Abstract
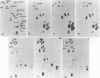
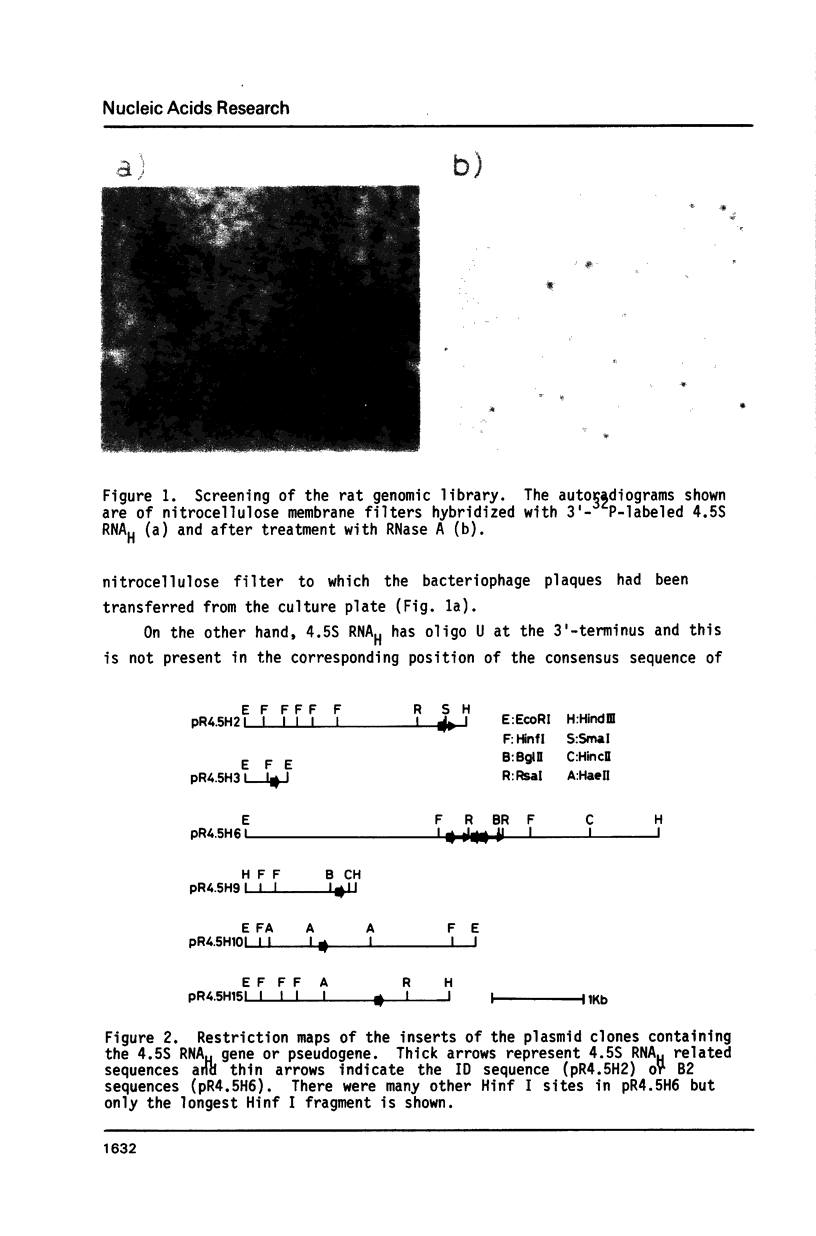
4.5S RNAH (4.5S RNA associated with poly A containing RNA) has extensive homology to major interspersed repeat B1 in rodent genomes. We developed a new cloning technique for screening genomic library that eliminates the signal produced by repeated sequences or pseudogenes and applied it to cloning of 4.5S RNAH genes. Six phage clones (2, 3, 6, 9, 10 and 15) which hybridize with 4.5S RNAH were isolated from a rat gene library by this method. The restriction fragments containing the 4.5S RNAH locus were subcloned into plasmids and sequenced. Clones 2, 3, 9 and 15 contained one to five base substitutions in the coding region for 4.5S RNAH and were probably pseudogenes. In clone 2, the 4.5S RNAH locus was linked directly with the identifier sequence. Clone 6 contained three copies of the 4.5S RNAH gene (6a, b and c) which were clustered in the same direction within 455 base pairs. 6b was linked directly with 6c and ubiquitous repetitive DNA sequences B2 were inserted immediately after 6a and 6c. These three sequences as well as the sequence in clone 10 were colinear with rat 4.5S RNAH. In an in vitro transcription system, only clone 10 gave intact 4.5S RNAH.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruce A. G., Uhlenbeck O. C. Reactions at the termini of tRNA with T4 RNA ligase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Oct;5(10):3665–3677. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.10.3665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowlkes D. M., Shenk T. Transcriptional control regions of the adenovirus VAI RNA gene. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):405–413. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90351-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli G., Hofstetter H., Birnstiel M. L. Two conserved sequence blocks within eukaryotic tRNA genes are major promoter elements. Nature. 1981 Dec 17;294(5842):626–631. doi: 10.1038/294626a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada F., Ikawa Y. A new series of RNAs associated with the genome of spleen focus forming virus (SFFV) and poly(A)-containing RNA from SFFV-infected cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Oct 25;7(4):895–908. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.4.895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada F., Kato N., Hoshino H. Series of 4.5S RNAs associated with poly(A)-containing RNAs of rodent cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Oct 25;7(4):909–917. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.4.909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada F., Kato N. Nucleotide sequences of 4.5S RNAs associated with poly(A)-containing RNAs of mouse and hamster cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Mar 25;8(6):1273–1285. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.6.1273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi K. A cloning vehicle suitable for strand separation. Gene. 1980 Oct;11(1-2):109–115. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90091-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes S. R., Jelinek W. R. Low molecular weight RNAs transcribed in vitro by RNA polymerase III from Alu-type dispersed repeats in Chinese hamster DNA are also found in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6130–6134. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes S. R., Toomey T. P., Leinwand L., Jelinek W. R. The Chinese hamster Alu-equivalent sequence: a conserved highly repetitious, interspersed deoxyribonucleic acid sequence in mammals has a structure suggestive of a transposable element. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Jul;1(7):573–583. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.7.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrick J. P., Wolin S. L., Rinke J., Lerner M. R., Steitz J. A. Ro small cytoplasmic ribonucleoproteins are a subclass of La ribonucleoproteins: further characterization of the Ro and La small ribonucleoproteins from uninfected mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;1(12):1138–1149. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.12.1138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashi K., Narayanan K. S., Adams H. R., Busch H. Utilization of the citric acid procedure and zonal ultracentrifugation for mass isolation of nuclear RNA from Walker 256 carcinosarcoma. Cancer Res. 1966 Jul;26(7):1582–1590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura T., Dahlberg J. E. Small ribonucleic acids of Escherichia coli. I. Characterization by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and fingerprint analysis. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jul 25;248(14):5024–5032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura T., Shimura Y., Sakano H., Ozeki H. Precursor molecules of Escherichia coli transfer RNAs accumulated in a temperature-sensitive mutant. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jul 25;96(1):69–86. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90182-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek W. R., Schmid C. W. Repetitive sequences in eukaryotic DNA and their expression. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:813–844. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.004121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek W. R., Toomey T. P., Leinwand L., Duncan C. H., Biro P. A., Choudary P. V., Weissman S. M., Rubin C. M., Houck C. M., Deininger P. L. Ubiquitous, interspersed repeated sequences in mammalian genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1398–1402. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek W., Leinwand L. Low molecular weight RNAs hydrogen-bonded to nuclear and cytoplasmic poly(A)-terminated RNA from cultured Chinese hamster ovary cells. Cell. 1978 Sep;15(1):205–214. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90095-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krayev A. S., Kramerov D. A., Skryabin K. G., Ryskov A. P., Bayev A. A., Georgiev G. P. The nucleotide sequence of the ubiquitous repetitive DNA sequence B1 complementary to the most abundant class of mouse fold-back RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Mar 25;8(6):1201–1215. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.6.1201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krayev A. S., Markusheva T. V., Kramerov D. A., Ryskov A. P., Skryabin K. G., Bayev A. A., Georgiev G. P. Ubiquitous transposon-like repeats B1 and B2 of the mouse genome: B2 sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 11;10(23):7461–7475. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.23.7461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Higa A. Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Fire A., Cano A., Sharp P. A., Gefter M. L. DNA-dependent transcription of adenovirus genes in a soluble whole-cell extract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3855–3859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner R. J., Bloom F. E., Lai C., Lerner R. A., Sutcliffe J. G. Brain-specific genes have identifier sequences in their introns. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):713–717. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peattie D. A. Direct chemical method for sequencing RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1760–1764. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters G., Harada F., Dahlberg J. E., Panet A., Haseltine W. A., Baltimore D. Low-molecular-weight RNAs of Moloney murine leukemia virus: identification of the primer for RNA-directed DNA synthesis. J Virol. 1977 Mar;21(3):1031–1041. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.3.1031-1041.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J. H. The origin and evolution of retroposons. Int Rev Cytol. 1985;93:187–279. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61375-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Brownlee G. G., Barrell B. G. A two-dimensional fractionation procedure for radioactive nucleotides. J Mol Biol. 1965 Sep;13(2):373–398. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80104-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeiro R., Darnell J. E. Competition hybridization by "pre-saturation" of HeLa cell DNA. J Mol Biol. 1969 Sep 28;44(3):551–562. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90379-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squires C., Lee F., Bertrand K., Squires C. L., Bronson M. J., Yanofsky C. Nucleotide sequence of the 5' end of tryptophan messenger RNA of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1976 May 15;103(2):351–381. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90317-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G., Milner R. J., Bloom F. E., Lerner R. A. Common 82-nucleotide sequence unique to brain RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):4942–4946. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.4942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G., Milner R. J., Gottesfeld J. M., Lerner R. A. Identifier sequences are transcribed specifically in brain. Nature. 1984 Mar 15;308(5956):237–241. doi: 10.1038/308237a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tani T., Watanabe-Nagasu N., Okada N., Ohshima Y. Molecular cloning and characterization of a gene for rat U2 small nuclear RNA. J Mol Biol. 1983 Aug 15;168(3):579–594. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80303-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe-Nagasu N., Itoh Y., Tani T., Okano K., Koga N., Okada N., Ohshima Y. Structural analysis of gene loci for rat U1 small nuclear RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1791–1801. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]