Abstract
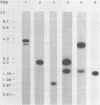
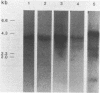
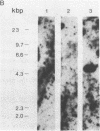
Comparative analysis of cosmid clones containing the human and feline c-sis genetic regions revealed the similar structural organization of these areas in the two species. The areas shared seven different genetic regions in and around the c-sis locus and of these was related to v-sis. Another region, 1.9 kbp in size and located about 8 kbp upstream of the v-sis homologous region in the human genome, also hybridized to the main c-sis transcriptional product of 3.5 kb. Comparison with a recently described c-sis cDNA clone (Collins et al., Nature 316, 748-750 (1985)) revealed that the 1.9 kbp DNA region contained a large 5' c-sis exon of at least 1050 bp. In this exon, the presumed initiation site of the predicted PDGF-2 containing precursor protein was located and appeared to be preceded by a large untranslated region. In the region immediately upstream of this exon, a TATA box and a consensus sequence for a potential Sp1 binding site were found at similar positions in both species. This region also exhibited promoter activity when tested in an assay in which coding sequences of bacterial chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT; acetyl-CoA: chloramphenicol 3-O-acetyltransferase, EC 2.3.1.28) were placed under its control. The five other DNA regions were found upstream and downstream of the human c-sis transcription unit and also in an intron. Four of them contained repetitive sequences. Hybridization analysis of human and feline c-sis containing cosmid clones with a mixed synthetic nucleotide probe, which corresponded to sequences encoding amino acid residues 2-7 of chain 1 of platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF-1), suggested that the c-sis cosmid clones did not include PDGF-1-specific genetic sequences.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antoniades H. N., Hunkapiller M. W. Human platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF): amino-terminal amino acid sequence. Science. 1983 May 27;220(4600):963–965. doi: 10.1126/science.6844921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett T. B., Gajdusek C. M., Schwartz S. M., McDougall J. K., Benditt E. P. Expression of the sis gene by endothelial cells in culture and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6772–6774. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betsholtz C., Westermark B., Ek B., Heldin C. H. Coexpression of a PDGF-like growth factor and PDGF receptors in a human osteosarcoma cell line: implications for autocrine receptor activation. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):447–457. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90452-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu I. M., Reddy E. P., Givol D., Robbins K. C., Tronick S. R., Aaronson S. A. Nucleotide sequence analysis identifies the human c-sis proto-oncogene as a structural gene for platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):123–129. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90307-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke M. F., Westin E., Schmidt D., Josephs S. F., Ratner L., Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C., Reitz M. S., Jr Transformation of NIH 3T3 cells by a human c-sis cDNA clone. 1984 Mar 29-Apr 4Nature. 308(5958):464–467. doi: 10.1038/308464a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins T., Ginsburg D., Boss J. M., Orkin S. H., Pober J. S. Cultured human endothelial cells express platelet-derived growth factor B chain: cDNA cloning and structural analysis. Nature. 1985 Aug 22;316(6030):748–750. doi: 10.1038/316748a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalla-Favera R., Gelmann E. P., Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F. A human onc gene homologous to the transforming gene (v-sis) of simian sarcoma virus. Nature. 1981 Jul 2;292(5818):31–35. doi: 10.1038/292031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E., Devare S. G., Robbins K. C., Aaronson S. A., Antoniades H. N. Simian sarcoma virus onc gene, v-sis, is derived from the gene (or genes) encoding a platelet-derived growth factor. Science. 1983 Jul 15;221(4607):275–277. doi: 10.1126/science.6304883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dull T. J., Gray A., Hayflick J. S., Ullrich A. Insulin-like growth factor II precursor gene organization in relation to insulin gene family. 1984 Aug 30-Sep 5Nature. 310(5980):777–781. doi: 10.1038/310777a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Control of eukaryotic messenger RNA synthesis by sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):774–778. doi: 10.1038/316774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efstratiadis A., Posakony J. W., Maniatis T., Lawn R. M., O'Connell C., Spritz R. A., DeRiel J. K., Forget B. G., Weissman S. M., Slightom J. L. The structure and evolution of the human beta-globin gene family. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):653–668. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90429-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eva A., Robbins K. C., Andersen P. R., Srinivasan A., Tronick S. R., Reddy E. P., Ellmore N. W., Galen A. T., Lautenberger J. A., Papas T. S. Cellular genes analogous to retroviral onc genes are transcribed in human tumour cells. Nature. 1982 Jan 14;295(5845):116–119. doi: 10.1038/295116a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm M., Berg P. Deletion mapping of DNA regions required for SV40 early region promoter function in vivo. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(5):457–481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazit A., Igarashi H., Chiu I. M., Srinivasan A., Yaniv A., Tronick S. R., Robbins K. C., Aaronson S. A. Expression of the normal human sis/PDGF-2 coding sequence induces cellular transformation. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):89–97. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90194-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Merlino G. T., Willingham M. C., Pastan I., Howard B. H. The Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat is a strong promoter when introduced into a variety of eukaryotic cells by DNA-mediated transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6777–6781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goustin A. S., Betsholtz C., Pfeifer-Ohlsson S., Persson H., Rydnert J., Bywater M., Holmgren G., Heldin C. H., Westermark B., Ohlsson R. Coexpression of the sis and myc proto-oncogenes in developing human placenta suggests autocrine control of trophoblast growth. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):301–312. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90083-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannink M., Donoghue D. J. Requirement for a signal sequence in biological expression of the v-sis oncogene. Science. 1984 Dec 7;226(4679):1197–1199. doi: 10.1126/science.6095451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldin C. H., Westermark B., Wasteson A. Chemical and biological properties of a growth factor from human-cultured osteosarcoma cells: resemblance with platelet-derived growth factor. J Cell Physiol. 1980 Nov;105(2):235–246. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041050207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii S., Xu Y. H., Stratton R. H., Roe B. A., Merlino G. T., Pastan I. Characterization and sequence of the promoter region of the human epidermal growth factor receptor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4920–4924. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaye M., McConathy E., Drohan W., Tong B., Deuel T., Maciag T. Modulation of the sis gene transcript during endothelial cell differentiation in vitro. Science. 1985 May 17;228(4701):882–885. doi: 10.1126/science.3890179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnsson A., Heldin C. H., Wasteson A., Westermark B., Deuel T. F., Huang J. S., Seeburg P. H., Gray A., Ullrich A., Scrace G. The c-sis gene encodes a precursor of the B chain of platelet-derived growth factor. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):921–928. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01908.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations close to the AUG initiator codon affect the efficiency of translation of rat preproinsulin in vivo. Nature. 1984 Mar 15;308(5956):241–246. doi: 10.1038/308241a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nistér M., Heldin C. H., Wasteson A., Westermark B. A glioma-derived analog to platelet-derived growth factor: demonstration of receptor competing activity and immunological crossreactivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):926–930. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratner L., Josephs S. F., Jarrett R., Reitz M. S., Jr, Wong-Staal F. Nucleotide sequence of transforming human c-sis cDNA clones with homology to platelet-derived growth factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 25;13(14):5007–5018. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.14.5007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins K. C., Antoniades H. N., Devare S. G., Hunkapiller M. W., Aaronson S. A. Structural and immunological similarities between simian sarcoma virus gene product(s) and human platelet-derived growth factor. Nature. 1983 Oct 13;305(5935):605–608. doi: 10.1038/305605a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Glomset J., Kariya B., Harker L. A platelet-dependent serum factor that stimulates the proliferation of arterial smooth muscle cells in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1207–1210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalken J. A., van den Ouweland A. M., Bloemers H. P., van de Ven W. J. Characterization of the feline c-abl proto-oncogene. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Feb 20;824(2):104–112. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(85)90086-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scher C. D., Shepard R. C., Antoniades H. N., Stiles C. D. Platelet-derived growth factor and the regulation of the mammalian fibroblast cell cycle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Aug 10;560(2):217–241. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(79)90020-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. An interactive graphics program for comparing and aligning nucleic acid and amino acid sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2951–2961. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiles C. D. The molecular biology of platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):653–655. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterfield M. D., Scrace G. T., Whittle N., Stroobant P., Johnsson A., Wasteson A., Westermark B., Heldin C. H., Huang J. S., Deuel T. F. Platelet-derived growth factor is structurally related to the putative transforming protein p28sis of simian sarcoma virus. Nature. 1983 Jul 7;304(5921):35–39. doi: 10.1038/304035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Zoelen E. J., van de Ven W. J., Franssen H. J., van Oostwaard T. M., van der Saag P. T., Heldin C. H., de Laat S. W. Neuroblastoma cells express c-sis and produce a transforming growth factor antigenically related to the platelet-derived growth factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;5(9):2289–2297. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.9.2289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Ouweland A. M., Breuer M. L., Steenbergh P. H., Schalken J. A., Bloemers H. P., Van de Ven W. J. Comparative analysis of the human and feline c-sis proto-oncogenes. Identification of 5' human c-sis coding sequences that are not homologous to the transforming gene of simian sarcoma virus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jun 24;825(2):140–147. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(85)90097-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]