14) | C10—N3—C18—C17 | 178.31 (15) |
| N1—Zn—N3—C18 | 177.89 (15) | Zn—N3—C18—C17 | −8.3 (2) |
| O2—Zn—N3—C18 | −107.66 (14) | C10—N3—C18—C13 | −1.2 (2) |
| Zn—O2—C1—O1 | −1.76 (17) | Zn—N3—C18—C13 | 172.15 (12) |
| Zn—O2—C1—C2 | 177.01 (16) | C16—C17—C18—N3 | −179.02 (16) |
| Zn—O1—C1—O2 | 2.01 (19) | C16—C17—C18—C13 | 0.5 (3) |
| Zn—O1—C1—C2 | −176.78 (14) | C12—C13—C18—N3 | 1.6 (2) |
| Zn—O3—C3—O4 | 5.5 (2) | C14—C13—C18—N3 | −179.25 (15) |
| Zn—O3—C3—C4 | −174.94 (12) | C12—C13—C18—C17 | −177.93 (16) |
| N2—N1—C6—C7 | 0.63 (19) | C14—C13—C18—C17 | 1.2 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C4—H4B···O3i | 0.98 | 2.57 | 3.544 (2) | 176 |
| C5—H5A···O2ii | 0.98 | 2.60 | 3.417 (3) | 141 |
| C7—H7···O2ii | 0.95 | 2.56 | 3.235 (2) | 128 |
| C9—H9C···O4iii | 0.98 | 2.36 | 3.274 (2) | 156 |
| C12—H12···O1iv | 0.95 | 2.51 | 3.310 (2) | 142 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+2, −y+2, −z+1; (ii) −x+2, −y+1, −z+1; (iii) −x+2, −y+1, −z+2; (iv) −x+1, −y+1, −z+2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: HB6839).
References
- Addison, A. W., Rao, T. N., Reedijk, J., van Rijn, J. & Verschoor, G. C. (1984). J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. pp. 1349–1356.
- Agilent (2012). CrysAlis PRO Agilent Technologies, Yarnton, England.
- Bai, S.-Q., Young, D. J. & Hor, T. S. A. (2011). Chem. Asian J. 6, 292–304. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bai, S.-Q., Young, A. M., Hu, J. J., Young, D. J., Zhang, X., Zong, Y., Xu, J., Zuo, J.-L. & Hor, T. S. A. (2012). CrystEngComm, 14, 961–971.
- Brandenburg, K. (2006). DIAMOND Crystal Impact GbR, Bonn, Germany.
- Chou, P.-T., Chi, Y., Chung, M.-W. & Lin, C.-C. (2011). Coord. Chem. Rev. 255, 2653–2665.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst. 30, 565.
- Najib, M. H. bin, Tan, A. L., Young, D. J., Ng, S. W. & Tiekink, E. R. T. (2012). Acta Cryst. E68, m571–m572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Savel’eva, Z. A., Popov, S. A., Klevtsova, R. F., Glinskaya, L. A., Uskov, E. M., Tkachev, A. V. & Larionov, S. V. (2009). Russ. Chem. Bull., Int. Ed 58, 1837–1840.
- Scott, F. L., Crowley, K. M. & Reilly, J. (1952). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 74, 3444–3445.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Wang, S. (2001). Coord. Chem. Rev. 215, 79–98.
- Westrip, S. P. (2010). J. Appl. Cryst. 43, 920–925.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812025664/hb6839sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812025664/hb6839Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report