Abstract
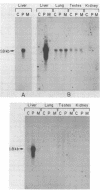
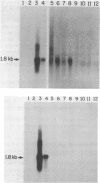
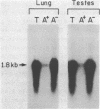
The tissue-specific expression of cytochrome P-450b and P-450e mRNAs was examined with synthetic 18-mer oligomer probes in the liver, lung, kidney, and testis of control and inducer pretreated adult rats. RNAs homologous to the P-450e probe were detected in trace amounts in control and 3-methylcholanthrene (MC) induced livers and at high levels in livers from phenobarbital (PB) induced animals. P-450e mRNA levels were below detection limits in the other tissues examined, regardless of pretreatment. In contrast, mRNAs homologous to the P-450b oligomer were detected at low levels in control and inducer pretreated lung and testis, and at high levels in PB induced liver. No P-450b mRNAs were detected in these assays in RNA isolates from the kidney or from control or MC pretreated liver. Solution hybridization data indicated that the rat lung contained 9-12%, and the testis, 6-9%, respectively, of the levels of P-450b mRNA measured in the PB induced liver. Results from oligo(dT)-cellulose and poly(U)-affinity experiments indicated that the hepatic mRNAs for P-450b and P-450e were present predominantly in the bound, polyadenylated fraction, whereas the homologous lung and testes P-450b mRNAs predominated in the flow-thru fractions.
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adesnik M., Bar-Nun S., Maschio F., Zunich M., Lippman A., Bard E. Mechanism of induction of cytochrome P-450 by phenobarbital. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 25;256(20):10340–10345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atchison M., Adesnik M. A cytochrome P-450 multigene family. Characterization of a gene activated by phenobarbital administration. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):11285–11295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black S. D., Tarr G. E., Coon M. J. Structural features of isozyme 2 of liver microsomal cytochrome P-450. Identification of a highly conserved cysteine-containing peptide. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14616–14619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capetanaki Y. G., Ngai J., Flytzanis C. N., Lazarides E. Tissue-specific expression of two mRNA species transcribed from a single vimentin gene. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):411–420. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90174-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conney A. H. Induction of microsomal enzymes by foreign chemicals and carcinogenesis by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: G. H. A. Clowes Memorial Lecture. Cancer Res. 1982 Dec;42(12):4875–4917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. J., Tukey R. H., Nebert D. W. Structural gene products of the Ah locus. Transcriptional regulation of cytochrome P1-450 and P3-450 mRNA levels by 3-methylcholanthrene. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 Jul;26(1):117–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guengerich F. P., Mason P. S. Immunological comparison of hepatic and extrahepatic cytochromes P-450. Mol Pharmacol. 1979 Jan;15(1):154–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardwick J. P., Gonzalez F. J., Kasper C. B. Transcriptional regulation of rat liver epoxide hydratase, NADPH-Cytochrome P-450 oxidoreductase, and cytochrome P-450b genes by phenobarbital. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):8081–8085. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huez G., Bruck C., Cleuter Y. Translational stability of native and deadenylylated rabbit globin mRNA injected into HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):908–911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson A., Favreau M. Possible involvement of poly(A) in protein synthesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 24;11(18):6353–6368. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.18.6353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leighton J. K., Kemper B. Differential induction and tissue-specific expression of closely related members of the phenobarbital-inducible rabbit cytochrome P-450 gene family. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 25;259(18):11165–11168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu A. Y., West S. B. Multiplicity of mammalian microsomal cytochromes P-45. Pharmacol Rev. 1979 Dec;31(4):277–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizukami Y., Fujii-Kuriyama Y., Muramatsu M. Multiplicity of deoxyribonucleic acid sequences with homology to a cloned complementary deoxyribonucleic acid coding for rat phenobarbital-inducible cytochrome P-450. Biochemistry. 1983 Mar 1;22(5):1223–1229. doi: 10.1021/bi00274a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizukami Y., Sogawa K., Suwa Y., Muramatsu M., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Gene structure of a phenobarbital-inducible cytochrome P-450 in rat liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3958–3962. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueckler M. M., Pitot H. C. Structure and function of rat liver polysome populations. I. Complexity, frequency distribution, and degree of uniqueness of free and membrane-bound polysomal polyadenylate-containing RNA populations. J Cell Biol. 1981 Aug;90(2):495–506. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.2.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omiecinski C. J., Hines R. N., Foldes R. L., Levy J. B., Bresnick E. Molecular induction by phenobarbital of a rat hepatic form of cytochrome P-450: expression of a 4-kilobase messenger RNA. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Dec;227(2):478–493. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90478-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omiecinski C. J., Walz F. G., Jr, Vlasuk G. P. Phenobarbital induction of rat liver cytochromes P-450b and P-450e. Quantitation of specific RNAs by hybridization to synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotide probes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3247–3250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rampersaud A., Walz F. G., Jr At least six forms of extremely homologous cytochromes P-450 in rat liver are encoded at two closely linked genetic loci. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6542–6546. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saidapet C., Khandekar P., Mendola C., Siddiqui M. A. Tissue specificity of 3'-untranslated sequence of myosin light chain gene: unexpected interspecies homology with repetitive DNA. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Sep;233(2):565–572. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90480-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. L., Kasper C. B. Genetic polymorphisms for a phenobarbital-inducible cytochrome P-450 map to the Coh locus in mice. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9585–9588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soares M. B., Ishii D. N., Efstratiadis A. Developmental and tissue-specific expression of a family of transcripts related to rat insulin-like growth factor II mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 25;13(4):1119–1134. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.4.1119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tukey R. H., Hannah R. R., Negishi M., Nebert D. W., Eisen H. J. The Ah locus: correlation of intranuclear appearance of inducer-receptor complex with induction of cytochrome P1-450 mRNA. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):275–284. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90427-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlasuk G. P., Ryan D. E., Thomas P. E., Levin W., Walz F. G., Jr Polypeptide patterns of hepatic microsomes from Long-Evans rats treated with different xenobiotics. Biochemistry. 1982 Nov 23;21(24):6288–6292. doi: 10.1021/bi00267a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. B., Johnson M. J., Hirose T., Miyake T., Kawashima E. H., Itakura K. The use of synthetic oligonucleotides as hybridization probes. II. Hybridization of oligonucleotides of mixed sequence to rabbit beta-globin DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Feb 25;9(4):879–894. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.4.879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. B., Shaffer J., Murphy R. F., Bonner J., Hirose T., Itakura K. Hybridization of synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotides to phi chi 174 DNA: the effect of single base pair mismatch. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 10;6(11):3543–3557. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.11.3543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walz F. G., Jr, Vlasuk G. P., Omiecinski C. J., Bresnick E., Thomas P. E., Ryan D. E., Levin W. Multiple, immunoidentical forms of phenobarbital-induced rat liver cytochromes P-450 are encoded by different mRNAs. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4023–4026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman D. J., Light D. R., Walsh C. Chiral sulfoxidations catalyzed by rat liver cytochromes P-450. Biochemistry. 1982 May 11;21(10):2499–2507. doi: 10.1021/bi00539a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wreschner D. H., Herzberg M. A new blotting medium for the simple isolation and identification of highly resolved messenger RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Feb 10;12(3):1349–1359. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.3.1349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan P. M., Ryan D. E., Levin W., Shively J. E. Identification and localization of amino acid substitutions between two phenobarbital-inducible rat hepatic microsomal cytochromes P-450 by micro sequence analyses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1169–1173. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]