Abstract
In the crystal structure of the title compound, C6H6NO2 +·NO3 −, the protonated cations are linked by N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds into chains along the b axis. The cations and anions are also linked by N—H⋯O and O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds. C—H⋯O interactions also occur. In the cation, the ring makes a dihedral angle of 10.1 (3)° with the carboxylate group.
Related literature
For related structures, see: Athimoolam & Rajaram (2005 ▶); Athimoolam & Natarajan (2007 ▶); Kutoglu & Scheringer (1983 ▶); Jebas et al. (2006 ▶); Slouf (2001 ▶); Ye et al. (2010 ▶). For graph-set descriptors, see: Etter (1990 ▶); Bernstein et al. (1995 ▶); Motherwell et al. (2000 ▶).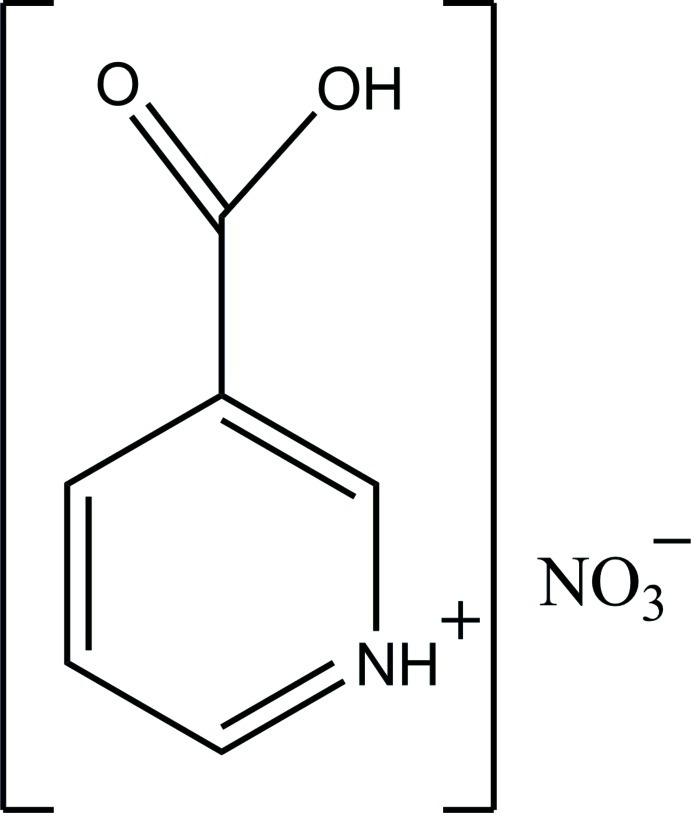
Experimental
Crystal data
C6H6NO2 +·NO3 −
M r = 186.13
Triclinic,
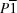
a = 6.7530 (4) Å
b = 7.5024 (4) Å
c = 8.4439 (5) Å
α = 81.895 (2)°
β = 82.215 (1)°
γ = 66.769 (2)°
V = 387.69 (4) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.14 mm−1
T = 293 K
0.40 × 0.20 × 0.10 mm
Data collection
Rigaku R-AXIS RAPID diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrystalClear; Rigaku, 2007 ▶) T min = 0.946, T max = 0.986
15468 measured reflections
1760 independent reflections
1102 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.046
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.050
wR(F 2) = 0.145
S = 1.13
1760 reflections
127 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.19 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.35 e Å−3
Data collection: CrystalClear (Rigaku, 2007 ▶); cell refinement: CrystalClear; data reduction: CrystalClear; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: DIAMOND (Brandenburg, 2004 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: publCIF (Westrip, 2010 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812028565/lx2240sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812028565/lx2240Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812028565/lx2240Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1—H1O⋯O4i | 0.92 (3) | 1.67 (3) | 2.5833 (19) | 169 (2) |
| N1—H1N⋯O2ii | 0.96 (3) | 2.08 (3) | 2.824 (2) | 133 (2) |
| N1—H1N⋯O4 | 0.96 (3) | 2.12 (3) | 2.921 (2) | 139 (2) |
| C3—H3⋯O3 | 0.93 | 2.45 | 3.330 (3) | 158 |
| C6—H6⋯O5iii | 0.93 | 2.37 | 3.259 (2) | 160 |
| C5—H5⋯O3iv | 0.93 | 2.47 | 3.142 (2) | 129 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii) 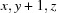 ; (iii)
; (iii) 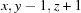 ; (iv)
; (iv) 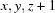 .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful for the National Plan for Science and Technology, KSU (NPST grant 09-ENE909–02) for funding this work.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Previously, the crystal structures of nicotinium derivatives containing diverse anions have been reported (Athimoolam & Rajaram, 2005; Athimoolam & Natarajan, 2007; Kutoglu & Scheringer, 1983; Jebas et al., 2006; Slouf, 2001; Ye et al., 2010). We report herein the crystal structure of the title compound.
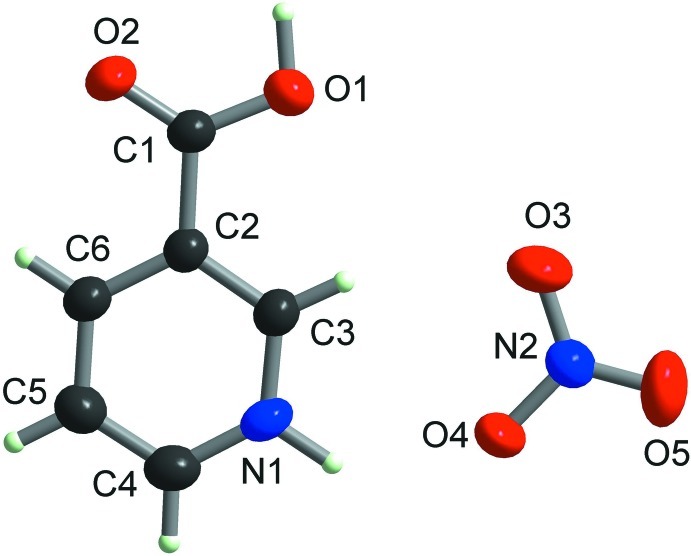
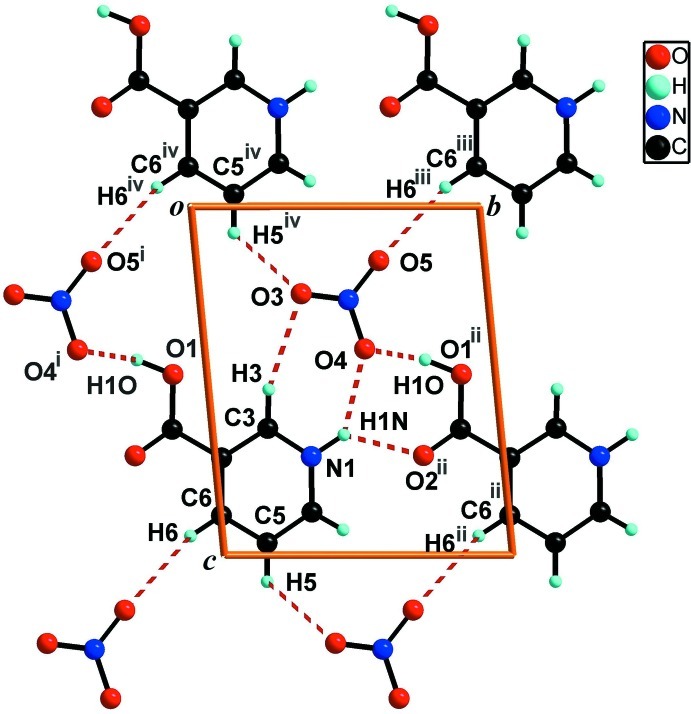
In the title molecule (Fig. 1), the nicotinium cation is planar with a maximum deviation for the carboxylate oxygen atom (O1) being 0.265 (2) Å. In the crystal structure (Fig. 2), the cations are linked by N—H···O hydrogen bonds (Table 1) into infinite chains along the [010] vector. Regarding the graph set descriptors (Etter, 1990; Bernstein et al., 1995; Motherwell et al., 2000), this N—H···O chain motif is described as C(6). The bifurcated N—H···O with O—H···O interactions (Table 1) are connecting the nicotinium with nitrates, thus defining a third-level discrete D33(13) hydrogen bond motif in the bc-plane (Fig. 2).
Experimental
The title compound was unintentionally obtained during a microwave irradiation (300 W, 150 oC, 10 min., MicroSynth, Milestone) reaction of Ce(OH)4 in diluted nitric acid with aqueous solution of nicotinic acid. After cooling, the solution was left undisturbed and colourless crystals were collected by filtration after one week.
Refinement
Aromatic carbon–bound H–atoms were placed in ideal calculated positions [C—H 0.93 Å, Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C)] and refined as riding atoms. Amine and hydroxyl hydrogen atoms were located from difference Fourier map and refined freely.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound with the atom numbering scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level. H atoms are presented as small spheres of arbitrary radius.
Fig. 2.
A view of the O—H···O, N—H···O and C—H···O interactions (dotted lines) in the crystal structure of the title compound. [Symmetry codes: (i) x,y - 1, z; (ii) x, y + 1, z; (iii) x,y + 1, z - 1; (iv) x, y, z - 1.]
Crystal data
| C6H6NO2+·NO3− | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 186.13 | F(000) = 192 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.594 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71075 Å |
| a = 6.7530 (4) Å | Cell parameters from 963 reflections |
| b = 7.5024 (4) Å | θ = 3.3–27.5° |
| c = 8.4439 (5) Å | µ = 0.14 mm−1 |
| α = 81.895 (2)° | T = 293 K |
| β = 82.215 (1)° | Block, colourless |
| γ = 66.769 (2)° | 0.40 × 0.20 × 0.10 mm |
| V = 387.69 (4) Å3 |
Data collection
| Rigaku R-AXIS RAPID diffractometer | 1760 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1102 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.046 |
| Detector resolution: 10.0 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 27.5°, θmin = 3.3° |
| ω scans | h = −8→8 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrystalClear; Rigaku, 2007) | k = −9→9 |
| Tmin = 0.946, Tmax = 0.986 | l = −10→10 |
| 15468 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.050 | Hydrogen site location: difference Fourier map |
| wR(F2) = 0.145 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.13 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0739P)2 + 0.025P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 1760 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 127 parameters | Δρmax = 0.19 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.35 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2sigma(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.2671 (2) | −0.1191 (2) | 0.48174 (17) | 0.0528 (4) | |
| H1O | 0.277 (4) | −0.232 (4) | 0.443 (3) | 0.079 (8)* | |
| N1 | 0.2399 (3) | 0.3328 (2) | 0.7169 (2) | 0.0461 (5) | |
| H1N | 0.245 (4) | 0.449 (4) | 0.654 (3) | 0.086 (9)* | |
| C1 | 0.2321 (3) | −0.1404 (3) | 0.6385 (2) | 0.0405 (5) | |
| O2 | 0.2000 (3) | −0.2778 (2) | 0.71433 (17) | 0.0570 (5) | |
| N2 | 0.2859 (3) | 0.5132 (2) | 0.2675 (2) | 0.0461 (4) | |
| C2 | 0.2350 (3) | 0.0215 (2) | 0.7207 (2) | 0.0366 (4) | |
| O3 | 0.2861 (3) | 0.3523 (2) | 0.2502 (2) | 0.0723 (6) | |
| C3 | 0.2385 (3) | 0.1913 (3) | 0.6360 (2) | 0.0416 (5) | |
| H3 | 0.2399 | 0.2079 | 0.5247 | 0.050* | |
| O4 | 0.2781 (3) | 0.5540 (2) | 0.40863 (18) | 0.0698 (5) | |
| C4 | 0.2393 (3) | 0.3167 (3) | 0.8764 (3) | 0.0483 (5) | |
| H4 | 0.2410 | 0.4182 | 0.9273 | 0.058* | |
| C5 | 0.2361 (3) | 0.1507 (3) | 0.9645 (2) | 0.0497 (5) | |
| H5 | 0.2348 | 0.1381 | 1.0758 | 0.060* | |
| O5 | 0.2917 (3) | 0.6324 (3) | 0.1555 (2) | 0.0817 (6) | |
| C6 | 0.2350 (3) | 0.0018 (3) | 0.8862 (2) | 0.0439 (5) | |
| H6 | 0.2341 | −0.1126 | 0.9449 | 0.053* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0802 (11) | 0.0451 (9) | 0.0395 (9) | −0.0309 (8) | 0.0008 (7) | −0.0094 (6) |
| N1 | 0.0598 (11) | 0.0313 (9) | 0.0518 (11) | −0.0232 (8) | −0.0029 (8) | −0.0032 (7) |
| C1 | 0.0501 (11) | 0.0346 (10) | 0.0389 (11) | −0.0185 (9) | −0.0027 (8) | −0.0052 (8) |
| O2 | 0.0937 (12) | 0.0416 (8) | 0.0482 (9) | −0.0412 (8) | −0.0003 (8) | −0.0045 (7) |
| N2 | 0.0578 (11) | 0.0445 (10) | 0.0380 (9) | −0.0205 (8) | −0.0065 (7) | −0.0053 (7) |
| C2 | 0.0447 (10) | 0.0304 (9) | 0.0364 (10) | −0.0171 (8) | −0.0010 (8) | −0.0033 (7) |
| O3 | 0.1120 (14) | 0.0623 (11) | 0.0602 (11) | −0.0464 (10) | −0.0100 (9) | −0.0208 (8) |
| C3 | 0.0533 (12) | 0.0346 (10) | 0.0390 (10) | −0.0202 (9) | −0.0018 (8) | −0.0025 (8) |
| O4 | 0.1353 (15) | 0.0522 (10) | 0.0359 (9) | −0.0481 (10) | −0.0118 (9) | −0.0077 (7) |
| C4 | 0.0580 (13) | 0.0421 (11) | 0.0514 (13) | −0.0237 (10) | −0.0038 (9) | −0.0126 (9) |
| C5 | 0.0660 (14) | 0.0477 (12) | 0.0408 (12) | −0.0264 (11) | −0.0052 (10) | −0.0077 (9) |
| O5 | 0.1135 (15) | 0.0740 (12) | 0.0513 (10) | −0.0380 (11) | −0.0075 (9) | 0.0208 (9) |
| C6 | 0.0585 (12) | 0.0352 (10) | 0.0419 (11) | −0.0230 (9) | −0.0024 (9) | −0.0031 (8) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—C1 | 1.311 (2) | N2—O4 | 1.261 (2) |
| O1—H1O | 0.92 (3) | C2—C3 | 1.377 (2) |
| N1—C4 | 1.335 (3) | C2—C6 | 1.385 (3) |
| N1—C3 | 1.344 (3) | C3—H3 | 0.9300 |
| N1—H1N | 0.96 (3) | C4—C5 | 1.364 (3) |
| C1—O2 | 1.213 (2) | C4—H4 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C2 | 1.489 (3) | C5—C6 | 1.379 (3) |
| N2—O5 | 1.214 (2) | C5—H5 | 0.9300 |
| N2—O3 | 1.236 (2) | C6—H6 | 0.9300 |
| C1—O1—H1O | 107.7 (16) | N1—C3—C2 | 118.93 (18) |
| C4—N1—C3 | 123.13 (17) | N1—C3—H3 | 120.5 |
| C4—N1—H1N | 120.2 (16) | C2—C3—H3 | 120.5 |
| C3—N1—H1N | 116.7 (16) | N1—C4—C5 | 119.72 (18) |
| O2—C1—O1 | 124.77 (18) | N1—C4—H4 | 120.1 |
| O2—C1—C2 | 121.11 (18) | C5—C4—H4 | 120.1 |
| O1—C1—C2 | 114.11 (16) | C4—C5—C6 | 119.0 (2) |
| O5—N2—O3 | 123.04 (18) | C4—C5—H5 | 120.5 |
| O5—N2—O4 | 119.22 (18) | C6—C5—H5 | 120.5 |
| O3—N2—O4 | 117.74 (17) | C5—C6—C2 | 120.39 (18) |
| C3—C2—C6 | 118.80 (17) | C5—C6—H6 | 119.8 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 121.64 (17) | C2—C6—H6 | 119.8 |
| C6—C2—C1 | 119.56 (16) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O1—H1O···O4i | 0.92 (3) | 1.67 (3) | 2.5833 (19) | 169 (2) |
| N1—H1N···O2ii | 0.96 (3) | 2.08 (3) | 2.824 (2) | 133 (2) |
| N1—H1N···O4 | 0.96 (3) | 2.12 (3) | 2.921 (2) | 139 (2) |
| C3—H3···O3 | 0.93 | 2.45 | 3.330 (3) | 158 |
| C6—H6···O5iii | 0.93 | 2.37 | 3.259 (2) | 160 |
| C5—H5···O3iv | 0.93 | 2.47 | 3.142 (2) | 129 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, y−1, z; (ii) x, y+1, z; (iii) x, y−1, z+1; (iv) x, y, z+1.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: LX2240).
References
- Athimoolam, S. & Natarajan, S. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, o2656.
- Athimoolam, S. & Rajaram, R. K. (2005). Acta Cryst. E61, o2764–o2767.
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 34, 1555–1573.
- Brandenburg, K. (2004). DIAMOND Crystal Impact GbR, Bonn, Germany.
- Etter, M. C. (1990). Acc. Chem. Res. 23, 120–126.
- Jebas, S. R., Balasubramanian, T. & Light, M. E. (2006). Acta Cryst. E62, o3481–o3482.
- Kutoglu, A. & Scheringer, C. (1983). Acta Cryst. C39, 232–234.
- Motherwell, W. D. S., Shields, G. P. & Allen, F. H. (2000). Acta Cryst. B56, 466–473. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Rigaku (2007). CrystalClear Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Slouf, M. (2001). Acta Cryst. E57, o61–o62. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Westrip, S. P. (2010). J. Appl. Cryst. 43, 920–925.
- Ye, H.-Y., Chen, L.-Z. & Xiong, R.-G. (2010). Acta Cryst. B66, 387–395. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812028565/lx2240sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812028565/lx2240Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812028565/lx2240Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report