Abstract
In the title molecule, C16H25NO4, the non-H atoms, except for the two tert-butyl groups, are roughly planar (r.m.s. deviation of the non-H atoms = 0.086 Å). In the crystal, molecules are linked into inversion dimers by pairs of N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming R 2 2(10) ring motifs.
Related literature
For complexes of Schiff bases containing a pyrrole unit, see: Wu et al. (2003 ▶); Wang et al. (2008 ▶). For the synthesis of the title compound, see: Sun et al. (2003 ▶).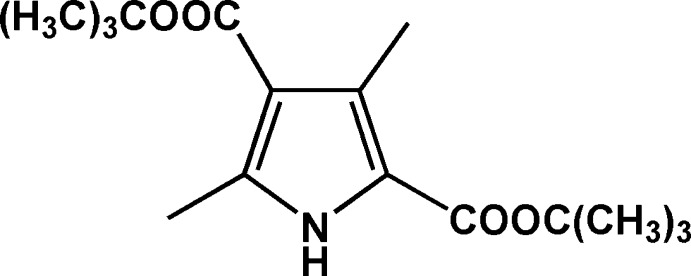
Experimental
Crystal data
C16H25NO4
M r = 295.37
Triclinic,

a = 5.8976 (10) Å
b = 11.511 (2) Å
c = 13.460 (2) Å
α = 103.956 (4)°
β = 90.078 (3)°
γ = 104.804 (3)°
V = 855.5 (3) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.08 mm−1
T = 296 K
0.21 × 0.19 × 0.16 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2007 ▶) T min = 0.983, T max = 0.987
4496 measured reflections
2989 independent reflections
1704 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.023
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.058
wR(F 2) = 0.150
S = 1.04
2989 reflections
191 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.27 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.21 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2007 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2007 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812026700/vm2177sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812026700/vm2177Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812026700/vm2177Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1A⋯O1i | 0.873 (17) | 2.087 (18) | 2.933 (3) | 163.2 (12) |
Symmetry code: (i)  .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for financial support by the Doctoral Foundation of Henan Polytechnic University (B2009–70 648364).
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Schiff bases containing pyrrole units have been extensively investigated due to their excellent coordination abilities (Wu et al., 2003; Wang et al., 2008). However, tert-butyl pyrrole-2-carboxylate derivatives are important intermediates to form 2-formyl pyrroles (Sun et al., 2003). As part of our studies on bis(pyrrol-2-yl-methyleneamine) ligands, the crystal structure of the title compound is reported here.
In the title molecule (Fig. 1), except for the two tert-butyl groups, the non-hydrogen atoms are situated in a fair plane (r.m.s. deviation of the non-hydrogen atoms being 0.2542 Å). In the crystal, the molecules are linked into a centrosymmetric dimer by two intermolecular N—H···O hydrogen bonds (Table 1), forming a R22(10) ring motif (Fig. 2).
Experimental
The di-tert-butyl 3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrrole-2,4-dicarboxylate was prepared by a Knorr-type reaction from the condensation of tert-butyl acetoacetate and tert-butyl oximinoacetoacetate according to literature (Sun et al., 2003).
Refinement
All methyl H atoms were positioned geometrically (C—H = 0.96 Å) and refined as riding with Uiso(H) = 1.5Ueq. Atom H1A was positioned geometrically with the N1—H1A distance free to refine and Uiso(H1A) = 1.2Ueq(N1).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure shown with 30% probability displacement ellipsoids.
Fig. 2.
The dimer of the title compounds formed via N—H···O hydrogen bonds shown as dashed lines. Unlabelled atoms are related with the labelled ones by symmetry operation -1 - x, -y, -z.
Crystal data
| C16H25NO4 | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 295.37 | F(000) = 320 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.147 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 5.8976 (10) Å | Cell parameters from 771 reflections |
| b = 11.511 (2) Å | θ = 3.2–20.5° |
| c = 13.460 (2) Å | µ = 0.08 mm−1 |
| α = 103.956 (4)° | T = 296 K |
| β = 90.078 (3)° | Plate, colorless |
| γ = 104.804 (3)° | 0.21 × 0.19 × 0.16 mm |
| V = 855.5 (3) Å3 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART CCD diffractometer | 2989 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1704 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.023 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 25.0°, θmin = 1.9° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2007) | h = −6→6 |
| Tmin = 0.983, Tmax = 0.987 | k = −13→13 |
| 4496 measured reflections | l = −16→13 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.058 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.150 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.04 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0557P)2 + 0.202P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2989 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 191 parameters | Δρmax = 0.27 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.21 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | −0.2311 (4) | 0.1845 (2) | −0.08222 (19) | 0.0471 (7) | |
| C2 | −0.1610 (4) | 0.2579 (2) | −0.14921 (19) | 0.0476 (7) | |
| C3 | −0.3401 (5) | 0.2180 (2) | −0.23018 (19) | 0.0478 (7) | |
| C4 | −0.5147 (5) | 0.1215 (2) | −0.2090 (2) | 0.0484 (7) | |
| C5 | 0.0637 (5) | 0.3586 (3) | −0.1403 (2) | 0.0673 (9) | |
| H5A | 0.1527 | 0.3670 | −0.0781 | 0.101* | |
| H5B | 0.0276 | 0.4356 | −0.1393 | 0.101* | |
| H5C | 0.1540 | 0.3375 | −0.1980 | 0.101* | |
| C6 | −0.7463 (5) | 0.0472 (3) | −0.2626 (2) | 0.0691 (9) | |
| H6A | −0.8212 | −0.0121 | −0.2255 | 0.104* | |
| H6B | −0.7229 | 0.0045 | −0.3308 | 0.104* | |
| H6C | −0.8440 | 0.1015 | −0.2660 | 0.104* | |
| C7 | −0.1316 (4) | 0.1787 (2) | 0.0145 (2) | 0.0479 (7) | |
| C8 | 0.1962 (5) | 0.2870 (3) | 0.1451 (2) | 0.0537 (7) | |
| C9 | 0.2769 (5) | 0.1727 (3) | 0.1469 (2) | 0.0726 (9) | |
| H9A | 0.3721 | 0.1553 | 0.0903 | 0.109* | |
| H9B | 0.1424 | 0.1032 | 0.1415 | 0.109* | |
| H9C | 0.3674 | 0.1870 | 0.2101 | 0.109* | |
| C10 | 0.0441 (5) | 0.3201 (3) | 0.2315 (2) | 0.0693 (9) | |
| H10A | −0.0005 | 0.3935 | 0.2274 | 0.104* | |
| H10B | 0.1301 | 0.3351 | 0.2960 | 0.104* | |
| H10C | −0.0944 | 0.2529 | 0.2263 | 0.104* | |
| C11 | 0.4029 (6) | 0.3960 (3) | 0.1429 (3) | 0.0819 (10) | |
| H11A | 0.3469 | 0.4670 | 0.1417 | 0.123* | |
| H11B | 0.4861 | 0.3754 | 0.0827 | 0.123* | |
| H11C | 0.5067 | 0.4147 | 0.2030 | 0.123* | |
| C12 | −0.3408 (5) | 0.2728 (3) | −0.3174 (2) | 0.0549 (7) | |
| C13 | −0.5671 (6) | 0.2464 (3) | −0.4787 (2) | 0.0673 (9) | |
| C14 | −0.3574 (7) | 0.2685 (4) | −0.5428 (3) | 0.1043 (13) | |
| H14A | −0.3103 | 0.1930 | −0.5657 | 0.156* | |
| H14B | −0.2298 | 0.3317 | −0.5022 | 0.156* | |
| H14C | −0.3990 | 0.2948 | −0.6012 | 0.156* | |
| C15 | −0.6498 (7) | 0.3616 (4) | −0.4426 (3) | 0.1023 (13) | |
| H15A | −0.7827 | 0.3448 | −0.4023 | 0.153* | |
| H15B | −0.6943 | 0.3873 | −0.5009 | 0.153* | |
| H15C | −0.5252 | 0.4265 | −0.4017 | 0.153* | |
| C16 | −0.7630 (8) | 0.1391 (4) | −0.5360 (3) | 0.1329 (19) | |
| H16A | −0.8932 | 0.1267 | −0.4935 | 0.199* | |
| H16B | −0.7085 | 0.0654 | −0.5536 | 0.199* | |
| H16C | −0.8123 | 0.1567 | −0.5976 | 0.199* | |
| N1 | −0.4459 (4) | 0.10303 (19) | −0.12068 (16) | 0.0492 (6) | |
| H1A | −0.526 (2) | 0.0471 (17) | −0.0913 (9) | 0.059* | |
| O1 | −0.2209 (3) | 0.10146 (17) | 0.06093 (14) | 0.0565 (5) | |
| O2 | 0.0654 (3) | 0.26788 (16) | 0.04613 (13) | 0.0594 (6) | |
| O3 | −0.2064 (4) | 0.3672 (2) | −0.32547 (15) | 0.0789 (7) | |
| O4 | −0.5120 (4) | 0.20430 (18) | −0.38930 (14) | 0.0728 (7) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0392 (15) | 0.0471 (16) | 0.0494 (16) | 0.0026 (13) | −0.0034 (13) | 0.0109 (13) |
| C2 | 0.0431 (16) | 0.0459 (16) | 0.0501 (16) | 0.0040 (13) | 0.0011 (13) | 0.0133 (13) |
| C3 | 0.0487 (17) | 0.0433 (15) | 0.0484 (16) | 0.0059 (13) | −0.0017 (13) | 0.0123 (12) |
| C4 | 0.0481 (17) | 0.0447 (16) | 0.0490 (16) | 0.0062 (13) | −0.0060 (13) | 0.0117 (13) |
| C5 | 0.0580 (19) | 0.069 (2) | 0.066 (2) | −0.0086 (16) | −0.0064 (16) | 0.0271 (16) |
| C6 | 0.062 (2) | 0.065 (2) | 0.068 (2) | −0.0084 (16) | −0.0152 (16) | 0.0191 (16) |
| C7 | 0.0364 (15) | 0.0501 (16) | 0.0511 (16) | 0.0022 (13) | −0.0015 (13) | 0.0109 (14) |
| C8 | 0.0435 (16) | 0.0598 (18) | 0.0503 (17) | 0.0019 (14) | −0.0090 (13) | 0.0121 (14) |
| C9 | 0.056 (2) | 0.088 (2) | 0.078 (2) | 0.0266 (18) | −0.0060 (16) | 0.0190 (18) |
| C10 | 0.068 (2) | 0.070 (2) | 0.064 (2) | 0.0160 (17) | 0.0038 (17) | 0.0075 (16) |
| C11 | 0.058 (2) | 0.089 (2) | 0.079 (2) | −0.0151 (18) | −0.0104 (17) | 0.0205 (18) |
| C12 | 0.0551 (18) | 0.0514 (18) | 0.0541 (17) | 0.0048 (15) | −0.0033 (15) | 0.0152 (14) |
| C13 | 0.067 (2) | 0.075 (2) | 0.0572 (19) | 0.0036 (17) | −0.0113 (17) | 0.0290 (16) |
| C14 | 0.103 (3) | 0.154 (4) | 0.063 (2) | 0.040 (3) | 0.009 (2) | 0.033 (2) |
| C15 | 0.105 (3) | 0.133 (4) | 0.092 (3) | 0.050 (3) | 0.004 (2) | 0.050 (2) |
| C16 | 0.137 (4) | 0.125 (3) | 0.107 (3) | −0.041 (3) | −0.073 (3) | 0.053 (3) |
| N1 | 0.0457 (14) | 0.0490 (13) | 0.0491 (13) | 0.0005 (11) | −0.0029 (11) | 0.0181 (11) |
| O1 | 0.0495 (12) | 0.0582 (12) | 0.0572 (12) | −0.0030 (9) | −0.0060 (9) | 0.0240 (10) |
| O2 | 0.0486 (12) | 0.0636 (13) | 0.0566 (12) | −0.0083 (10) | −0.0105 (9) | 0.0220 (9) |
| O3 | 0.0853 (16) | 0.0726 (15) | 0.0676 (14) | −0.0133 (13) | −0.0132 (12) | 0.0327 (11) |
| O4 | 0.0795 (15) | 0.0684 (14) | 0.0620 (13) | −0.0075 (11) | −0.0240 (11) | 0.0292 (11) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| C1—C2 | 1.375 (3) | C9—H9C | 0.9600 |
| C1—N1 | 1.381 (3) | C10—H10A | 0.9600 |
| C1—C7 | 1.450 (4) | C10—H10B | 0.9600 |
| C2—C3 | 1.422 (3) | C10—H10C | 0.9600 |
| C2—C5 | 1.504 (3) | C11—H11A | 0.9600 |
| C3—C4 | 1.394 (3) | C11—H11B | 0.9600 |
| C3—C12 | 1.462 (4) | C11—H11C | 0.9600 |
| C4—N1 | 1.337 (3) | C12—O3 | 1.200 (3) |
| C4—C6 | 1.490 (3) | C12—O4 | 1.342 (3) |
| C5—H5A | 0.9600 | C13—O4 | 1.466 (3) |
| C5—H5B | 0.9600 | C13—C15 | 1.502 (5) |
| C5—H5C | 0.9600 | C13—C16 | 1.505 (4) |
| C6—H6A | 0.9600 | C13—C14 | 1.512 (5) |
| C6—H6B | 0.9600 | C14—H14A | 0.9600 |
| C6—H6C | 0.9600 | C14—H14B | 0.9600 |
| C7—O1 | 1.220 (3) | C14—H14C | 0.9600 |
| C7—O2 | 1.328 (3) | C15—H15A | 0.9600 |
| C8—O2 | 1.479 (3) | C15—H15B | 0.9600 |
| C8—C10 | 1.506 (4) | C15—H15C | 0.9600 |
| C8—C9 | 1.514 (4) | C16—H16A | 0.9600 |
| C8—C11 | 1.516 (4) | C16—H16B | 0.9600 |
| C9—H9A | 0.9600 | C16—H16C | 0.9600 |
| C9—H9B | 0.9600 | N1—H1A | 0.873 (17) |
| C2—C1—N1 | 107.7 (2) | C8—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—C7 | 134.1 (2) | H10A—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| N1—C1—C7 | 118.2 (2) | H10B—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 106.5 (2) | C8—C11—H11A | 109.5 |
| C1—C2—C5 | 126.9 (2) | C8—C11—H11B | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—C5 | 126.6 (2) | H11A—C11—H11B | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 107.8 (2) | C8—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—C12 | 127.0 (2) | H11A—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—C12 | 125.2 (2) | H11B—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| N1—C4—C3 | 107.2 (2) | O3—C12—O4 | 123.1 (3) |
| N1—C4—C6 | 120.3 (2) | O3—C12—C3 | 125.1 (3) |
| C3—C4—C6 | 132.5 (2) | O4—C12—C3 | 111.8 (2) |
| C2—C5—H5A | 109.5 | O4—C13—C15 | 108.9 (3) |
| C2—C5—H5B | 109.5 | O4—C13—C16 | 102.4 (2) |
| H5A—C5—H5B | 109.5 | C15—C13—C16 | 111.3 (3) |
| C2—C5—H5C | 109.5 | O4—C13—C14 | 111.3 (3) |
| H5A—C5—H5C | 109.5 | C15—C13—C14 | 111.4 (3) |
| H5B—C5—H5C | 109.5 | C16—C13—C14 | 111.2 (3) |
| C4—C6—H6A | 109.5 | C13—C14—H14A | 109.5 |
| C4—C6—H6B | 109.5 | C13—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| H6A—C6—H6B | 109.5 | H14A—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| C4—C6—H6C | 109.5 | C13—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| H6A—C6—H6C | 109.5 | H14A—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| H6B—C6—H6C | 109.5 | H14B—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| O1—C7—O2 | 124.6 (2) | C13—C15—H15A | 109.5 |
| O1—C7—C1 | 123.5 (2) | C13—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| O2—C7—C1 | 111.9 (2) | H15A—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| O2—C8—C10 | 109.2 (2) | C13—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| O2—C8—C9 | 109.9 (2) | H15A—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| C10—C8—C9 | 112.8 (2) | H15B—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| O2—C8—C11 | 101.8 (2) | C13—C16—H16A | 109.5 |
| C10—C8—C11 | 111.4 (2) | C13—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—C11 | 111.2 (3) | H16A—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C8—C9—H9A | 109.5 | C13—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C8—C9—H9B | 109.5 | H16A—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| H9A—C9—H9B | 109.5 | H16B—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C8—C9—H9C | 109.5 | C4—N1—C1 | 110.9 (2) |
| H9A—C9—H9C | 109.5 | C4—N1—H1A | 124.5 (8) |
| H9B—C9—H9C | 109.5 | C1—N1—H1A | 124.6 (8) |
| C8—C10—H10A | 109.5 | C7—O2—C8 | 122.9 (2) |
| C8—C10—H10B | 109.5 | C12—O4—C13 | 122.3 (2) |
| H10A—C10—H10B | 109.5 | ||
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | −0.3 (3) | C2—C3—C12—O3 | −9.7 (5) |
| C7—C1—C2—C3 | −179.0 (3) | C4—C3—C12—O4 | −12.0 (4) |
| N1—C1—C2—C5 | −178.9 (2) | C2—C3—C12—O4 | 170.3 (2) |
| C7—C1—C2—C5 | 2.5 (5) | C3—C4—N1—C1 | 0.2 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.4 (3) | C6—C4—N1—C1 | −177.7 (2) |
| C5—C2—C3—C4 | 179.0 (3) | C2—C1—N1—C4 | 0.1 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—C12 | 178.5 (3) | C7—C1—N1—C4 | 179.0 (2) |
| C5—C2—C3—C12 | −3.0 (4) | O1—C7—O2—C8 | −2.5 (4) |
| C2—C3—C4—N1 | −0.3 (3) | C1—C7—O2—C8 | 176.8 (2) |
| C12—C3—C4—N1 | −178.3 (3) | C10—C8—O2—C7 | −63.0 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C6 | 177.1 (3) | C9—C8—O2—C7 | 61.2 (3) |
| C12—C3—C4—C6 | −0.9 (5) | C11—C8—O2—C7 | 179.2 (2) |
| C2—C1—C7—O1 | −177.3 (3) | O3—C12—O4—C13 | −7.2 (5) |
| N1—C1—C7—O1 | 4.1 (4) | C3—C12—O4—C13 | 172.8 (3) |
| C2—C1—C7—O2 | 3.3 (4) | C15—C13—O4—C12 | −63.2 (4) |
| N1—C1—C7—O2 | −175.2 (2) | C16—C13—O4—C12 | 178.9 (3) |
| C4—C3—C12—O3 | 168.0 (3) | C14—C13—O4—C12 | 60.0 (4) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1A···O1i | 0.873 (17) | 2.087 (18) | 2.933 (3) | 163.2 (12) |
Symmetry code: (i) −x−1, −y, −z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: VM2177).
References
- Bruker (2007). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA .
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sun, L., Liang, C., Shirazian, S., Zhou, Y., Miller, T., Cui, J., Fukuda, J. Y., Chu, J.-Y., Nematalla, A., Wang, X., Chen, H., Sistla, A., Luu, T. C., Tang, F., Wei, J. & Tang, C. (2003). J. Med. Chem. 46, 1116–1119. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y., Yang, Z.-Y. & Chen, Z.-N. (2008). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 18, 298–303. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z. K., Chen, Q. Q., Xiong, S. X., Xin, B., Zhao, Z. W., Jiang, L. J. & Ma, J. S. (2003). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 42, 3271–3274. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812026700/vm2177sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812026700/vm2177Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812026700/vm2177Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




