Abstract
The title compound, C13H13ClN2O3, was synthesized in the course of the search for novel bioactive pyrimidine derivatives. The C—O—C angle at the phenoxy O atom is widened to 119.87 (18)°. The dihedral angle between the pyrimidine and benzene rings is 64.2 (3)°.
Related literature
For the biological activity of pyrimidine derivatives, see: Amin et al. (2011 ▶); Chen et al. (2009 ▶); Popova et al. (1999 ▶); Sagi et al. (2011 ▶); Stec et al. (2008 ▶). For related structures of 2-phenoxypyrimidines, see: Shah Bakhtiar et al. (2009a ▶,b
▶). For standard bond lengths, see: Allen et al. (1987 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C13H13ClN2O3
M r = 280.70
Monoclinic,
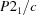
a = 8.3998 (17) Å
b = 23.145 (5) Å
c = 7.7967 (16) Å
β = 117.28 (3)°
V = 1347.2 (6) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.29 mm−1
T = 113 K
0.30 × 0.25 × 0.20 mm
Data collection
Rigaku SCXmini diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrystalClear; Rigaku, 2008 ▶) T min = 0.912, T max = 0.942
11307 measured reflections
2358 independent reflections
1899 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.039
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.054
wR(F 2) = 0.134
S = 1.09
2358 reflections
174 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.62 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.52 e Å−3
Data collection: CrystalClear (Rigaku, 2008 ▶); cell refinement: CrystalClear; data reduction: CrystalClear; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812026220/yk2059sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812026220/yk2059Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812026220/yk2059Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Science Foundation of Nantong University Xinglin College (grant No. 2010 K132) and the Scientific Research Foundation for Talent Introduction of Nantong University.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
In the past few years, many pyrimidine derivatives have drawn much attention in agrochemical and medicinal research because of their diverse bioactivities such as fungicidal, herbicidal and pharmacological activities (Popova et al., 1999; Stec et al., 2008; Chen et al., 2009; Amin et al., 2011; Sagi et al., 2011). In the search of novel biologically active molecules, we have synthesized new pyrimidines. We report here the crystal structure of the target compound. It contains two planar groups, the benzene ring (C7/C8/C9/C10/C11/C12), and the substituted pyrimidine ring (N1/C1/C2/C3/N2/C6) (Fig.1). All bond lengths and angles in the title compound lie within normal ranges (Allen et al., 1987) and are similar to those observed in the related 2-phenoxypyrimidines (Shah Bakhtiar et al., 2009a,b). The plane of pyrimidine ring makes a dihedral angle of 64.2 (3)° with the plane of benzene ring.
Experimental
[4-(4,6-dimethoxypyrimidin-2-yloxy)phenyl]methanol (5 mmol) was dissolved in 50 ml of CH2Cl2. Thionyl chloride (5.5 mmol) was then added dropwise, while cooling on an ice bath. The resulting solution was heated to 298 K for 3 h, and the mixture was poured into 50 ml of ice water. The organic layer was washed with saturated brine(3 x 30 ml) and dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate. The solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure, and the residue was recrystallized from a mixture of petroleum ether/ethyl acetate to obtain colourless crystals. Mp: 354–356 K.
Refinement
All H atoms were placed in calculated positions, with C—H = 0.93, 0.96 and 0.97Å for CH, CH3 and CH2 groups, respectively, and included in the final cycles of refinement using a riding model, with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C).
Figures
Fig. 1.
View of the title compound showing atom labelling scheme. Thermal ellipsoids drawn at the 30% probability level.
Crystal data
| C13H13ClN2O3 | F(000) = 584 |
| Mr = 280.70 | Dx = 1.384 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 11126 reflections |
| a = 8.3998 (17) Å | θ = 3.1–27.6° |
| b = 23.145 (5) Å | µ = 0.29 mm−1 |
| c = 7.7967 (16) Å | T = 113 K |
| β = 117.28 (3)° | Prism, colourless |
| V = 1347.2 (6) Å3 | 0.30 × 0.25 × 0.20 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Rigaku SCXmini diffractometer | 2358 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1899 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.039 |
| Detector resolution: 14.22 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 25.0°, θmin = 3.1° |
| ω and φ scans | h = −9→9 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrystalClear; Rigaku, 2008) | k = −27→27 |
| Tmin = 0.912, Tmax = 0.942 | l = −9→9 |
| 11307 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.054 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.134 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.09 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0495P)2 + 0.8134P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2358 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 174 parameters | Δρmax = 0.62 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.52 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All s.u.'s (except the s.u. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell s.u.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of s.u.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between s.u.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell s.u.'s is used for estimating s.u.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 1.0641 (3) | 0.96956 (10) | 0.2361 (4) | 0.0471 (6) | |
| C2 | 1.2474 (3) | 0.97248 (11) | 0.3080 (4) | 0.0517 (6) | |
| H2 | 1.3138 | 1.0040 | 0.3785 | 0.062* | |
| C3 | 1.3259 (3) | 0.92547 (10) | 0.2683 (3) | 0.0446 (6) | |
| C4 | 1.5903 (4) | 0.87913 (13) | 0.2908 (5) | 0.0638 (8) | |
| H4A | 1.5472 | 0.8434 | 0.3166 | 0.096* | |
| H4B | 1.7177 | 0.8815 | 0.3689 | 0.096* | |
| H4C | 1.5624 | 0.8807 | 0.1569 | 0.096* | |
| C5 | 0.7922 (4) | 1.01267 (13) | 0.2028 (5) | 0.0692 (8) | |
| H5A | 0.7339 | 0.9971 | 0.0744 | 0.104* | |
| H5B | 0.7470 | 1.0507 | 0.2032 | 0.104* | |
| H5C | 0.7689 | 0.9882 | 0.2882 | 0.104* | |
| C6 | 1.0600 (3) | 0.88216 (10) | 0.1124 (3) | 0.0437 (6) | |
| C7 | 0.7881 (3) | 0.82754 (10) | −0.0485 (4) | 0.0454 (6) | |
| C8 | 0.7325 (3) | 0.78267 (11) | 0.0275 (4) | 0.0524 (6) | |
| H8 | 0.8158 | 0.7593 | 0.1241 | 0.063* | |
| C9 | 0.5507 (4) | 0.77293 (11) | −0.0426 (4) | 0.0509 (6) | |
| H9 | 0.5123 | 0.7425 | 0.0072 | 0.061* | |
| C10 | 0.4246 (3) | 0.80752 (11) | −0.1854 (3) | 0.0448 (6) | |
| C11 | 0.4845 (3) | 0.85228 (11) | −0.2603 (4) | 0.0507 (6) | |
| H11 | 0.4017 | 0.8758 | −0.3565 | 0.061* | |
| C12 | 0.6662 (4) | 0.86220 (11) | −0.1929 (4) | 0.0520 (6) | |
| H12 | 0.7054 | 0.8919 | −0.2446 | 0.062* | |
| C13 | 0.2290 (4) | 0.79504 (14) | −0.2462 (4) | 0.0653 (8) | |
| H13A | 0.2013 | 0.8076 | −0.1442 | 0.078* | |
| H13B | 0.2104 | 0.7536 | −0.2602 | 0.078* | |
| Cl1 | 0.07844 (11) | 0.82848 (5) | −0.46320 (16) | 0.1037 (4) | |
| N1 | 0.9659 (3) | 0.92397 (8) | 0.1384 (3) | 0.0452 (5) | |
| N2 | 1.2352 (2) | 0.87930 (9) | 0.1678 (3) | 0.0450 (5) | |
| O1 | 0.9816 (3) | 1.01557 (8) | 0.2666 (3) | 0.0647 (6) | |
| O2 | 1.5055 (2) | 0.92689 (8) | 0.3357 (3) | 0.0565 (5) | |
| O3 | 0.9740 (2) | 0.83341 (7) | 0.0165 (3) | 0.0576 (5) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0597 (15) | 0.0372 (13) | 0.0493 (14) | 0.0004 (11) | 0.0293 (13) | −0.0034 (11) |
| C2 | 0.0567 (15) | 0.0407 (14) | 0.0558 (15) | −0.0089 (11) | 0.0242 (13) | −0.0105 (12) |
| C3 | 0.0450 (13) | 0.0441 (14) | 0.0448 (14) | −0.0059 (11) | 0.0206 (11) | −0.0004 (11) |
| C4 | 0.0492 (15) | 0.0636 (18) | 0.079 (2) | 0.0021 (13) | 0.0293 (15) | −0.0057 (15) |
| C5 | 0.073 (2) | 0.0577 (18) | 0.091 (2) | 0.0119 (15) | 0.0504 (18) | −0.0029 (16) |
| C6 | 0.0476 (13) | 0.0373 (13) | 0.0476 (14) | −0.0038 (10) | 0.0232 (11) | −0.0047 (10) |
| C7 | 0.0420 (12) | 0.0390 (13) | 0.0553 (15) | −0.0055 (10) | 0.0223 (11) | −0.0138 (11) |
| C8 | 0.0535 (15) | 0.0410 (14) | 0.0590 (16) | 0.0046 (11) | 0.0227 (13) | 0.0017 (12) |
| C9 | 0.0594 (15) | 0.0390 (14) | 0.0620 (16) | −0.0044 (11) | 0.0345 (14) | 0.0017 (12) |
| C10 | 0.0468 (13) | 0.0457 (14) | 0.0438 (13) | −0.0065 (11) | 0.0224 (11) | −0.0096 (11) |
| C11 | 0.0515 (14) | 0.0496 (15) | 0.0443 (14) | −0.0016 (11) | 0.0163 (12) | 0.0027 (11) |
| C12 | 0.0577 (15) | 0.0454 (15) | 0.0546 (15) | −0.0115 (12) | 0.0271 (13) | −0.0012 (12) |
| C13 | 0.0529 (16) | 0.077 (2) | 0.0670 (18) | −0.0118 (14) | 0.0280 (14) | −0.0035 (16) |
| Cl1 | 0.0508 (5) | 0.1230 (9) | 0.1064 (8) | −0.0071 (5) | 0.0095 (5) | 0.0305 (6) |
| N1 | 0.0478 (11) | 0.0396 (11) | 0.0497 (12) | 0.0002 (9) | 0.0236 (10) | −0.0043 (9) |
| N2 | 0.0444 (11) | 0.0408 (11) | 0.0518 (12) | −0.0035 (9) | 0.0238 (10) | −0.0049 (9) |
| O1 | 0.0698 (12) | 0.0451 (11) | 0.0882 (15) | 0.0026 (9) | 0.0442 (11) | −0.0150 (10) |
| O2 | 0.0443 (9) | 0.0555 (11) | 0.0666 (12) | −0.0082 (8) | 0.0227 (9) | −0.0125 (9) |
| O3 | 0.0451 (10) | 0.0445 (10) | 0.0826 (13) | −0.0061 (8) | 0.0288 (9) | −0.0208 (9) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| C1—N1 | 1.341 (3) | C6—O3 | 1.363 (3) |
| C1—O1 | 1.350 (3) | C7—C12 | 1.379 (4) |
| C1—C2 | 1.378 (4) | C7—C8 | 1.378 (4) |
| C2—C3 | 1.379 (3) | C7—O3 | 1.410 (3) |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C8—C9 | 1.385 (4) |
| C3—N2 | 1.337 (3) | C8—H8 | 0.9300 |
| C3—O2 | 1.351 (3) | C9—C10 | 1.386 (4) |
| C4—O2 | 1.442 (3) | C9—H9 | 0.9300 |
| C4—H4A | 0.9600 | C10—C11 | 1.391 (3) |
| C4—H4B | 0.9600 | C10—C13 | 1.514 (3) |
| C4—H4C | 0.9600 | C11—C12 | 1.387 (4) |
| C5—O1 | 1.435 (3) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C5—H5A | 0.9600 | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| C5—H5B | 0.9600 | C13—Cl1 | 1.760 (3) |
| C5—H5C | 0.9600 | C13—H13A | 0.9700 |
| C6—N1 | 1.322 (3) | C13—H13B | 0.9700 |
| C6—N2 | 1.332 (3) | ||
| N1—C1—O1 | 119.3 (2) | C7—C8—C9 | 118.8 (2) |
| N1—C1—C2 | 123.4 (2) | C7—C8—H8 | 120.6 |
| O1—C1—C2 | 117.2 (2) | C9—C8—H8 | 120.6 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 115.5 (2) | C8—C9—C10 | 121.4 (2) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 122.3 | C8—C9—H9 | 119.3 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 122.3 | C10—C9—H9 | 119.3 |
| N2—C3—O2 | 118.8 (2) | C9—C10—C11 | 118.5 (2) |
| N2—C3—C2 | 124.0 (2) | C9—C10—C13 | 117.5 (2) |
| O2—C3—C2 | 117.2 (2) | C11—C10—C13 | 124.0 (2) |
| O2—C4—H4A | 109.5 | C12—C11—C10 | 120.7 (2) |
| O2—C4—H4B | 109.5 | C12—C11—H11 | 119.6 |
| H4A—C4—H4B | 109.5 | C10—C11—H11 | 119.6 |
| O2—C4—H4C | 109.5 | C7—C12—C11 | 119.3 (2) |
| H4A—C4—H4C | 109.5 | C7—C12—H12 | 120.4 |
| H4B—C4—H4C | 109.5 | C11—C12—H12 | 120.4 |
| O1—C5—H5A | 109.5 | C10—C13—Cl1 | 114.6 (2) |
| O1—C5—H5B | 109.5 | C10—C13—H13A | 108.6 |
| H5A—C5—H5B | 109.5 | Cl1—C13—H13A | 108.6 |
| O1—C5—H5C | 109.5 | C10—C13—H13B | 108.6 |
| H5A—C5—H5C | 109.5 | Cl1—C13—H13B | 108.6 |
| H5B—C5—H5C | 109.5 | H13A—C13—H13B | 107.6 |
| N1—C6—N2 | 129.5 (2) | C6—N1—C1 | 114.1 (2) |
| N1—C6—O3 | 119.1 (2) | C6—N2—C3 | 113.5 (2) |
| N2—C6—O3 | 111.5 (2) | C1—O1—C5 | 118.6 (2) |
| C12—C7—C8 | 121.2 (2) | C3—O2—C4 | 118.3 (2) |
| C12—C7—O3 | 121.5 (2) | C6—O3—C7 | 119.87 (18) |
| C8—C7—O3 | 117.1 (2) |
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: YK2059).
References
- Allen, F. H., Kennard, O., Watson, D. G., Brammer, L., Orpen, A. G. & Taylor, R. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. S1–19.
- Amin, K. M., Awadalla, F. M., Eissa, A. A. M., Abou-Seri, S. M. & Hassan, G. S. (2011). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 19, 6087–6097. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Chen, C. N., Lv, L. L., Ji, F. Q., Chen, Q., Xu, H., Niu, C. W., Xi, Z. & Yang, G. F. (2009). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 17, 3011–3017. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Popova, L. M., Trishina, A. U., Vershilov, S. V., Ginak, A. I. & Maksimov, B. N. (1999). J. Fluorine Chem. 96, 51–56.
- Rigaku (2008). CrystalClear Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
- Sagi, V. N., Liu, T. Y., Lu, X. Y., Bartfai, T. & Roberts, E. (2011). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 21, 7210–7215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Shah Bakhtiar, N., Abdullah, Z. & Ng, S. W. (2009a). Acta Cryst. E65, o114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Shah Bakhtiar, N., Abdullah, Z. & Ng, S. W. (2009b). Acta Cryst. E65, o1858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Stec, M. M., Bo, Y. X., Chakrabarti, P. P., Liao, L., Ncube, M., Tamayo, N., Tamir, R., Gavva, N. R., Treanor, J. J. S. & Norman, M. H. (2008). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 18, 5118–5122. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812026220/yk2059sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812026220/yk2059Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812026220/yk2059Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report



