Abstract
In the title compound, C20H18BrN5, the bromophenyl-substituted quinazoline unit is essentially planar [maximum deviation = 0.098 (3) Å] and makes a dihedral angle of 56.04 (14)° with the imidazole ring. In the crystal, molecules are associated by pairs of N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds to form inversion dimers. All the quinazoline planar systems are oriented almost perpendicular to the [110] direction, making π–π interactions possible between adjacent dimers [centroid–centroid distances = 3.7674 (16) and 3.7612 (17) Å]. There are also a number of C—H⋯π interactions present. The crystal is a nonmerohedral twin, with a minor twin fraction of 0.47.
Related literature
For general background on the biological properties of imidazo quinazolines, see: Aguilar et al. (2002 ▶); Rohini et al. (2009 ▶). For imidazo quinazoline structures, see: Asproni et al. (2011 ▶); Connolly et al. (2005 ▶). For synthetic details, see: Okano et al. (2009 ▶).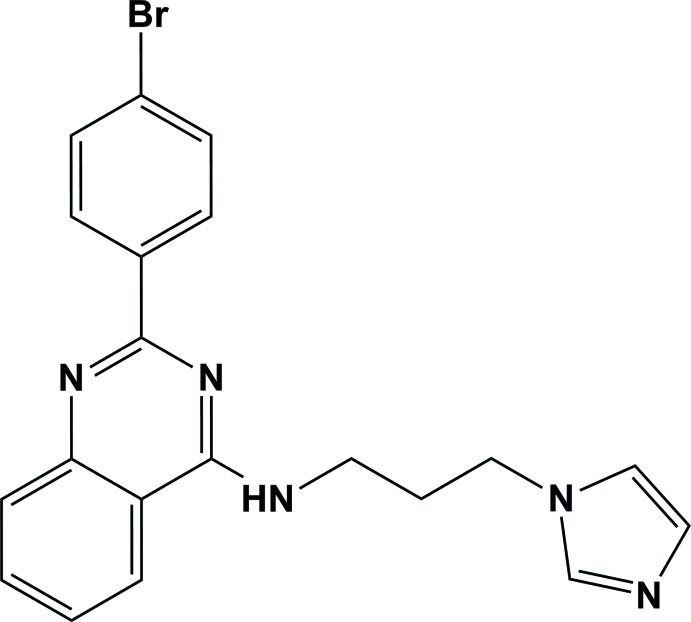
Experimental
Crystal data
C20H18BrN5
M r = 408.30
Triclinic,

a = 8.8557 (7) Å
b = 9.5113 (6) Å
c = 11.3730 (7) Å
α = 99.682 (5)°
β = 101.432 (6)°
γ = 97.211 (6)°
V = 912.96 (11) Å3
Z = 2
Cu Kα radiation
μ = 3.17 mm−1
T = 180 K
0.4 × 0.2 × 0.07 mm
Data collection
Agilent SuperNova, Dual, Cu, Atlas diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2010 ▶) T min = 0.343, T max = 1.000
6845 measured reflections
6845 independent reflections
6259 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.073
wR(F 2) = 0.216
S = 1.12
6845 reflections
236 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.94 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.87 e Å−3
Data collection: CrysAlis PRO (Agilent, 2010 ▶); cell refinement: CrysAlis PRO; data reduction: CrysAlis PRO; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: OLEX2 (Dolomanov et al., 2009 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: OLEX2 and publCIF (Westrip, 2010 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812028115/su2454sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812028115/su2454Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812028115/su2454Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
Cg1 is the centroid of the N2,N5,C1–C3 ring; Cg3 is the centroid of the C11–C16 ring; Cg4 is the centroid of the C19–C24 ring.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N9—H9⋯N2i | 0.86 | 2.14 | 2.949 (4) | 156 |
| C1—H1⋯Cg4ii | 0.93 | 2.84 | 3.605 (3) | 140 |
| C4—H4⋯Cg3iii | 0.93 | 2.78 | 3.509 (4) | 136 |
| C14—H14⋯Cg1iv | 0.93 | 2.88 | 3.527 (3) | 128 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 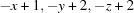 ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  ; (iv)
; (iv)  .
.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Imidazo quinazolines (Connolly et al., 2005; Asproni et al., 2011) are heterocyclic compounds that exhibit a wide range of biological activities such as, antibacterial, antifungal, and antitumor (Rohini et al., 2009). The importance of this type of structure is linked to the fact that new drugs are permanently required owing to the fact that microorganisms are mutating continuously (Aguilar et al., 2002).
In the title compound, Fig. 1, the bromophenyl substituted quinazoline unit is essentially planar, with a maximum deviation 0.098 (3)Å for atom C20, and makes a dihedral angle of 56.04 (14) ° with the imidazole ring.
In the crystal, the molecules are associated via N-H···N hydrogen bonds, involving the imidazole function (N2) and the NH group to form inversion dimers (Table 1 and Fig. 2). All the planar quinazoline systems are oriented almost perpendicular to direction [110] making π···π interactions possible between adjacent dimers [Fig 3; Cg2···Cg4i 3.7674 (16) Å; Cg3···Cg4i 3.7612 (17) Å; symmetry code (i) -x+2, -y+1, -z+2; Cg2, Cg3 and Cg4 are the centroids of rings (N25,C10,C11,C16,N17,C18), (C11-C16) and (C19-C20), respectively]. There are also a number of C-H···π interactions present (Table 1).
Experimental
Both the starting reagent, 4-chloro-2-(4-bromophenyl)quinazoline, and the title compound were synthesized as described by (Okano et al., 2009). To a stirred solution of 0.4 g of 4-chloro-2-(4-bromophenyl)quinazoline (1,3 mmol) in 6 ml of N,N-dimethylformamide, a mixture of 0.4 ml of Et3N (2.6 mmol) and 0.2 ml of 1-(3-aminopropyl)-imidazole (1.6 mmol) were added. The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 4 h. After completion of the reaction 30 ml of cold water were added giving a white precipitate of the title compound that was purified in acetone [Yield 95%]. Recrystallization in acetone at room temperature afforded colourless plate-like crystals suitable for X-ray diffraction analysis (M.p. 438-440 K).
Refinement
The crystal is a non-merohedral twin, with a minor twin fraction of 0.47. Two components rotated by 180 ° around an axis close to the a axis were used to produce an HKLF5 file that was used in the refinement. The H atoms were included in calculated positions and treated as riding atoms: N-H = 0.86 Å, C-H = 0.93 and 0.97 Å for CH and CH2 H atoms, respectively, with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(parent N or C atom).
Figures
Fig. 1.
A view of the molecular structure of the title molecule with the atom numbering. The displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
Fig. 2.

A partial view perpendicular to (110) of the crystal packing of the title compound, showing the N-H···N hydrogen bonded (blue dashed lines; Table 1) inversion dimers and the overlap of the inversion related bromophenyl substituted quinazoline units.
Fig. 3.

A view along the c axis of the crystal packing of the title compound. Hydrogen bonds are shown as blue dashed lines (see Table 1 for details).
Crystal data
| C20H18BrN5 | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 408.30 | F(000) = 416 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.485 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Melting point = 438–440 K |
| a = 8.8557 (7) Å | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.5418 Å |
| b = 9.5113 (6) Å | Cell parameters from 4656 reflections |
| c = 11.3730 (7) Å | θ = 4.0–72.6° |
| α = 99.682 (5)° | µ = 3.17 mm−1 |
| β = 101.432 (6)° | T = 180 K |
| γ = 97.211 (6)° | Plate, colourless |
| V = 912.96 (11) Å3 | 0.4 × 0.2 × 0.07 mm |
Data collection
| Agilent SuperNova, Dual, Cu, Atlas diffractometer | 6845 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: SuperNova (Cu) X-ray Source | 6259 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Mirror monochromator | Rint = 0.000 |
| Detector resolution: 10.4679 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 73.4°, θmin = 4.1° |
| ω scans | h = −10→10 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2010) | k = −11→11 |
| Tmin = 0.343, Tmax = 1.000 | l = −14→14 |
| 6845 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.073 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.216 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.12 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.1707P)2 + 0.1234P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 6845 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 236 parameters | Δρmax = 0.94 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.87 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. Bond distances, angles etc. have been calculated using the rounded fractional coordinates. All su's are estimated from the variances of the (full) variance-covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account in the estimation of distances, angles and torsion angles |
| Refinement. The crystal is twinned. Two components rotated by 180 degrees around an axis close to the a axis were used to produce an hklf5 file that was used in the refinement. The twin fraction is 0.47. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Br26 | 1.29926 (4) | 0.38228 (3) | 0.53762 (3) | 0.0344 (2) | |
| N2 | 0.3265 (3) | 0.9940 (3) | 0.7534 (3) | 0.0332 (8) | |
| N5 | 0.5204 (3) | 0.8708 (2) | 0.7429 (2) | 0.0226 (6) | |
| N9 | 0.8641 (3) | 0.8764 (3) | 1.0859 (2) | 0.0249 (7) | |
| N17 | 1.2170 (3) | 0.6321 (2) | 1.1230 (2) | 0.0219 (6) | |
| N25 | 1.0223 (2) | 0.7362 (2) | 1.0039 (2) | 0.0208 (6) | |
| C1 | 0.3882 (3) | 0.8826 (3) | 0.7826 (3) | 0.0271 (8) | |
| C3 | 0.4247 (4) | 1.0562 (3) | 0.6895 (3) | 0.0363 (10) | |
| C4 | 0.5446 (4) | 0.9818 (3) | 0.6823 (3) | 0.0320 (9) | |
| C6 | 0.6173 (3) | 0.7581 (3) | 0.7585 (3) | 0.0281 (8) | |
| C7 | 0.6775 (3) | 0.7528 (3) | 0.8922 (3) | 0.0244 (8) | |
| C8 | 0.7867 (3) | 0.8907 (3) | 0.9637 (3) | 0.0243 (8) | |
| C10 | 0.9798 (3) | 0.7984 (3) | 1.1023 (2) | 0.0211 (7) | |
| C11 | 1.0576 (3) | 0.7841 (3) | 1.2228 (2) | 0.0202 (7) | |
| C12 | 1.0225 (3) | 0.8494 (3) | 1.3326 (3) | 0.0272 (8) | |
| C13 | 1.1050 (4) | 0.8314 (3) | 1.4436 (3) | 0.0300 (8) | |
| C14 | 1.2239 (3) | 0.7465 (3) | 1.4478 (3) | 0.0276 (8) | |
| C15 | 1.2587 (3) | 0.6803 (3) | 1.3418 (3) | 0.0256 (8) | |
| C16 | 1.1774 (3) | 0.6981 (3) | 1.2261 (3) | 0.0210 (7) | |
| C18 | 1.1381 (3) | 0.6553 (3) | 1.0193 (2) | 0.0201 (7) | |
| C19 | 1.1755 (3) | 0.5861 (3) | 0.9036 (2) | 0.0198 (7) | |
| C20 | 1.0851 (3) | 0.5960 (3) | 0.7895 (3) | 0.0243 (7) | |
| C21 | 1.1213 (3) | 0.5346 (3) | 0.6819 (3) | 0.0259 (8) | |
| C22 | 1.2489 (3) | 0.4630 (3) | 0.6873 (3) | 0.0240 (8) | |
| C23 | 1.3403 (3) | 0.4505 (3) | 0.7974 (3) | 0.0258 (8) | |
| C24 | 1.3025 (3) | 0.5117 (3) | 0.9049 (3) | 0.0231 (7) | |
| H1 | 0.34540 | 0.81910 | 0.82590 | 0.0320* | |
| H3 | 0.41070 | 1.13760 | 0.65600 | 0.0440* | |
| H4 | 0.62630 | 1.00180 | 0.64420 | 0.0380* | |
| H6A | 0.70550 | 0.77570 | 0.72110 | 0.0340* | |
| H6B | 0.55640 | 0.66490 | 0.71630 | 0.0340* | |
| H7A | 0.73260 | 0.67130 | 0.89680 | 0.0290* | |
| H7B | 0.58930 | 0.73740 | 0.93000 | 0.0290* | |
| H8A | 0.86520 | 0.91490 | 0.91860 | 0.0290* | |
| H8B | 0.72720 | 0.96950 | 0.97080 | 0.0290* | |
| H9 | 0.83500 | 0.91890 | 1.14850 | 0.0300* | |
| H12 | 0.94310 | 0.90500 | 1.33010 | 0.0330* | |
| H13 | 1.08190 | 0.87550 | 1.51590 | 0.0360* | |
| H14 | 1.27960 | 0.73500 | 1.52300 | 0.0330* | |
| H15 | 1.33660 | 0.62310 | 1.34600 | 0.0310* | |
| H20 | 1.00000 | 0.64450 | 0.78660 | 0.0290* | |
| H21 | 1.06090 | 0.54110 | 0.60670 | 0.0310* | |
| H23 | 1.42530 | 0.40190 | 0.79930 | 0.0310* | |
| H24 | 1.36270 | 0.50330 | 0.97950 | 0.0280* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Br26 | 0.0438 (3) | 0.0463 (3) | 0.0199 (2) | 0.0198 (2) | 0.0142 (2) | 0.0076 (2) |
| N2 | 0.0312 (12) | 0.0421 (14) | 0.0294 (13) | 0.0157 (11) | 0.0077 (11) | 0.0076 (12) |
| N5 | 0.0226 (10) | 0.0276 (11) | 0.0187 (11) | 0.0058 (8) | 0.0035 (9) | 0.0079 (9) |
| N9 | 0.0255 (11) | 0.0311 (12) | 0.0193 (11) | 0.0132 (9) | 0.0041 (9) | 0.0035 (9) |
| N17 | 0.0201 (10) | 0.0284 (11) | 0.0188 (11) | 0.0081 (8) | 0.0040 (8) | 0.0066 (9) |
| N25 | 0.0192 (9) | 0.0281 (11) | 0.0164 (11) | 0.0075 (8) | 0.0041 (8) | 0.0049 (9) |
| C1 | 0.0240 (12) | 0.0355 (14) | 0.0251 (14) | 0.0070 (11) | 0.0086 (11) | 0.0102 (12) |
| C3 | 0.0420 (17) | 0.0329 (15) | 0.0386 (19) | 0.0120 (12) | 0.0108 (14) | 0.0131 (14) |
| C4 | 0.0318 (14) | 0.0332 (15) | 0.0347 (17) | 0.0042 (11) | 0.0114 (12) | 0.0131 (13) |
| C6 | 0.0297 (13) | 0.0333 (14) | 0.0211 (14) | 0.0133 (11) | 0.0043 (11) | 0.0009 (11) |
| C7 | 0.0221 (12) | 0.0281 (13) | 0.0257 (14) | 0.0093 (10) | 0.0046 (10) | 0.0101 (11) |
| C8 | 0.0269 (13) | 0.0260 (13) | 0.0219 (14) | 0.0088 (10) | 0.0031 (11) | 0.0092 (11) |
| C10 | 0.0186 (11) | 0.0244 (12) | 0.0202 (13) | 0.0044 (9) | 0.0034 (10) | 0.0049 (10) |
| C11 | 0.0190 (11) | 0.0244 (12) | 0.0168 (13) | 0.0024 (9) | 0.0039 (9) | 0.0038 (10) |
| C12 | 0.0254 (12) | 0.0342 (15) | 0.0213 (14) | 0.0093 (11) | 0.0052 (11) | 0.0008 (12) |
| C13 | 0.0322 (14) | 0.0384 (15) | 0.0175 (14) | 0.0070 (12) | 0.0060 (11) | −0.0014 (12) |
| C14 | 0.0289 (13) | 0.0334 (14) | 0.0180 (13) | 0.0033 (11) | −0.0001 (11) | 0.0055 (11) |
| C15 | 0.0231 (12) | 0.0328 (14) | 0.0224 (14) | 0.0071 (10) | 0.0031 (10) | 0.0102 (12) |
| C16 | 0.0197 (11) | 0.0243 (12) | 0.0195 (13) | 0.0024 (9) | 0.0050 (10) | 0.0063 (10) |
| C18 | 0.0187 (11) | 0.0244 (12) | 0.0185 (13) | 0.0036 (9) | 0.0053 (10) | 0.0063 (10) |
| C19 | 0.0183 (11) | 0.0250 (12) | 0.0177 (13) | 0.0045 (9) | 0.0054 (9) | 0.0066 (10) |
| C20 | 0.0199 (11) | 0.0351 (14) | 0.0190 (13) | 0.0092 (10) | 0.0023 (10) | 0.0072 (11) |
| C21 | 0.0253 (12) | 0.0358 (14) | 0.0172 (13) | 0.0085 (11) | 0.0024 (10) | 0.0072 (11) |
| C22 | 0.0283 (13) | 0.0289 (13) | 0.0163 (13) | 0.0051 (10) | 0.0097 (10) | 0.0029 (11) |
| C23 | 0.0264 (12) | 0.0311 (13) | 0.0241 (14) | 0.0127 (10) | 0.0095 (11) | 0.0068 (11) |
| C24 | 0.0217 (12) | 0.0308 (13) | 0.0197 (13) | 0.0081 (10) | 0.0041 (10) | 0.0108 (11) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Br26—C22 | 1.906 (3) | C19—C24 | 1.401 (4) |
| N2—C1 | 1.313 (4) | C19—C20 | 1.408 (4) |
| N2—C3 | 1.379 (4) | C20—C21 | 1.380 (4) |
| N5—C1 | 1.346 (4) | C21—C22 | 1.387 (4) |
| N5—C4 | 1.372 (4) | C22—C23 | 1.382 (4) |
| N5—C6 | 1.467 (4) | C23—C24 | 1.385 (4) |
| N9—C8 | 1.459 (4) | C1—H1 | 0.9300 |
| N9—C10 | 1.340 (4) | C3—H3 | 0.9300 |
| N17—C16 | 1.365 (4) | C4—H4 | 0.9300 |
| N17—C18 | 1.314 (3) | C6—H6A | 0.9700 |
| N25—C10 | 1.321 (3) | C6—H6B | 0.9700 |
| N25—C18 | 1.359 (3) | C7—H7A | 0.9700 |
| N9—H9 | 0.8600 | C7—H7B | 0.9700 |
| C3—C4 | 1.356 (5) | C8—H8A | 0.9700 |
| C6—C7 | 1.520 (5) | C8—H8B | 0.9700 |
| C7—C8 | 1.526 (4) | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| C10—C11 | 1.443 (3) | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| C11—C16 | 1.417 (4) | C14—H14 | 0.9300 |
| C11—C12 | 1.408 (4) | C15—H15 | 0.9300 |
| C12—C13 | 1.377 (5) | C20—H20 | 0.9300 |
| C13—C14 | 1.403 (4) | C21—H21 | 0.9300 |
| C14—C15 | 1.373 (4) | C23—H23 | 0.9300 |
| C15—C16 | 1.417 (5) | C24—H24 | 0.9300 |
| C18—C19 | 1.487 (3) | ||
| C1—N2—C3 | 104.7 (3) | C22—C23—C24 | 118.6 (3) |
| C1—N5—C4 | 106.9 (2) | C19—C24—C23 | 121.4 (3) |
| C1—N5—C6 | 126.4 (2) | N2—C1—H1 | 124.00 |
| C4—N5—C6 | 126.7 (3) | N5—C1—H1 | 124.00 |
| C8—N9—C10 | 121.2 (2) | N2—C3—H3 | 125.00 |
| C16—N17—C18 | 115.5 (2) | C4—C3—H3 | 125.00 |
| C10—N25—C18 | 118.1 (2) | N5—C4—H4 | 127.00 |
| C8—N9—H9 | 119.00 | C3—C4—H4 | 127.00 |
| C10—N9—H9 | 119.00 | N5—C6—H6A | 109.00 |
| N2—C1—N5 | 112.3 (3) | N5—C6—H6B | 109.00 |
| N2—C3—C4 | 110.4 (3) | C7—C6—H6A | 109.00 |
| N5—C4—C3 | 105.7 (3) | C7—C6—H6B | 109.00 |
| N5—C6—C7 | 112.6 (2) | H6A—C6—H6B | 108.00 |
| C6—C7—C8 | 112.8 (2) | C6—C7—H7A | 109.00 |
| N9—C8—C7 | 112.5 (2) | C6—C7—H7B | 109.00 |
| N9—C10—N25 | 117.6 (2) | C8—C7—H7A | 109.00 |
| N9—C10—C11 | 121.7 (2) | C8—C7—H7B | 109.00 |
| N25—C10—C11 | 120.8 (2) | H7A—C7—H7B | 108.00 |
| C10—C11—C12 | 124.6 (3) | N9—C8—H8A | 109.00 |
| C12—C11—C16 | 120.0 (2) | N9—C8—H8B | 109.00 |
| C10—C11—C16 | 115.4 (2) | C7—C8—H8A | 109.00 |
| C11—C12—C13 | 120.4 (3) | C7—C8—H8B | 109.00 |
| C12—C13—C14 | 120.0 (3) | H8A—C8—H8B | 108.00 |
| C13—C14—C15 | 120.6 (3) | C11—C12—H12 | 120.00 |
| C14—C15—C16 | 120.8 (3) | C13—C12—H12 | 120.00 |
| N17—C16—C11 | 122.8 (3) | C12—C13—H13 | 120.00 |
| C11—C16—C15 | 118.2 (3) | C14—C13—H13 | 120.00 |
| N17—C16—C15 | 119.0 (3) | C13—C14—H14 | 120.00 |
| N17—C18—C19 | 118.2 (2) | C15—C14—H14 | 120.00 |
| N25—C18—C19 | 114.5 (2) | C14—C15—H15 | 120.00 |
| N17—C18—N25 | 127.4 (2) | C16—C15—H15 | 120.00 |
| C20—C19—C24 | 118.3 (2) | C19—C20—H20 | 120.00 |
| C18—C19—C20 | 120.6 (2) | C21—C20—H20 | 120.00 |
| C18—C19—C24 | 121.2 (2) | C20—C21—H21 | 120.00 |
| C19—C20—C21 | 120.8 (3) | C22—C21—H21 | 120.00 |
| C20—C21—C22 | 119.1 (3) | C22—C23—H23 | 121.00 |
| Br26—C22—C23 | 119.7 (2) | C24—C23—H23 | 121.00 |
| Br26—C22—C21 | 118.4 (2) | C19—C24—H24 | 119.00 |
| C21—C22—C23 | 121.9 (3) | C23—C24—H24 | 119.00 |
| C3—N2—C1—N5 | 0.8 (4) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | −178.9 (3) |
| C1—N2—C3—C4 | −0.5 (4) | C16—C11—C12—C13 | 0.6 (4) |
| C4—N5—C1—N2 | −0.8 (4) | C10—C11—C16—N17 | −0.4 (4) |
| C6—N5—C1—N2 | −179.2 (3) | C10—C11—C16—C15 | 179.8 (3) |
| C1—N5—C4—C3 | 0.4 (3) | C12—C11—C16—N17 | −180.0 (3) |
| C6—N5—C4—C3 | 178.8 (3) | C12—C11—C16—C15 | 0.2 (4) |
| C1—N5—C6—C7 | −58.8 (4) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | −0.6 (5) |
| C4—N5—C6—C7 | 123.2 (3) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | −0.3 (5) |
| C10—N9—C8—C7 | 73.6 (3) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | 1.1 (4) |
| C8—N9—C10—N25 | 0.7 (4) | C14—C15—C16—N17 | 179.1 (3) |
| C8—N9—C10—C11 | 179.7 (3) | C14—C15—C16—C11 | −1.0 (4) |
| C18—N17—C16—C11 | 1.1 (4) | N17—C18—C19—C20 | 174.0 (3) |
| C18—N17—C16—C15 | −179.0 (3) | N17—C18—C19—C24 | −7.1 (4) |
| C16—N17—C18—N25 | −0.4 (4) | N25—C18—C19—C20 | −5.5 (4) |
| C16—N17—C18—C19 | −179.9 (2) | N25—C18—C19—C24 | 173.4 (3) |
| C18—N25—C10—N9 | −179.2 (3) | C18—C19—C20—C21 | 178.6 (3) |
| C18—N25—C10—C11 | 1.8 (4) | C24—C19—C20—C21 | −0.3 (4) |
| C10—N25—C18—N17 | −1.1 (4) | C18—C19—C24—C23 | −178.2 (3) |
| C10—N25—C18—C19 | 178.4 (2) | C20—C19—C24—C23 | 0.7 (4) |
| N2—C3—C4—N5 | 0.1 (4) | C19—C20—C21—C22 | −0.3 (4) |
| N5—C6—C7—C8 | −63.8 (3) | C20—C21—C22—Br26 | −178.8 (2) |
| C6—C7—C8—N9 | −170.6 (2) | C20—C21—C22—C23 | 0.5 (4) |
| N9—C10—C11—C12 | −0.6 (5) | Br26—C22—C23—C24 | 179.2 (2) |
| N9—C10—C11—C16 | 179.9 (3) | C21—C22—C23—C24 | −0.1 (4) |
| N25—C10—C11—C12 | 178.4 (3) | C22—C23—C24—C19 | −0.5 (4) |
| N25—C10—C11—C16 | −1.2 (4) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg1 is the centroid of the N2,N5,C1–C3 ring; Cg3 is the centroid of the C11–C16 ring; Cg4 is the centroid of the C19–C24 ring.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N9—H9···N2i | 0.86 | 2.14 | 2.949 (4) | 156 |
| C1—H1···Cg4ii | 0.93 | 2.84 | 3.605 (3) | 140 |
| C4—H4···Cg3iii | 0.93 | 2.78 | 3.509 (4) | 136 |
| C14—H14···Cg1iv | 0.93 | 2.88 | 3.527 (3) | 128 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y+2, −z+2; (ii) x−1, y, z; (iii) −x+2, −y+2, −z+2; (iv) x+1, y, z+1.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: SU2454).
References
- Agilent (2010). CrysAlis PRO Agilent Technologies, Yarnton, Oxfordshire, England.
- Aguilar, L., Gimenez, M. J., García-Rey, C. & Martin, J. E. (2002). Antimicrob. Chemother. 50 (Suppl. C), 93–100. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Asproni, B., Murineddu, G., Pau, A., Pinna, G. A., Langgård, M., Christoffersen, C. T., Nielsen, J. & Kehler, J. (2011). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 19, 642–649. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Connolly, D. J., Cusack, D. O., Sullivan, T. P. & Guiry, P. J. (2005). Tetrahedron, 61, 10153–10202.
- Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K. & Puschmann, H. (2009). J. Appl. Cryst. 42, 339–341.
- Okano, M., Mito, J., Maruyama, Y., Masuda, H., Niwa, T., Nakagawa, S., Nakamura, Y. & Matsuura, A. (2009). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 17, 119–132. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Rohini, R., Shanker, K., Reddy, P. M., Ho, Y.-P. & Ravinder, V. (2009). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 44 3330–3339. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Westrip, S. P. (2010). J. Appl. Cryst. 43, 920–925.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812028115/su2454sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812028115/su2454Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812028115/su2454Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report



