Abstract
In the title compound, C21H24N4O2, inversion-related molecules are linked into dimers through pairs of N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, which generate R 2 2(8) motifs. As well as dimer formation, an additional N—H⋯O hydrogen bond and two C—H⋯π contacts, involving H atoms from the phenyl ring and the pyrrole and benzene rings of the indole system, generate a three-dimensional network.
Related literature
For the biological activity of indole acetic acid derivatives and indomethacin, see: Klassen (2001 ▶); Kirnura & Doi (1998 ▶); Rossiter et al. (2002 ▶); Shahab et al. (2009 ▶). For related structures, see: Trask et al. (2004 ▶); Gelbrich et al. (2007 ▶). For hydrogen-bond motifs, see: Bernstein et al. (1995 ▶).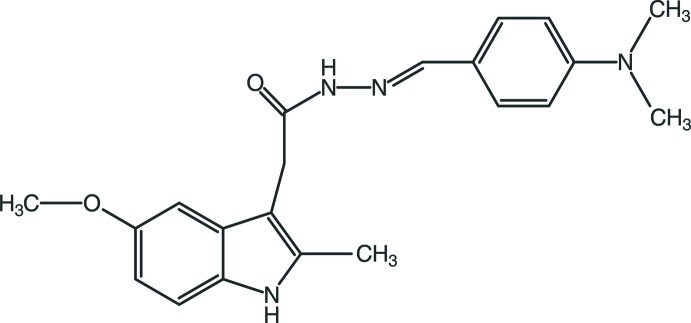
Experimental
Crystal data
C21H24N4O2
M r = 364.44
Monoclinic,

a = 9.600 (5) Å
b = 7.548 (4) Å
c = 25.802 (14) Å
β = 95.10 (1)°
V = 1862.2 (17) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.09 mm−1
T = 100 K
0.10 × 0.01 × 0.01 mm
Data collection
Rigaku Saturn724+ diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrystalClear; Rigaku, 2001 ▶) T min = 0.992, T max = 0.999
10458 measured reflections
3280 independent reflections
2386 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.048
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.069
wR(F 2) = 0.159
S = 1.15
3280 reflections
248 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.21 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.27 e Å−3
Data collection: CrystalClear (Rigaku, 2001 ▶); cell refinement: CrystalClear (Rigaku, 2001 ▶); data reduction: CrystalClear; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 1997 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: WinGX (Farrugia, 1999 ▶) and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812026013/sj5239sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812026013/sj5239Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812026013/sj5239Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
Cg1 and Cg2 are the centroids of the N1/C1–C3/C8 and C3–C8 rings, respectively.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1⋯O2i | 0.88 | 2.21 | 2.984 (3) | 147 |
| N2—H2⋯O1ii | 0.88 | 1.97 | 2.854 (3) | 179 |
| C18—H18⋯Cg2iii | 0.95 | 2.84 | 3.692 (4) | 151 |
| C19—H19⋯Cg1iii | 0.95 | 2.72 | 3.508 (4) | 141 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Higher Education Ministry of Iraq for financial support. They also thank Manchester Metropolitan University and the UK National Crystallography Service, University of Southampton, for supporting this study.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) is the main auxin in plants, controlling many important physiological processes including cell enlargement and division, tissue differentiation, and responses to light and gravity (Shahab et al., 2009). In addition, derivatives of substituted indole-acetic acid are active oxidative pro-drugs with potential of cancer therapy (Rossiter et al., 2002). Indomethacin is an example of IAA derivatives exhibits anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antipyretic properties and is therefore used to treat acute and chronic pain (Klassen, 2001; Kirnura & Doi, 1998). As part of our interest in production of potential pharmaceutical active compounds based on well known pharmacophores e.g indomethacin, we are herein reporting the synthesis and crystal structure of the title compound.
In the title molecule (I), Fig. 1, the 1H-indole system (N1\C1—C8) is essentially planar [maximum deviation -0.025 (3) Å for atom C1] and makes a dihedral angle of 73.65 (12) ° with the (C14–C19) benzene ring. The bond lengths and angles are normal and comparable to those observed in the related structures (Trask et al., 2004; Gelbrich et al., 2007).
In the crystal structure, molecules form a dimer, in which a pair of N1—H1···O2 hydrogen bonds generate an intermolecular R22(8) ring (Bernstein, et al., 1995; Table 1, Fig. 2). These dimers are further linked by the N2—H2···O1 hydrogen bonds. Two additional C—H···π interactions also contribute to an extensive three dimensional network (Table 1).
Experimental
A solution of 341 mg (1 mmol) 2-{1-[(4-chlorophenyl)carbonyl]-2-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl}acetohydrazide in 30 ml ethanol was added to a solution of 149 mg (1 mmol) 4-(dimethylamino)benzaldehyde in 20 ml ethanol in presence of few drops of catalytic glacial acetic acid and refluxed at 350 K for 6 h. On evaporating the excess solvent, a mass solid product was collected, washed with cold ethanol and dried. The crude product was recrystallized from ethanol to afford the title compound in a good yield (77%). Pure crystals suitable for X-ray diffraction were grown by slow evaporation of ethanol solution of the product at room temperature (m.p. 381 K).
Refinement
All H-atoms were placed in calculated positions [N—H = 0.88 Å, C—H (aromatic) = 0.95 Å, C—H (methyl) = 0.98 Å and C—H (methylene) = 0.99 Å] and were refined by using a riding model approximation, with Uiso(H) = 1.2 or 1.5 Ueq(C,N).
Figures
Fig. 1.
View of the title compound with the atom numbering scheme. Displacement ellipsoids for non-H atoms are drawn at the 50% probability level.
Fig. 2.
View of the molecular packing and the dimers formed through N—H···O hydrogen bonds of viewed along the b axis. Hydrogen atoms not involved in hydrogen bonding have been omitted for clarity.
Crystal data
| C21H24N4O2 | F(000) = 776 |
| Mr = 364.44 | Dx = 1.300 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71075 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 5554 reflections |
| a = 9.600 (5) Å | θ = 2.5–31.2° |
| b = 7.548 (4) Å | µ = 0.09 mm−1 |
| c = 25.802 (14) Å | T = 100 K |
| β = 95.10 (1)° | Needle, colourless |
| V = 1862.2 (17) Å3 | 0.10 × 0.01 × 0.01 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Rigaku Saturn724+ diffractometer | 3280 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: Rotating Anode | 2386 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Confocal monochromator | Rint = 0.048 |
| Detector resolution: 28.5714 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 25.0°, θmin = 3.1° |
| profile data from ω–scans | h = −11→10 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrystalClear; Rigaku, 2001) | k = −8→8 |
| Tmin = 0.992, Tmax = 0.999 | l = −30→30 |
| 10458 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.069 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.159 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.15 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0588P)2 + 0.6401P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3280 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 248 parameters | Δρmax = 0.21 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.27 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. Bond distances, angles etc. have been calculated using the rounded fractional coordinates. All su's are estimated from the variances of the (full) variance-covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account in the estimation of distances, angles and torsion angles |
| Refinement. Refinement on F2 for ALL reflections except those flagged by the user for potential systematic errors. Weighted R-factors wR and all goodnesses of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The observed criterion of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating -R-factor-obs etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R-factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.1627 (2) | 0.5758 (2) | 0.03536 (8) | 0.0319 (7) | |
| O2 | 0.3022 (2) | 0.7669 (2) | 0.21269 (8) | 0.0334 (7) | |
| N1 | 0.3847 (2) | 0.0787 (3) | 0.15126 (9) | 0.0291 (8) | |
| N2 | 0.1218 (2) | 0.3244 (3) | −0.00973 (9) | 0.0294 (8) | |
| N3 | 0.1684 (2) | 0.1639 (3) | −0.02855 (9) | 0.0283 (8) | |
| N4 | 0.1656 (2) | −0.5960 (3) | −0.14532 (10) | 0.0326 (9) | |
| C1 | 0.3807 (3) | 0.1057 (4) | 0.09794 (11) | 0.0270 (9) | |
| C2 | 0.3661 (3) | 0.2837 (3) | 0.08759 (11) | 0.0239 (8) | |
| C3 | 0.3558 (3) | 0.3719 (4) | 0.13661 (11) | 0.0250 (9) | |
| C4 | 0.3339 (3) | 0.5484 (4) | 0.15053 (11) | 0.0250 (9) | |
| C5 | 0.3263 (3) | 0.5893 (4) | 0.20232 (12) | 0.0272 (9) | |
| C6 | 0.3425 (3) | 0.4582 (4) | 0.24098 (11) | 0.0300 (10) | |
| C7 | 0.3625 (3) | 0.2838 (4) | 0.22774 (12) | 0.0305 (10) | |
| C8 | 0.3676 (3) | 0.2404 (4) | 0.17560 (12) | 0.0271 (9) | |
| C9 | 0.3920 (3) | −0.0469 (4) | 0.06217 (12) | 0.0319 (10) | |
| C10 | 0.2608 (3) | 0.8097 (4) | 0.26328 (12) | 0.0358 (10) | |
| C11 | 0.3555 (3) | 0.3737 (4) | 0.03525 (11) | 0.0274 (9) | |
| C12 | 0.2068 (3) | 0.4328 (4) | 0.01983 (11) | 0.0262 (9) | |
| C13 | 0.0743 (3) | 0.0759 (4) | −0.05616 (12) | 0.0312 (10) | |
| C14 | 0.1025 (3) | −0.0925 (4) | −0.08031 (11) | 0.0277 (9) | |
| C15 | 0.2347 (3) | −0.1724 (4) | −0.07641 (12) | 0.0301 (10) | |
| C16 | 0.2558 (3) | −0.3363 (4) | −0.09783 (11) | 0.0293 (10) | |
| C17 | 0.1459 (3) | −0.4293 (4) | −0.12538 (11) | 0.0273 (9) | |
| C18 | 0.0138 (3) | −0.3465 (4) | −0.13131 (12) | 0.0314 (10) | |
| C19 | −0.0058 (3) | −0.1828 (4) | −0.10940 (12) | 0.0316 (10) | |
| C20 | 0.2987 (3) | −0.6849 (4) | −0.13441 (12) | 0.0331 (10) | |
| C21 | 0.0517 (3) | −0.6876 (4) | −0.17479 (13) | 0.0372 (10) | |
| H1 | 0.39620 | −0.02420 | 0.16710 | 0.0350* | |
| H2 | 0.03410 | 0.35570 | −0.01740 | 0.0350* | |
| H4 | 0.32440 | 0.63850 | 0.12470 | 0.0300* | |
| H6 | 0.33980 | 0.48990 | 0.27650 | 0.0360* | |
| H7 | 0.37260 | 0.19470 | 0.25380 | 0.0370* | |
| H9A | 0.30800 | −0.12060 | 0.06220 | 0.0480* | |
| H9B | 0.47450 | −0.11770 | 0.07380 | 0.0480* | |
| H9C | 0.40100 | −0.00320 | 0.02690 | 0.0480* | |
| H10A | 0.18490 | 0.73070 | 0.27160 | 0.0540* | |
| H10B | 0.22840 | 0.93280 | 0.26350 | 0.0540* | |
| H10C | 0.34080 | 0.79490 | 0.28930 | 0.0540* | |
| H11A | 0.38590 | 0.29080 | 0.00870 | 0.0330* | |
| H11B | 0.41840 | 0.47780 | 0.03660 | 0.0330* | |
| H13 | −0.01760 | 0.12310 | −0.06100 | 0.0370* | |
| H15 | 0.31160 | −0.11210 | −0.05860 | 0.0360* | |
| H16 | 0.34650 | −0.38750 | −0.09390 | 0.0350* | |
| H18 | −0.06220 | −0.40390 | −0.15050 | 0.0380* | |
| H19 | −0.09560 | −0.12940 | −0.11410 | 0.0380* | |
| H20A | 0.37050 | −0.62330 | −0.15230 | 0.0500* | |
| H20B | 0.29080 | −0.80760 | −0.14670 | 0.0500* | |
| H20C | 0.32490 | −0.68400 | −0.09680 | 0.0500* | |
| H21A | −0.02660 | −0.70150 | −0.15320 | 0.0560* | |
| H21B | 0.08360 | −0.80470 | −0.18520 | 0.0560* | |
| H21C | 0.02110 | −0.61870 | −0.20590 | 0.0560* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0352 (12) | 0.0256 (11) | 0.0337 (12) | 0.0026 (9) | −0.0034 (10) | −0.0007 (9) |
| O2 | 0.0435 (13) | 0.0253 (11) | 0.0317 (12) | −0.0023 (10) | 0.0048 (10) | −0.0037 (9) |
| N1 | 0.0331 (14) | 0.0228 (13) | 0.0304 (15) | 0.0052 (11) | −0.0033 (11) | 0.0032 (11) |
| N2 | 0.0279 (13) | 0.0251 (14) | 0.0338 (15) | 0.0055 (11) | −0.0052 (11) | −0.0033 (11) |
| N3 | 0.0326 (14) | 0.0221 (13) | 0.0301 (14) | 0.0016 (11) | 0.0026 (11) | 0.0005 (11) |
| N4 | 0.0258 (13) | 0.0269 (14) | 0.0439 (17) | 0.0008 (11) | −0.0031 (12) | −0.0045 (12) |
| C1 | 0.0215 (14) | 0.0291 (16) | 0.0300 (17) | 0.0024 (13) | 0.0003 (12) | −0.0029 (14) |
| C2 | 0.0187 (13) | 0.0247 (15) | 0.0277 (16) | 0.0015 (12) | −0.0014 (12) | −0.0004 (13) |
| C3 | 0.0172 (13) | 0.0268 (16) | 0.0304 (17) | −0.0008 (12) | −0.0012 (12) | 0.0006 (13) |
| C4 | 0.0257 (15) | 0.0219 (15) | 0.0267 (16) | −0.0021 (12) | −0.0021 (12) | 0.0048 (13) |
| C5 | 0.0264 (15) | 0.0220 (15) | 0.0323 (17) | −0.0008 (13) | −0.0015 (13) | −0.0017 (13) |
| C6 | 0.0357 (17) | 0.0310 (17) | 0.0230 (16) | −0.0004 (14) | 0.0018 (13) | 0.0004 (14) |
| C7 | 0.0355 (17) | 0.0294 (17) | 0.0258 (17) | −0.0002 (14) | −0.0017 (13) | 0.0062 (14) |
| C8 | 0.0240 (15) | 0.0245 (15) | 0.0317 (17) | 0.0023 (13) | −0.0032 (12) | 0.0015 (14) |
| C9 | 0.0319 (16) | 0.0271 (16) | 0.0362 (18) | 0.0017 (13) | 0.0011 (14) | −0.0028 (14) |
| C10 | 0.0412 (18) | 0.0318 (17) | 0.0348 (19) | −0.0010 (15) | 0.0065 (15) | −0.0076 (15) |
| C11 | 0.0292 (15) | 0.0269 (16) | 0.0255 (16) | −0.0034 (13) | 0.0000 (13) | 0.0005 (13) |
| C12 | 0.0310 (16) | 0.0252 (16) | 0.0224 (16) | 0.0015 (13) | 0.0019 (13) | 0.0040 (13) |
| C13 | 0.0286 (16) | 0.0291 (17) | 0.0355 (18) | −0.0004 (13) | 0.0008 (14) | −0.0009 (14) |
| C14 | 0.0265 (15) | 0.0263 (16) | 0.0306 (17) | −0.0014 (13) | 0.0047 (13) | 0.0007 (13) |
| C15 | 0.0252 (15) | 0.0313 (17) | 0.0333 (18) | −0.0030 (13) | 0.0001 (13) | −0.0028 (14) |
| C16 | 0.0239 (15) | 0.0302 (17) | 0.0337 (18) | 0.0011 (13) | 0.0016 (13) | 0.0002 (14) |
| C17 | 0.0282 (15) | 0.0235 (16) | 0.0300 (17) | −0.0011 (13) | 0.0018 (13) | 0.0019 (13) |
| C18 | 0.0242 (15) | 0.0295 (17) | 0.0397 (19) | −0.0042 (13) | −0.0010 (13) | 0.0015 (15) |
| C19 | 0.0247 (15) | 0.0300 (17) | 0.0396 (19) | 0.0020 (13) | 0.0009 (13) | 0.0009 (14) |
| C20 | 0.0322 (17) | 0.0320 (18) | 0.0346 (19) | 0.0042 (14) | 0.0008 (14) | −0.0015 (14) |
| C21 | 0.0340 (17) | 0.0291 (17) | 0.047 (2) | −0.0033 (14) | −0.0047 (15) | −0.0053 (15) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—C12 | 1.239 (3) | C15—C16 | 1.377 (4) |
| O2—C5 | 1.390 (3) | C16—C17 | 1.406 (4) |
| O2—C10 | 1.435 (4) | C17—C18 | 1.410 (4) |
| N1—C1 | 1.388 (4) | C18—C19 | 1.379 (4) |
| N1—C8 | 1.389 (4) | C4—H4 | 0.9500 |
| N2—N3 | 1.394 (3) | C6—H6 | 0.9500 |
| N2—C12 | 1.344 (4) | C7—H7 | 0.9500 |
| N3—C13 | 1.285 (4) | C9—H9A | 0.9800 |
| N4—C17 | 1.379 (4) | C9—H9B | 0.9800 |
| N4—C20 | 1.449 (4) | C9—H9C | 0.9800 |
| N4—C21 | 1.451 (4) | C10—H10A | 0.9800 |
| N1—H1 | 0.8800 | C10—H10B | 0.9800 |
| N2—H2 | 0.8800 | C10—H10C | 0.9800 |
| C1—C2 | 1.375 (4) | C11—H11A | 0.9900 |
| C1—C9 | 1.486 (4) | C11—H11B | 0.9900 |
| C2—C3 | 1.441 (4) | C13—H13 | 0.9500 |
| C2—C11 | 1.507 (4) | C15—H15 | 0.9500 |
| C3—C4 | 1.401 (4) | C16—H16 | 0.9500 |
| C3—C8 | 1.411 (4) | C18—H18 | 0.9500 |
| C4—C5 | 1.380 (4) | C19—H19 | 0.9500 |
| C5—C6 | 1.404 (4) | C20—H20A | 0.9800 |
| C6—C7 | 1.378 (4) | C20—H20B | 0.9800 |
| C7—C8 | 1.390 (4) | C20—H20C | 0.9800 |
| C11—C12 | 1.515 (4) | C21—H21A | 0.9800 |
| C13—C14 | 1.452 (4) | C21—H21B | 0.9800 |
| C14—C19 | 1.404 (4) | C21—H21C | 0.9800 |
| C14—C15 | 1.401 (4) | ||
| C5—O2—C10 | 117.2 (2) | C5—C4—H4 | 121.00 |
| C1—N1—C8 | 109.0 (2) | C5—C6—H6 | 120.00 |
| N3—N2—C12 | 122.0 (2) | C7—C6—H6 | 120.00 |
| N2—N3—C13 | 114.3 (2) | C6—C7—H7 | 121.00 |
| C17—N4—C20 | 119.9 (2) | C8—C7—H7 | 121.00 |
| C17—N4—C21 | 120.6 (2) | C1—C9—H9A | 110.00 |
| C20—N4—C21 | 119.5 (2) | C1—C9—H9B | 110.00 |
| C8—N1—H1 | 125.00 | C1—C9—H9C | 109.00 |
| C1—N1—H1 | 126.00 | H9A—C9—H9B | 109.00 |
| N3—N2—H2 | 119.00 | H9A—C9—H9C | 109.00 |
| C12—N2—H2 | 119.00 | H9B—C9—H9C | 109.00 |
| N1—C1—C2 | 109.2 (2) | O2—C10—H10A | 109.00 |
| N1—C1—C9 | 120.3 (3) | O2—C10—H10B | 109.00 |
| C2—C1—C9 | 130.5 (3) | O2—C10—H10C | 110.00 |
| C3—C2—C11 | 125.0 (2) | H10A—C10—H10B | 109.00 |
| C1—C2—C11 | 127.8 (3) | H10A—C10—H10C | 109.00 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 107.2 (2) | H10B—C10—H10C | 109.00 |
| C2—C3—C8 | 107.1 (2) | C2—C11—H11A | 110.00 |
| C4—C3—C8 | 119.4 (3) | C2—C11—H11B | 110.00 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 133.5 (3) | C12—C11—H11A | 109.00 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 118.9 (3) | C12—C11—H11B | 109.00 |
| O2—C5—C4 | 115.2 (3) | H11A—C11—H11B | 108.00 |
| O2—C5—C6 | 123.6 (3) | N3—C13—H13 | 119.00 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 121.2 (3) | C14—C13—H13 | 119.00 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 120.4 (3) | C14—C15—H15 | 119.00 |
| C6—C7—C8 | 118.9 (3) | C16—C15—H15 | 119.00 |
| N1—C8—C7 | 131.3 (3) | C15—C16—H16 | 119.00 |
| C3—C8—C7 | 121.1 (3) | C17—C16—H16 | 119.00 |
| N1—C8—C3 | 107.5 (3) | C17—C18—H18 | 120.00 |
| C2—C11—C12 | 110.8 (2) | C19—C18—H18 | 120.00 |
| N2—C12—C11 | 118.7 (3) | C14—C19—H19 | 119.00 |
| O1—C12—N2 | 120.4 (3) | C18—C19—H19 | 119.00 |
| O1—C12—C11 | 120.9 (3) | N4—C20—H20A | 109.00 |
| N3—C13—C14 | 122.8 (3) | N4—C20—H20B | 109.00 |
| C13—C14—C19 | 119.8 (3) | N4—C20—H20C | 109.00 |
| C15—C14—C19 | 116.9 (3) | H20A—C20—H20B | 109.00 |
| C13—C14—C15 | 123.3 (3) | H20A—C20—H20C | 109.00 |
| C14—C15—C16 | 121.5 (3) | H20B—C20—H20C | 109.00 |
| C15—C16—C17 | 121.4 (3) | N4—C21—H21A | 109.00 |
| N4—C17—C16 | 121.5 (3) | N4—C21—H21B | 110.00 |
| C16—C17—C18 | 117.4 (3) | N4—C21—H21C | 109.00 |
| N4—C17—C18 | 121.1 (3) | H21A—C21—H21B | 109.00 |
| C17—C18—C19 | 120.5 (3) | H21A—C21—H21C | 109.00 |
| C14—C19—C18 | 122.2 (3) | H21B—C21—H21C | 109.00 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 121.00 | ||
| C10—O2—C5—C6 | −14.5 (4) | C4—C3—C8—C7 | −2.2 (4) |
| C10—O2—C5—C4 | 165.7 (2) | C2—C3—C4—C5 | 178.5 (3) |
| C8—N1—C1—C2 | 2.1 (3) | C4—C3—C8—N1 | 178.4 (2) |
| C8—N1—C1—C9 | −178.1 (2) | C2—C3—C8—C7 | 179.6 (3) |
| C1—N1—C8—C7 | 179.3 (3) | C3—C4—C5—C6 | 1.1 (4) |
| C1—N1—C8—C3 | −1.3 (3) | C3—C4—C5—O2 | −179.0 (2) |
| C12—N2—N3—C13 | 180.0 (3) | C4—C5—C6—C7 | −1.9 (4) |
| N3—N2—C12—C11 | −3.1 (4) | O2—C5—C6—C7 | 178.3 (3) |
| N3—N2—C12—O1 | 179.0 (2) | C5—C6—C7—C8 | 0.6 (4) |
| N2—N3—C13—C14 | 178.6 (3) | C6—C7—C8—C3 | 1.4 (4) |
| C20—N4—C17—C18 | −174.1 (3) | C6—C7—C8—N1 | −179.2 (3) |
| C21—N4—C17—C18 | 2.5 (4) | C2—C11—C12—O1 | 84.2 (3) |
| C21—N4—C17—C16 | −178.4 (3) | C2—C11—C12—N2 | −93.7 (3) |
| C20—N4—C17—C16 | 5.1 (4) | N3—C13—C14—C15 | −1.1 (5) |
| C9—C1—C2—C3 | 178.2 (3) | N3—C13—C14—C19 | 179.1 (3) |
| N1—C1—C2—C11 | −179.3 (3) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | 176.9 (3) |
| C9—C1—C2—C11 | 0.9 (5) | C19—C14—C15—C16 | −3.3 (4) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | −2.0 (3) | C13—C14—C19—C18 | −177.2 (3) |
| C11—C2—C3—C8 | 178.5 (3) | C15—C14—C19—C18 | 3.0 (4) |
| C11—C2—C3—C4 | 0.7 (5) | C14—C15—C16—C17 | 1.1 (5) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −176.8 (3) | C15—C16—C17—N4 | −177.7 (3) |
| C1—C2—C11—C12 | 105.6 (3) | C15—C16—C17—C18 | 1.5 (4) |
| C3—C2—C11—C12 | −71.3 (4) | N4—C17—C18—C19 | 177.4 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—C8 | 1.1 (3) | C16—C17—C18—C19 | −1.8 (4) |
| C8—C3—C4—C5 | 0.9 (4) | C17—C18—C19—C14 | −0.5 (5) |
| C2—C3—C8—N1 | 0.1 (3) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg1 and Cg2 are the centroids of the N1/C1–C3/C8 and C3–C8 rings, respectively.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1···O2i | 0.88 | 2.21 | 2.984 (3) | 147 |
| N2—H2···O1ii | 0.88 | 1.97 | 2.854 (3) | 179 |
| C11—H11A···N3 | 0.99 | 2.42 | 2.814 (4) | 103 |
| C18—H18···Cg2iii | 0.95 | 2.84 | 3.692 (4) | 151 |
| C19—H19···Cg1iii | 0.95 | 2.72 | 3.508 (4) | 141 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, y−1, z; (ii) −x, −y+1, −z; (iii) −x, −y, −z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: SJ5239).
References
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N. L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 34, 1555–1573.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst. 30, 565.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst. 32, 837–838.
- Gelbrich, T., Haddow, M. F. & Griesser, U. J. (2007). Acta Cryst C63, o451–o453. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Kirnura, T. & Doi, K. (1998). Histol. Histopathol. 13, 29–36.
- Klassen, L. J. (2001). CJHP, 54, 37-39.
- Rigaku (2001). CrystalClear, The Woodlands, Texas, USA.
- Rossiter, S., Folkes, L. K. & Wardman, P. (2002). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 12, 2523–2526. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Shahab, S., Ahmed, N. & Khan, N. S. (2009). Afr. J. Agric. Res. 4, 1312–1316.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Trask, A. V., Shan, N., Jones, W. & Motherwell, W. D. S. (2004). Acta Cryst. E60, o508–o509.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812026013/sj5239sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812026013/sj5239Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812026013/sj5239Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




