Abstract
In the title compound, C18H18N2O, the dihedral angle between the indole system and the phenyl ring is 17.2 (2)°. The crystal packing features two N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, which link the molecules into layers parallel to (001). The absolute configuration was determined by the synthetic procedure and was set according to the starting material.
Related literature
For background to the synthesis of chiral non-racemic acetamide indole compounds, see: Kochanowska-Karamyan & Hamann (2010 ▶). For their use in the synthesis of nitrogen heterocyclic compounds and indole alkaloids, see: Suárez-Castillo et al. (2006 ▶); Chiou et al. (2009 ▶).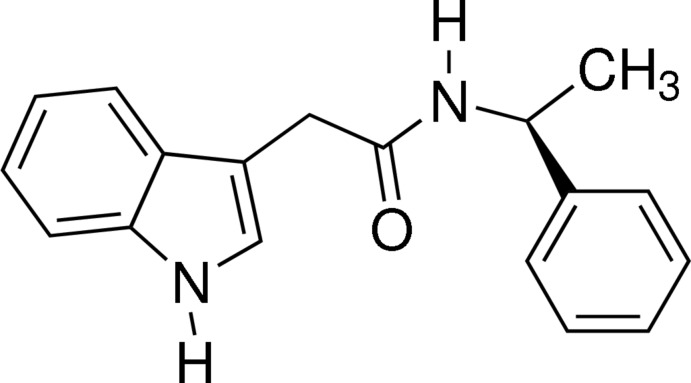
Experimental
Crystal data
C18H18N2O
M r = 278.34
Orthorhombic,
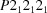
a = 7.307 (4) Å
b = 8.559 (4) Å
c = 25.674 (9) Å
V = 1605.7 (13) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.07 mm−1
T = 298 K
0.65 × 0.6 × 0.1 mm
Data collection
Siemens P4 diffractometer
Absorption correction: ψ scan (North et al., 1968 ▶) T min = 0.646, T max = 1
2937 measured reflections
2126 independent reflections
1146 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.045
3 standard reflections every 97 reflections intensity decay: 1%
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.065
wR(F 2) = 0.161
S = 1.05
2126 reflections
199 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.15 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.15 e Å−3
Data collection: XSCANS (Siemens, 1994 ▶); cell refinement: XSCANS; data reduction: XSCANS; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 (Farrugia, 1997 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812028450/bt5951sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812028450/bt5951Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812028450/bt5951Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1N⋯O1i | 0.89 (5) | 2.03 (5) | 2.891 (4) | 163 (4) |
| N2—H2N⋯O1ii | 0.96 (6) | 1.91 (6) | 2.847 (5) | 164 (4) |
Symmetry codes: (i) 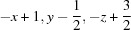 ; (ii)
; (ii) 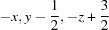 .
.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful for financial support by projects VIEP-BUAP and CONACyT CB-2009–01/128747. JR and OR thank CONACyT for doctoral scholarships. Special thanks go to Dr Marcos Flores-Alamo (USAI/FQ/UNAM) for useful comments.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The synthesis of chiral non racemic acetamides indole compounds is an original area of interest in organic chemistry (Kochanowska-Karamyan & Hamann, 2010) because they are useful intermediates for the synthesis of diverse interesting nitrogen heterocyclic compounds and indole alkaloids derivatives and natural products (Suárez-Castillo et al., 2006; Chiou et al., 2009).
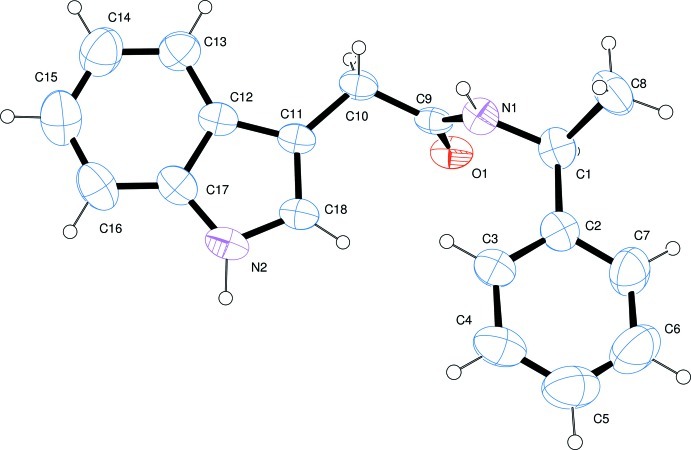
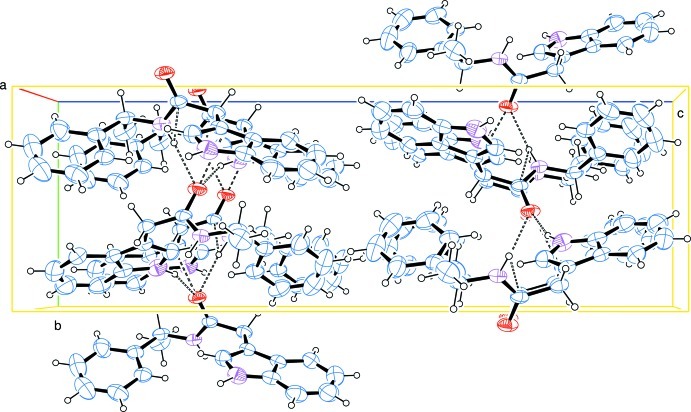
In the title compound the N1 atom in a planar conformation from the plane between C9, H1N and C1 with an r.m.s. deviation of 0.012Å. The N1—C9 [1.322 (5) Å] and C9—O1 [1.254 (4) Å] distances show electron delocalization along the N1—C9—O1 system. The indole group shows a torsion angle of 102.1 (4)° from the plane placed by N1/C9/C10/C11 and phenyl ring C2—C7 shows a torsion angle of 92.3 (4)° from plane C9/N1/C1/C2. The crystal packing is stabilized by two hydrogen bond interactions [N1—H1N···O1 and N2—H2N···O1] linking the molecules into planes parallel to (0 0 1) (Table 1).
Experimental
The title compound, C18H18N2O, was obtained dissolving indolic acid (0.96 mmol, 0.277 g) and boric acid (0.30 mmol, 0.020 g) in 88 ml of toluene under N2 atmosphere. Once the mixture was colorless, (S)-(-)-phenylethylamine was added and heated under reflux by 16 h. After that, mixture was cooled and hexane (0.5 L) was added. Finally, white solid was obtained and crystalized from an ethyl acetate/diethylether solution; m. p. 94–96 °C. [α]D25 = -45.7° (c 1.5, CH2Cl2); IR (KBr)1643 cm-1. 1H NMR (CDCl3, 400 MHz) δ (p.p.m.), J(Hz) 9.24 (s, 1H), 7.48 (d, J=8.0, 1H),7.26 (d, J=8.4, 1H), 7.17–7.05 (m, 6H),6.85 (d, J=2.4, 1H), 6.32 (d, J=8.0, 1H), 5.12 (m, 1H), 3.69 (d, J=3.2, 2H), 1.24 (d, J=7.2, 3H). 13C NMR (CDCl3,100 MHz) δ (p.p.m.) 22.2, 33.8, 49.1, 108.2,112.1, 118.8–128.8, 136.9, 143.4, 171.8.
Refinement
H atom bonded to N atoms were located in a difference Fourier map and they were isotropically refined. H atoms bonded to C atoms were placed in geometrical idealized positions and refined as riding on their parent atoms, with C—H = 0.93–0.98 Å and with Uiso(H) = 1.2 Ueq(C) or Ueq(H) = 1.5 Ueq(C) for methyl groups. In the absence of anomalous scatterers, the absolute configuration could not be determined. It was set according to the starting material and Friedel pairs were merged.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of title compound, with atom labels and 30% probability displacement ellipsoids for non-H atoms.
Fig. 2.
Molecular packing of title compound, viewed down the a axis, showing hydrogen bonds and intramolecular interaction (dashed lines).
Crystal data
| C18H18N2O | F(000) = 592 |
| Mr = 278.34 | Dx = 1.151 Mg m−3 |
| Orthorhombic, P212121 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: P 2ac 2ab | Cell parameters from 24 reflections |
| a = 7.307 (4) Å | θ = 12.6–22.7° |
| b = 8.559 (4) Å | µ = 0.07 mm−1 |
| c = 25.674 (9) Å | T = 298 K |
| V = 1605.7 (13) Å3 | Prism, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.65 × 0.6 × 0.1 mm |
Data collection
| Siemens P4 diffractometer | Rint = 0.045 |
| Graphite monochromator | θmax = 27.5°, θmin = 2.5° |
| 2θ/ω scans | h = −2→9 |
| Absorption correction: ψ scan (North et al., 1968) | k = −4→11 |
| Tmin = 0.646, Tmax = 1 | l = −11→33 |
| 2937 measured reflections | 3 standard reflections every 97 reflections |
| 2126 independent reflections | intensity decay: 1% |
| 1146 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.065 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.161 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.05 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0706P)2 + 0.0614P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2126 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 199 parameters | Δρmax = 0.15 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.15 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All s.u.'s (except the s.u. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell s.u.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of s.u.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between s.u.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell s.u.'s is used for estimating s.u.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.3536 (4) | 1.0472 (3) | 0.73306 (10) | 0.0732 (8) | |
| C9 | 0.4310 (5) | 0.9265 (4) | 0.74986 (14) | 0.0574 (9) | |
| N1 | 0.5307 (5) | 0.8365 (4) | 0.71908 (12) | 0.0630 (8) | |
| C2 | 0.4248 (5) | 0.7787 (4) | 0.62951 (15) | 0.0702 (11) | |
| N2 | −0.0448 (5) | 0.6926 (4) | 0.81406 (16) | 0.0822 (10) | |
| C1 | 0.5641 (6) | 0.8626 (4) | 0.66407 (15) | 0.0712 (11) | |
| H1 | 0.5511 | 0.9749 | 0.6576 | 0.085* | |
| C3 | 0.2953 (5) | 0.6773 (5) | 0.64922 (16) | 0.0714 (11) | |
| H3 | 0.2874 | 0.6622 | 0.685 | 0.086* | |
| C12 | 0.1826 (5) | 0.7462 (4) | 0.86932 (15) | 0.0647 (10) | |
| C11 | 0.2352 (5) | 0.8019 (4) | 0.81856 (14) | 0.0594 (9) | |
| C10 | 0.4134 (5) | 0.8780 (4) | 0.80602 (14) | 0.0636 (10) | |
| H10A | 0.5117 | 0.8061 | 0.8144 | 0.076* | |
| H10B | 0.4278 | 0.9696 | 0.8279 | 0.076* | |
| C17 | 0.0087 (6) | 0.6788 (4) | 0.86442 (18) | 0.0752 (11) | |
| C18 | 0.0937 (5) | 0.7666 (5) | 0.78644 (16) | 0.0735 (11) | |
| H18 | 0.0899 | 0.7887 | 0.751 | 0.088* | |
| C4 | 0.1767 (7) | 0.5977 (6) | 0.6164 (2) | 0.0978 (15) | |
| H4 | 0.091 | 0.5291 | 0.6303 | 0.117* | |
| C16 | −0.0813 (7) | 0.6093 (6) | 0.9064 (2) | 0.0980 (15) | |
| H16 | −0.1963 | 0.5641 | 0.9025 | 0.118* | |
| C13 | 0.2681 (7) | 0.7464 (5) | 0.91787 (17) | 0.0867 (13) | |
| H13 | 0.3831 | 0.791 | 0.9223 | 0.104* | |
| C7 | 0.4333 (8) | 0.7996 (6) | 0.57627 (19) | 0.1064 (17) | |
| H7 | 0.5194 | 0.867 | 0.5619 | 0.128* | |
| C8 | 0.7594 (6) | 0.8189 (6) | 0.6517 (2) | 0.0986 (15) | |
| H8A | 0.7763 | 0.7089 | 0.6572 | 0.148* | |
| H8B | 0.8407 | 0.8761 | 0.6741 | 0.148* | |
| H8C | 0.7856 | 0.8439 | 0.616 | 0.148* | |
| C15 | 0.0072 (10) | 0.6104 (7) | 0.9535 (2) | 0.121 (2) | |
| H15 | −0.0488 | 0.5643 | 0.9822 | 0.146* | |
| C14 | 0.1770 (10) | 0.6781 (7) | 0.9594 (2) | 0.1179 (18) | |
| H14 | 0.2318 | 0.678 | 0.9921 | 0.141* | |
| C6 | 0.3115 (11) | 0.7186 (9) | 0.5442 (2) | 0.138 (2) | |
| H6 | 0.3174 | 0.7333 | 0.5084 | 0.166* | |
| C5 | 0.1852 (9) | 0.6192 (9) | 0.5639 (3) | 0.127 (2) | |
| H5 | 0.1053 | 0.5664 | 0.5419 | 0.153* | |
| H1N | 0.589 (6) | 0.757 (6) | 0.7342 (17) | 0.104 (16)* | |
| H2N | −0.147 (8) | 0.659 (6) | 0.7935 (18) | 0.130 (18)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0751 (18) | 0.0429 (13) | 0.1016 (18) | 0.0091 (14) | −0.0245 (16) | 0.0040 (13) |
| C9 | 0.051 (2) | 0.0402 (18) | 0.080 (2) | −0.0085 (19) | −0.018 (2) | −0.0014 (17) |
| N1 | 0.072 (2) | 0.0403 (16) | 0.0771 (19) | 0.0031 (17) | −0.0018 (18) | 0.0044 (15) |
| C2 | 0.071 (3) | 0.057 (2) | 0.083 (3) | 0.021 (2) | 0.006 (2) | −0.0071 (19) |
| N2 | 0.060 (2) | 0.082 (2) | 0.105 (3) | −0.009 (2) | −0.013 (2) | −0.014 (2) |
| C1 | 0.084 (3) | 0.0426 (19) | 0.087 (3) | 0.000 (2) | 0.008 (2) | 0.0062 (18) |
| C3 | 0.061 (2) | 0.061 (2) | 0.092 (3) | 0.010 (2) | −0.001 (2) | −0.001 (2) |
| C12 | 0.064 (2) | 0.050 (2) | 0.080 (3) | 0.003 (2) | −0.006 (2) | −0.0140 (19) |
| C11 | 0.055 (2) | 0.0468 (18) | 0.076 (2) | 0.0019 (18) | −0.0107 (19) | −0.0103 (17) |
| C10 | 0.057 (2) | 0.0533 (18) | 0.081 (2) | −0.0030 (19) | −0.013 (2) | −0.0078 (18) |
| C17 | 0.073 (3) | 0.054 (2) | 0.099 (3) | −0.004 (2) | 0.006 (3) | −0.016 (2) |
| C18 | 0.062 (2) | 0.076 (2) | 0.083 (2) | −0.007 (2) | −0.013 (2) | −0.004 (2) |
| C4 | 0.075 (3) | 0.084 (3) | 0.135 (4) | 0.002 (3) | −0.012 (3) | −0.027 (3) |
| C16 | 0.090 (3) | 0.082 (3) | 0.122 (4) | −0.014 (3) | 0.029 (3) | −0.017 (3) |
| C13 | 0.099 (3) | 0.075 (3) | 0.086 (3) | −0.009 (3) | −0.010 (3) | −0.009 (2) |
| C7 | 0.120 (4) | 0.113 (4) | 0.086 (3) | 0.000 (4) | 0.020 (3) | −0.018 (3) |
| C8 | 0.065 (3) | 0.109 (4) | 0.121 (4) | −0.007 (3) | 0.015 (3) | 0.023 (3) |
| C15 | 0.155 (6) | 0.097 (4) | 0.112 (4) | −0.020 (4) | 0.034 (4) | −0.008 (3) |
| C14 | 0.150 (5) | 0.114 (4) | 0.090 (3) | −0.013 (5) | −0.001 (4) | −0.004 (3) |
| C6 | 0.148 (6) | 0.181 (7) | 0.085 (3) | 0.015 (6) | −0.009 (4) | −0.037 (4) |
| C5 | 0.103 (4) | 0.149 (6) | 0.130 (5) | 0.013 (5) | −0.022 (4) | −0.053 (5) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—C9 | 1.254 (4) | C10—H10B | 0.97 |
| C9—N1 | 1.322 (5) | C17—C16 | 1.395 (6) |
| C9—C10 | 1.506 (5) | C18—H18 | 0.93 |
| N1—C1 | 1.451 (5) | C4—C5 | 1.361 (7) |
| N1—H1N | 0.89 (5) | C4—H4 | 0.93 |
| C2—C3 | 1.380 (5) | C16—C15 | 1.372 (7) |
| C2—C7 | 1.380 (6) | C16—H16 | 0.93 |
| C2—C1 | 1.529 (5) | C13—C14 | 1.387 (7) |
| N2—C17 | 1.356 (5) | C13—H13 | 0.93 |
| N2—C18 | 1.388 (5) | C7—C6 | 1.396 (8) |
| N2—H2N | 0.96 (6) | C7—H7 | 0.93 |
| C1—C8 | 1.509 (6) | C8—H8A | 0.96 |
| C1—H1 | 0.98 | C8—H8B | 0.96 |
| C3—C4 | 1.388 (6) | C8—H8C | 0.96 |
| C3—H3 | 0.93 | C15—C14 | 1.377 (8) |
| C12—C13 | 1.394 (6) | C15—H15 | 0.93 |
| C12—C17 | 1.401 (6) | C14—H14 | 0.93 |
| C12—C11 | 1.440 (5) | C6—C5 | 1.353 (9) |
| C11—C18 | 1.357 (5) | C6—H6 | 0.93 |
| C11—C10 | 1.491 (5) | C5—H5 | 0.93 |
| C10—H10A | 0.97 | ||
| O1—C9—N1 | 121.5 (4) | C16—C17—C12 | 122.3 (5) |
| O1—C9—C10 | 121.2 (4) | C11—C18—N2 | 110.3 (4) |
| N1—C9—C10 | 117.3 (3) | C11—C18—H18 | 124.9 |
| C9—N1—C1 | 125.8 (3) | N2—C18—H18 | 124.9 |
| C9—N1—H1N | 116 (3) | C5—C4—C3 | 120.4 (6) |
| C1—N1—H1N | 118 (3) | C5—C4—H4 | 119.8 |
| C3—C2—C7 | 118.4 (4) | C3—C4—H4 | 119.8 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 122.6 (4) | C15—C16—C17 | 117.1 (5) |
| C7—C2—C1 | 118.9 (4) | C15—C16—H16 | 121.5 |
| C17—N2—C18 | 108.5 (3) | C17—C16—H16 | 121.5 |
| C17—N2—H2N | 136 (3) | C14—C13—C12 | 118.2 (5) |
| C18—N2—H2N | 115 (3) | C14—C13—H13 | 120.9 |
| N1—C1—C8 | 109.0 (4) | C12—C13—H13 | 120.9 |
| N1—C1—C2 | 112.4 (3) | C2—C7—C6 | 119.4 (5) |
| C8—C1—C2 | 113.1 (4) | C2—C7—H7 | 120.3 |
| N1—C1—H1 | 107.4 | C6—C7—H7 | 120.3 |
| C8—C1—H1 | 107.4 | C1—C8—H8A | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—H1 | 107.4 | C1—C8—H8B | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 120.9 (4) | H8A—C8—H8B | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.5 | C1—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.5 | H8A—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| C13—C12—C17 | 119.1 (4) | H8B—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| C13—C12—C11 | 133.6 (4) | C16—C15—C14 | 121.7 (6) |
| C17—C12—C11 | 107.3 (3) | C16—C15—H15 | 119.2 |
| C18—C11—C12 | 105.8 (3) | C14—C15—H15 | 119.2 |
| C18—C11—C10 | 129.2 (4) | C15—C14—C13 | 121.6 (6) |
| C12—C11—C10 | 125.0 (3) | C15—C14—H14 | 119.2 |
| C11—C10—C9 | 113.7 (3) | C13—C14—H14 | 119.2 |
| C11—C10—H10A | 108.8 | C5—C6—C7 | 121.8 (6) |
| C9—C10—H10A | 108.8 | C5—C6—H6 | 119.1 |
| C11—C10—H10B | 108.8 | C7—C6—H6 | 119.1 |
| C9—C10—H10B | 108.8 | C6—C5—C4 | 119.1 (6) |
| H10A—C10—H10B | 107.7 | C6—C5—H5 | 120.5 |
| N2—C17—C16 | 129.6 (4) | C4—C5—H5 | 120.5 |
| N2—C17—C12 | 108.1 (4) | ||
| O1—C9—N1—C1 | 0.1 (5) | C11—C12—C17—N2 | −0.5 (4) |
| C10—C9—N1—C1 | 179.8 (3) | C13—C12—C17—C16 | −1.0 (6) |
| C9—N1—C1—C8 | 141.5 (4) | C11—C12—C17—C16 | 178.3 (4) |
| C9—N1—C1—C2 | −92.3 (4) | C12—C11—C18—N2 | 0.2 (4) |
| C3—C2—C1—N1 | −6.3 (5) | C10—C11—C18—N2 | 178.6 (3) |
| C7—C2—C1—N1 | 176.6 (4) | C17—N2—C18—C11 | −0.6 (5) |
| C3—C2—C1—C8 | 117.6 (4) | C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.5 (7) |
| C7—C2—C1—C8 | −59.5 (5) | N2—C17—C16—C15 | 179.1 (4) |
| C7—C2—C3—C4 | 0.2 (6) | C12—C17—C16—C15 | 0.5 (7) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −176.9 (4) | C17—C12—C13—C14 | 0.5 (6) |
| C13—C12—C11—C18 | 179.4 (4) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | −178.7 (4) |
| C17—C12—C11—C18 | 0.2 (4) | C3—C2—C7—C6 | 0.2 (7) |
| C13—C12—C11—C10 | 1.0 (6) | C1—C2—C7—C6 | 177.4 (5) |
| C17—C12—C11—C10 | −178.3 (3) | C17—C16—C15—C14 | 0.5 (8) |
| C18—C11—C10—C9 | 2.6 (5) | C16—C15—C14—C13 | −1.0 (9) |
| C12—C11—C10—C9 | −179.3 (3) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | 0.5 (8) |
| O1—C9—C10—C11 | 77.6 (4) | C2—C7—C6—C5 | −0.3 (9) |
| N1—C9—C10—C11 | −102.1 (4) | C7—C6—C5—C4 | 0.0 (10) |
| C18—N2—C17—C16 | −178.1 (4) | C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.4 (9) |
| C18—N2—C17—C12 | 0.7 (4) | C11—C10—C9—N1 | −102.1 (4) |
| C13—C12—C17—N2 | −179.9 (4) | C2—C1—N1—C9 | −92.3 (4) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1N···O1i | 0.89 (5) | 2.03 (5) | 2.891 (4) | 163 (4) |
| N2—H2N···O1ii | 0.96 (6) | 1.91 (6) | 2.847 (5) | 164 (4) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, y−1/2, −z+3/2; (ii) −x, y−1/2, −z+3/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: BT5951).
References
- Chiou, W.-H., Lin, G.-H., Hsu, C.-C., Chaterpaul, S. & Ojima, I. (2009). Org. Lett. 11, 2659–2662. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst. 30, 565.
- Kochanowska-Karamyan, A. J. & Hamann, M. T. (2010). Chem. Rev. 110, 4489–4497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- North, A. C. T., Phillips, D. C. & Mathews, F. S. (1968). Acta Cryst. A24, 351–359.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Siemens (1994). XSCANS Siemens Analytical X-ray Instruments Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Suárez-Castillo, O. R., Sánchez-Zavala, M., Meléndez-Rodríguez, M., Castelán-Duarte, L. E., Morales-Ríos, M. S. & Joseph-Nathan, P. (2006). Tetrahedron, 62, 3040–3051.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812028450/bt5951sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812028450/bt5951Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812028450/bt5951Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report